第二十八讲——GUI编程
第二十八讲——GUI编程
常用组件
- 窗口
- 弹窗
- 面板
- 文本框
- 列表框
- 按钮
- 监听事件
- 鼠标
- 键盘事件
- 破解工具
1. ——简介
GUI的核心; AWT(底层) SWing(高级些)
不流行的原因;
- 界面不美观
- 需要jre环境
学习的目的;
-
可以写出自己想要的小工具
-
工作的时候可以,需要维护到SWing界面 概率很小
-
了解MVC架构,了解监听
2. ——AWT(抽象窗口工具包)
-
1 AWT 介绍
-
包含了很多类,和接口! GUI !
-
元素; 窗口,按钮,文本框
-
java.awt ;
3——Frame
我的 JAVA 第一个图像界面窗口
Application
package Xiang.Lesson01;
import java.awt.*;
// GUI的第一个界面
public class TestFrame {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Frame
Frame frame = new Frame("我的第一个JAVA图像界面窗口");
// 1. 需要设置可见性
frame.setVisible(true);
// 2. 设置窗口大小
frame.setSize(500,500);
// 3. 弹出的初始位置
frame.setLocation(400,400);
// 4. 设置大小固定
frame.setResizable(false);
// 5. 设置背景颜色 Color
frame.setBackground(Color.pink);
//frame.setBackground(new Color(50, 50, 0, 50));
}
}
利用封装实现多个窗口
Application
package Xiang.Lesson01;
import java.awt.*;
public class TestFrame01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 展示多个窗口 new
MyFrame myFrame1 = new MyFrame(100,100,200,200,Color.cyan);
MyFrame myFrame2 = new MyFrame(300,100,200,200,Color.yellow);
MyFrame myFrame3 = new MyFrame(100,300,200,200,Color.pink);
MyFrame myFrame4 = new MyFrame(300,300,200,200,Color.orange);
}
}
class MyFrame extends Frame {
static int id = 0; // 计数器
// 能起到计数效果是 static 类变量的作用 如果是实例变量的话 会随着 “new” 进行跟新 而类变量不参与实例化因此起到计数的作用
public MyFrame(int x,int y ,int w ,int h,Color color){
super("MyFrame+"+(++id));
//new Frame("MyFrame+"+(++id)); no
setBackground(color);
setBounds(x,y,w,h);
setVisible(true);
}
}
/**
* 1. 实例化对象的实质就是在调用构造器 因此在用构造方法时 使用父类的方法不用实例化 其实已经实例化 可以直接使用父类方法
* 2. super 是在调用父类的构造器 默认自己会调用父类无参构造
* 3. 知道 id 为什么走new后不为0 是因为 ++i 是先+-后赋值 所以呢0 的++0 不可能为0
*/
/**
* super("MyFrame+"+(++id));
* new Frame("MyFrame+"+(++id));
* -是不一样的 super 表示父类的构造器但是功能不同 下面运行起来 窗口没有字符
* -在讲构造器的时候说过 super 的作用是调用父类构造器 避免在子类构造器中使用 new 父类
*/
布局很重要!!!!!!
4.——Panel
Panel 无法单独显示必须添加到某个容器中
关于 在Panel 中添加 Button 无法显示 可以通过设置 Button 的大小位置 和改变布局 来解决
Application
package Demo;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建窗口
Frame frame = new Frame("I LOVE YOU!!");
// 创建面板
Panel panel = new Panel();
// 1. 设置布局
frame.setLayout(null); // 这里如果不设置null 就默认把窗口置顶 就看不见面板了
// 2. 设置 Frame
// 1. 设置窗口可见性
frame.setVisible(true);
// 2. 设置窗口大小 + 初始位置
frame.setBounds(500,500,500,500);
// 3. 设置 设置窗口是否可调整
frame.setResizable(true);
// 4. 设置窗口背景颜色
frame.setBackground(Color.orange);
// 3. 设置 Panel 面板跟随窗口调整
// 1. 设置面板可见性
panel.setVisible(true);
// 2. 设置面板位置(相对于窗口 相对坐标) + 大小
panel.setBounds(100,100,300,300);
// 3. 设置面板颜色
panel.setBackground(Color.green);
// 4. 关联窗口面板
frame.add(panel);
// 5. 监听事件; 监听窗口关闭事件 System.exit(0);
// 适配器模式
frame.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
@Override
//窗口点击关闭时 需要做的事
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
//super.windowClosing(e);
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
}
5.——布局管理器
- 流式布局(默认) FlowLayout
- 东西南北中 BorderLayout
- 表格布局 GirdLayout
流式布局
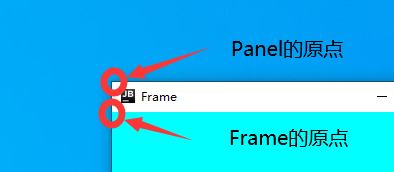
注意!!!在使用 Panel 做布局添加组件时要考虑到标题栏,因为 Frame 和 Panel 的原点不一样
在JFrame中不存在这个问题 所以不去深究
Application
package Demo;
import java.awt.*;
public class DemoFlowLayout {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame frame = new Frame();
// 设置大小,背景,可见性
frame.setBackground(Color.green);
frame.setSize(200,150);
frame.setVisible(true);
// 设置布局 流式布局 会一个个排列进行布局
frame.setLayout(new FlowLayout());// 默认居中
// frame.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT)); 左对齐
// frame.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.RIGHT)); 右对齐
// 组件-按钮
Button button1 = new Button("button1");
Button button2 = new Button("button2");
Button button3 = new Button("button3");
button1.setBackground(new Color(255,0,255));
// 添加按钮
frame.add(button1);
frame.add(button2);
frame.add(button3);
}
}
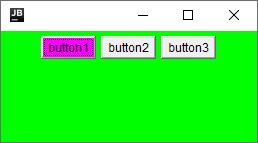
会进行一个个排列
东西南北中布局
Application
package Demo;
import java.awt.*;
public class DemoBorderLayout {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame frame = new Frame("DemoBorderLayout");
// 设置窗口
frame.setBounds(500,500,500,500);
frame.setVisible(true);
frame.setLayout(new BorderLayout());// 及其重要
// 创建按钮
Button east = new Button("east"); // 东
Button west = new Button("west"); // 西
Button south = new Button("south"); // 南
Button north = new Button("north"); // 北
Button center = new Button("center"); // 中
// 设置按钮布局
frame.add(east,BorderLayout.EAST);
frame.add(west,BorderLayout.WEST);
frame.add(south,BorderLayout.SOUTH);
frame.add(north,BorderLayout.NORTH);
frame.add(center,BorderLayout.CENTER);
//frame.add(new Button(),BorderLayout.CENTER);
}
}
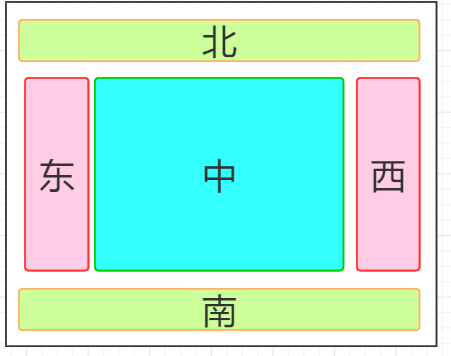
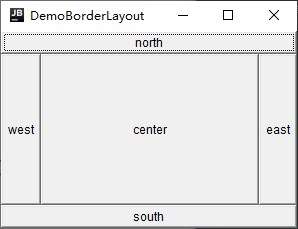
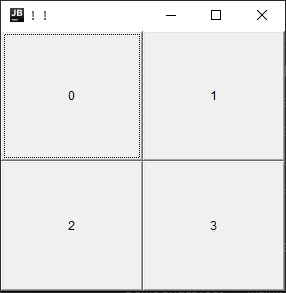
表格布局(Grid)
Application
package Demo;
import java.awt.*;
public class DemoGridLayout {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame frame = new Frame("一个小题目!!");
// 1. 设置窗口
frame.setBounds(0,0,300,300);
frame.setVisible(true);
frame.setBackground(Color.black);
// 2. 创建按钮
Button i1 = new Button("1");
Button i2 = new Button("2");
Button i3 = new Button("3");
Button i4 = new Button("4");
// 3. 添加按钮
frame.setLayout(new GridLayout(2,2));
// frame.add(i1);
// frame.add(i2);
// frame.add(i3);
// frame.add(i4);
for (int i = 0; i <4 ; i++) {
frame.add(new Button(i+""));
}
}
}
6.——事件监听
事件监听: 当某个事情发生的时候,执行什么。 当摁下 关闭窗口时执行什么
Application
package Demo;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
public class TestActionEvent {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 按下按钮,触发一些事件
Frame frame = new Frame();
Button button = new Button();
frame.add(button);
frame.pack();
frame.setVisible(true);
// 监听按钮事件
// 也可以调用匿名内部类但是不推荐用
// button.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
// @Override
// public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent actionEvent) {
// System.out.println("aaa");
// }
// });
MyActionListener myActionListener = new MyActionListener();
button.addActionListener(myActionListener);
CloseWindow(frame);// 关闭窗口
}
// 关闭窗口事件 写成方法
public static void CloseWindow(Frame frame){
frame.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
}
// 不同的按钮 可以写进同一个事件类 由 类中的方法来判定走那一个程序
// 按钮事件监听
class MyActionListener implements ActionListener{
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent actionEvent) {
System.out.println("aaa");
}
}
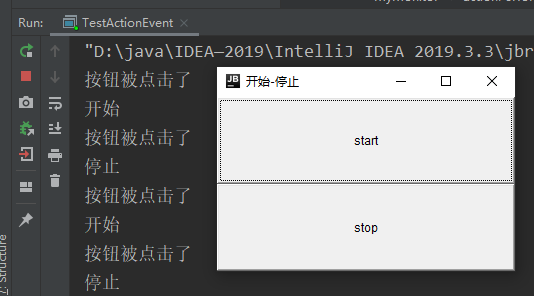
同一个监听类实现多个事件
Application
package Demo;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
public class TestActionEvent {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 两个按钮 实现同一个监听
// 开始 停止
Frame frame = new Frame("开始-停止");
Button button = new Button("start");
Button button1 = new Button("stop");
frame.setBounds(500,500,500,500);
frame.setVisible(true);
frame.setLayout(new GridLayout(2,1));
frame.add(button);
frame.add(button1);
MyMonitor myMonitor = new MyMonitor();
//
button.setActionCommand("开始");
button1.setActionCommand("停止");
button.addActionListener(myMonitor);
button1.addActionListener(myMonitor);
}
}
// 多个按钮可以写在一个监听类
class MyMonitor implements ActionListener{
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
System.out.println("按钮被点击了");
if (e.getActionCommand().equals("1")){
System.out.println(e.getActionCommand());
} else{
System.out.println(e.getActionCommand());
}
}
}
7.——TextField
TextField 的使用
package Demo;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
public class TestText01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 启动 !!!
// main 方法里只有启动 没有其他的东西
closeWindow(new MyFrame1());
}
public static void closeWindow(Frame frame){
frame.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
}
class MyFrame1 extends Frame{
public MyFrame1(){
// 建立简单窗口
super("我的窗口");
setVisible(true);
setBounds(500,500,500,500);
setResizable(true);
//pack();
// 创建一个输入文本框 并把功能添加到窗口中
TextField textField = new TextField();
add(textField);
//监听这个文本框输入的文字 并把功能添加到输入框中
MyActionListener myActionListener = new MyActionListener();
// 按下 enter 就会触发输入框的事件
textField.addActionListener(myActionListener);
textField.setEchoChar('*');
}
}
class MyActionListener implements ActionListener{
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// 1. 获得一些资源 返回一个对象(是 Object 类型) 强转成 TextField 类型
TextField field = (TextField) e.getSource();
//最初发生 Event 的对象。
// 2. 获取文本框的内容 并打印
System.out.println(field.getText());
field.setText(""); // 按下 enter 执行完本方法内容 就会清空 null ""
}
}
D:\java\IDEA—2019\IntelliJ IDEA 2019.3.3\lib\idea_rt.jar=49771:D:\java\IDEA—2019\IntelliJ IDEA 2019.3.3\bin" -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 -classpath F:\Application\out\production\Application Demo.TestText01
窗前明月光,疑是地上霜
Process finished with exit code 0
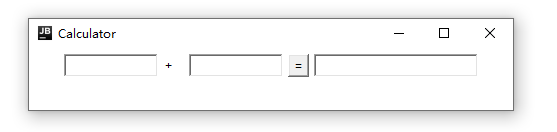
简易计算器
简易计算器 版本一 面向过程
package Demo;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
public class TestCalc {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 简易计算器
closeWindow(new Calculator());
}
public static void closeWindow(Frame frame){
frame.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter(){
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
}
// 计算器面板
class Calculator extends Frame{
public Calculator(){
super("Calculator");
setBounds(500,500,500,100);
setVisible(true);
TextField t0 = new TextField(10);// 字符数
TextField t1 = new TextField(10);
TextField t2 = new TextField(20);
// 3 个文本框
// 1 个按钮
Button button = new Button("=");
// 添加组件功能 按下 = 把数字相加 并显示
button.addActionListener(new MyActionListener1(t0,t1,t2));
// 1 个标签
Label label = new Label("+");
// 创建布局
setLayout(new FlowLayout());
add(t0);
add(label);
add(t1);
add(button);
add(t2);
}
}
// 添加文本框监听事件
class MyActionListener1 implements ActionListener{
// 将其它类的值 传递进来
private TextField num1,num2,num3;
// 构造器没有返回值!!!
public MyActionListener1(TextField num1,TextField num2,TextField num3){
this.num1 = num1;
this.num2 = num2;
this.num3 = num3;
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// 1.获取 num1 和 num2
int i1 = Integer.parseInt(num1.getText());
int i2 = Integer.parseInt(num2.getText());
// 2.相加并 赋值给第三框
num3.setText(String.valueOf(i1+i2));
//num3.setText(""+(i1+i2));
// 3.清除第一和第二
num1.setText("");
num2.setText("");
/**
* - get 技能
* + 用构造器传递数据
* + = 号两个的值不可以互相传递 t3 的改变是因为构造器的构造方法
*/
}
}
用构造器来传递值
计算器版本二 完全面对对象写法 回忆组合
Application
package Work;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
/**
* 22.06
* @author 夏天的风
*/
public class Work603 {
public static void main(String[]args){
// 启动
new MyFrame00().loadFrame();
}
}
class MyFrame00 extends Frame {
/**
* 可以不写构造器
* 正常写 类中 属性方法分开
*/
// 属性
// 三个文本框 一个按钮 一个标签
TextField t1 = new TextField(10);
TextField t2 = new TextField(10);
TextField t3 = new TextField(20);
Button b = new Button("=");
Label label = new Label("+");
// 方法
public void loadFrame(){
setVisible(true);
setBackground(Color.cyan);
pack();
// 按钮添加功能
setLayout(new FlowLayout());
add(t1);
add(label);
add(t2);
add(b);
add(t3);
//这里的this 就是 MyFrame00
b.addActionListener(new MyMonitor00(this));
// 关闭方法
addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
}
// 监听器类
class MyMonitor00 implements ActionListener {
// 获取计算器对象 在一个类中组合另一个类、
// 和之前不同的是 把对象传进来了
MyFrame00 myFrame00 = null; // null 的意思应该是空的对象 默认的对象
public MyMonitor00(MyFrame00 myFrame00) {
this.myFrame00 = myFrame00;
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent actionEvent) {
// 按下按钮
// 1. 获取 t1 t2 set t3的值为 t1+t2
int i = Integer.parseInt(myFrame00.t1.getText())+Integer.parseInt(myFrame00.t2.getText());
myFrame00.t3.setText(String.valueOf(i));
// 2. 按下按钮 t1 t2 清空
myFrame00.t1.setText("");
myFrame00.t2.setText("");
}
}
- 用构造器 传递对象
- 学会 对象和对象 组合 来传递对象
new Student = null;创建空对象
这里 复习了一个 包装类的概念 从 TextField
计算器版本三 内部类 回忆内部类
更好的包装
package Work;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
/**
* 22.06
* @author 夏天的风
*/
public class Work603 {
public static void main(String[]args){
// 启动
new MyFrame00().loadFrame();
}
}
class MyFrame00 extends Frame {
/**
* 可以不写构造器
* 正常写 类中 属性方法分开
*/
// 属性
// 三个文本框 一个按钮 一个标签
TextField t1 = new TextField(10);
TextField t2 = new TextField(10);
TextField t3 = new TextField(20);
Button b = new Button("=");
Label label = new Label("+");
// 方法
public void loadFrame(){
setVisible(true);
setBackground(Color.cyan);
pack();
// 按钮添加功能
setLayout(new FlowLayout());
add(t1);
add(label);
add(t2);
add(b);
add(t3);
b.addActionListener(new MyMonitor00());
// 关闭方法
addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
// 监听器类 是 MyFrame00 的内部类可以直接拿外部类的属性
// 内部类 最大的好处就是畅通无阻的访问外部类的属性和方法!!!
class MyMonitor00 implements ActionListener {
// 就不需要构造器传递 对象了
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent actionEvent) {
// 按下按钮
// 1. 获取 t1 t2 set t3的值为 t1+t2
int i = Integer.parseInt(t1.getText())+Integer.parseInt(t2.getText());
t3.setText(String.valueOf(i));
// 2. 按下按钮 t1 t2 清空
t1.setText("");
t2.setText("");
}
}
}
使用内部类优化代码
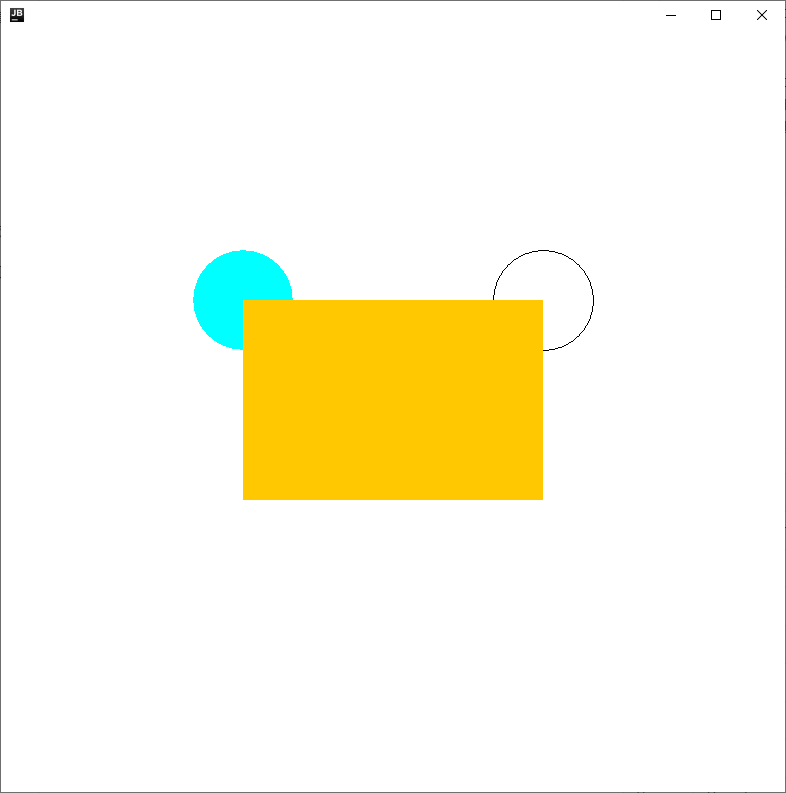
8.——画笔 Paint
Application
package Demo;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
public class MyPaint {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 方法
new MyPaints().loadFrame();
}
}
class MyPaints extends Frame {
public void loadFrame(){
setBackground(Color.white);
setBounds(200,200,800,800);
setVisible(true);
setResizable(true);
addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
@Override
public void paint(Graphics g) {
// 画笔 需要颜色 可以画画
g.setColor(Color.cyan);
// 园
g.fillOval(200,250,100,100);// 两个值可以画椭圆 实心的
g.setColor(Color.black);
g.drawOval(500,250,100,100); // 空心的
g.setColor(Color.orange);
g.fillRect(250,300,300,200);
// 养成习惯 画笔用完 将他还原最初的颜色
}
}
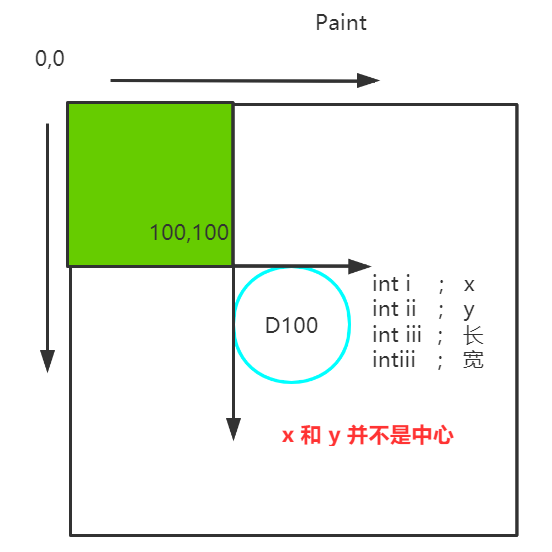
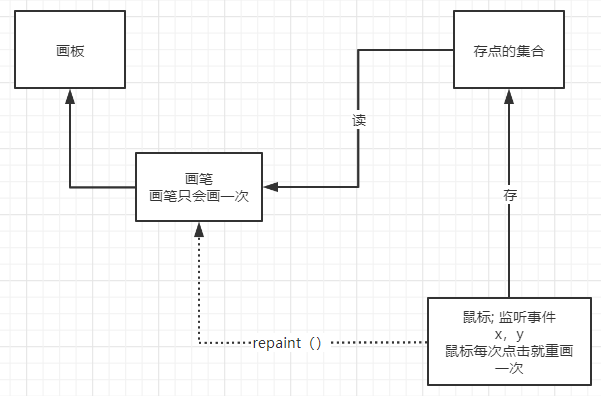
9.——鼠标监听事件 模拟画图工具
Application
package Test;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.MouseAdapter;
import java.awt.event.MouseEvent;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class Test04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new MyFrame("画图");
}
}
class MyFrame extends Frame{
// 画画需要 画笔, 需要监听鼠标当前位置,需要集合来储存这个点
ArrayList points;
public MyFrame(String title){
super(title);
setBounds(200,200,500,500);
setVisible(true);
addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
// 存鼠标点击的点
points = new ArrayList<>();
// 鼠标监听器,针对对钱方面
this.addMouseListener(new MyMouseListener());
}
@Override
public void paint(Graphics g) {
// 画画 监听鼠标的事件
Iterator iterator = points.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
Point point = (Point)iterator.next();
// 强制转换这一步是必要的 !!!
g.setColor(Color.cyan);
g.fillOval(point.x,point.y,10,10);
}
}
// 添加一个点到界面上
public void addPaint(Point point){
points.add(point);
}
// 适配器模式
private class MyMouseListener extends MouseAdapter {
// 鼠标 按下 弹起 不放
@Override
public void mousePressed(MouseEvent e) {
// 鼠标按下事件
MyFrame myFrame = (MyFrame) e.getSource();
// 我们点击的时候 就会在界面上产生一个点
// 这个点就是鼠标的点
myFrame.addPaint(new Point(e.getX(),e.getY()));
// 每次点击鼠标都需要重新画一边
myFrame.repaint();//刷新 30帧 这个东西必要加 不加就 点不上去 原因 不知道 !!!
}
}
}

思路
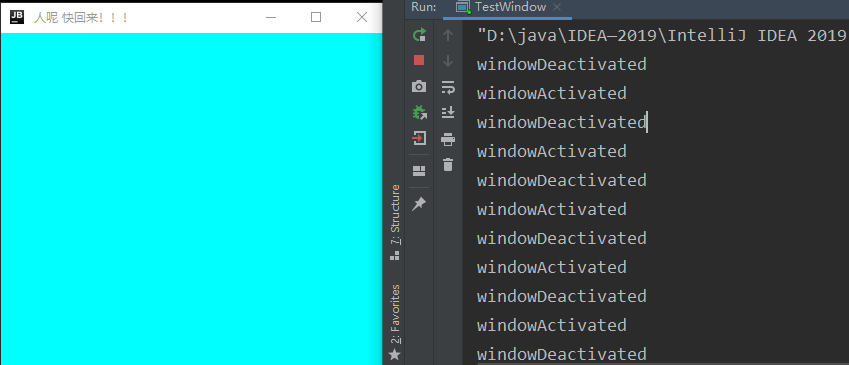
10.——窗口监听
顾名思义 就是关于 窗口的监听事件 主要围绕 WIndowAdapter 中的常用功能来讲
查看 Api 文档技巧
在查找 WindowAdapter 下的方法什么意思 我用 ApI 在 java.awt 下面找根本找不到
因为通过ctrl + B 发现 WindowAdapter 在 java.awt.event 下 这小小错误 浪费我好多时间!
1. 先 Ctrl + B 查找位置 再用位置去查文档!!!


Application
package Test;
/**
* 怎么做到多个窗口 独立关闭?
* 最后也没做到 emm...
*/
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
public class TestWindow {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 启动!
MyWindowFrame w1 = new MyWindowFrame(200,200,400,400);
}
}
class MyWindowFrame extends Frame{
// 建议使用内部类 开销小
public MyWindowFrame(int x,int y,int w,int h){
setBackground(Color.cyan);
setVisible(true);
setBounds(x,y,w, h);
setTitle("我的窗口!!!");
// 感受一下 WindowAdapter 的所有功能
addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
@Override
// 窗口打开 实际没有反应
public void windowOpened(WindowEvent e) {
System.out.println("WindowOpened");
}
@Override
// 正在关闭中 在点击关闭的进行时 的时候 操作
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.out.println("WindowClosing");
}
@Override
// 已经关闭 关闭之后的操作
public void windowClosed(WindowEvent e) {
System.out.println("WindowClosed");
}
@Override
// 窗口被激活 激活就是鼠标是否点击了窗口 焦点是否在窗口上
public void windowActivated(WindowEvent e) {
MyWindowFrame myWindowFrame = (MyWindowFrame)e.getSource();
myWindowFrame.setTitle("欢迎回家~ :)");
System.out.println("windowActivated");
}
@Override
// 窗口没有被激活
public void windowDeactivated(WindowEvent e) {
MyWindowFrame myWindowFrame = (MyWindowFrame)e.getSource();
myWindowFrame.setTitle(" 人呢 快回来!!!");
System.out.println("windowDeactivated");
}
});
/**
// 匿名内部类
addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
*/
// addWindowListener(new MyWindowListener());
}
/**
class MyWindowListener extends WindowAdapter{
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
//System.exit(520);// 正常退出 是直接关闭程序 所以也是关闭窗口的方法
setVisible(false); // 隐藏窗口 隐藏后程序还在运行 但是我们找不到窗口所在 所以要避免这种操作
}
}
*/
}
"D:\java\IDEA—2019\IntelliJ IDEA 2019.3.3\jbr\bin\java.exe" "-javaagent:D:\java\IDEA—2019\IntelliJ IDEA 2019.3.3\lib\idea_rt.jar=51351:D:\java\IDEA—2019\IntelliJ IDEA 2019.3.3\bin" -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 -classpath F:\Application\out\production\Application Test.TestWindow
windowDeactivated
windowActivated
windowDeactivated
windowActivated
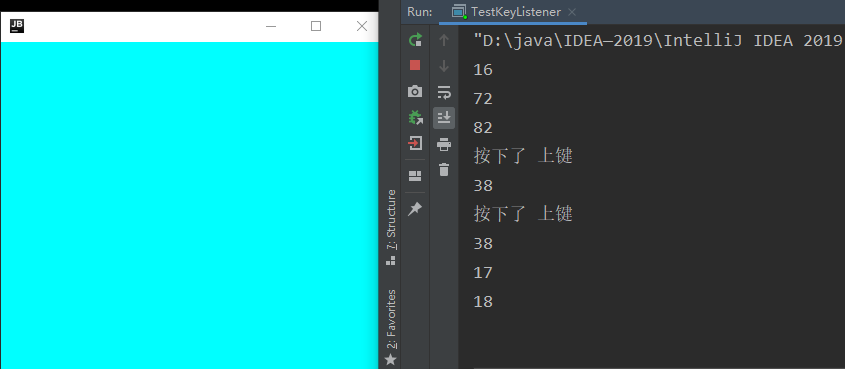
11.——键盘监听事件
Application
package Test;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.KeyAdapter;
import java.awt.event.KeyEvent;
/**
* 键盘监听
* 按下某个键 能执行某个命令
*/
public class TestKeyListener {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new KeyFrame();
}
}
class KeyFrame extends Frame{
KeyFrame(){
setVisible(true);
setBounds(200,200,400,400);
setBackground(Color.cyan);
addKeyListener(new KeyAdapter() {
@Override
// 按下
public void keyPressed(KeyEvent e) {
int keyCode = e.getKeyCode();
// 获取当前键盘按下的 keyCode 的值
if (keyCode== KeyEvent.VK_UP){// 用 Vk_XXX 去搜索想要的 键
System.out.println("按下了 上键");
}
System.out.println(e.getKeyCode());
System.out.println(e.getKeyText(keyCode));
// 根据 keyCode 获取摁下的键名称
}
});
}
}
F:\Application\out\production\Application Test.TestKeyListener
16
72
82
按下了 上键
38
按下了 上键
38
17
18
3.——Swing
AWT是底层 Swing是封装能做下拉框、选择框、能做一些更高级的东西
Application
package Work;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class JFrameDemo {
// init(); 初始化 是一个普通的方法
public void init(){
//-----------------------
// JFrame 顶级窗口
// JFrame 继承了 Frame 的方法
JFrame jf = new JFrame("这是一个 JFrame 窗口");
jf.setVisible(true);
jf.setBounds(500,950,400,400);
jf.setResizable(true);
// jf.setBackground(Color.cyan);
// 背景颜色并没有变化 这里涉及到容器的概念
// 获得一个容器 容器的颜色才是背景的颜色 Container 容器
Container container = jf.getContentPane();// 获取内容面板
container.setBackground(Color.cyan);
//----------------------
// 设置标签 Label 在这里就是 JLabel
JLabel jlabel = new JLabel("天道酬勤");
// 设置标签的字体大小
Font font = new Font("Default",Font.PLAIN,50);
jlabel.setFont(font);
// 让文本标签居中 设置水平对齐
jlabel.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.CENTER);
//-------------------------
jf.add(jlabel);
//-----------------------
/** 关闭事件
* - 如果是 Frame 的话还需要 添加窗口监听、窗口适配器、最后重写方法,
* - JFrame 是升级过的类 它已经写有了(我们自己也能单独写一个关闭方法) 关闭事件的方法 只要调用就行
* */
// 设置 默认 的 关闭 操作 (窗口 常数)
jf.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);// (3) 效果一样
/** Constants
* - int DO_NOTHING_ON_CLOSE = 0;
* 什么也不做的关闭
* - int HIDE_ON_CLOSE = 1;
* 隐藏窗口
* - int DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE = 2;
* 当最后一个窗口关闭时 执行、、、
* - int EXIT_ON_CLOSE = 3;
* 关闭窗口
*/
//-----------------------
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new JFrameDemo().init();
}
}
1.——Dialog
弹窗
Application
package Demo;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
public class DialogDemo extends JFrame {
public DialogDemo(){
// 建立 JFrame 主面板
this.setTitle("MyJFrame");
this.setLocation(800,400);
this.setSize(500,300);
this.setVisible(true);
this.setResizable(true);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
// JFrame 放东西 容器
Container container = this.getContentPane();
container.setBackground(Color.green);
// 绝对布局 除东南西北中、表格布局、流式布局 的第四个常见布局 是根据设定的坐标来进行布局
container.setLayout(null);// null 绝对布局
// 按钮
JButton jbutton = new JButton("Dialog");// 创建 Dialog
jbutton.setBounds(30,30,200,50);
// 点击按钮 弹出弹窗 (监听事件)
jbutton.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent actionEvent) {
// 点击启动弹窗 并设置只能弹出一个弹窗
if (MyDialog.i == 0){
new MyDialog();
} else {
System.out.println("警告! 只能弹出一个弹窗!");
};
}
});
container.add(jbutton);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 启动 !
new DialogDemo();
}
}
// 弹窗
class MyDialog extends JDialog{
// 计数器 用来计数是否弹出 | 0 则弹出 非0 报错
static int i = 0;
public MyDialog() {
// 打开弹窗 i = 1
++i;
this.setVisible(true);
this.setBounds(100,100,400,200);
this.setTitle("JDialog");
this.setResizable(true);
// 弹窗自带的 默认关闭操作 如果你写了 会报警
// this.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
Container container = this.getContentPane();
container.setBackground(Color.cyan);
JLabel jLabel = new JLabel("放弃幻想,全力斗争");
jLabel.setFont(new Font("Default",Font.BOLD,30));
jLabel.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.CENTER);
container.add(jLabel);
// 关闭弹窗 i = 0
this.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
--i;
}
});
}
}
2.——JLabel
ICON
图标 jLabel.setIcon(iconDemo);
Application
package Work;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
// 图标, 需要实现类, 因为标签是写在窗口上的 所以需要继承JFrame
public class IconDemo extends JFrame implements Icon {
private int Width ;
private int height ;
public IconDemo(){} // 无参构造
public IconDemo(int width, int height) {
this.Width = width;
this.height = height;
}
public void init(){
// JFrame 的基本参数
setVisible(true);
setResizable(true);
setBounds(400,400,500,500);
IconDemo iconDemo= new IconDemo(20,20);
// 图标可以放在标签上 可以放在按钮上
JLabel jLabel = new JLabel("iconTest",iconDemo,SwingConstants.CENTER);
Container container = this.getContentPane();
container.add(jLabel);
this.setVisible(true);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
@Override
public void paintIcon(Component c, Graphics g, int x, int y) {
// x , y 表示标签的位置
g.setColor(Color.cyan);
g.fillOval(x+20,y,Width,height);
}
@Override
public int getIconWidth() {
return Width;
}
@Override
public int getIconHeight() {
return height;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new IconDemo().init();
}
}
ImageIcon
Application
package Work;
import javafx.geometry.HorizontalDirection;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.net.URL;
// 图名 Icon
public class ImageIconDemo extends JFrame{
public ImageIconDemo() {
// JFrame 基本参数
setBounds(100,100,400,400);
setVisible(true);
setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
// 获取图片的地址
// 图片在类的同级目录下 通过这个类来获取当前类路径下的东西
JLabel jLabel = new JLabel("ImageIcon");
URL url = ImageIconDemo.class.getResource("plmm.png");// 留意中文名
// url 是一个具体的地址
ImageIcon imageIcon= new ImageIcon(url);// 命名不要与官方冲突了
// ImageIcon 也是 Icon
jLabel.setIcon(imageIcon);
jLabel.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.CENTER);
// 他说上下左右肯定不是 windows 的
Container container = this.getContentPane();
container.add(jLabel);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ImageIconDemo();
}
}

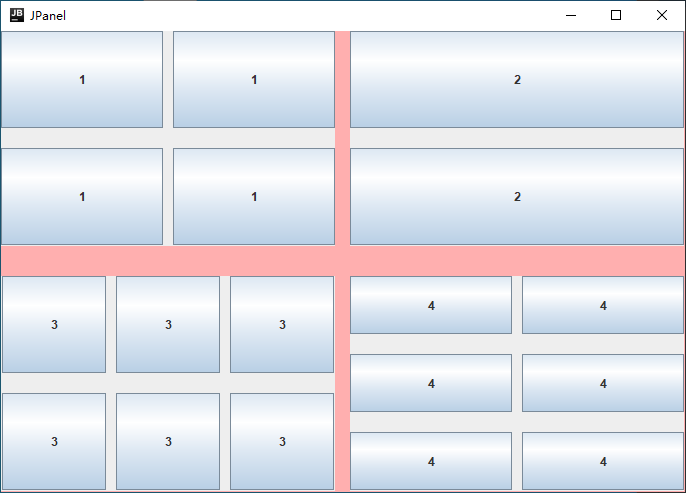
3.—— JPanel
主要讲 new GridLayout() 中后面两个参数 hgap - 横向 vgap - 纵向 间距
container.setLayout(new GridLayout(2,2,15,30));// 横向 与 纵向 间距
Application
package Work;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class JPanelDemo extends JFrame {
public JPanelDemo() {
this.setVisible(true);
this.setResizable(true);
this.setBounds(400,200,700,500);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
Container container = this.getContentPane();
container.setBackground(Color.pink);
container.setLayout(new GridLayout(2,2,15,30));// 横向 与 纵向 间距
JPanel jPanel1 = new JPanel(new GridLayout(2,2,10,20));
JPanel jPanel2 = new JPanel(new GridLayout(2,1,10,20));
JPanel jPanel3 = new JPanel(new GridLayout(2,3,10,20));
JPanel jPanel4 = new JPanel(new GridLayout(3,2,10,20));
jPanel1.add(new JButton("1"));
jPanel1.add(new JButton("1"));
jPanel1.add(new JButton("1"));
jPanel1.add(new JButton("1"));
jPanel2.add(new JButton("2"));
jPanel2.add(new JButton("2"));
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
jPanel3.add(new JButton("3"));
}
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
jPanel4.add(new JButton("4"));
}
container.add(jPanel1);
container.add(jPanel2);
container.add(jPanel3);
container.add(jPanel4);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new JPanelDemo();
}
}
JScrollPane
Scroll 面板就是多了个滚动条的功能的面板 目前理解
ScrollPanel
// JScroll 面板
JScrollPane jScrollPane = new JScrollPane(jTextArea);
// 添加文本域
Application
package Work;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class JScrollDemo extends JFrame {
public JScrollDemo() {
this.setVisible(true);
this.setResizable(true);
this.setBounds(400,200,500,700);
this.setTitle("JScroll");
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
Container container = this.getContentPane();
container.setBackground(Color.black);
container.setLayout(new GridLayout(1,2,20,0));
// 文本域
JTextArea jTextArea = new JTextArea(50,50);
// row 行 col 列 设置的越大么 好像越容易把滚动条激活出来
jTextArea.setText("你能看的多远 , 是否能决定你走的多远?");
// 文本框
JTextField jTextField = new JTextField("你心里所向往的 , 是否决定你能实现的 ? ",20);
// 参数指 默认显示字数
jTextField.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.CENTER);
// 普通面板 好像不支持文本域 只能写文本框
JPanel jPanel = new JPanel();
jPanel.setBackground(Color.orange);
jPanel.add(jTextField);
// JScroll 面板
JScrollPane jScrollPane = new JScrollPane(jTextArea); // 添加文本域
container.add(jPanel);
container.add(jScrollPane);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new JScrollDemo();
}
}
4.——JButton
JButton——普通图片按钮
新技能!—— 鼠标悬浮显示
JButton jButton = new JButton ( ) ;
jButton.setToolTipText ( "悬浮显示的内容 " ) ;
Application
package Work;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.net.URL;
public class JButtonDemo01 extends JFrame {
public JButtonDemo01 (){
// JFrame 基本参数
this.setTitle("图片按钮");
this.setVisible(true);
this.setResizable(true);
this.setBounds(400,500,200,200);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
Container container = this.getContentPane();
// 图片——>图标
URL url = JButtonDemo01.class.getResource("TX0.jpg");
Icon icon = new ImageIcon(url);
// 图标放在按钮上
// 关于按钮的大小应该与布局有关 这里不做延申
JButton jButton = new JButton();
jButton.setIcon(icon);
jButton.setToolTipText("这是一个图片按钮" );// 提示悬浮窗
// add
container.add(jButton);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new JButtonDemo01();
}
}
鼠标悬浮显示
JRadioButton
Appliction
package Work;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class JButtonDemo02 extends JFrame {
public JButtonDemo02 (){
this.setVisible(true);
this.setResizable(true);
this.setTitle("JRadioButton——ButtonGroup");
this.setBounds(400,500,400,300);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
Container container = this.getContentPane();
// 单选框 JRadioButton
JRadioButton jRadioButton01 = new JRadioButton("JRadioButton01");
JRadioButton jRadioButton02 = new JRadioButton("JRadioButton02");
JRadioButton jRadioButton03 = new JRadioButton("JRadioButton03");
jRadioButton02.setToolTipText("这是一个单选框");
// 单选组 ButtonGroup 由于单选框只能选择一个 所以 要建组 一个组里只能选一个
// 意味着不设置 ButtonGroup 会变成 “复选框”
ButtonGroup buttonGroup = new ButtonGroup();
buttonGroup.add(jRadioButton01);
buttonGroup.add(jRadioButton02);
buttonGroup.add(jRadioButton03);
container.add(jRadioButton01,BorderLayout.WEST);
container.add(jRadioButton02,BorderLayout.CENTER);
container.add(jRadioButton03,BorderLayout.EAST);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new JButtonDemo02();
}
}
JCheckBox
Application
package Work;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class JButtonDemo03 extends JFrame {
public JButtonDemo03 (){
this.setVisible(true);
this.setResizable(true);
this.setTitle("CheckBox");
this.setBounds(400,500,400,300);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
Container container = this.getContentPane();
container.setLayout(new GridLayout(2,1,0,50));
// 多选框
JCheckBox jCheckBox01 = new JCheckBox("checkBox——01");
JCheckBox jCheckBox02 = new JCheckBox("checkBox——02");
jCheckBox01.setToolTipText("这是一个复选框");
jCheckBox01.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.CENTER);
jCheckBox02.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.CENTER);
container.add(jCheckBox01);
container.add(jCheckBox02);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new JButtonDemo03();
}
}
5.——JComboBox—JList
JComboBox(下拉框)
Application
package Work;
import javafx.scene.control.ComboBox;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
public class TestComboBoxDemo01 extends JFrame{
public TestComboBoxDemo01() {
this.setTitle("ComboBox");
this.setVisible(true);
this.setResizable(true);
this.setBounds(400,500,400,170);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
Container container = this.getContentPane();
container.setBackground(Color.blue);
container.setLayout(new GridLayout(2,1,0,30));
JLabel jLabel = new JLabel("环球国际影院");
jLabel.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.CENTER);
Font font = new Font("default",Font.PLAIN,40);
jLabel.setFont(font);
JComboBox status = new JComboBox();
status.setToolTipText("status");
status.setBackground(Color.cyan);
status.addItem(null);
status.addItem(null);// 空的下标都为 -1
status.addItem("正在热映");
status.addItem("已下架");
status.addItem("即将上映");
status.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent actionEvent) {
JComboBox status = (JComboBox) actionEvent.getSource();
System.out.println("获取选择下标; "+status.getSelectedIndex());// 获取选择下标
System.out.println("获取选择项目; "+status.getSelectedItem());// 获取选择项目
System.out.println("获取选择行动命令; "+status.getActionCommand());// 获取选择行动命令
System.out.println("toString; "+status.toString());
System.out.println("-----------------------------------");
}
});
container.add(jLabel);
container.add(status);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new TestComboBoxDemo01();
}
}
"D:\java\IDEA—2019\IntelliJ IDEA 2019.3.3\jbr\bin\java.exe"
// ---------------------------------
获取选择下标; -1
获取选择项目; null
获取选择行动命令; comboBoxChanged
toString; javax.swing.JComboBox[,0,82,387x52,layout=javax.swing.plaf.metal.MetalComboBoxUI$MetalComboBoxLayoutManager,alignmentX=0.0,alignmentY=0.0,border=,flags=328,maximumSize=,minimumSize=,preferredSize=,isEditable=false,lightWeightPopupEnabled=true,maximumRowCount=8,selectedItemReminder=]
// ---------------------------------
获取选择下标; 2
获取选择项目; 正在热映
获取选择行动命令; comboBoxChanged
toString; javax.swing.JComboBox[,0,82,387x52,layout=javax.swing.plaf.metal.MetalComboBoxUI$MetalComboBoxLayoutManager,alignmentX=0.0,alignmentY=0.0,border=,flags=328,maximumSize=,minimumSize=,preferredSize=,isEditable=false,lightWeightPopupEnabled=true,maximumRowCount=8,selectedItemReminder=正在热映]
// ---------------------------------
获取选择下标; 3
获取选择项目; 已下架
获取选择行动命令; comboBoxChanged
toString; javax.swing.JComboBox[,0,82,387x52,layout=javax.swing.plaf.metal.MetalComboBoxUI$MetalComboBoxLayoutManager,alignmentX=0.0,alignmentY=0.0,border=,flags=328,maximumSize=,minimumSize=,preferredSize=,isEditable=false,lightWeightPopupEnabled=true,maximumRowCount=8,selectedItemReminder=已下架]
JList
Application
package Work;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.Vector;
public class TestComboBoxDemo02 extends JFrame {
public TestComboBoxDemo02() {
this.setTitle("JList");
this.setVisible(true);
this.setResizable(true);
this.setBounds(400,500,240,170);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
Container container = this.getContentPane();
container.setLayout(new GridLayout(1,2,50,0));
// 生成列表的内容
// String[]
String[] contents = {"1","2","3","4","5","6"};
// Vector 集合
Vector vector = new Vector();
vector.add("张三");
vector.add("李四");
vector.add("王五");
vector.add("赵六");
// 把内容放入列表中
JList jList00 = new JList(contents);
JList jList01 = new JList(vector);
// 把列表放进容器
container.add(jList00);
container.add(jList01);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new TestComboBoxDemo02();
}
}
6.——关于Text
- JTextField
- JTextArea
- JPassworkField
Application
package Work;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.*;
public class TestTextDemo01 extends JFrame {
public TestTextDemo01() {
this.setTitle("Text");
this.setVisible(true);
this.setResizable(true);
this.setBounds(400,200,500,350);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
Container container = this.getContentPane();
container.setLayout(new GridLayout(3,1));
// 1. 文本框
JTextField jTextField00 = new JTextField("Hello",20);// 最多可以放20字符
container.add(jTextField00,BorderLayout.NORTH);// 但是利用布局后 会被填充不止可以放20 尽量使用绝对 null 布局
// 2. 密码框
JPasswordField jPasswordField = new JPasswordField();
jPasswordField.setEchoChar('*');
container.add(jPasswordField);
// 3. 文本域 一般么 配合 Scroll 使用
JTextArea jTextArea = new JTextArea();
container.add(jTextArea);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new TestTextDemo01();
}
}

4.———啊威十八式
getScreenSize — ToolKit
获取系统屏幕尺寸
Toolkit toolkit = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit(); // 1. 获取工具包
Dimension screenSize = toolkit.getScreenSize(); // 2. 从工具包获取屏幕尺寸 并声明名为 screenSize 的 Dimension 规格类
int screenWidth = screenSize.width; // 屏幕的宽
int screenHeight = screenSize.height; // 屏幕的高
关于需要拖动窗口才显示组件的问题
// 只要把 setVisble(); 放在最后就会直接显示
去除标题栏
frame.setUndecorated(true)// 是否不加粉饰

新增单词
| 2 | Component | 组件 | com婆嫩t | |
| 3 | button | 按钮 | 巴腾嗯 but | |
| 4 | Label | 标签 | 来伯 | |
| 5 | Container | 容器 | 坑tai那er | contains |
| 6 | Window | 窗口 | ||
| 7 | Frame | 窗口框架 | 弗雷姆 | |
| 8 | Dialog | 对话框 | 戴尔洛格 | |
| 9 | Panel | 面板 | 帕内尔 | |
| 10 | Applet | 小程序 | applet | |
| 11 | setVisible | 可见的 | visi伯 | |
| 12 | setLocation | 初始位置 | 勒凯寻 | |
| 13 | setBackground | 背景颜色 | back格乱的 | |
| 14 | setResizable | 是否可以调整大小 | 瑞size able | |
| 15 | setBounds | 窗口; 初始位置+初始大小 | 邦兹 | |
| 16 | closing | 结束 (关闭窗口事件) | 可漏sing | |
| 17 | Listener | 监听器 | 雷森ner | |
| 18 | Adapter | 适配器 | 额打噗t | |
| 19 | Layout | 排列布局 | 勒 out | |
| 20 | flowLayout | 流式布局 | 弗 low 勒 out | |
| 21 | LEFT | 左 | 来复特 | |
| 22 | RIGHT | 右 | 瑞t | |
| 23 | BorderLayout | 东西南北中布局 | border 勒 out | |
| 24 | east | 东 | 伊斯特 | |
| 25 | west | 西 | 韦斯特 | |
| 26 | south | 南 | 嫂偶th(夫) | |
| 27 | north | 北 | north(懦夫) | |
| 28 | center | 中 | 森特 | |
| 29 | grid | 栅格布局 | 戈瑞的 | |
| 30 | TextArea | 文本域 | ||
| 31 | action | 行动00 | 埃克申 | |
| 32 | Event | 事件 | e 稳t | |
| 33 | monitor | 监视器 | 莫尼特 mo ni tor | |
| 34 | getActionCommand | 获取行动命令 | 孔慢的 | |
| 35 | TextField | 文本输入框 | 泰丝可特菲尔德 | Field | 区域 字段 |
| 36 | getSource | 获取资源 最初发生 Event 的对象 | 苏尔斯 | 最初发生 Event 的对象 (Object) |
| 37 | actionPerformed | 行动 执行 | Per for me d | |
| 38 | setEchoChar | 回送 | 埃口 | setEchoChar('*'); |
| 39 | Calculator | 计算器 | 靠k累的 | |
| 40 | paint | 画笔 | 潘t | |
| 41 | draw | 画画 | jio | |
| 42 | Oval | 园 | 偶翁 | |
| 43 | Rect | 矩形 | 瑞克特 | |
| 44 | title | 标题 | 抬头~ | |
| 45 | points | 点 | 波因茨 | |
| 46 | repaint | 重画 | re潘t | |
| 47 | Opened | 打开 | O本de | |
| 48 | Closed | 已经关闭的 | ||
| 49 | Activated | 激活 | a可特维特的 | 窗口在聚焦状态 |
| 50 | Deactivated | 没有激活 | D啊可特维特的 | 窗口没有被聚焦 |
| 51 | Pressed | 按下 | 噗瑞丝的 | |
| 52 | Released | 弹起 | 瑞丽丝的 | |
| 53 | Typed | 打字 | type d | |
| 54 | getKeyCode | 返回与此事件中的键关联的整数 keyCode。 | 返回 某键的 整数表达 Event.getKeyText ( keyCode ) | |
| 55 | Graphics | 图形 | 戈ra 费cs | (Graphics g) |
| 56 | Swing | 用户界面开发工具包 | 斯温 | |
| 57 | init | 初始化 | 因乃t | init() |
| 58 | Operation | 操作 | 哦per 乱 寻 | setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); |
| 59 | constants | 常数 | 康s等s | final 常量| constants 常数 // setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); |
| 60 | container | 容器 | 坑泰奈儿 | |
| 61 | Pane | 窗格 | 潘恩 | jFrame.getContentPane(); |
| 62 | Horizontal | 水平 | 胡rz然透 | |
| 63 | Alignment | 对齐 | 额莱门t | |
| 64 | Dialog | 弹窗 | 戴log | |
| 65 | Icon | 图标 | 唉孔 | 算是 Label 下的小组件吧 |
| 66 | ImageIcon | 图片图标 | in莫句 | new ImageIcon(url) |
| 67 | URL | 地址 | url | URL url = ImageIconDemo.class.getResource("plmm.png"); |
| 68 | setIcon | 设置(添加)图标 | ||
| 69 | scroll | 滚动条 | 丝古肉 | new ScrollPane ( ) ; |
| 70 | TextArea | 文本域 | 唉瑞雅 | |
| 71 | Tool | 工具 | to | |
| 72 | tip | 小部件 | 泰噗 | jButton.setToolTipText ( " 这是一个图片按钮 " ) ; |
| 73 | ButtonGroup | 单选组 | 古路pe | |
| 74 | RadioButton | 单选框 | 乱迪奥 | new JRadioButton ( ) ; |
| 75 | CheckBox | 复选框 | 恰可Box | new CheckBox ( ) ; |
| 76 | ComboBox | 下拉列表 | 空波Box | |
| 77 | status | 状态 | 丝得特s | |
| 78 | Item | 项目 | 物体 | 唉等 | |
| 79 | PassworkField | 密码框 | ||
| 80 | RelativeTo | 相对于 | 瑞了tf | frame.setLocationRelative(null) 窗口屏幕居中 |
| 81 | getDefaultToolkit | 工具包 | tokt | Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit(); |
| 82 | Dimension | 规格类 | 戴门寻 | dimension. getWidth(); |
| 83 | screen | 屏幕 | 斯克林 | green |
| 84 | Undecorated | 未加装饰的 | 嗯打口乱te | frame.setUndecorated ( true ) ; 去除标题栏 |


