第六周进度报告
这周主要学习了一些常用的API,以及Object类
常用API

package me.Study;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取到当前时间的毫秒值
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
System.out.println("6");
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - start);
int[] arr = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
int[] arr2 = new int [10];
System.arraycopy(arr,0,arr2,0,5);
for (int i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr2[i] + " ");
}
//终止当前Java虚拟机的进程
//0代表正常停止,非0代表异常停止
System.exit(0);
}
}
常用API
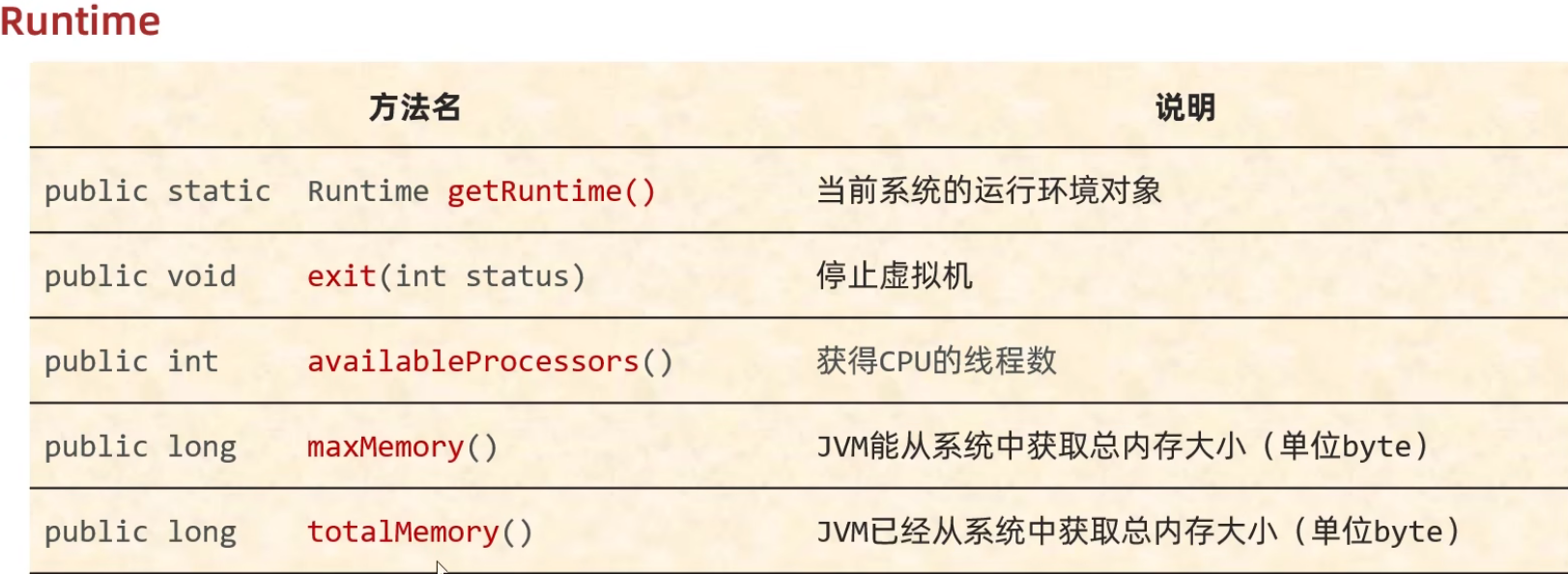
Runtime
package me.Study;
import java.io.IOException;
public class RuntimeStudy {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//Runtime
//获取Runtime对象 getRuntime()
//1.exit 停止虚拟机
//Runtime.getRuntime().exit(0);
//2.获取CPU的线程数
System.out.println(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());
//3.总内存大小,单位:byte
System.out.println(Runtime.getRuntime().maxMemory() / 1024 / 1024 );
//4.已经获取的总内存大小
System.out.println(Runtime.getRuntime().totalMemory() /1024 / 1024);
//5.剩余内存大小
System.out.println(Runtime.getRuntime().freeMemory() / 1024 / 1024);
//6.运行cmd命令
//shutdown命令
//-s 默认一分钟之后关机
//-s -t + 时间(秒) 定时关机
//-a 取消关机
//-r 重启
Runtime.getRuntime().exec("shutdown -a");
}
}
Object

package me.Study;
public class ObjectStudy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stiudent s = new Stiudent("Tom");
System.out.println(s.toString());
//Object中的toString返回字符串形式的地址
//在子类中要返回内容一般要重写
//Object 类中eauals 比较的是地址值,要比较类的内容一般要重写equals
Stiudent s2 = new Stiudent("Tom");
System.out.println(s.equals(s2));
String s1 = new String("abc");
StringBuilder s3 = new StringBuilder("abc");
System.out.println(s1.equals(s3));
System.out.println(s3.equals(s1));
}
}
深拷贝和浅拷贝
- 重写Object中的clone方法
- 让javabean类实现Cloneable接口
- 创建原对象并调用clone就可以了
Object类中clone是浅克隆
深克隆需要自己写
package me;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
public class CloneStudy {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
int[] data = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,0};
Person p1 = new Person("zhangsan",100001,data);
Person p2 = (Person)p1.clone();
Gson gson = new Gson();
String s = gson.toJson(p1);
Person p3 = gson.fromJson(s,Person.class);
p1.data[0] = 999;
System.out.println(p3);
}
}

Objects.equals(s1,s2)

BigInterge

public static void main(String[] args) {
BigInteger bg1 = new BigInteger(5,new Random());
BigInteger bg2 = new BigInteger("999999999");
BigInteger bg3 = BigInteger.valueOf(888888);
BigInteger bg4 = bg2.add(bg3);
System.out.println(bg1);
System.out.println(bg2);
System.out.println(bg3);
System.out.println(bg4);
}
BigInteger构造方法小结:
- 如果BigInteger表示的数字没有超过long的范围,可以用静态方法获取
- 如果BigInteger表示的超出long的范围,可以用构造方法获取
- 对象一旦创建,BigInteger内部记录的值不能发生改变
- 只要进行计算都会产生一个新的BigInteger对象
BigInteger的成员方法

System.out.println(bg2.add(bg3));
System.out.println(bg2.multiply(bg2));
System.out.println(bg2.divide(bg3));
System.out.println(bg2.subtract(bg3));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bg2.divideAndRemainder(bg3)));
System.out.println(bg2.max(bg3));
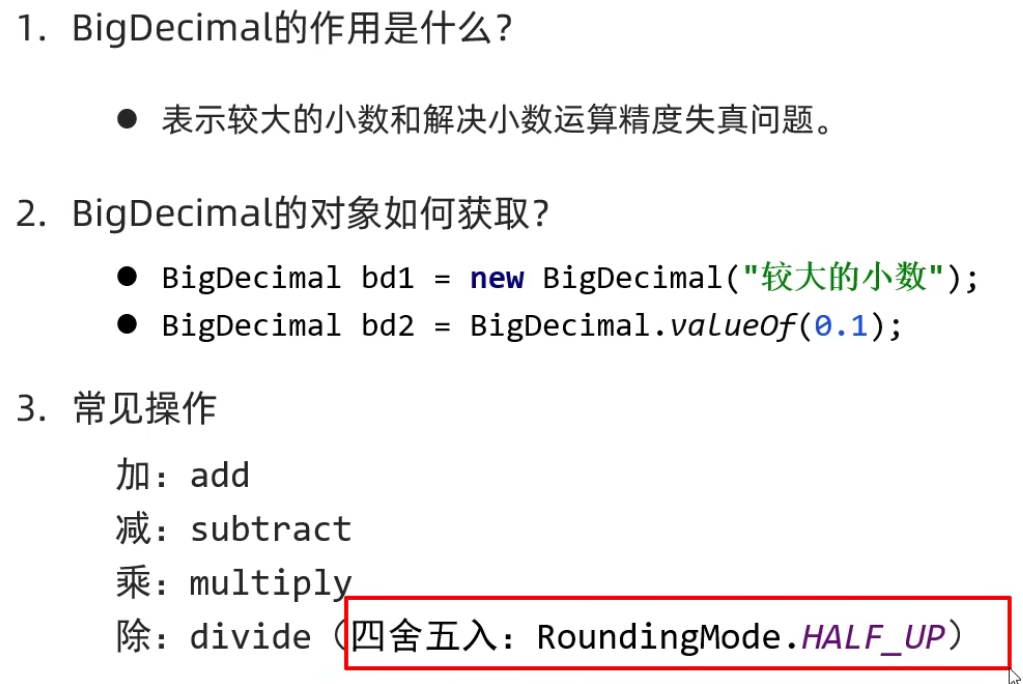
BigDecimal
//直接传入小数,不精确,不建议使用
BigDecimal bd1 = new BigDecimal(0.9);
//传入字符串小数,精确
BigDecimal bd2 = new BigDecimal("0.9");
//通过静态方法Valueof()创建对象
BigDecimal bd3 = BigDecimal.valueOf(9);
BigDecimal bd4 = BigDecimal.valueOf(9);
System.out.println(bd1);
System.out.println(bd2);
System.out.println(bd3);
//如果valueof()传递的是0~9之间的数,那么方法会返回已将创建好的对象,不会重新创建对象
System.out.println(bd3 == bd4);
BigDecimal中的成员方法

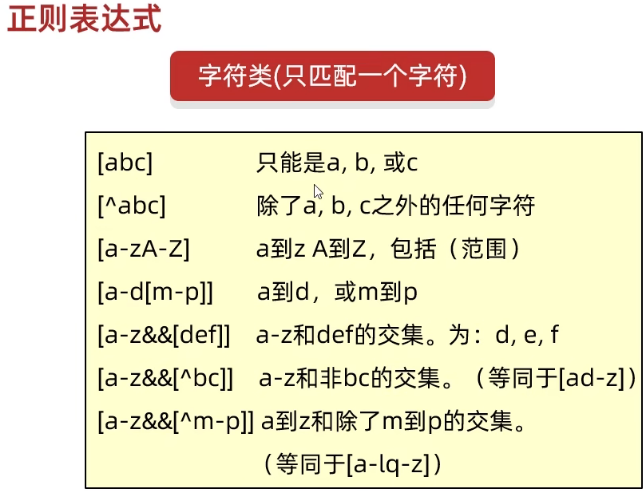
正则表达式
正则表达式可以校验字符串是否满足一定的规则,并用来校验数据格式的合法性
sout("\"") 此时\表示转义字符,改变了后面那个双引号原本的含义

System.out.println("s".matches("[abs]"));
System.out.println("s".matches("."));
System.out.println("s".matches("[^s]"));
System.out.println("s".matches("[a-z]"));
System.out.println("s".matches("[^d]"));
System.out.println("s".matches("\\d"));
System.out.println("s".matches("\\w"));
System.out.println("_".matches("\\w"));
System.out.println("_".matches("\\W"));
System.out.println("b".matches("a-z"));
System.out.println("b".matches("[a-z]"));
System.out.println("abvdef88g".matches("\\w{5,}"));
System.out.println("abcdegf123".matches("[a-z]{3,}"));



