平衡二叉树,B树
AVL树(平衡二叉树)
AVL树本质上是一颗二叉查找树,但是它又具有以下特点:
1、 它是一棵空树或它的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1
2、 左右两个子树都是一棵平衡二叉树。
AVL树解决了普通二叉查找树演化为线性导致线性查找时间问题
AVL树平衡的操作主要有:
1、左-左型:做右旋。
2、右-右型:做左旋转。
3、左-右型:先做左旋,后做右旋。
4、右-左型:先做右旋,再做左旋。
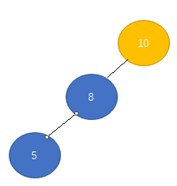
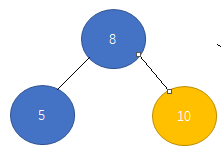
右旋:把左孩子变成父节点,原来的父节点变成左孩子的右孩子,见下图(左左型)。
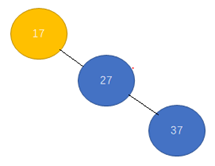
左旋:把右孩子变成父节点,原来的父节点变成右孩子的左孩子,见下图(右右型)。

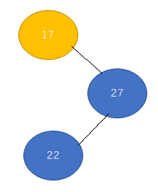
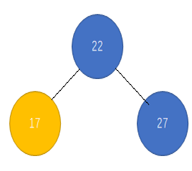
下面是右左型的平衡操作

实现代码(没有编写测试用例,可能会有一些边界未处理问题)

public class AVL { public class AVLNode{ int height; AVLNode leftChild; AVLNode rightChild; AVLNode parent; int value; } public int getHeight(AVLNode node) { if (node == null) { return 0; }else { return node.height; } } /** * 左左型不平衡,进行右旋操作 * @param LL_type_node */ public void R_Rotate(AVLNode LL_type_node) { if (LL_type_node != null) { AVLNode left = LL_type_node.leftChild; // 取出要旋转节点的左孩子 AVLNode parent = LL_type_node.parent; // 取出要旋转节点的父节点 LL_type_node.leftChild = left.rightChild; // 左孩子的右孩子变成父节点的左孩子 left.rightChild.parent = LL_type_node; left.rightChild = LL_type_node; // 左孩子的右节点变为其原来的父节点 // 更新父节点 LL_type_node.parent = left; left.parent = parent; // 检查原来要旋转节点是其父节点的左孩子还是右孩子 if (parent.leftChild == LL_type_node) { parent.leftChild = left; }else if (parent.rightChild == LL_type_node) { parent.rightChild = left; } LL_type_node.height = Math.max(getHeight(LL_type_node.leftChild), getHeight(LL_type_node.rightChild)) + 1; left.height = Math.max(getHeight(left.leftChild), getHeight(left.rightChild)) + 1; parent.height = Math.max(getHeight(parent.leftChild), getHeight(parent.rightChild)) + 1; } } /** * 右右型不平衡,进行左旋操作 * @param LL_type_node */ public void L_Rotate(AVLNode RR_type_node) { if (RR_type_node != null) { AVLNode right = RR_type_node.leftChild; // 取出要旋转节点的右孩子 AVLNode parent = RR_type_node.parent; // 取出要旋转节点的父节点 RR_type_node.rightChild = right.leftChild; // 右孩子的左孩子变成父节点的右孩子 right.leftChild.parent = RR_type_node; right.leftChild = RR_type_node; // 左孩子的右节点变为其原来的父节点 // 更新父节点 RR_type_node.parent = right; right.parent = parent; // 检查原来要旋转节点是其父节点的左孩子还是右孩子 if (parent.leftChild == RR_type_node) { parent.leftChild = right; }else if (parent.rightChild == RR_type_node) { parent.rightChild = right; } RR_type_node.height = Math.max(getHeight(RR_type_node.leftChild), getHeight(RR_type_node.rightChild)) + 1; right.height = Math.max(getHeight(right.leftChild), getHeight(right.rightChild)) + 1; parent.height = Math.max(getHeight(parent.leftChild), getHeight(parent.rightChild)) + 1; } } /** * 左右型,先左旋,后右旋 * @param LR_type_node */ public void L_R_Rotate(AVLNode LR_type_node) { if (LR_type_node != null) { L_Rotate(LR_type_node.leftChild); R_Rotate(LR_type_node); } } /** * 左右型,先右旋,后左旋 * @param LR_type_node */ public void R_L_Rotate(AVLNode RL_type_node) { if (RL_type_node != null) { R_Rotate(RL_type_node.rightChild); L_Rotate(RL_type_node); } } public AVLNode insertAVLTree(AVLNode root, AVLNode toInsert) { AVLNode rtRoot = root; if (toInsert != null) { if (root != null) { if (root.value > toInsert.value) { rtRoot.leftChild = insertAVLTree(root.leftChild, toInsert); //插入后看看是否需要调整 if (getHeight(rtRoot.leftChild) - getHeight(rtRoot.rightChild) == 2) { // 左左型,进行右旋 if (toInsert.value < rtRoot.leftChild.value) { R_Rotate(rtRoot); }else { // 左右型 L_R_Rotate(rtRoot); } } }else if (root.value < toInsert.value) { rtRoot.rightChild = insertAVLTree(root.rightChild, toInsert); //插入后看看是否需要调整 if (getHeight(rtRoot.rightChild) - getHeight(rtRoot.leftChild) == 2) { // 右右型,进行左旋 if (toInsert.value > rtRoot.rightChild.value) { L_Rotate(rtRoot); }else { // 右左型 R_L_Rotate(rtRoot); } } } }else { rtRoot = toInsert; } } rtRoot.height = Math.max(getHeight(rtRoot.leftChild), getHeight(rtRoot.rightChild)) + 1; return rtRoot; } public void deleteNode(AVLNode root, int value) { if (root != null) { if (value < root.value) { deleteNode(root.leftChild, value); int lh = getHeight(root.leftChild); int rh = getHeight(root.rightChild); if (rh - lh == 2) { if(getHeight(root.rightChild.rightChild) > getHeight(root.rightChild.leftChild)){ // 右右型 L_Rotate(root); }else{ // 右左型 R_L_Rotate(root); } } }else if (value > root.value) { deleteNode(root.rightChild, value); int lh = getHeight(root.leftChild); int rh = getHeight(root.rightChild); if (lh - rh == 2) { if(getHeight(root.leftChild.leftChild) > getHeight(root.leftChild.rightChild)){ // 左左型 R_Rotate(root); }else{ // 左右型 L_R_Rotate(root); } } }else { AVLNode toDeleteParent = root.parent; if (root.leftChild == null) { /* 要删除节点的左子树为空,那么该节点可以直接删除而不用找后继节点(因为后继就是它的右 * 孩子,如果它的右孩子也为空,那说明它是个叶子节点,可直接删) */ if (root == toDeleteParent.leftChild) { toDeleteParent.leftChild = root.rightChild; if (toDeleteParent.leftChild != null) { toDeleteParent.leftChild.parent = toDeleteParent; } }else { toDeleteParent.rightChild = root.rightChild; if (toDeleteParent.rightChild != null) { toDeleteParent.rightChild.parent = toDeleteParent; } } }else if (root.rightChild == null) { /* 要删除节点的右子树为空,那么该节点可以直接删除而不用找后继节点(因为后继就是它的父 * 节点,如果它的左孩子也为空,那说明它是个叶子节点,可直接删) */ if (root == toDeleteParent.leftChild) { toDeleteParent.leftChild = root.leftChild; if (toDeleteParent.leftChild != null) { toDeleteParent.leftChild.parent = toDeleteParent; } }else { toDeleteParent.rightChild = root.leftChild; if (toDeleteParent.rightChild != null) { toDeleteParent.rightChild.parent = toDeleteParent; } } }else { int next = getHeight(root); root.value = next; // 用后继代替待删除节点 deleteNode(root.rightChild, next); // 删除后继 int lh = getHeight(root.leftChild); int rh = getHeight(root.rightChild); if (lh - rh == 2) { if(getHeight(root.leftChild.leftChild) > getHeight(root.leftChild.rightChild)){ // 左左型 R_Rotate(root); }else{ // 左右型 L_R_Rotate(root); } } } } root.height = Math.max(getHeight(root.leftChild), getHeight(root.leftChild)) + 1; } } /** * 取得当前节点的后继 * @param currentNode * @return */ public int getNextNodeValue(AVLNode currentNode) { if ((currentNode = currentNode.rightChild) != null) { while(currentNode.leftChild != null){ currentNode = currentNode.leftChild; } } return currentNode.value; } }
红黑树
红黑树是近似平衡的二叉查找树,它相比AVL树在调整的时候可以减少旋转次数,它具有以下特点
1、节点是红色或黑色。
2、根节点是黑色。
3、每个红色节点的两个子节点都是黑色。(从每个叶子到根的所有路径上不能有两个连续的红色节点)
4、从任一节点到其每个叶子的所有路径都包含相同数目的黑色节点。
这些约束强制了红黑树的关键性质: 从根到叶子的最长的可能路径不多于最短的可能路径的两倍长。结果是这个树大致上是平衡的。因为操作比如插入、删除和查找某个值的最坏情况时间都要求与树的高度成比例,这个在高度上的理论上限允许红黑树在最坏情况下都是高效的,而不同于普通的二叉查找树。
红黑树的插入删除过程较为复杂,详细请参考以下博客
红黑树插入:https://www.cnblogs.com/CarpenterLee/p/5503882.html
红黑树删除:https://www.cnblogs.com/CarpenterLee/p/5525688.html
B树
一棵m阶B树(balanced tree of order m)是一棵平衡的m路搜索树。它或者是空树,或者是满足下列性质的树:
1、根结点至少有两个子女;
2、每个非根节点所包含的关键字个数 j 满足:┌m/2┐ - 1 <= j <= m - 1;即每个节点最多有m棵子树(至于为什么去m/2的上界,我的理解应该是为了树的平衡性质以及树的高度不会太高)
3、除根结点以外的所有结点(不包括叶子结点)的度数正好是关键字总数加1,故内部子树个数 k 满足:┌m/2┐ <= k <= m ;
4、所有的叶子结点都位于同一层。
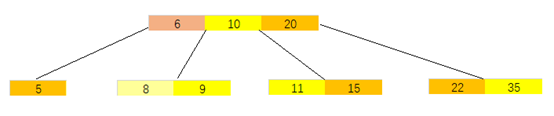
下图是一棵4阶B树(指针域未画出来),4阶指的是某个节点最多有4棵子树。

B树节点的插入:往上图的4阶B树插入关键字6。插入6,进入根节点的左子树,找到合适位置插入,此时关键字6所在的节点包含 {5, 6, 8, 9} 共NUM = 4个关键字,不满足4阶B树性质(最多有4-1个关键字),进行分裂,分裂点为 NUM / 2向上取整,故在关键字6,插入后的结果为见下图。插入操作要注意的就是分裂的关键字是作为新的节点,加入其父节点中,然后判断此时父节点是否需要分裂。
B树节点的删除:
相比B树的插入稍微复杂一些,当从B-树中删除一个关键字Ki时,总的分为以下两种情况:
如果该关键字所在的结点不是最下层的非叶子结点,则先需要把此关键字与它在B树中后继对换位置,即以指针Pi所指子树中的最小关键字Y代替Ki,然后在相应的结点中删除Y。
如果该关键字所在的结点正好是最下层的非叶子结点,这种情况下,会有以下两种可能:
1、若该关键字Ki所在结点中的关键字个数不小于┌m/2┐,则可以直接从该结点中删除该关键字和相应指针即可。
2、若该关键字Ki所在结点中的关键字个数小于┌m/2┐,则直接从结点中删除关键字会导致此结点中所含关键字个数小于┌m/2┐-1 。这种情况下,需考察该结点在B树中的左或右兄弟结点,从兄弟结点中移若干个关键字到该结点中来(这也涉及它们的双亲结点中的一个关键字要作相应变化),使两个结点中所含关键字个数基本相同;但如果其兄弟结点的关键字个数也很少,刚好等于┌m/2┐-1 ,这种移动则不能进行,这种情形下,需要把删除了关键字Ki的结点、它的兄弟结点及它们双亲结点中的一个关键字合并为一个结点。能力有限,无法画动图,上面的理论也比较难懂,建议直接在网上找个视频教程看看了解删除的过程。
还有一种B树的变形B+树,它与B树的区别在于非叶节点仅作为索引作用,不保存具体信息,并且所有的叶节点构成一条有序链表。它相比B树的优点在于一个内存块可以存储更多的关键字(因为B+树只存索引,而B树还保存着信息,所有B+树关键字占用内存少),减少了磁盘io,另外由于所有的叶子节点构成有序链表,所有可以方便的进行范围查询。更多详细请参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_26222859/article/details/80631121






【推荐】还在用 ECharts 开发大屏?试试这款永久免费的开源 BI 工具!
【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步