Spring Data ElasticSearch 及Kibana调用Restful
什么是spring Data
Spring Data是一个用于简化数据库访问,并支持云服务的开源框架。其主要目标是使得对数据的访问变得方便快 捷,并支持map-reduce框架和云计算数据服务。 Spring Data可以极大的简化JPA的写法,可以在几乎不用写实现 的情况下,实现对数据的访问和操作。除了CRUD外,还包括如分页、排序等一些常用的功能。 Spring Data的官网:http://projects.spring.io/spring-data/
Spring Data常用的功能模块如下:
spring data commons spring data JPA spring data Redis spring data for Apache Solr spring data ElasticSearch
什么是Spring Data ElasticSearch
Spring Data ElasticSearch 基于 spring data API 简化 elasticSearch操作,将原始操作elasticSearch的客户端API 进 行封装 。Spring Data为Elasticsearch项目提供集成搜索引擎。Spring Data Elasticsearch POJO的关键功能区域为 中心的模型与Elastichsearch交互文档和轻松地编写一个存储库数据访问层。 官方网站:http://projects.spring.io/spring-data-elasticsearch/
引入坐标
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
# ES #开启 Elasticsearch 仓库(默认值:true) spring.data.elasticsearch.repositories.enabled=true #默认 9300 是 Java 客户端的端口。9200 是支持 Restful HTTP 的接口 spring.data.elasticsearch.cluster-nodes = 127.0.0.1:9300 #spring.data.elasticsearch.cluster-name Elasticsearch 集群名(默认值: elasticsearch) #spring.data.elasticsearch.cluster-nodes 集群节点地址列表,用逗号分隔。如果没有指定,就启动一个客户端节点 #spring.data.elasticsearch.propertie 用来配置客户端的额外属性 #连接超时的时间 spring.data.elasticsearch.properties.transport.tcp.connect_timeout=120s
/** 其中,注解解释如下: @Document(indexName="blob3",type="article"): indexName:索引的名称(必填项) type:索引的类型 @Id:主键的唯一标识 @Field(index=true,analyzer="ik_smart",store=true,searchAnalyzer="ik_smart",type = FieldType.text) index:是否索引 analyzer:存储时使用的分词器 searchAnalyze:搜索时使用的分词器 store:是否存储 type: 数据类型 注: 一旦添加了@Filed注解,所有的默认值都不再生效。此外,如果添加了@Filed注解,那么type字段必须指定。 所以一般不用添加。 */ @Document(indexName = "blog3",type = "article") public class Article { //@Field(store = true,type = FieldType.Integer) private Integer id; @Field(index = true,store = true,analyzer = "ik_smart",searchAnalyzer = "ik_smart",type = FieldType.text) private String title; @Field(index = true,store = true,analyzer = "ik_smart",searchAnalyzer = "ik_smart",type = FieldType.text) private String content;
增删改查
test
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @SpringBootTest(classes = ApplicationRun.class) public class TestSpringDataES { @Autowired private ArticleService as; @Test //保存 public void testSave(){ Article a = new Article(); a.setId(1); a.setTitle("elasticSearch 3.0版本发布...更新"); a.setContent("ElasticSearch是一个基于Lucene的搜索服务器。它提供了一个分布式多用户能力的全文搜索引擎,基于RESTful web接口"); as.save(a); } @Test//修改 public void testUpdate(){ Article a = new Article(); a.setId(1); a.setTitle("elasticSearch 3.01版本发布...更新"); a.setContent("ElasticSearch是一个基于Lucene的搜索服务器。它提供了一个分布式多用户能力的全文搜索引擎,基于RESTful web接口"); as.save(a); } @Test //删除 public void testDelete(){ Article a = new Article(); a.setId(1); as.delete(a); } @Test //批量保存 public void testSave2(){ for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) { Article a = new Article(); a.setId(i); a.setTitle(i+"elasticSearch 3.0版本发布...更新"); a.setContent(i+"ElasticSearch是一个基于Lucene的搜索服务器。它提供了一个分布式多用户能力的全文搜索引擎,基于RESTful web接口"); as.save(a); } } @Test //查询所有保存 public void testFindAll(){ Iterable<Article> list = as.findAll(); for (Article article : list) { System.out.println(article); } } @Test public void TestFindByPage(){ // Pageable pageable= PageRequest.of(1,10); Pageable pageable= PageRequest.of(1,10, Sort.by(Sort.Order.asc("id;"))); Page page = as.findByPage(pageable); List<Article> list = page.getContent(); for (Article article : list) { System.out.println(article); } } @Test //根据title查询 public void testFindByTitle(){ List<Article> list = as.findByTitle("版本"); for (Article article : list) { System.out.println(article); } } @Test //根据title查询 public void testFindByTitlePage(){ Pageable pageable=PageRequest.of(0,20,Sort.by(Sort.Order.asc("id"))); Page page = as.findByTitle("版本", pageable); List<Article> list = page.getContent(); for (Article article : list) { System.out.println(article); } } }
service
public interface ArticleService { //保存 public void save(Article article); //删除 public void delete(Article article); //查询 public Iterable<Article> findAll(); //分页查询 public Page findByPage(Pageable pageable); public List<Article> findByTitle(String title); public Page findByTitle(String title,Pageable pageable); }
impl
@Service public class ArticleServiceImpl implements ArticleService { @Autowired private ArticleDao articleDao; @Override public void save(Article article) { articleDao.save(article); } @Override public void delete(Article article) { articleDao.delete(article); } @Override//Sort.by(Sort.Order.asc("id") 根据id排序 public Iterable<Article> findAll() { return articleDao.findAll(Sort.by(Sort.Order.asc("id"))); } @Override public Page findByPage(Pageable pageable) { return articleDao.findAll(pageable); } @Override public List<Article> findByTitle(String title) { return articleDao.findByTitle(title); } @Override public Page findByTitle(String title, Pageable pageable) { return articleDao.findByTitle(title,pageable); } }
dao
//ElasticsearchRepository<实体类,实体类的主键类型> : 提供了CRUD的操作 public interface ArticleDao extends ElasticsearchRepository<Article,Integer> { //根据title字段查询 public List<Article> findByTitle(String title); public Page findByTitle(String title, Pageable pageable); }
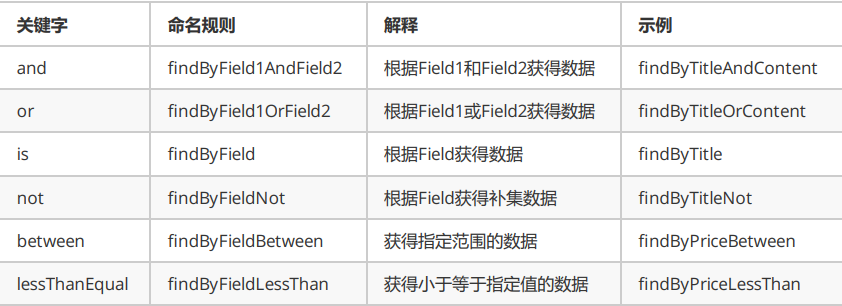
常用查询命名规则
Kibana是一个基于Node.js的Elasticsearch索引库数据统计工具,可以利用Elasticsearch的聚合功能,生成各种图表,如柱形图,线状图,饼图等。
而且还提供了操作Elasticsearch索引数据的控制台,并且提供了一定的API提示,非常有利于我们学习Elasticsearch的语法。
安装
因为Kibana依赖于node,需要在windows下先安装Node.js,然后安装kibana,最新版本与elasticsearch保持一致,也是5.6.8
解压即可!
运行
进入安装目录下的bin目录-->双击kibana.bat
发现kibana的监听端口是5601
控制台
进入之后选择左侧的DevTools菜单,即可进入控制台页面,在页面右侧,我们就可以输入请求,访问Elasticsearch了。
创建索引库
语法
Elasticsearch采用Rest风格API,因此其API就是一次http请求,你可以用任何工具发起http请求 创建索引的请求格式: - 请求方式:PUT - 请求路径:/索引库名
使用kibana创建

相当于是省去了elasticsearch的服务器地址
而且还有语法提示,非常舒服。
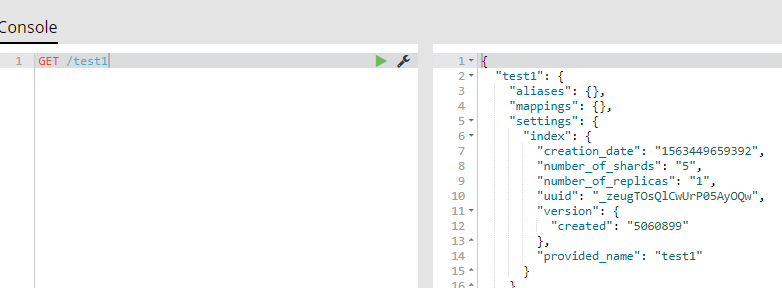
查看索引数据库
语法
GET /索引库名
删除索引库
语法
DELETE /索引库名
类型及映射操作
有了`索引库`,等于有了数据库中的`database`。接下来就需要索引库中的`类型`了,也就是数据库中的`表`。创建数据库表需要设置字段约束,索引库也一样,
在创建索引库的类型时,需要知道这个类型下有哪些字段,每个字段有哪些**约束**信息,这就叫做`字段映射(mapping)` 字段的约束我们在学习Lucene中我们都见到过,包括到不限于: - 字段的数据类型 - 是否要存储 - 是否要索引 - 是否分词 - 分词器是什么
创建字段映射
语法
PUT /索引库名/_mapping/类型名称 { "properties": { "字段名": { "type": "类型", "index": true, "store": true, "analyzer": "分词器" } } }
-
-
type:类型,可以是text、long、short、date、integer、object等
-
index:是否索引,默认为true
-
store:是否存储,默认为false
-
analyzer:分词器,这里的
ik_max_word即使用ik分词器
查看映射关系
语法
GET /索引库名/_mapping
附录:映射属性
1)type
Elasticsearch中支持的数据类型非常丰富:
这里说几个关键的:
-
String类型,又分两种:
-
text:可分词,不可参与聚合
-
keyword:不可分词,数据会作为完整字段进行匹配,可以参与聚合
-
-
Numerical:数值类型,分两类
-
基本数据类型:long、interger、short、byte、double、float、half_float
-
浮点数的高精度类型:scaled_float
-
需要指定一个精度因子,比如10或100。elasticsearch会把真实值乘以这个因子后存储,取出时再还原。
-
-
-
Date:日期类型
elasticsearch可以对日期格式化为字符串存储,但是建议我们存储为毫秒值,存储为long,节省空间。
-
Array:数组类型
-
进行匹配时,任意一个元素满足,都认为满足
-
排序时,如果升序则用数组中的最小值来排序,如果降序则用数组中的最大值来排序
-
-
Object:对象
{
name:"Jack",
age:21,
girl:{
name: "Rose",
age:21
}
}
如果存储到索引库的是对象类型,例如上面的girl,会把girl编程两个字段:girl.name和girl.age
2)index
index影响字段的索引情况。
-
true:字段会被索引,则可以用来进行搜索过滤。默认值就是true
-
false:字段不会被索引,不能用来搜索
index的默认值就是true,也就是说你不进行任何配置,所有字段都会被索引。
但是有些字段是我们不希望被索引的,比如商品的图片信息,就需要手动设置index为false。
3)store
是否将数据进行额外存储。
在学习lucene和solr时,我们知道如果一个字段的store设置为false,那么在文档列表中就不会有这个字段的值,用户的搜索结果中不会显示出来。
但是在Elasticsearch中,即便store设置为false,也可以搜索到结果。
原因是Elasticsearch在创建文档索引时,会将文档中的原始数据备份,保存到一个叫做_source的属性中。而且我们可以通过过滤_source来选择哪些要显示,哪些不显示。
而如果设置store为true,就会在_source以外额外存储一份数据,多余,因此一般我们都会将store设置为false,事实上,store的默认值就是false。
4)boost
权重,新增数据时,可以指定该数据的权重,权重越高,得分越高,排名越靠前。
一次创建索引库和类型
put /索引库名 { "settings":{ "索引库属性名":"索引库属性值" }, "mappings":{ "类型名":{ "properties":{ "字段名":{ "映射属性名":"映射属性值" } } } } }
文档操作
新增文档
通过POST请求,可以向一个已经存在的索引库中添加文档数据。
POST /索引库名/类型名 { "key":"value" }
另外,需要注意的是,在响应结果中有个_id字段,这个就是这条文档数据的唯一标示,以后的增删改查都依赖这个id作为唯一标示。
可以看到id的值为:r9c1KGMBIhaxtY5rlRKv,这里我们新增时没有指定id,所以是ES帮我们随机生成的id。
查看文档
根据rest风格,新增是post,查询应该是get,不过查询一般都需要条件,这里我们把刚刚生成数据的id带上。
通过kibana查看数据:
GET /test1/goods/r9c1KGMBIhaxtY5rlRKv
新增文档并自定义id
POST /索引库名/类型/id值 { ... } 示例: POST /test1/goods/2 { "title":"大米手机", "images":"http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg", "price":2899.00 }
修改数据
把刚才新增的请求方式改为PUT,就是修改了。不过修改必须指定id,
-
id对应文档存在,则修改
-
id对应文档不存在,则新增
比如,我们把使用id为3,不存在,则应该是新增:
PUT /test1/goods/3 { "title":"超米手机", "images":"http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg", "price":3899.00, "stock": 100, "saleable":true }
我们再次执行刚才的请求,不过把数据改一下:
PUT /test1/goods/3 { "title":"超大米手机", "images":"http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg", "price":3299.00, "stock": 100, "saleable":true }
删除数据
删除使用DELETE请求,同样,需要根据id进行删除:
语法
DELETE /索引库名/类型名/id值
查询
-
基本查询
-
_source过滤 -
结果过滤
-
高级查询
-
GET /索引库名/_search { "query":{ "查询类型":{ "查询条件":"查询条件值" } } }
这里的query代表一个查询对象,里面可以有不同的查询属性
-
查询类型:
-
例如:
match_all,match,term,range等等
-
-
查询条件:查询条件会根据类型的不同,写法也有差异
GET /test1/_search { "query":{ "match_all": {} } }
-
-
match_all:代表查询所有
匹配查询
我们先加入一条数据
PUT /test1/goods/3 { "title":"小米电视4A", "images":"http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg", "price":3899.00 }
-
or关系
match
GET /test1/_search { "query":{ "match":{ "title":"小米电视" } } }
-
and关系
某些情况下,我们需要更精确查找,我们希望这个关系变成and,可以这样做:
GET /goods/_search { "query":{ "match":{ "title":{"query":"小米电视","operator":"and"} } } }
词条匹配
GET /test1/_search { "query":{ "term":{ "price":2699.00 } } }
POST /test1/goods/4 { "title":"apple手机", "images":"http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg", "price":6899.00 }
GET /test1/_search { "query": { "fuzzy": { "title": "appla" } } }
上面的查询,也能查询到apple手机
我们可以通过fuzziness来指定允许的编辑距离:
GET /test1/_search { "query": { "fuzzy": { "title": { "value":"appla", "fuzziness":1 } } } }
排序
GET /test1/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"title": "小米手机"
}
},
"sort": [
{
"price": {
"order": "desc"
}
}
]
}
分页
elasticsearch的分页与mysql数据库非常相似,都是指定两个值:
-
from:开始位置
-
size:每页大小
GET /test1/_search { "query": { "match_all": {} }, "sort": [ { "price": { "order": "asc" } } ], "from": 3, "size": 3 }
高亮
高亮原理:
-
服务端搜索数据,得到搜索结果
-
把搜索结果中,搜索关键字都加上约定好的标签
-
前端页面提前写好标签的CSS样式,即可高亮
elasticsearch中实现高亮的语法比较简单:
GET /test1/_search { "query": { "match": { "title": "手机" } }, "highlight": { "pre_tags": "<em>", "post_tags": "</em>", "fields": { "title": {} } } }
在使用match查询的同时,加上一个highlight属性:
-
pre_tags:前置标签
-
post_tags:后置标签
-
fields:需要高亮的字段
-


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号