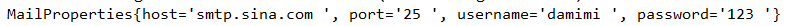Spring Boot入门
写在前面:整理的一些浅显的springboot入门知识点,部分内容借助相关资料.
Spring Boot
Spring1.0:jdk1.5刚出,配置都是xml格式
Spring2.0:xml与注解结合
Spring3.0:Spring注解已经非常完善,Spring推荐java配置代替以前的xml
原有Spring优缺点分析
Spring的优点分析
Spring是Java企业版(Java Enterprise Edition,JEE,也称J2EE)的轻量级代替品。无需开发重量级的Enterprise JavaBean(EJB),Spring为企业级Java开发提供了一种相对简单的方法,通过依赖注入和面向切面编程,用简单的Java对象(Plain Old Java Object,POJO)实现了EJB的功能。
Spring的缺点分析
虽然Spring的组件代码是轻量级的,但它的配置却是重量级的。一开始,Spring用XML配置,而且是很多XML配置。Spring 2.5引入了基于注解的组件扫描,这消除了大量针对应用程序自身组件的显式XML配置。Spring 3.0引入了基于Java的配置,这是一种类型安全的可重构配置方式,可以代替XML。
所有这些配置都代表了开发时的损耗。因为在思考Spring特性配置和解决业务问题之间需要进行思维切换,所以编写配置挤占了编写应用程序逻辑的时间。和所有框架一样,Spring实用,但与此同时它要求的回报也不少。
除此之外,项目的依赖管理也是一件耗时耗力的事情。在环境搭建时,需要分析要导入哪些库的坐标,而且还需要分析导入与之有依赖关系的其他库的坐标,一旦选错了依赖的版本,随之而来的不兼容问题就会严重阻碍项目的开发进度。
SpringBoot的概述
SpringBoot解决上述Spring的缺点
SpringBoot对上述Spring的缺点进行的改善和优化,基于约定优于配置的思想,可以让开发人员不必在配置与逻辑业务之间进行思维的切换,全身心的投入到逻辑业务的代码编写中,从而大大提高了开发的效率,一定程度上缩短了项目周期。
SpringBoot的特点
-
为基于Spring的开发提供更快的入门体验
-
开箱即用,没有代码生成,也无需XML配置。同时也可以修改默认值来满足特定的需求
-
提供了一些大型项目中常见的非功能性特性,如嵌入式服务器、安全、指标,健康检测、外部配置等
-
SpringBoot不是对Spring功能上的增强,而是提供了一种快速使用Spring的方式
SpringBoot的核心功能
-
起步依赖
起步依赖本质上是一个Maven项目对象模型(Project Object Model,POM),定义了对其他库的传递依赖,这些东西加在一起即支持某项功能。
简单的说,起步依赖就是将具备某种功能的坐标打包到一起,并提供一些默认的功能。
-
自动配置
Spring Boot的自动配置是一个运行时(更准确地说,是应用程序启动时)的过程,考虑了众多因素,才决定Spring配置应该用哪个,不该用哪个。该过程是Spring自动完成的。
Spring Boot 入门
1.创建一个maven项目并添加依赖
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2.编写引导类使用注解配置
package com.jia; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; @SpringBootApplicationpublic class SpringBootApplicationRunner { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringBootApplicationRunner.class,args); } } 这里多了一个@SpringBootApplication注解 @Configuration: 用于定义一个配置类 @EnableAutoConfiguration :Spring Boot 会自动根据你 jar 包的依赖来自动配置项目。 @ComponentScan: 告诉Spring 哪个packages 的用注解标识的类会被 spring自动扫描并且装入 bean 容器。
3.测试环境搭建结果
http://localhost:8080
SpringMVC传统环境搭建对比
1.创建Maven项目,引入坐标
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>2.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jsp-api</artifactId>
<version>2.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.0.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.0.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2.修改web.xml,配置前端控制器
<!-- 配置前端控制器:DispatcherServlet -->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>DispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>DispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
3.配置springmvc.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!-- 配置创建容器时要扫描的包 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.jia.web.controller"></context:component-scan> <!-- 配置视图解析器 --> <bean id="viewResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"> <property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/pages/"></property> <property name="suffix" value=".jsp"></property> </bean>
<!-- 开启spring对注解mvc的支持 --> <mvc:annotation-driven/> </beans>
4.创建控制器
package com.jia.web.controller; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; @Controllerpublic class UserController { @RequestMapping("/hello") public String sayHello() { return "success"; } }
5.编写index.jsp
<a href="hello">访问控制器</a>
6.编写/pages/success.jsp页面
执行成功!
用springboot实现
使用 Spring MVC和 Spring Boot整合实现浏览器输出Hello Spring Boot!
package com.jia.web.controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestControllerpublic class HelloSpringBoot { @RequestMapping("/hello") public String hello(){ return "hello Spring Boot!"; } } @RestController注解: 其实就是@Controller 和@ResponseBody注解加在一起
Spring Boot整合
1.整合Mybatis
需求
使用 Spring Boot + Spring MVC + mybatis 框架组合实现用户查询
导入数据库表
USE db1; CREATE TABLE `user` ( `id` BIGINT(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `username` VARCHAR(100) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '用户名', `password` VARCHAR(100) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '密码', `name` VARCHAR(100) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '姓名', PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=INNODB AUTO_INCREMENT=7 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; INSERT INTO `user` VALUES ('1', 'zhangsan', '123456', '张三'); INSERT INTO `user` VALUES ('2', 'lisi', '123456', '李四'); INSERT INTO `user` VALUES ('3', 'wangwu', '123456', '王五'); INSERT INTO `user` VALUES ('4', 'zhangwei', '123456', '张伟'); INSERT INTO `user` VALUES ('5', 'lina', '123456', '李娜'); INSERT INTO `user` VALUES ('6', 'lilei', '123456', '李磊');
创建Maven工程引入坐标
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.6</version>
</dependency>
<!--springBoot的Mybatis启动器-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
加入springboot配置文件
在 src/main/resources 下添加 application.properties 配置文件,内容如下
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db1 spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=root
创建引导类
package com.jia; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; @SpringBootApplicationpublic class SpringBootApplicationRunner { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringBootApplicationRunner.class,args); } }
后端实现
1.创建实体类
package com.jia.domain; import java.io.Serializable; public class User implements Serializable{ private long id; private String username; private String password; private String name; 其他略 }
2.创建Dao接口
和之前的方式一样,只是多了两个注解 @Mapper:声明 Mapper接口 @Select:声明这个接口所需要使用的 sql,当然,有查询的注解,肯定就有增删改的注解。 @Mapperpublic interface UserDao { @Select("select * from user") public List<User> findAll(); }
3.创建service接口和实现类
public interface UserService { public List<User> findAll(); } @Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{ @Autowired private UserDao userDao; public List<User> findAll() { return userDao.findAll(); } }
4.创建controller
@RestController @RequestMapping("/user")public class UserController { @Autowired private UserService userService;
@RequestMapping("/findAll") public List<User> findUsers(){ return userService.findAll(); } }
5.测试
运行引导类 Application,打开浏览器输入 http://127.0.0.1:8080/user/findAll
2.整合redis
注解方式实现添加缓存
1.加入依赖
<!--redis使用器-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-redis</artifactId>
<version>1.3.8.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
2.修改引导类
@SpringBootApplication@EnableCaching //开启缓存public class SpringBootApplicationRunner { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringBootApplicationRunner.class,args); } }
3.注意实现序列化接口
需要修改实体,让实体实现序列化接口 ,这里我们一开始就已经实现
4.实现添加/删除缓存
@Servicepublic class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{ @Autowired private UserDao userDao; //用于存入redis //value:指定存入redis中的。key是用于动态生成秘钥的一个字符串。需要使用spring的el表达式。 //但是如果不想写spring的el表达式的话,需要用单引号套起来 @Cacheable(value = "findAll",key = "'user.findAll'") public List<User> findAll() { System.out.println("查询了数据库"); return userDao.findAll(); } //用于清除redis缓存 //allEntries:是否全部清除 @CacheEvict(value = "findAll",key = "'user.findAll'",allEntries = true) public void update(){ System.out.println("update执行了"); } } 这样设置完成后,执行findAll()方法就会使用缓存,如果缓存没有就添加缓存,而queryUserByName(String name)方法则是删除缓存 @Cacheable:添加/使用缓存 @CacheEvict:删除缓存 属性 value 是缓存的名字,在执行的时候,会找叫这个名字的缓存使用/删除 属性 key 默认情况下是空串””,是 Spring 的一种表达式语言 SpEL,我们这里可以随意指定,但是需要注意 一定要加单引号 属性 allEntries 指定是否清空整个缓存区。
3.整合Junit
1.引入坐标
在 pom.xml中加入测试依赖 <!-- 配置测试启动器 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.编写测试类
// @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @RunWith(SpringRunner.class)//参数:SpringBootApplicationRunner是自己定义的启动类 @SpringBootTest(classes = SpringBootApplicationRunner.class)public class SpringBootJunitTest { @Autowired private UserService userService;
@Test public void test1(){ List<User> users = userService.findAll(); for (User user : users) { System.out.println(user); } } } SpringRunner 与 SpringJUnit4ClassRunner 是继承关系,但是没有不同的地方,只是看起来子类 SpringRunner 要短一些而已。 @SpringBootTest 注解的 class 属性要指定引导类的class
SpringBoot的属性注入
1.读取核心配置文件
SpringBoot强调的是约定大于配置,因此遵循约定,我们就能节省很多配置,
文件名必须是:application.properties,SpringBoot会自动加载这个文件,无需我们指定加载的文件的名称。
新建一个测试类
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @SpringBootTest(classes = SpringBootApplicationRunner.class) public class ConfigFileTest { @Autowired private Environment env; //读取核心配置文件 @Test public void test1(){ System.out.println(env.getProperty("spring.datasource.username")); System.out.println(env.getProperty("spring.datasource.password")); } }
2.读取自定义配置文件
在工程的 src/main/resources 下构建自定义配置文件mail.properties, 内容如下
mail.host=smtp.sina.com mail.port=25 mail.username=damimi mail.password=123
编辑配置类
- 在类上通过@ConfigurationProperties注解声明当前类为属性读取类 - `prefix="mail"`读取属性文件中,前缀为mail的值。 - 在类上定义各个属性,名称必须与属性文件中`mail.`后面部分一致 @Configuration//或写Component @PropertySource(value = "classpath:mail.properties") @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mail") public class MailProperties { private String host;//smtp.sina.com private String port;//=25 private String username;//=damimi private String password;//=123 其他略 }
测试类
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @SpringBootTest(classes = SpringBootApplicationRunner.class) public class ConfigFileTest { @Autowired private MailProperties mailProperties;//读取自定义配置文件 @Test public void test2(){ System.out.println(mailProperties); }
结果
3.读取yml文件
配置文件除了可以使用application.properties类型,还可以使用后缀名为:.yml或者.yaml的类型,也就是:application.yml或者application.yaml
语法格式
普通数据: key:value 在 key和 value 中必须有一个空格 对象数据: mail: host: smtp.sina.com port: 25 username: damimi password: 123
获取方式
SpringBoot强调的是约定大于配置,因此遵循约定,我们就能节省很多配置:
-
首先,属性文件的名称有变化,文件名必须是:application
-
其次,要注入的属性的变量名要和配置文件中的属性名的最后一部分保持一致
-
最后,要在类上声明这些属性在属性文件中的共同的前缀,并提供getter和setter方法
创建application.yml文件
spring: datasource: driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db1 username: root password: root mail: host: smtp.sina.com port: 25 username: damimi password: 123456
创建配置类实现序列化接口
第一种:使用@Value注解配合Spring的 EL表达式 @Value("${mail.host}") private String mailHost; 第二种方式:使用@ConfigurationProperties注解 @Configuration @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mail") public class MailYml implements Serializable { private String host; private String port; private String username; private String password; 其他略 }
测试代码
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @SpringBootTest(classes = SpringBootApplicationRunner.class) public class ConfigFileTest { @Autowired private MailYml mailYml; //读取yml文件 @Test public void test3(){ System.out.println(mailYml); } }
Spring Boot 原理分析
起步依赖原理分析
<parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId> <version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version> <relativePath>../../spring-boot-dependencies</relativePath> </parent>
按住Ctrl点击pom.xml中的spring-boot-starter-dependencies,跳转到了spring-boot-starter-dependencies的pom.xml,xml配置如下(只摘抄了部分重点配置)
<properties>
<activemq.version>5.15.3</activemq.version>
<antlr2.version>2.7.7</antlr2.version>
<appengine-sdk.version>1.9.63</appengine-sdk.version>
<artemis.version>2.4.0</artemis.version>
<aspectj.version>1.8.13</aspectj.version>
<assertj.version>3.9.1</assertj.version>
<atomikos.version>4.0.6</atomikos.version>
<bitronix.version>2.1.4</bitronix.version>
<build-helper-maven-plugin.version>3.0.0</build-helper-maven-plugin.version>
<byte-buddy.version>1.7.11</byte-buddy.version>
... ... ...
</properties>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-test</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
... ... ...
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<build>
<pluginManagement>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.jetbrains.kotlin</groupId>
<artifactId>kotlin-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${kotlin.version}</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.jooq</groupId>
<artifactId>jooq-codegen-maven</artifactId>
<version>${jooq.version}</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version>
</plugin>
... ... ...
</plugins>
</pluginManagement>
</build>
从上面的spring-boot-starter-dependencies的pom.xml中我们可以发现,一部分坐标的版本、依赖管理、插件管理已经定义好,所以我们的SpringBoot工程继承spring-boot-starter-parent后已经具备版本锁定等配置了。所以起步依赖的作用就是进行依赖的传递。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd" xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starters</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version>
<name>Spring Boot Web Starter</name>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-json</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate.validator</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId>
<version>6.0.9.Final</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>5.0.5.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.0.5.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
从上面的spring-boot-starter-web的pom.xml中我们可以发现,spring-boot-starter-web就是将web开发要使用的spring-web、spring-webmvc等坐标进行了“打包”,这样我们的工程只要引入spring-boot-starter-web起步依赖的坐标就可以进行web开发了,同样体现了依赖传递的作用.
自动配置原理分析
按住Ctrl点击查看启动类MySpringBootApplication上的注解@SpringBootApplication
@SpringBootApplication public class MySpringBootApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(MySpringBootApplication.class); } }
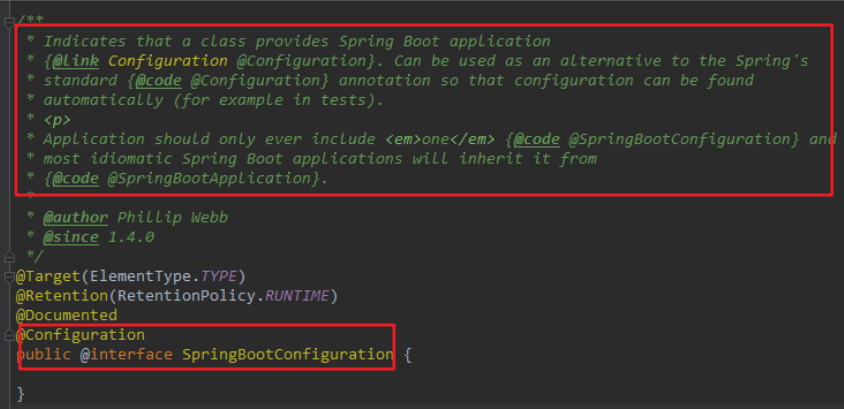
注解@SpringBootApplication的源码
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Inherited @SpringBootConfiguration @EnableAutoConfiguration @ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class), @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) }) public @interface SpringBootApplication { /** * Exclude specific auto-configuration classes such that they will never be applied. * @return the classes to exclude */ @AliasFor(annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class) Class<?>[] exclude() default {}; ... ... ... }
其中,
@SpringBootConfiguration:等同与@Configuration,既标注该类是Spring的一个配置类
@EnableAutoConfiguration:SpringBoot自动配置功能开启
关于这个注解,官网上有一段说明:
The second class-level annotation is
@EnableAutoConfiguration. This annotation tells Spring Boot to “guess” how you want to configure Spring, based on the jar dependencies that you have added. Sincespring-boot-starter-webadded Tomcat and Spring MVC, the auto-configuration assumes that you are developing a web application and sets up Spring accordingly.
简单翻译以下:
第二级的注解
@EnableAutoConfiguration,告诉SpringBoot基于你所添加的依赖,去“猜测”你想要如何配置Spring。比如我们引入了spring-boot-starter-web,而这个启动器中帮我们添加了tomcat、SpringMVC的依赖。此时自动配置就知道你是要开发一个web应用,所以就帮你完成了web及SpringMVC的默认配置了!
总结,SpringBoot内部对大量的第三方库或Spring内部库进行了默认配置,这些配置是否生效,取决于我们是否引入了对应库所需的依赖,如果有那么默认配置就会生效。
按住Ctrl点击查看注解@EnableAutoConfiguration
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Inherited @AutoConfigurationPackage @Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class) public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration { ... ... ... }
其中,@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class) 导入了AutoConfigurationImportSelector类
按住Ctrl点击查看AutoConfigurationImportSelector源码
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) { ... ... ... List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes); configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations); Set<String> exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes); checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions); configurations.removeAll(exclusions); configurations = filter(configurations, autoConfigurationMetadata); fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions); return StringUtils.toStringArray(configurations); } protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) { List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames( getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), getBeanClassLoader()); return configurations; }
其中,SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames 方法的作用就是从META-INF/spring.factories文件中读取指定类对应的类名称列表
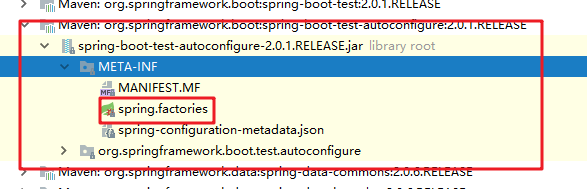
spring.factories 文件中有关自动配置的配置信息如下:
... ... ...
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.function.client.WebClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.MultipartAutoConfiguration,\
... ... ...
上面配置文件存在大量的以Configuration为结尾的类名称,这些类就是存有自动配置信息的类,而SpringApplication在获取这些类名后再加载
我们以ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration为例来分析源码:
@Configuration @AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE) @ConditionalOnClass(ServletRequest.class) @ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET) @EnableConfigurationProperties(ServerProperties.class) @Import({ ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration.BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar.class, ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedTomcat.class, ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedJetty.class, ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedUndertow.class }) public class ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration { ... ... ... }
其中,
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ServerProperties.class) 代表加载ServerProperties服务器配置属性类
进入ServerProperties.class源码如下:
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "server", ignoreUnknownFields = true) public class ServerProperties { /** * Server HTTP port. */ private Integer port; /** * Network address to which the server should bind. */ private InetAddress address; ... ... ... }
其中,
prefix = "server" 表示SpringBoot配置文件中的前缀,SpringBoot会将配置文件中以server开始的属性映射到该类的字段中。
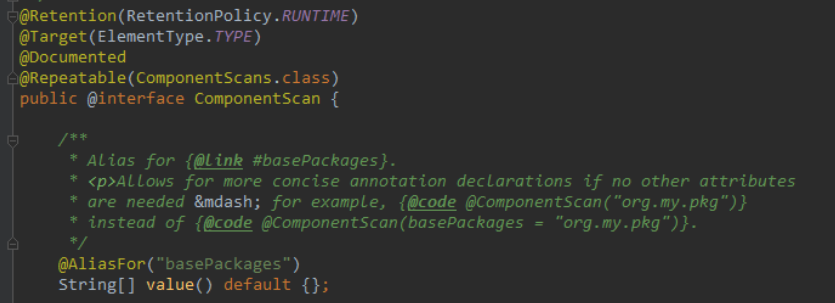
继续查看注释
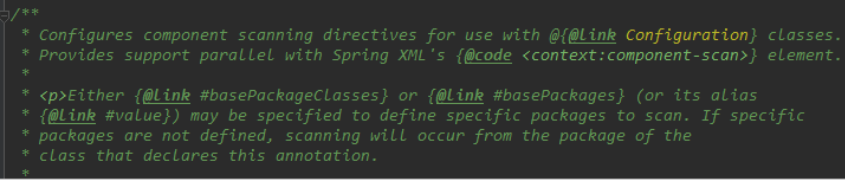
大概的意思:
配置组件扫描的指令。提供了类似与
<context:component-scan>标签的作用通过basePackageClasses或者basePackages属性来指定要扫描的包。如果没有指定这些属性,那么将从声明这个注解的类所在的包开始,扫描包及子包
而我们的@SpringBootApplication注解声明的类就是main函数所在的启动类,因此扫描的包是该类所在包及其子包。因此,一般启动类会放在一个比较前的包目录中。