DispatcherServlet是怎么处理请求的?
上篇文章总结了DispatcherServlet的核心功能,今天趁热打铁,系统梳理DispatcherServlet处理请求的流程。
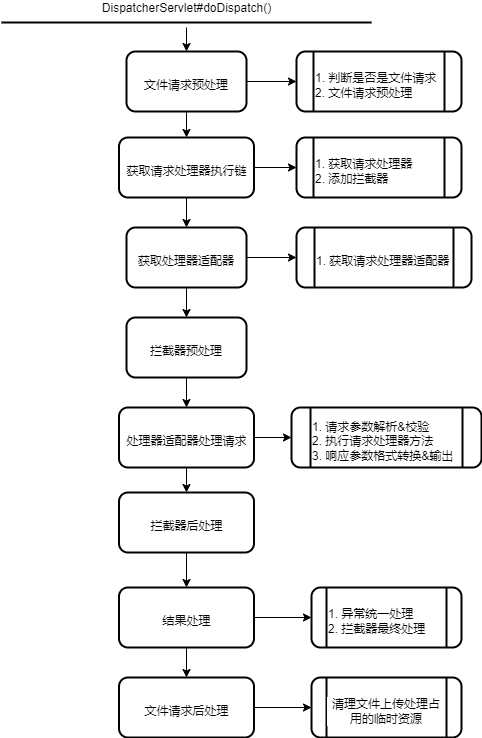
DispatcherServlet处理请求的核心方法是doDispatch()。在处理过程中,会协同使用各组件的功能,共同完成对请求的处理。
以下是doDispatch()的执行流程图:
以下是doDispatch()的源码:
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
// 1、文件请求预处理
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// 2、获取请求处理器执行链
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// 3、获取处理器适配器
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = HttpMethod.GET.matches(method);
if (isGet || HttpMethod.HEAD.matches(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
// 4、拦截器预处理
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// 5、处理器适配器处理请求
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
// 6、拦截器后处理
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
}
// 7、结果处理
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// 8、文件请求后处理
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
1 文件请求预处理
DispatcherServlet在处理请求时,首先会使用MultipartResolver进行文件请求处理。
具体文件请求源码位于org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet#checkMultipart:
protected HttpServletRequest checkMultipart(HttpServletRequest request) throws MultipartException {
if (this.multipartResolver != null && this.multipartResolver.isMultipart(request)) {
if (WebUtils.getNativeRequest(request, MultipartHttpServletRequest.class) != null) {
if (DispatcherType.REQUEST.equals(request.getDispatcherType())) {
logger.trace("Request already resolved to MultipartHttpServletRequest, e.g. by MultipartFilter");
}
}
else if (hasMultipartException(request)) {
logger.debug("Multipart resolution previously failed for current request - " +
"skipping re-resolution for undisturbed error rendering");
}
else {
try {
return this.multipartResolver.resolveMultipart(request);
}
catch (MultipartException ex) {
if (request.getAttribute(WebUtils.ERROR_EXCEPTION_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
logger.debug("Multipart resolution failed for error dispatch", ex);
// Keep processing error dispatch with regular request handle below
}
else {
throw ex;
}
}
}
}
// If not returned before: return original request.
return request;
}
首先,会判断当前请求是否是文件请求,主要通过请求头Content-Type是否以multipart/开头进行判断。
如果是文件请求,由于可能在Filter阶段进行文件处理,因此还需要判断是否已经进行过文件处理。
如果没有进行文件处理,则会使用MultipartResolver进行实际文件处理。
在Spring中,MultipartResolver有两种实现类:
StandardServletMultipartResolver:底层根据Servlet 3.0+规范实现。CommonsMultipartResolver:底层根据Apache的commons-fileupload工具实现。
虽然这两个实现类的底层原理有所不同,但它们对文件的处理方式基本一致:
- 将HTTP文件流保存到本地临时文件。
- 将本地临时文件封装成
MultipartHttpServletRequest对象返回。
2. 获取请求处理器执行链
文件请求预处理完成后,会获取请求处理器执行链:
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {
HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
}
获取请求处理器执行链会经历以下两个步骤
- 根据请求地址/请求方法等信息,从
HandlerMapping中获取对应的处理器(简单来说,就是开发人员定义在@Controller中定义的对应方法)。 - 根据配置信息,添加拦截器。
3 获取处理器适配器
获取完处理器执行链后,会根据处理器获取对应的处理器适配器。
HandlerMapping和HandlerAdapter一一对应。
一般来说,不同HandlerMapping会返回不同的处理器,通过判断HandlerAdapter适配的处理器类型,即可获取到对应的处理器适配器:
protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException {
if (this.handlerAdapters != null) {
for (HandlerAdapter adapter : this.handlerAdapters) {
if (adapter.supports(handler)) {
return adapter;
}
}
}
throw new ServletException("No adapter for handler [" + handler +
"]: The DispatcherServlet configuration needs to include a HandlerAdapter that supports this handler");
}
4 拦截器预处理
获取处理器适配器后,接下来是正式对请求的处理。
首先会进行拦截器的预处理,会遍历拦截器依次进行处理,只有所有拦截器的预处理通过后,才能进行处理器的实际调用。
boolean applyPreHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
for (int i = 0; i < this.interceptorList.size(); i++) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = this.interceptorList.get(i);
if (!interceptor.preHandle(request, response, this.handler)) {
triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null);
return false;
}
this.interceptorIndex = i;
}
return true;
}
5 处理器适配器处理请求
当所有拦截器的预处理通过后,会使用处理器适配器处理请求。
该阶段是Spring MVC最核心也最复杂的步骤:
- 根据
@RequestParam、@RequestBody等注解将请求数据转换成形参对象。 - 根据
@Validated等注解对请求数据进行校验。 - 通过反射执行处理器方法。
- 根据
@ResponseBody等注解将返回值进行数据格式处理并输出。
6 拦截器后处理
处理器适配器处理请求完成后,会进行拦截器后处理。此时拦截器的调用顺序正好和预处理顺序相反:
void applyPostHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable ModelAndView mv)
throws Exception {
for (int i = this.interceptorList.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = this.interceptorList.get(i);
interceptor.postHandle(request, response, this.handler, mv);
}
}
7 结果处理
当拦截器后处理接收后,会对处理器适配器处理请求的结果进行处理:
- 对上述所有步骤中出现的异常进行统一处理。
- 视图渲染和输出(前后端分离项目可以不考虑这一步骤)
- 拦截器的最终处理
private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
@Nullable HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, @Nullable ModelAndView mv,
@Nullable Exception exception) throws Exception {
boolean errorView = false;
if (exception != null) {
if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) {
logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception);
mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException) exception).getModelAndView();
}
else {
Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null);
mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception);
errorView = (mv != null);
}
}
// Did the handler return a view to render?
if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) {
render(mv, request, response);
if (errorView) {
WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request);
}
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No view rendering, null ModelAndView returned.");
}
}
if (WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Concurrent handling started during a forward
return;
}
if (mappedHandler != null) {
// Exception (if any) is already handled..
mappedHandler.triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null);
}
}
8 文件请求后处理
当上述请求都处理完成,会进行文件请求后处理,其本质上就是将文件预处理产生的本地临时文件删除,释放占用的系统资源。


