Java 8
Java 8
Java8具有更快的运行速度,对底层的数据结构进行了修改,编程书写代码更少,提供了更加便利的Stream API,使用并行更简单,减少了空指针异常的产生,提供了一个容器类减少空指针异常。
Lambda 表达式
简介
一种匿名函数,类似一段可以传递的代码,将代码像传递数据一样在程序中进行传递。Lambda表达式基于数学中的λ演算得名,直接对应于其中的lambda抽象(lambda abstraction),是一个匿名函数,即没有函数名的函数。
示例
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("This is a inner class");
}
}; //匿名内部类
Thread thread = new Thread(runnable);
thread.start();
Runnable runnable_new = () -> System.out.println("This is a Lambda!");
Thread thread_new = new Thread(runnable_new);
thread_new.start();
System.out.println("------------------");
}
}
语法
Lambda表达式中引入了 -> 操作符,箭头操作符的左侧对应参数列表,箭头右侧为需要执行的功能,需要“函数式接口”支持,即接口中只有一个抽象方法,可以使用@FuctionalInterface修饰,加强检查。
int i = 8;
Runnable runnable = () -> System.out.println("This is implement" + i);
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Test<T,R>{
public void method();
public void method(int i);
public int method(int i,int j);
public boolean method(int i,float j);
public R method(T t1,T T2);
}//仅作为举例 以下对每种情况具体进行了实现。
Test test;
//无参无返回值
test = () -> System.out.println("This is implement");
//单个参数无返回值
test = (i) -> System.out.prinln("This is i" + i);
test = x -> System.out.println("This is i" + i);
//两个参数返回值
Test test = (i,j) -> {
System.out.prinln("This is i" + i);
System.out.prinln("This is i" + j);
return i+j;
}
//多个参数单条语句返回值
Test test = (i,j) -> i+j;
Teat test =(int i,float j) -> !(i+j);
//泛型
(i,j) -> i+j;
函数式接口
Lambda表达式需要依赖函数式接口,因此,Java8中内置了多种接口,简介四种核心函数式接口。
消费型接口
Consumer<T>
void accept(T t);
提供型接口
Supplier<T>
T get();
函数式接口
Function<T,R>
R apply(T t);
判断型接口
Predicate<T>
boolean test(T t);
其他接口
BiFunction<T,U,R>
R apply(T t,U u);
UnaryOperator<T>
T apply(T t);
BinaryOperator<T>
T apply(T t1,T t2);
ToIntFunction<T>
ToLongFunction<T>
ToDubleFunction<T>
//返回int、long、double
IntFunction<R>
LongFunction<R>
DoubleFunction<R>
//返回R
示例
public void hello(String name,Consumer<String> consumer){
consumer.accept(name);
}
public String getDate(String data, Supplier<String> supplier){
return data +": "+ supplier.get();
}
public String resoleString(String string, Function<String,String> function)
{
return function.apply(string);
}
public List<String> filterString(List<String> list,Predicate<String> predicate){
List<String> stringList= new ArrayList<>();
for (String string : list){
if(predicate.test(string)){
stringList.add(string);
}
}
return stringList;
}
@Test
public void test(){
hello("Wang",(name) -> System.out.println("Hello ! I am " + name));
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
String now = getDate("Now",() -> {
Date d = new Date();
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
return sdf.format(d);
});
System.out.println(now);
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
System.out.println("\tThis is a String with blank! ");
String result = resoleString("\t\t\tThis is a String with blank! ", (string) -> string.trim());
result = resoleString(result, (string) -> string.substring(5,20));
System.out.println(result);
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("1234","abcd","http","a","Java and Oracle");
list = filterString(list,(s) -> s.length() > 5);
for (String string : list)
System.out.println(string);
}
方法引用与构造器引用
Lambda 体中已经实现了的方法,可以进行使用,使用中只要遵循接口参数列表与构造或方法的参数返回值对应即可,带给你全新的体验。
使用方法
- 对象 :: 实例方法名
- 类 :: 静态方法名
- 类 :: 实例方法名
Consumer<String> consumer = (x) -> System.out.println(x);
Consumer<String> consumer = System.out::println;
//实现方法的参数列表和引用方法必须保持一致
Integer integer = new Integer(10);
Supplier<Integer> supplier = integer::toString;
Supplier<ExecutorService> serviceSupplier= Executors::newCachedThreadPool;
BiPredicate<String,String> predicate = String::equals; //等效于(x,y) -> x.equals(y);
/* 哈哈哈 这还是Java吗? 哈哈哈*/ // a.method(b) 才可使用
- 类名 :: new
Supplier<Integer> integer = Integer::new;
//无参构造器
Function<int,Integer> integer = Integer::new;
//一个参数构造器
//构造器的选择取决于Function中的方法参数,参数列表与构造器必须对应!
- 类型 :: new
Function<Integer,String[]> function = (10) -> new String[x];
Function<Integer,String[]> function = String[]::new;
Stream API
Stream 不是集合元素,它不是数据结构并不保存数据,它是有关算法和计算的,它更像一个高级版本Iterator。原始版本的Iterator,用户只能显式地一个一个遍历元素并对其执行某些操作;高级版本的 Stream,用户只要给出需要对其包含的元素执行什么操作,比如 “过滤掉长度大于 10的字符串”、“获取每个字符串的首字母”等,Stream 会隐式地在内部进行遍历,做出相应的数据转换,数据源本身可以是无限的。

获取方式
- 从 Collection 和数组
- Collection.stream()
- Collection.parallelStream() 并行流!在执行迭代时是多线程完成的!
- Arrays.stream(T array) or Stream.of()
- 从 BufferedReader
- java.io.BufferedReader.lines()
- 静态工厂
- java.util.stream.IntStream.range()
- java.nio.file.Files.walk()
- 自己构建
- java.util.Spliterator
- 其他方式
- Random.ints()
- BitSet.stream()
- Pattern.splitAsStream(java.lang.CharSequence)
- JarFile.stream()
示例
//使用方法
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("1234","abcd","http","a","Java and Oracle");
Stream<String> stream = list.stream();
int[] ints = new int[20];
IntStream intStream = Arrays.stream(ints);
final Stream<int[]> intsStream = Stream.of(ints);
Stream<Integer> integerStream = Stream.iterate(0, (seed) -> seed+2);
integerStream.limit(10).forEach(System.out::println);
Stream.generate(() -> Math.random()).limit(10).forEach(System.out::println);
中间操作
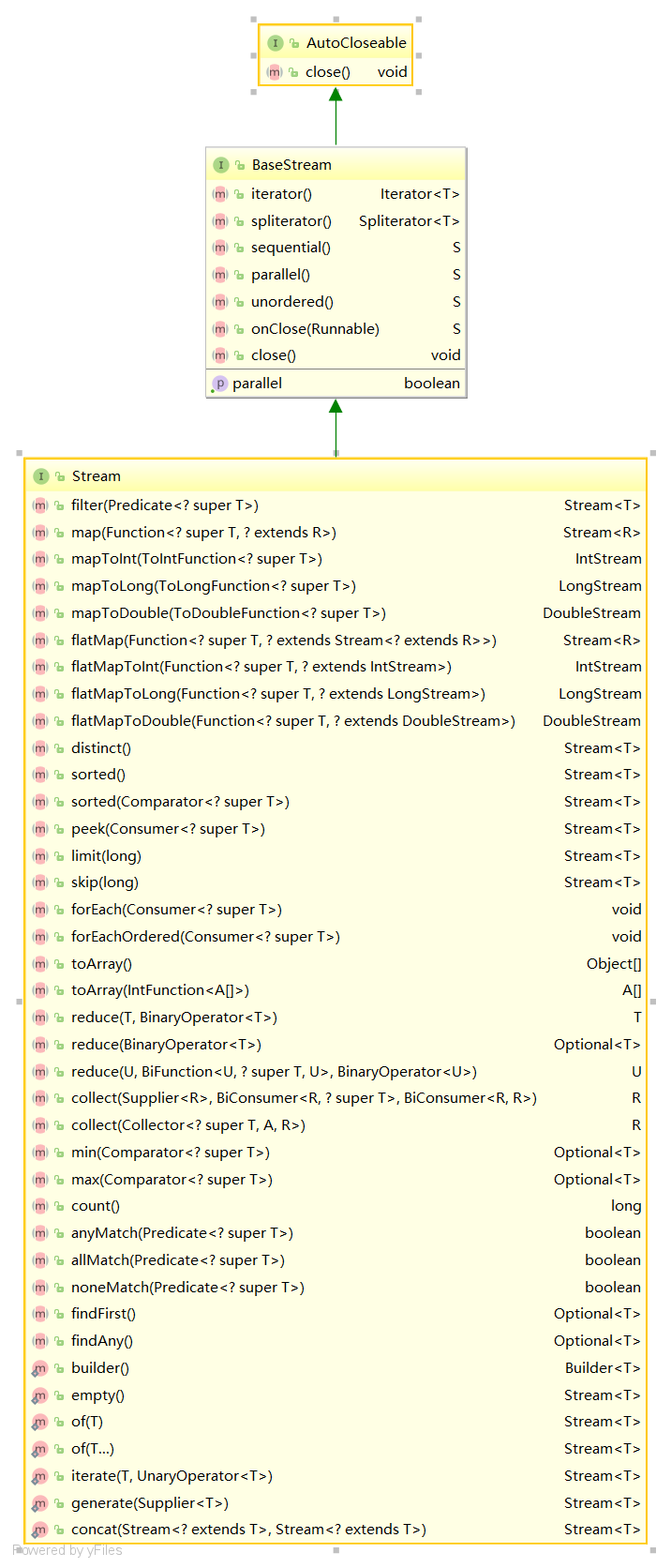
/*过滤、切片*/
filter
从流中排除指定元素
limit
截断流,限定流中元素个数
skip(n)
跳过n各元素,超过流元素个数,这返回空流
distinct()
去除重复元素
//链式调用中未执行终止操作时(forEach(...)),不会执行任何操作。
//当结果已经满足条件,则不继续执行后方筛选条件,即具备短路特点。
/*映射*/
map(Function<T t,R r>)
将函数应用到每个元素中,并将结果映射为一个新的参数
flatmap
经函数作为参数应用到每个元素上,返回流连接形成的新流。
/*排序*/
sorted()
sorted((a,b) -> a>b?a:b)
/* 想到前段时间阿里的面试题
* 一个巨大的数组统计每个数字的出现次数
*/
@Test
public void testMap(){
int a[]=new int[1000];
for(int i=0;i<10000;i++){
a[i]=(int) ( Math.random() *100 );
}//模拟数组
final IntStream stream = Arrays.stream(a);
stream.distinct().sorted().forEach((i) ->{
System.out.print("This is "+i+ " count : ");
long count = Arrays.stream(a).filter((num) -> num == i).count();
System.out.print(count +"\n");
});
}
终止操作
##查找匹配
allMach
#是否匹配所有元素
anyMatch
#至少匹配一个元素
noneMatch
#是否没有匹配所有元素
findFirst
#返回匹配的第一个元素
findAny
#随机返回一个元素
count
#统计元素个数
max
#返回最大元素
min
#返回最小元素
##归约
reduce(初始值,(下一次执行初始值,流中的元素))
Optional<Double> option = employees.stream().map(Employee::getSalary).reduce(Double::sum);
#####map-reduce模式#####
#将流中的元素反复匹配执行操作
##收集
collect
#按照一定方式,进行结果收集,即将结果收集起来,可以使用一个工具类Collectors
employee.stream().map(Employee::getNmae).collect(Collectors.toList());
#最终返回值一个List<String> 列表,存储姓名属性
Collectors.groupby
#分组
Collectors.summarizingDoutble
#数据处理方式
Collectors.joining
#字符串
并行流&串行流
Fork/Join框架
将任务分拆成多个小任务,细分到无法再继续分,执行后将所有的结果进行合并得到结果,在并发包的文章里,有写到过,也举了一个计算的例子,这个框架的特点就是,当任务进行拆分后,采用工作窃取模式,可以提高计算时对CPU的利用率。工作窃取模式即当前队列无法获取任务时,将去一个其他拆分队列的任务进行执行。
并行流
List.stream().parallelStream()
//执行处理时底层使用Fork/Join框架
接口默认方法与静态方法
原接口中只能有全局静态常量和抽象方法,在java8中可以给接口添加添加默认方法。默认方法冲突时继承大于实现,多实现必须重写冲突默认方法。接口可以书写静态方法,使用时,直接使用接口对象调用。
public interface NewInterface{
default String getDefaultMethod(){
return "This is a default Method";
}
public static void getStaticMethod(){
System.out.println("This is a static method from a interface !");
}//NewInterface.getStaticMethod()
}
时间API
原时间相关api存在线程安全问题,使用起来较为复杂,java8中添加全新的时间api,多线程可以直接使用,线程安全。
java.time
#日期
java.time.chrono
#特殊时间记录方式
java.time.format
#日期格式化
java.time.temporal
#运算推算日期
java.time.zone
#时区相关设置
操作
//使用时间
@Test
public void testNewDate(){
//LocalDate LocalTime LocalDateTime
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println(localDateTime);
-----------------------------------
localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2018,9,13,23,44);
System.out.println(localDateTime);
-----------------------------------
localDateTime = localDateTime.plusYears(2);
System.out.println(localDateTime);
-----------------------------------
localDateTime = localDateTime.minusYears(2);
System.out.println(localDateTime);
}
//时间戳
@Test
public void testTimeInstant(){
//Unix 1970.1.1 0.0.0 到现在毫秒 协调世界时
Instant instant = Instant.now();
//设置时间偏移量
instant.atOffset(ZoneOffset.offHours(8));
//获取毫秒
System.out.println(instant.toEpochMilli());
//运算
Instant.ofEpochSecond(60);//1971.1.1 0.1.0
//计算间隔
Duration duration = Duration.between(instant_end , instant_begin);
Period period = Period.between(localDate_end , localDate_begin);
}
其他
注解
java8中可以对方法进行重复注解。
@Repeatable(MoreAnnotations.class)
public @interface MoreAnnotation{
String value9() default "注解";
}
public @interface MoreAnnotations{
MoreAnnotation[] values();
}
@MoreAnnotation
@MoreAnnotation
@MoreAnnotation
public void method(){}
类型注解
private @NonNull Object obj = null
//不支持
HashMap
碰撞产生的链表在长度大于8时将会产生红黑树

ConcurrentHashMap
原16段并发锁改为CAS算法,同时也具备红黑树。
内存模型



【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】博客园社区专享云产品让利特惠,阿里云新客6.5折上折
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步