201712-2放学
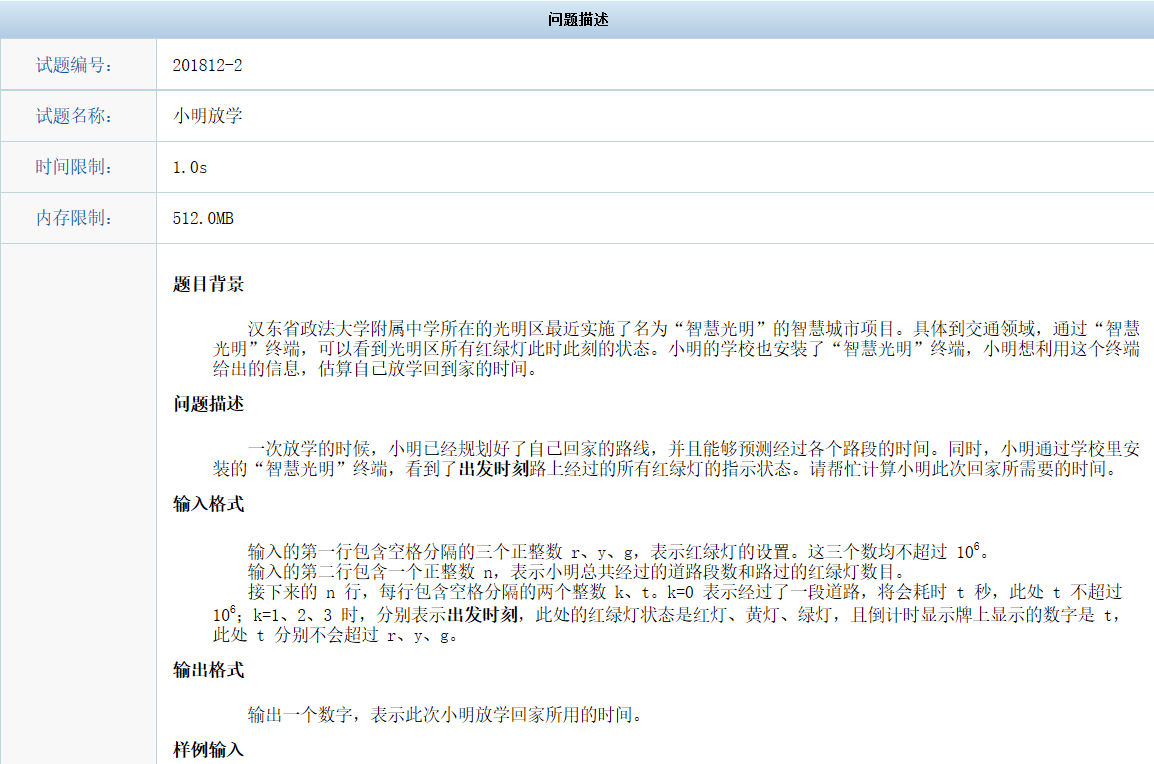

70分运行超时#
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//结构体,记录每个路口状态和所剩时间
struct status {
int color;
int time;
};
int r, y, g;
status st[100001];
//函数,得到下一个灯色,所剩时间为最大
status nextOf(status now)
{
status next = { 0,0 };
switch (now.color)
{
case 1: {//red
next.color = 3;
next.time = g;
break;
}
case 2: {//yellow
next.color = 1;
next.time = r;
break;
}
case 3: {//green
next.color = 2;
next.time = y;
break;
}
default:break;
}
return next;
}
//函数:需要再此灯处耗费多少时间
int cost(status now)
{
switch (now.color)
{
case 1: {//red
return now.time;
}
case 2: {//yellow
return now.time + r;
}
case 3: {//green
return 0;
}
default:return now.time;
}
}
//设计函数,参数为当前状态,所剩时间和经过时间,返回末状态和所剩时间
status fun(status now, long long ltime)
{
status t = { 0,0 };
if (now.color == 0)
{
t.color = now.color;
t.time = now.time;
return t;
}
while (now.time < ltime)
{
ltime -= now.time;
now = nextOf(now);
}
t.color = now.color;
t.time = now.time - ltime;
/*if (now.time >= ltime)
{
t.color = now.color;
t.time = now.time - ltime;
}
else
{
t = fun(nextOf(now), ltime - now.time);
}*/
return t;
}
int main()
{
cin >> r >> y >> g;
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> st[i].color >> st[i].time;
}
long long sum = 0;//经过时间
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (st[i].color == 0)
{
sum += st[i].time;
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
st[j] = fun(st[j], st[i].time);
}
}
else
{
sum += cost(st[i]);
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
st[j] = fun(st[j], cost(st[i]));
}
}
}
cout << sum << endl;;
return 0;
}
满分瞅他人的,#
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//结构体,记录每个路口状态和所剩时间
struct status {
int color;
int time;
};
int r, y, g;
status st[100001];
//函数,得到下一个灯色,所剩时间为最大
status nextOf(status now)
{
status next = { 0,0 };
switch (now.color)
{
case 1: {//red
next.color = 3;
next.time = g;
break;
}
case 2: {//yellow
next.color = 1;
next.time = r;
break;
}
case 3: {//green
next.color = 2;
next.time = y;
break;
}
default:break;
}
return next;
}
//函数:需要再此灯处耗费多少时间
int cost(status now)
{
switch (now.color)
{
case 1: {//red
return now.time;
}
case 2: {//yellow
return now.time + r;
}
case 3: {//green
return 0;
}
default:return now.time;
}
}
//设计函数,参数为当前状态,所剩时间和经过时间,返回末状态和所剩时间
status fun(status now, long long ltime)
{
status t = { 0,0 };
if (now.color == 0)
{
t.color = now.color;
t.time = now.time;
return t;
}
while (now.time < ltime)
{
ltime -= now.time;
now = nextOf(now);
}
t.color = now.color;
t.time = now.time - ltime;
/*if (now.time >= ltime)
{
t.color = now.color;
t.time = now.time - ltime;
}
else
{
t = fun(nextOf(now), ltime - now.time);
}*/
return t;
}
int main()
{
cin >> r >> y >> g;
int n;
cin >> n;
long long sum = 0;//经过时间
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> st[i].color >> st[i].time;
if (st[i].color == 0)
{
sum += st[i].time;
}
else
{
sum+= cost(fun(st[i], sum%(r+g+y)));
}
}
cout << sum << endl;;
return 0;
}
就一个关键,将sum%(r+g+y)。迭代或者递归次数限制到了常数级
还有一个就是fun函数对于0即经过一段道路的处理
上面是迭代
下面是递归
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//结构体,记录每个路口状态和所剩时间
struct status {
int color;
int time;
};
int r, y, g;
status st[100001];
//函数,得到下一个灯色,所剩时间为最大
status nextOf(status now)
{
status next = { 0,0 };
switch (now.color)
{
case 1: {//red
next.color = 3;
next.time = g;
break;
}
case 2: {//yellow
next.color = 1;
next.time = r;
break;
}
case 3: {//green
next.color = 2;
next.time = y;
break;
}
default:break;
}
return next;
}
//函数:需要再此灯处耗费多少时间
int cost(status now)
{
switch (now.color)
{
case 1: {//red
return now.time;
}
case 2: {//yellow
return now.time + r;
}
case 3: {//green
return 0;
}
default:return now.time;
}
}
//设计函数,参数为当前状态,所剩时间和经过时间,返回末状态和所剩时间
status fun(status now, long long ltime)
{
status t = { 0,0 };
/*if (now.color == 0)
{
t.color = now.color;
t.time = now.time;
return t;
}
while (now.time < ltime)
{
ltime -= now.time;
now = nextOf(now);
}
t.color = now.color;
t.time = now.time - ltime;
*/
if (now.color == 0)
{
t.color = now.color;
t.time = now.time;
return t;
}
if (now.time >= ltime)
{
t.color = now.color;
t.time = now.time - ltime;
}
else
{
t = fun(nextOf(now), ltime - now.time);
}
return t;
}
int main()
{
cin >> r >> y >> g;
int n;
cin >> n;
long long sum = 0;//经过时间
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> st[i].color >> st[i].time;
if (st[i].color == 0)
{
sum += st[i].time;
}
else
{
sum+= cost(fun(st[i], sum%(r+g+y)));
}
}
cout << sum << endl;;
return 0;
}
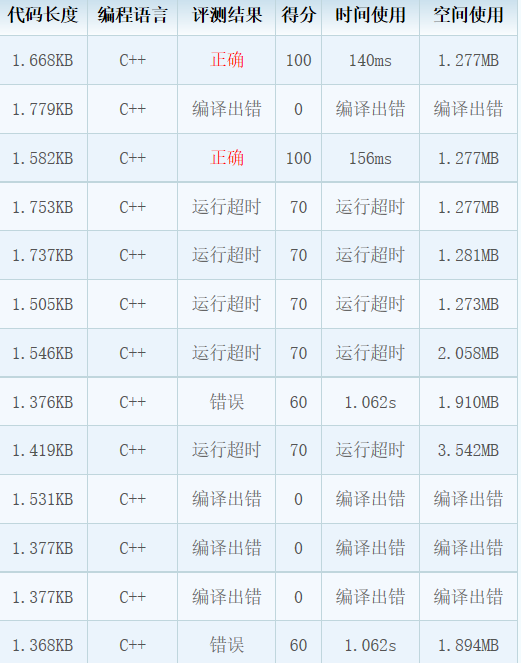
递归调用耗时少点,偶然还是必然?





