mybatis(一、原理,一对多,多对一查询)
MyBatis框架及原理分析
MyBatis 是支持定制化 SQL、存储过程以及高级映射的优秀的持久层框架,其主要就完成2件事情:
- 封装JDBC操作
- 利用反射打通Java类与SQL语句之间的相互转换
MyBatis的主要设计目的就是让我们对执行SQL语句时对输入输出的数据管理更加方便,所以方便地写出SQL和方便地获取SQL的执行结果才是MyBatis的核心竞争力。
MyBatis的配置
MyBatis框架和其他绝大部分框架一样,需要一个配置文件,其配置文件大致如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<settings>
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="false"/>
<!--<setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING"/> <!– 打印日志信息 –>-->
</settings>
<typeAliases>
<typeAlias type="com.luo.dao.UserDao" alias="User"/>
</typeAliases>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/> <!--事务管理类型-->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="username" value="luoxn28"/>
<property name="password" value="123456"/>
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://192.168.1.150/ssh_study"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="userMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
以上配置中,最重要的是数据库参数的配置,比如用户名密码等,如果配置了数据表对应的mapper文件,则需要将其加入到<mappers>节点下。
MyBatis的主要成员
- Configuration MyBatis所有的配置信息都保存在Configuration对象之中,配置文件中的大部分配置都会存储到该类中
- SqlSession 作为MyBatis工作的主要顶层API,表示和数据库交互时的会话,完成必要数据库增删改查功能
- Executor MyBatis执行器,是MyBatis 调度的核心,负责SQL语句的生成和查询缓存的维护
- StatementHandler 封装了JDBC Statement操作,负责对JDBC statement 的操作,如设置参数等
- ParameterHandler 负责对用户传递的参数转换成JDBC Statement 所对应的数据类型
- ResultSetHandler 负责将JDBC返回的ResultSet结果集对象转换成List类型的集合
- TypeHandler 负责java数据类型和jdbc数据类型(也可以说是数据表列类型)之间的映射和转换
- MappedStatement MappedStatement维护一条<select|update|delete|insert>节点的封装
- SqlSource 负责根据用户传递的parameterObject,动态地生成SQL语句,将信息封装到BoundSql对象中,并返回
- BoundSql 表示动态生成的SQL语句以及相应的参数信息
以上主要成员在一次数据库操作中基本都会涉及,在SQL操作中重点需要关注的是SQL参数什么时候被设置和结果集怎么转换为JavaBean对象的,这两个过程正好对应StatementHandler和ResultSetHandler类中的处理逻辑。
(图片来自《深入理解mybatis原理》 MyBatis的架构设计以及实例分析)
MyBatis的初始化
MyBatis的初始化的过程其实就是解析配置文件和初始化Configuration的过程,MyBatis的初始化过程可用以下几行代码来表述:
String resource = "mybatis.xml";
// 加载mybatis的配置文件(它也加载关联的映射文件)
InputStream inputStream = null;
try {
inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 构建sqlSession的工厂
sessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
首先会创建SqlSessionFactory建造者对象,然后由它进行创建SqlSessionFactory。这里用到的是建造者模式,建造者模式最简单的理解就是不手动new对象,而是由其他类来进行对象的创建。
// SqlSessionFactoryBuilder类
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
return build(parser.parse()); // 开始进行解析了 :)
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
XMLConfigBuilder对象会进行XML配置文件的解析,实际为configuration节点的解析操作。
// XMLConfigBuilder类
public Configuration parse() {
if (parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
parsed = true;
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return configuration;
}
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
//issue #117 read properties first
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));
loadCustomVfs(settings);
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));
settingsElement(settings);
// read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
/* 处理environments节点数据 */
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
在configuration节点下会依次解析properties/settings/.../mappers等节点配置。在解析environments节点时,会根据transactionManager的配置来创建事务管理器,根据dataSource的配置来创建DataSource对象,这里面包含了数据库登录的相关信息。在解析mappers节点时,会读取该节点下所有的mapper文件,然后进行解析,并将解析后的结果存到configuration对象中。
// XMLConfigBuilder类
private void environmentsElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
if (environment == null) {
environment = context.getStringAttribute("default");
}
for (XNode child : context.getChildren()) {
String id = child.getStringAttribute("id");
if (isSpecifiedEnvironment(id)) {
/* 创建事务管理器 */
TransactionFactory txFactory = transactionManagerElement(child.evalNode("transactionManager"));
DataSourceFactory dsFactory = dataSourceElement(child.evalNode("dataSource"));
DataSource dataSource = dsFactory.getDataSource();
/* 建造者模式 设计模式 */
Environment.Builder environmentBuilder = new Environment.Builder(id)
.transactionFactory(txFactory)
.dataSource(dataSource);
configuration.setEnvironment(environmentBuilder.build());
}
}
}
}
// 解析单独的mapper文件
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage);
} else {
String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource");
String url = child.getStringAttribute("url");
String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class");
if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse(); // 开始解析mapper文件了 :)
} else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(url);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) {
Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass);
configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface);
} else {
throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one.");
}
}
}
}
}
解析完MyBatis配置文件后,configuration就初始化完成了,然后根据configuration对象来创建SqlSession,到这里时,MyBatis的初始化的征程已经走完了。
// SqlSessionFactoryBuilder类
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}
MyBatis的SQL查询流程
SQL语句的执行才是MyBatis的重要职责,该过程就是通过封装JDBC进行操作,然后使用Java反射技术完成JavaBean对象到数据库参数之间的相互转换,这种映射关系就是有TypeHandler对象来完成的,在获取数据表对应的元数据时,会保存该表所有列的数据库类型,大致逻辑如下所示:
/* Get resultSet metadata */
ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData();
int column = metaData.getColumnCount();
for (int i = 1; i <= column; i++) {
JdbcType jdbcType = JdbcType.forCode(metaData.getColumnType(i));
typeHandlers.add(TypeHandlerRegistry.getTypeHandler(jdbcType));
columnNames.add(metaData.getColumnName(i));
}
使用如下代码进行SQL查询操作:
sqlSession = sessionFactory.openSession();
User user = sqlSession.selectOne("com.luo.dao.UserDao.getUserById", 1);
System.out.println(user);
创建sqlSession的过程其实就是根据configuration中的配置来创建对应的类,然后返回创建的sqlSession对象。调用selectOne方法进行SQL查询,selectOne方法最后调用的是selectList,在selectList中,会查询configuration中存储的MappedStatement对象,mapper文件中一个sql语句的配置对应一个MappedStatement对象,然后调用执行器进行查询操作。
// DefaultSqlSession类
public <T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) {
// Popular vote was to return null on 0 results and throw exception on too many.
List<T> list = this.<T>selectList(statement, parameter);
if (list.size() == 1) {
return list.get(0);
} else if (list.size() > 1) {
throw new TooManyResultsException("Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: " + list.size());
} else {
return null;
}
}
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
执行器在query操作中,优先会查询缓存是否命中,命中则直接返回,否则从数据库中查询。
// CachingExecutor类
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
/* 获取关联参数的sql,boundSql */
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
/* 创建cache key值 */
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
/* 获取二级缓存实例 */
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null) {
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, parameterObject, boundSql);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
list = delegate.<E> query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
return delegate.<E> query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List<E> list;
/**
* 先往localCache中插入一个占位对象,这个地方
*/
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
/* 往缓存中写入数据,也就是缓存查询结果 */
localCache.putObject(key, list);
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}
真正的doQuery操作是由SimplyExecutor代理来完成的,该方法中有2个子流程,一个是SQL参数的设置,另一个是SQL查询操作和结果集的封装。
// SimpleExecutor类
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
/* 子流程1: SQL查询参数的设置 */
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
/* 子流程2: SQL查询操作和结果集封装 */
return handler.<E>query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
子流程1 SQL查询参数的设置:
首先获取数据库connection连接,然后准备statement,然后就设置SQL查询中的参数值。打开一个connection连接,在使用完后不会close,而是存储下来,当下次需要打开连接时就直接返回。
// SimpleExecutor类
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
/* 获取Connection连接 */
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
/* 准备Statement */
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
/* 设置SQL查询中的参数值 */
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
// DefaultParameterHandler类
public void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) {
/**
* 设置SQL参数值,从ParameterMapping中读取参数值和类型,然后设置到SQL语句中
*/
ErrorContext.instance().activity("setting parameters").object(mappedStatement.getParameterMap().getId());
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if (parameterMappings != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < parameterMappings.size(); i++) {
ParameterMapping parameterMapping = parameterMappings.get(i);
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) {
Object value;
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) { // issue #448 ask first for additional params
value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
} else if (parameterObject == null) {
value = null;
} else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {
value = parameterObject;
} else {
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
}
TypeHandler typeHandler = parameterMapping.getTypeHandler();
JdbcType jdbcType = parameterMapping.getJdbcType();
if (value == null && jdbcType == null) {
jdbcType = configuration.getJdbcTypeForNull();
}
try {
typeHandler.setParameter(ps, i + 1, value, jdbcType);
} catch (TypeException e) {
throw new TypeException("Could not set parameters for mapping: " + parameterMapping + ". Cause: " + e, e);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new TypeException("Could not set parameters for mapping: " + parameterMapping + ". Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
}
}
子流程2 SQL查询结果集的封装:
// SimpleExecutor类
public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement;
// 执行查询操作
ps.execute();
// 执行结果集封装
return resultSetHandler.<E> handleResultSets(ps);
}
// DefaultReseltSetHandler类
public List<Object> handleResultSets(Statement stmt) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("handling results").object(mappedStatement.getId());
final List<Object> multipleResults = new ArrayList<Object>();
int resultSetCount = 0;
/**
* 获取第一个ResultSet,同时获取数据库的MetaData数据,包括数据表列名、列的类型、类序号等。
* 这些信息都存储在了ResultSetWrapper中了
*/
ResultSetWrapper rsw = getFirstResultSet(stmt);
List<ResultMap> resultMaps = mappedStatement.getResultMaps();
int resultMapCount = resultMaps.size();
validateResultMapsCount(rsw, resultMapCount);
while (rsw != null && resultMapCount > resultSetCount) {
ResultMap resultMap = resultMaps.get(resultSetCount);
handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, multipleResults, null);
rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt);
cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
resultSetCount++;
}
String[] resultSets = mappedStatement.getResultSets();
if (resultSets != null) {
while (rsw != null && resultSetCount < resultSets.length) {
ResultMapping parentMapping = nextResultMaps.get(resultSets[resultSetCount]);
if (parentMapping != null) {
String nestedResultMapId = parentMapping.getNestedResultMapId();
ResultMap resultMap = configuration.getResultMap(nestedResultMapId);
handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, null, parentMapping);
}
rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt);
cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
resultSetCount++;
}
}
return collapseSingleResultList(multipleResults);
}
ResultSetWrapper是ResultSet的包装类,调用getFirstResultSet方法获取第一个ResultSet,同时获取数据库的MetaData数据,包括数据表列名、列的类型、类序号等,这些信息都存储在ResultSetWrapper类中了。然后调用handleResultSet方法来来进行结果集的封装。
// DefaultResultSetHandler类
private void handleResultSet(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, List<Object> multipleResults, ResultMapping parentMapping) throws SQLException {
try {
if (parentMapping != null) {
handleRowValues(rsw, resultMap, null, RowBounds.DEFAULT, parentMapping);
} else {
if (resultHandler == null) {
DefaultResultHandler defaultResultHandler = new DefaultResultHandler(objectFactory);
handleRowValues(rsw, resultMap, defaultResultHandler, rowBounds, null);
multipleResults.add(defaultResultHandler.getResultList());
} else {
handleRowValues(rsw, resultMap, resultHandler, rowBounds, null);
}
}
} finally {
// issue #228 (close resultsets)
closeResultSet(rsw.getResultSet());
}
}
这里调用handleRowValues方法进行结果值的设置。
// DefaultResultSetHandler类
public void handleRowValues(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, ResultHandler<?> resultHandler, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultMapping parentMapping) throws SQLException {
if (resultMap.hasNestedResultMaps()) {
ensureNoRowBounds();
checkResultHandler();
handleRowValuesForNestedResultMap(rsw, resultMap, resultHandler, rowBounds, parentMapping);
} else {
// 封装数据
handleRowValuesForSimpleResultMap(rsw, resultMap, resultHandler, rowBounds, parentMapping);
}
}
private void handleRowValuesForSimpleResultMap(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, ResultHandler<?> resultHandler, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultMapping parentMapping)
throws SQLException {
DefaultResultContext<Object> resultContext = new DefaultResultContext<Object>();
skipRows(rsw.getResultSet(), rowBounds);
while (shouldProcessMoreRows(resultContext, rowBounds) && rsw.getResultSet().next()) {
ResultMap discriminatedResultMap = resolveDiscriminatedResultMap(rsw.getResultSet(), resultMap, null);
Object rowValue = getRowValue(rsw, discriminatedResultMap);
storeObject(resultHandler, resultContext, rowValue, parentMapping, rsw.getResultSet());
}
}
private Object getRowValue(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap) throws SQLException {
final ResultLoaderMap lazyLoader = new ResultLoaderMap();
// createResultObject为新创建的对象,数据表对应的类
Object rowValue = createResultObject(rsw, resultMap, lazyLoader, null);
if (rowValue != null && !hasTypeHandlerForResultObject(rsw, resultMap.getType())) {
final MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(rowValue);
boolean foundValues = this.useConstructorMappings;
if (shouldApplyAutomaticMappings(resultMap, false)) {
// 这里把数据填充进去,metaObject中包含了resultObject信息
foundValues = applyAutomaticMappings(rsw, resultMap, metaObject, null) || foundValues;
}
foundValues = applyPropertyMappings(rsw, resultMap, metaObject, lazyLoader, null) || foundValues;
foundValues = lazyLoader.size() > 0 || foundValues;
rowValue = (foundValues || configuration.isReturnInstanceForEmptyRow()) ? rowValue : null;
}
return rowValue;
}
private boolean applyAutomaticMappings(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, MetaObject metaObject, String columnPrefix) throws SQLException {
List<UnMappedColumnAutoMapping> autoMapping = createAutomaticMappings(rsw, resultMap, metaObject, columnPrefix);
boolean foundValues = false;
if (autoMapping.size() > 0) {
// 这里进行for循环调用,因为user表中总共有7列,所以也就调用7次
for (UnMappedColumnAutoMapping mapping : autoMapping) {
// 这里将esultSet中查询结果转换为对应的实际类型
final Object value = mapping.typeHandler.getResult(rsw.getResultSet(), mapping.column);
if (value != null) {
foundValues = true;
}
if (value != null || (configuration.isCallSettersOnNulls() && !mapping.primitive)) {
// gcode issue #377, call setter on nulls (value is not 'found')
metaObject.setValue(mapping.property, value);
}
}
}
return foundValues;
}
mapping.typeHandler.getResult会获取查询结果值的实际类型,比如我们user表中id字段为int类型,那么它就对应Java中的Integer类型,然后通过调用statement.getInt("id")来获取其int值,其类型为Integer。metaObject.setValue方法会把获取到的Integer值设置到Java类中的对应字段。
// MetaObject类
public void setValue(String name, Object value) {
PropertyTokenizer prop = new PropertyTokenizer(name);
if (prop.hasNext()) {
MetaObject metaValue = metaObjectForProperty(prop.getIndexedName());
if (metaValue == SystemMetaObject.NULL_META_OBJECT) {
if (value == null && prop.getChildren() != null) {
// don't instantiate child path if value is null
return;
} else {
metaValue = objectWrapper.instantiatePropertyValue(name, prop, objectFactory);
}
}
metaValue.setValue(prop.getChildren(), value);
} else {
objectWrapper.set(prop, value);
}
}
metaValue.setValue方法最后会调用到Java类中对应数据域的set方法,这样也就完成了SQL查询结果集的Java类封装过程。最后贴一张调用栈到达Java类的set方法中的快照:
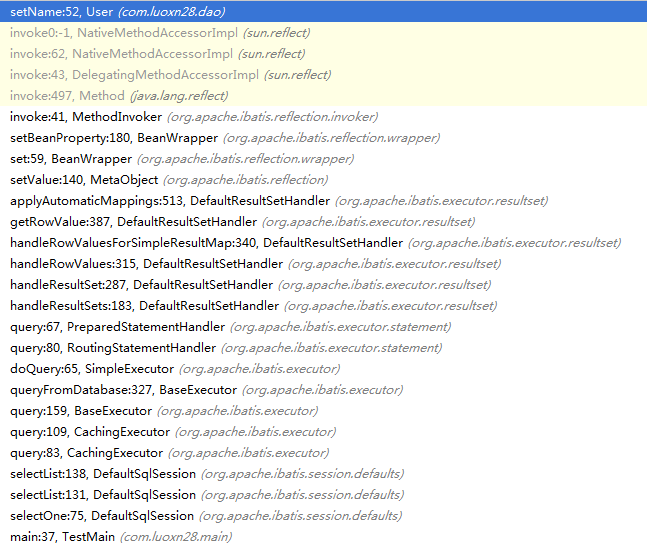
MyBatis缓存
MyBatis提供查询缓存,用于减轻数据库压力,提高性能。MyBatis提供了一级缓存和二级缓存。
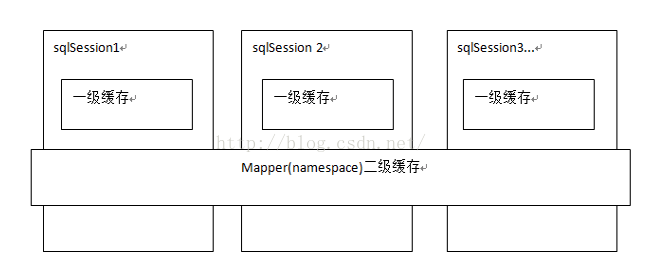
一级缓存是SqlSession级别的缓存,每个SqlSession对象都有一个哈希表用于缓存数据,不同SqlSession对象之间缓存不共享。同一个SqlSession对象对象执行2遍相同的SQL查询,在第一次查询执行完毕后将结果缓存起来,这样第二遍查询就不用向数据库查询了,直接返回缓存结果即可。MyBatis默认是开启一级缓存的。
二级缓存是mapper级别的缓存,二级缓存是跨SqlSession的,多个SqlSession对象可以共享同一个二级缓存。不同的SqlSession对象执行两次相同的SQL语句,第一次会将查询结果进行缓存,第二次查询直接返回二级缓存中的结果即可。MyBatis默认是不开启二级缓存的,可以在配置文件中使用如下配置来开启二级缓存:
<settings>
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
</settings>
当SQL语句进行更新操作(删除/添加/更新)时,会清空对应的缓存,保证缓存中存储的都是最新的数据。MyBatis的二级缓存对细粒度的数据级别的缓存实现不友好,比如如下需求:对商品信息进行缓存,由于商品信息查询访问量大,但是要求用户每次都能查询最新的商品信息,此时如果使用mybatis的二级缓存就无法实现当一个商品变化时只刷新该商品的缓存信息而不刷新其它商品的信息,因为mybaits的二级缓存区域以mapper为单位划分,当一个商品信息变化会将所有商品信息的缓存数据全部清空。解决此类问题需要在业务层根据需求对数据有针对性缓存,具体业务具体实现。
一对多,多对一查询
首先 数据库量表之间字段关系(没有主外键)
studentmajor表的id字段对应student表里major字段
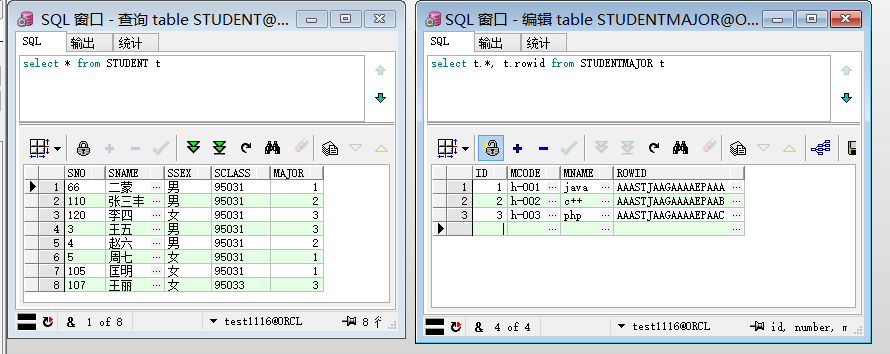
两个实体类
package com.model;
import java.util.Date;
public class Student {
private Integer sno;
private String sname;
private String ssex;
private Integer sclass;
private StudentMajor studentmajor;
public Student() {
super();
}
public Student(Integer sno, String sname, String ssex, Integer sclass, StudentMajor studentmajor) {
super();
this.sno = sno;
this.sname = sname;
this.ssex = ssex;
this.sclass = sclass;
this.studentmajor = studentmajor;
}
public StudentMajor getStudentmajor() {
return studentmajor;
}
public void setStudentmajor(StudentMajor studentmajor) {
this.studentmajor = studentmajor;
}
public Integer getSno() {
return sno;
}
public void setSno(Integer sno) {
this.sno = sno;
}
public String getSname() {
return sname;
}
public void setSname(String sname) {
this.sname = sname;
}
public String getSsex() {
return ssex;
}
public void setSsex(String ssex) {
this.ssex = ssex;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [sno=" + sno + ", sname=" + sname + ", ssex=" + ssex + ", sclass=" + sclass + ", studentmajor="
+ studentmajor + "]";
}
public Integer getSclass() {
return sclass;
}
public void setSclass(Integer sclass) {
this.sclass = sclass;
}
}
package com.model;
import java.util.List;
public class StudentMajor {
private Integer id;
private String mcode;
private String mname;
private List<Student> students;
public StudentMajor() {
super();
}
public StudentMajor(Integer id, String mcode, String mname, List<Student> students) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.mcode = mcode;
this.mname = mname;
this.students = students;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "StudentMajor [id=" + id + ", mcode=" + mcode + ", mname=" + mname + ", students=" + students + "]";
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getMcode() {
return mcode;
}
public void setMcode(String mcode) {
this.mcode = mcode;
}
public String getMname() {
return mname;
}
public void setMname(String mname) {
this.mname = mname;
}
public List<Student> getStudents() {
return students;
}
public void setStudents(List<Student> students) {
this.students = students;
}
}
定义两个接口
package com.dao;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import com.model.Student;
public interface StudentMapper {
/**
* 全表查询
*/
public List<Student> selectall();
/**
* 根据专业查人员,给一对多用
*/
public List<Student> selectz(Integer major);
}
package com.dao;
import java.util.List;
import com.model.StudentMajor;
public interface StudentMajorMapper {
/**
* 全表查询
* @return
*/
public List<StudentMajor> selectAll();
/**
* 根据主键查数据,给多对一用
* @param id
* @return
*/
public StudentMajor select(Integer id);
}
定义两个实体类的映射方法
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.dao.StudentMapper">
<!-- 多对一查询 -->
<resultMap type="Student" id="slist">
<!-- 跟一对一一样用association标签,实体类定义的成员,要跟数据库字段名对应上 -->
<association property="studentmajor" column="major"
select="com.dao.StudentMajorMapper.select"/> <!-- 用接口里定义的方法,根据student表中的major字段查出对应数据 -->
</resultMap>
<!-- 查全部 -->
<select id="selectall" resultMap="slist" >
select * from student
</select>
<!-- 根据专业查人员 -->
<select id="selectz" parameterType="Integer" resultType="student">
select * from student s where s.major=#{major}
</select>
</mapper>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.dao.StudentMajorMapper">
<!-- 一对多查询关联 -->
<resultMap type="StudentMajor" id="slist">
<!-- 实体类属性对应数据库的主键字段,不然主键会查不到 -->
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<!-- 用collection标签 ,也是实体类属性要对应数据库字段-->
<collection property="students" column="id"
select="com.dao.StudentMapper.selectz">
</collection>
</resultMap>
<!-- 全表查询 -->
<select id="selectAll" resultMap="slist">
select * from studentmajor
</select>
<!-- 根据主键查 -->
<select id="select" parameterType="Integer" resultType="StudentMajor">
select * from studentmajor where id=#{id}
</select>
</mapper>
JUnit测试
package com.util;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.dao.StudentMajorMapper;
import com.dao.StudentMapper;
import com.model.Student;
import com.model.StudentMajor;
public class JJJtest {
private SqlSession ss;
private StudentMapper sm;
private StudentMajorMapper smm;
@Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
ss=SqlSessionUtil.getSqlSession();
sm=ss.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
smm=ss.getMapper(StudentMajorMapper.class);
}
@After
public void tearDown() throws Exception {
ss.commit();
ss.close();
}
//一对多查询
public void test() {
List<StudentMajor> list=smm.selectAll();
for(StudentMajor a:list){
System.out.println(a);
}
}
//根据专业查人员,给一对多用
public void selectz(){
List<Student> l=sm.selectz(3);
for(Student a:l){
System.out.println(a);
}
}
//多对一查询
@Test
public void selectall() {
List<Student> st=sm.selectall();
for(Student tt:st){
System.out.println(tt);
}
}
//根据主键查询,给多对一用
public void select(){
StudentMajor a=smm.select(1);
System.out.println(a);
}
}
一对多查询结果

多对一查询结果

命运给予的,无论多少,皆需认真对待。朗如日月,清如水镜
------------------------------------------------------




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号