RequestMappingHandlerMapping请求地址映射的初始化流程
之前的文章里,介绍了DispatcherSerlvet处理请求的流程。
其中一个核心的步骤是:请求地址映射,即根据request获取对应的HandlerExcecutionChain。
为了后续的请求地址映射,在项目初始化时,需要先将request-handler映射关系缓存起来。
HandlerMapping有很多实现类,比如RequestMappingHandlerMapping、BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping和RouterFunctionMapping,它们分别对应不同的Controller接口定义规则。
这篇文章要介绍的是RequestMappingHandlerMapping请求地址映射的初始化流程。
大家看到RequestMappingHandlerMapping可能会感到陌生。
实际上,它是我们日常打交道最多的HandlerMapping实现类:它是@Controller和@RequestMapping的底层实现。
在RequestMappingHanlderMapping初始化时,会根据@Controller和@RequestMapping创建RequestMappingInfo,将request-handler映射关系缓存起来。
首先,我们简单来看一下RequestMappingHandlerMapping的类图:
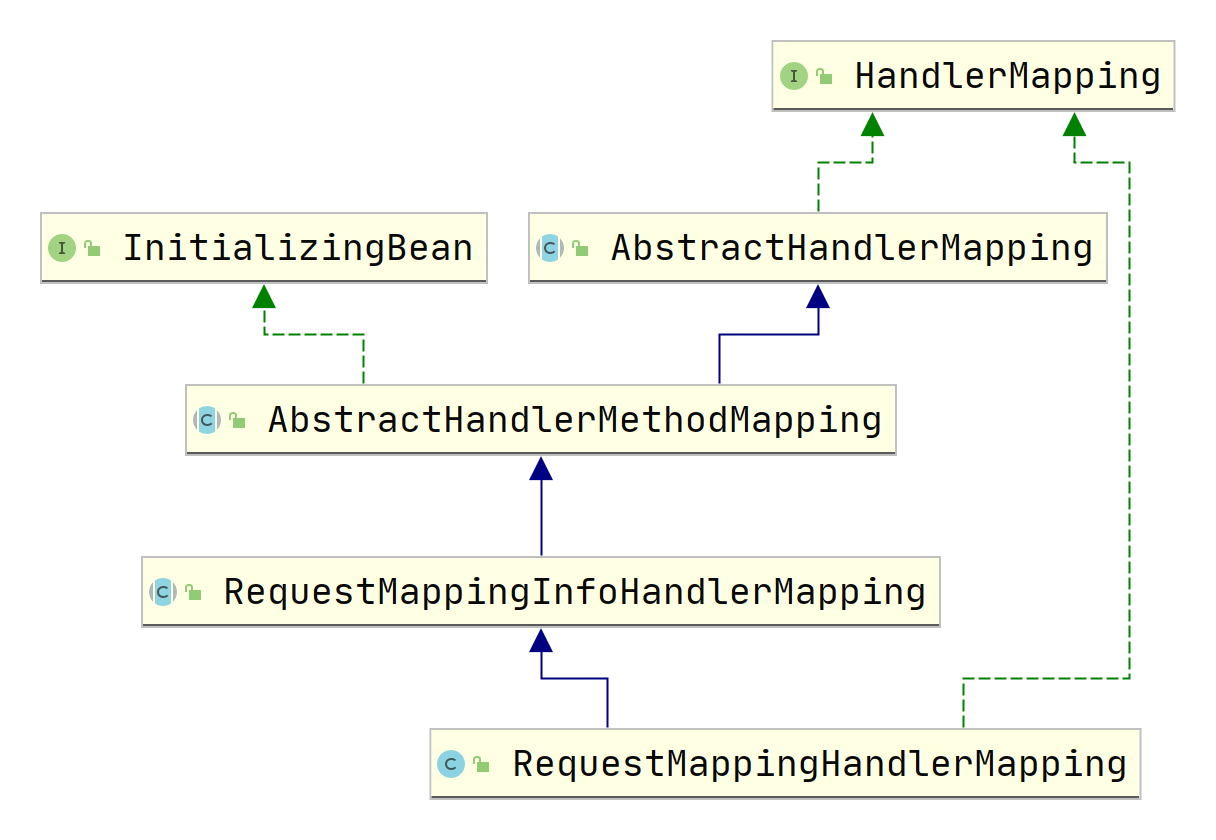
RequestMappingHandlerMapping实现了InitializingBean接口。
在Spring容器设置完所有bean的属性,以及执行完XxxAware接口的setXxx()方法后,会触发InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet()方法。
在AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的afterPropertiesSet()方法中,会完成请求地址映射的初始化流程:
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
initHandlerMethods();
}
在AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的initHandlerMethods方法中,会遍历容器中所有bean进行处理:
protected void initHandlerMethods() {
// 1、遍历所有bean的名称
for (String beanName : getCandidateBeanNames()) {
if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) {
// 2、解析bean
processCandidateBean(beanName);
}
}
handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods());
}
在AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的processCandidateBean方法中,会对bean进行筛选。如果该bean的类对象中包含@Controller或RequestMapping注解,会进一步遍历该类对象的各个方法:
protected void processCandidateBean(String beanName) {
Class<?> beanType = null;
try {
beanType = obtainApplicationContext().getType(beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// An unresolvable bean type, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it.
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Could not resolve type for bean '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
// 1、判断bean的类对象是否包含@Controller或@RequestMapping
if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) {
// 2、构造request-handler映射信息
detectHandlerMethods(beanName);
}
}
在RequestMappingHandlerMapping的isHandler()方法中,会判断当前类对象是否包含@Controller或@RequestMapping注解:
protected boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType) {
return (AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, Controller.class) ||
AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, RequestMapping.class));
}
在AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的detectHandlerMethods方法中,会构造并缓存request-handler信息:
protected void detectHandlerMethods(Object handler) {
Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String ?
obtainApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass());
if (handlerType != null) {
Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType);
// 1、遍历类对象的各个方法,返回Method-RequestMappingInfo映射
Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType,
(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>) method -> {
try {
// 2、构造request-handler请求地址映射
return getMappingForMethod(method, userType);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid mapping on handler class [" +
userType.getName() + "]: " + method, ex);
}
});
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(formatMappings(userType, methods));
}
else if (mappingsLogger.isDebugEnabled()) {
mappingsLogger.debug(formatMappings(userType, methods));
}
// 3、缓存request-handler请求地址映射
methods.forEach((method, mapping) -> {
Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, userType);
registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping);
});
}
}
在MethodIntrospector的selectMethods()方法中,会遍历类对象各个方法,调用RequestMappingHandlerMapping的getMappingForMethod()方法,构造request地址信息:
- 如果该方法满足书写规则,即含有
@RequestMapping,会返回RequestMappingInfo对象 - 如果该方法不满足书写规则,会返回
null。
MethodIntrospector的selectMethods()方法会将所有request地址信息不为null的Method-RequestMappingInfo映射返回。
在RequestMappingHandlerMapping的getMappingForMethod()方法中,会构造完整的request地址信息。主要包括以下步骤:
- 构造方法级别的
request地址信息 - 构造类级别的
request地址信息 - 整合两个级别的
request地址信息,构造出完整的request地址信息
RequestMappingHandlerMapping的getMappingForMethod()方法源码如下:
protected RequestMappingInfo getMappingForMethod(Method method, Class<?> handlerType) {
// 1、构造方法级别的request-handler信息
RequestMappingInfo info = createRequestMappingInfo(method);
if (info != null) {
// 2、构造类级别的request-handler信息
RequestMappingInfo typeInfo = createRequestMappingInfo(handlerType);
if (typeInfo != null) {
// 3、整合两个级别的request-handler信息,构造出完整的request-handler信息
info = typeInfo.combine(info);
}
String prefix = getPathPrefix(handlerType);
if (prefix != null) {
info = RequestMappingInfo.paths(prefix).options(this.config).build().combine(info);
}
}
return info;
}
构造request地址信息很简单,只是从@RequestMapping注解中获取各个属性,创建RequestMappingInfo(在实际请求地址映射时,会对所有属性进行校验):
protected RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(
RequestMapping requestMapping, @Nullable RequestCondition<?> customCondition) {
RequestMappingInfo.Builder builder = RequestMappingInfo
.paths(resolveEmbeddedValuesInPatterns(requestMapping.path()))
.methods(requestMapping.method())
.params(requestMapping.params())
.headers(requestMapping.headers())
.consumes(requestMapping.consumes())
.produces(requestMapping.produces())
.mappingName(requestMapping.name());
if (customCondition != null) {
builder.customCondition(customCondition);
}
return builder.options(this.config).build();
}
在整合request地址信息过程中,会分别调用各个属性的整合规则进行整合:
public RequestMappingInfo combine(RequestMappingInfo other) {
String name = combineNames(other);
PathPatternsRequestCondition pathPatterns =
(this.pathPatternsCondition != null && other.pathPatternsCondition != null ?
this.pathPatternsCondition.combine(other.pathPatternsCondition) : null);
PatternsRequestCondition patterns =
(this.patternsCondition != null && other.patternsCondition != null ?
this.patternsCondition.combine(other.patternsCondition) : null);
RequestMethodsRequestCondition methods = this.methodsCondition.combine(other.methodsCondition);
ParamsRequestCondition params = this.paramsCondition.combine(other.paramsCondition);
HeadersRequestCondition headers = this.headersCondition.combine(other.headersCondition);
ConsumesRequestCondition consumes = this.consumesCondition.combine(other.consumesCondition);
ProducesRequestCondition produces = this.producesCondition.combine(other.producesCondition);
RequestConditionHolder custom = this.customConditionHolder.combine(other.customConditionHolder);
return new RequestMappingInfo(name, pathPatterns, patterns,
methods, params, headers, consumes, produces, custom, this.options);
}
不同的属性有不同的整合规则,比如对于methods、params和headers会取并集,而对于consumes和produces方法级别优先取方法级别配置信息。
介绍完request地址信息的构造过程,我们回到AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的detectHandlerMethods方法中。此时,我们得到了Method-RequestMappingInfo映射信息。
接下来,会遍历这个映射,筛选出实际可执行的方法(即非私有的、非静态的和非超类的)。
最终,将可执行的方法对应的request-handler信息缓存起来。核心代码位于AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.MappingRegistry内部类的register()方法:
public void register(T mapping, Object handler, Method method) {
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().lock();
try {
// 1、创建HandlerMethod对象,即handler
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method);
// 2、校验该request地址信息是否已经存在
validateMethodMapping(handlerMethod, mapping);
// 3、缓存path-RequestMappingInfo映射
Set<String> directPaths = AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.this.getDirectPaths(mapping);
for (String path : directPaths) {
this.pathLookup.add(path, mapping);
}
// 4、缓存name-RequestMappingInfo映射
String name = null;
if (getNamingStrategy() != null) {
name = getNamingStrategy().getName(handlerMethod, mapping);
addMappingName(name, handlerMethod);
}
// 5、缓存CORS配置信息
CorsConfiguration corsConfig = initCorsConfiguration(handler, method, mapping);
if (corsConfig != null) {
corsConfig.validateAllowCredentials();
this.corsLookup.put(handlerMethod, corsConfig);
}
// 6、缓存RequestMappingInfo-MappingRegistration信息
this.registry.put(mapping,
new MappingRegistration<>(mapping, handlerMethod, directPaths, name, corsConfig != null));
}
finally {
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
需要注意的是,在这个过程中还会缓存跨域配置信息,主要是@CrossOrigin注解方式的跨域配置信息。
在RequestMappingHandlerMapping的initCorsConfiguration()方法中,会获取类级别和方法级别的@CrossOrigin信息,构造出完整的跨域配置信息:
protected CorsConfiguration initCorsConfiguration(Object handler, Method method, RequestMappingInfo mappingInfo) {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method);
Class<?> beanType = handlerMethod.getBeanType();
// 1、获取类级别的@CrossOrigin信息
CrossOrigin typeAnnotation = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(beanType, CrossOrigin.class);
// 2、获取方法级别的@CrossOrigin信息
CrossOrigin methodAnnotation = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(method, CrossOrigin.class);
if (typeAnnotation == null && methodAnnotation == null) {
return null;
}
// 3、整合两个级别的@CrossOrigin信息
CorsConfiguration config = new CorsConfiguration();
updateCorsConfig(config, typeAnnotation);
updateCorsConfig(config, methodAnnotation);
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(config.getAllowedMethods())) {
for (RequestMethod allowedMethod : mappingInfo.getMethodsCondition().getMethods()) {
config.addAllowedMethod(allowedMethod.name());
}
}
return config.applyPermitDefaultValues();
}
在整合@CrossOrigin信息过程中,有三种情况:
- 对于
origins、originPatterns、allowedHeaders、exposedHeaders和methods等列表属性,会获取全部。 - 对于
allowCredentials,会优先获取方法级别的配置。 - 对于
maxAge,会获取最大值。
至此,我们走完了RequestMappingHandlerMapping中请求地址映射的初始化流程。最后总结一下流程如下:
- 遍历容器中所有
bean对象 - 如果
bean的类对象含有@Controller或@RequestMapping注解,进行下一步 - 遍历
bean的类对象的所有方法,根据方法的@RequestMapping注解,构造RequestMappingInfo对象 - 遍历
Method-RequestMappingInfo映射,过滤出可执行方法 - 缓存各种
request-handler映射信息,同时会缓存@CrossOrigin的跨域配置信息
此时,我们可以充分理解到,request-handler请求地址映射信息中request和handler的含义:
request:主要是@RequestMapping中含有的各个属性的信息,会被封装成RequestMappingInfo对象。handler:标注@RequestMapping的方法,会被封装成HandlerMethod对象。



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构