JavaScript:JavaScript语法的详细介绍
JavaScript语法:只要Java会了,基本上javascript语法就会了。
——变量的定义
——程序的结构控制
——数组操作
——函数的定义即使用
基本的test.html代码如下,它会导入下面的test.js中的javascript代码:
<!doctype html> <html lang="zh-CN"> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <meta name="description" content=hello.html""> <meta name="keywords" content="hello,html,js"> <title>javascript的程序开发</title> <script type="text/javascript" src="test.js"></script> </head> <body> </body> </html>
1.变量的定义
在Java中如果要定义变量语法:“数据类型 变量名称 = 内容”。对于数据类型,Java中有很多,还有许多自定义的类型。Javascript很简单,可以不声明类型直接编写变量,变量类型是根据其设置的内容来决定的。
范例:观察test.js程序代码
temp = 10; //temp类型为整型 window.alert(temp + temp); //20

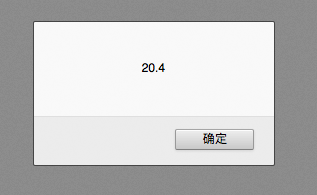
temp = 10.2; //temp类型为浮点型 window.alert(temp + temp); //20.4
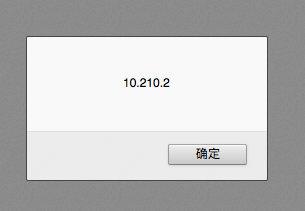
temp = "10.2"; //temp类型为字符串 window.alert(temp + temp); //10.210.2
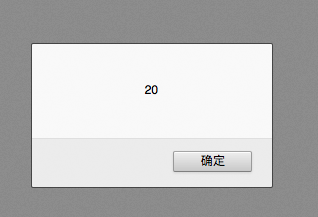
temp = "10.2"; //temp类型为字符串 temp = 10 ; //temp类型为整型,类型被修改 window.alert(temp + temp); //20

可以发现,整个javascript操作当中,并没有那么严格的语法要求。因为从正常来讲,javascript应该是美工学的,不是程序开发人员来学的。所以它最初设计的逻辑性没有这么滴强。
如果有需要也可以使用var来定义变量。
var temp = 10 ; window.alert(temp + temp);//20
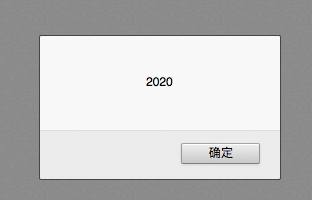
var temp = 10 ; temp = "20" //改变类型,变成字符串 window.alert(temp + temp); //2020
javascript没有必要这么概念的复杂,一帮情况下,在javascript定义全局变量的时候使用。其实都可以不使用,只是一个好的编程习惯,仅此而已。
既然说到了字符串的问题了,那么也就产生新的事情了。即字符串方面的操作:
字符串的比较:
var temp = "hello"; alert(temp == "hello"); //ture

字符串判断是否为空:没有equals方法
方式一:
var temp = "hello"; alert(temp != ""); //ture
方式二:
var temp = "hello"; alert(temp != null); //ture

字符串替换:
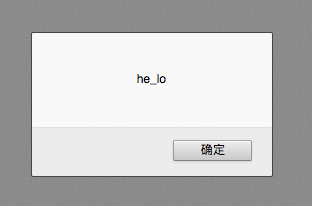
var temp = "hello"; alert(temp.replace("l","_")); //将l替换成下划线,he_lo
字符串子串的获取:
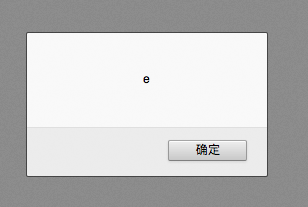
var temp = "hello"; alert(temp.substring("1",2)); //从角标1开始到角标2结束的子串,不包括尾, e
字符串长度:
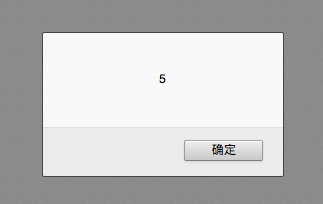
var temp = "hello" alert(temp.length); //5
发现,java大部分的习惯性操作,在javascrip里面都是存在的。
2.程序的结构控制
程序逻辑就是if、else、switch、while、for循环。
范例:使用if分支语句
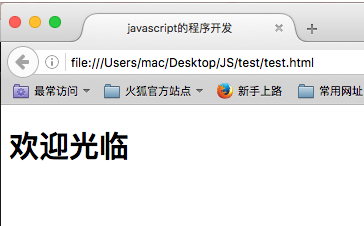
var temp = "hello"; if (temp == "hello") { document.write("<h1>欢迎光临</h1>"); }else{ document.write("<h1>你去死吧</h1>"); }
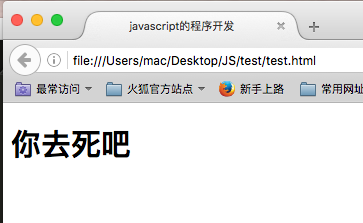
var temp = ""; if (temp == "hello") { document.write("<h1>欢迎光临</h1>"); }else{ document.write("<h1>你去死吧</h1>"); }
范例:使用while语句
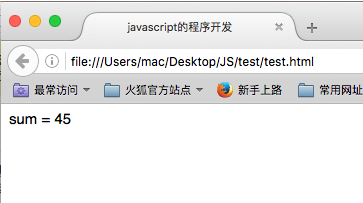
var temp = 0; var sum = 0; while(temp < 10){ sum += temp; temp ++; } document.write("sum = "+sum); //45
范例:使用for循环语句
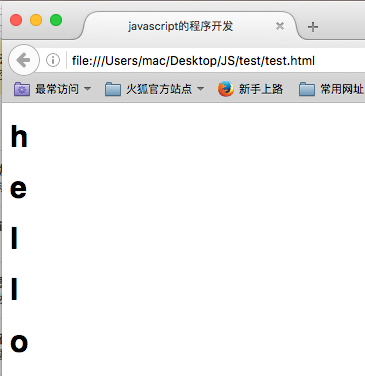
var temp = "hello"; for (i = 0; i < temp.length; i++) { document.write("<h1>"+temp[i]+"</h1>"); // h e l l o };
范例:使用switch语句
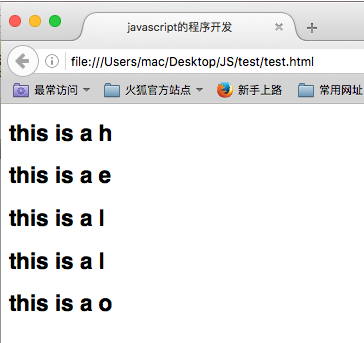
var temp = "hello"; for (var i = 0; i < temp.length; i++) { switch(temp[i]){ case 'h': document.write("<h2>this is a h</h2>"); break; case 'e': document.write("<h2>this is a e</h2>"); break; case 'l': document.write("<h2>this is a l</h2>"); break; case 'o': document.write("<h2>this is a o</h2>"); break; } };
范例:打印乘法口诀表
console.log("*******控制台调试代码*******");
document.write("<table border='1'>");
for (var i = 1; i <= 9; i++) {
document.write("<tr>");
for (var j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
document.write("<td>"+j+" * "+i+" = "+ (i*j) +"</td>");
};
for (var j = 1; j <= 9-i; j++) {
document.write("<td> </td>");
};
document.write("</tr>");
};
document.write("</table>");

另外告诉一点,以后如果想进行代码的错误调试,可以通过如下语句完成:
console.log(一些信息),用它来取代alert()和document.write(),从而在后台做代码的检察观测,如下效果图:

3.数组操作
数组是一个类,使用的是Array类描述数组概念。可以使用length取得数组的长度,也可以使用索引的方式设置内容。
范例:求数组的长度
var data = new Array(3); //3个元素的内容 document.write("<h1>数组长度:" + data.length + "</h1>");

范例:通过索引设置和获取数组的值
var data = new Array(3); //3个元素的内容 data[0] = 10; data[1] = 20; data[2] = 30; document.write("<h1>数组长度:" + data.length + "</h1>"); for (var i = 0; i < data.length; i++) { document.write("<h1>" + data[i] + "</h1>"); };
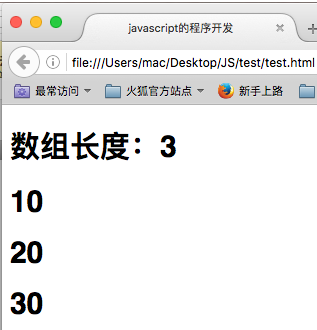
范例:数组大小自动扩充
var data = new Array(3); //3个元素的内容 data[0] = 10; data[1] = 20; data[2] = 30; data[5] = 30; document.write("<h1>数组长度:" + data.length + "</h1>"); for (var i = 0; i < data.length; i++) { document.write("<h1>" + data[i] + "</h1>"); };

javascript中的数组的设计是一个很牛的设计思想,可以随意动态的扩充大小。但是如果没有的内容,它不会用0、null来描述,使用”undefined”来描述。
4.函数的定义即使用(Function)
如果现在使用Java来定义一个方法,格式是这样的:
[public | protected | private] [static] [abstract] [final] [native] [synchronized] 方法返回值 方法名称(参数类型 变量,… | 参数类型...变量 ) [throws 异常,异常,…]{
//方法代码
[return 返回值];
}
那么在javascript中,函数的定义非常简单:
function 函数名称(参数){
[return 返回值];
}
定义函数的时候不需要考虑返回值的类型,如果要返回,那么就直接编写return就行。
范例:定义函数1
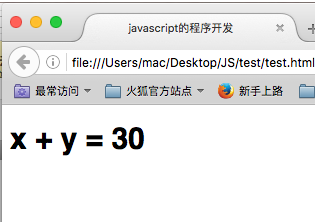
function add (x,y) { return x + y; } document.write("<h1>" + "x + y = " + add(10,20) +"</h1>");

最厉害的是在调用函数的时候,函数的参数可以随便写:
范例:定义函数2
function add (x,y) { return x + y; } document.write("<h1>" + "x + y = " + add(10,20,30,40,50,60) +"</h1>");
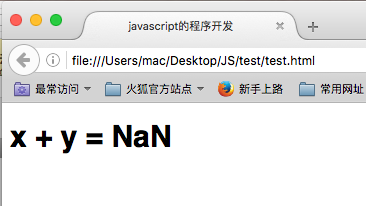
在调用函数的时候如果参数不足,则参数的内容会自动使用”undefined”进行表示,肯定无法进行正确的计算。
范例:定义函数3
function add (x,y) { return x + y; } document.write("<h1>" + "x + y = " + add(10) +"</h1>");
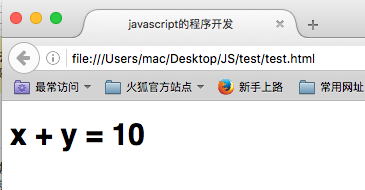
如果在参数不足的情况下依然要保证计算的完整,那么就使用“函数名称.argments”判断,此操作表示的是所有函数的参数的内容,艺术组的形式操作,使用length能够判断长度。
范例:定义函数4
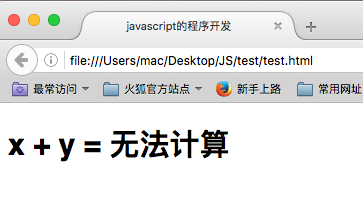
function add (x,y) { if (add.arguments.length == 2) { return x + y; }else if (add.arguments.length == 1) { return x; }else{ return "无法计算"; } }
document.write("<h1>" + "x + y = " + add(10) +"</h1>");
document.write("<h1>" + "x + y = " + add(10,20) +"</h1>");
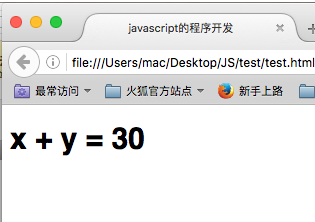
document.write("<h1>" + "x + y = " + add(10,20,30) +"</h1>");
需要注意的是,在javascript里面也存在面向对象的编程。都是以函数为基础的。
范例:观察面向对象
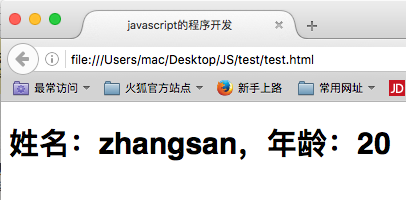
function Person (name,age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.toString = function(){ //表示为类中扩充方法 return "姓名:" + this.name + ",年龄:"+this.age; } } document.write("<h1>" + new Person("zhangsan",20) +"</h1>");
如果代码中写的是”function(){}”的操作,那么表示的是匿名函数。
总结:
<1>、javascript的语法完全考虑到美工的不理智型而设计的;
<2>、javascript的语法都是短小精悍为主;
<3>、javascript原本就不是一个面向对象的编程语言,所以支持的面向对象,只是一个娱乐。




