python读取yaml文件
yaml文件可以存储多种不同类型的数据(字符串、数字、元组、列表、字典等);
所有的数据都是以冒号和缩进的形式进行存储,严格区分大小写、中英文状态;
yaml文件示例:
1 # yaml文件中通过#号进行注释 2 # ①存储字典格式数据 3 test1: 4 login: 5 user: buxiubuzhi 6 password: 123456 7 8 # 或者 9 test2: {login:{user: buxiubuzhi,password: 123456}} 10 # 读取到的数据: 11 # { 12 #'test1': {'login': {'user': 'buxiubuzhi', 'password': 123456}}, 13 #'test2': {'login': {'user': 'buxiubuzhi', 'password': 123456}} 14 #} 15 # 读取到的数据的数据类型: <class 'dict'> 16 17 # ②存储列表格式数据 18 19 - test: 第一个测试用例 20 - test: 第二个测试用例 21 - test: 第三个测试用例 22 23 #读取到的数据: [{'test': '第一个测试用例'}, {'test': '第二个测试用例'}, {'test': '第三个测试用例'}] 24 #读取到的数据的数据类型: <class 'list'> 25 26 27 # 或者 28 [test: 第一个测试用例,test: 第二个测试用例, test: 第三个测试用例] 29 # 读取到的数据: [{'test': '第一个测试用例'}, {'test': '第二个测试用例'}, {'test': '第三个测试用例'}] 30 # 读取到的数据的数据类型: <class 'list'> 31 32 # ③ 数据的锚点 通过&创建锚点 33 userInfo: &userInfo 34 username: buxiubuzhi 35 password: 123456 36 phoneNumber: 19999999999 37 38 # 注册时需要用到用户信息 通过*引用锚点 << 代表锚点插入的位置 39 register: 40 <<: *userInfo 41 42 #输出结果 43 # { 44 # 'userInfo': {'username': 'buxiubuzhi', 'password': 123456, 'phoneNumber': 19999999999}, 45 # 'register': {'username': 'buxiubuzhi', 'password': 123456, 'phoneNumber': 19999999999} 46 # } 47 48 userInfo: &userInfo 49 username: &username buxiubuzhi 50 password: &password 123456 51 phoneNumber: 19999999999 52 53 # 登录时只需要引用用户名和密码 54 login: 55 username: *username 56 password: *password 57 58 # 输出结果 59 #{ 60 # 'userInfo': {'username': 'buxiubuzhi', 'password': 123456, 'phoneNumber': 19999999999}, 61 # 'login': {'username': 'buxiubuzhi', 'password': 123456} 62 #}
1.python读取一个yaml文件
# 导包 import yaml # 定义yaml文件路径 yaml_path = r'D:\Python_Script\new_framework\source_file\login_page.yaml' # 获取文件流对象 with open(yaml_path,'rb')as fileOpen: # 通过safe_load 读取文件流 value = yaml.safe_load(fileOpen) print('读取到的数据:',value) print('读取到的数据的数据类型:',type(value))
2.将数据写入到yaml文件
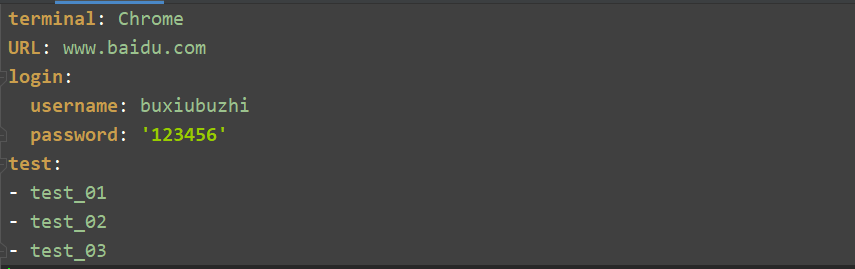
1 # 定义yaml文件路径 2 yaml_path = r'./source_file/test1.yaml' 3 4 # 将复杂类型写入到yaml文件中 5 data = { 6 "terminal" : "Chrome", 7 "URL": "www.baidu.com", 8 "login":{"username":"buxiubuzhi","password":"123456"}, 9 "test":["test_01","test_02","test_03"] 10 } 11 12 # 写入文件,如果文件不存在将会自动创建 13 with open(yaml_path,mode="w",encoding="utf-8") as fp: 14 yaml.dump(data,fp)
写入结果:

虽然数据成功写入了,但是有一个问题,写入之后的顺序发生了改变,有时候我们希望数据有一定的关联性数据顺序不能发生改变,那该怎么样呢?
第二种写入数据的方法,yaml模块的升级版:ruamel.yaml
1 # 安装模块:ruamel.yaml 2 # pip install ruamel.yaml 3 4 # 导包 5 from ruamel import yaml 6 7 # 定义yaml文件路径 8 yaml_path = r'./source_file/test1.yaml' 9 10 # 将复杂类型写入到yaml文件中 11 data = { 12 "terminal" : "Chrome", 13 "URL": "www.baidu.com", 14 "login":{"username":"buxiubuzhi","password":"123456"}, 15 "test":["test_01","test_02","test_03"] 16 } 17 18 # 写入文件,如果文件不存在将会自动创建 19 with open(yaml_path,mode="w",encoding="utf-8") as fp: 20 yaml.dump(data,fp,Dumper=yaml.RoundTripDumper) # 只需要添加参数:Dumper=yaml.RoundTripDumper
写入结果: