Java基础语法
Java基础语法
注释
- 注释不会被执行,是给写代码的人看的
- 注释需要注意规范
- 单行注释
- 多行注释
- 文档注释
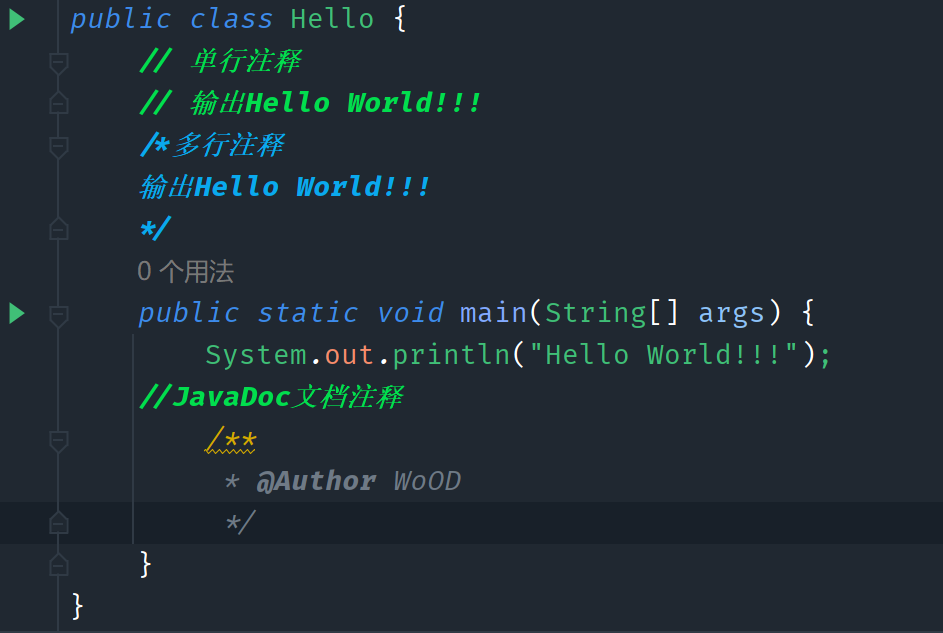
JavaDoc
生成自身的API文档
//找到需要生成JavaDoc的java文件路径 //在cmd下输入以下 javadoc -encoding UTF-8 -charset UTF-8 JavaDoc.java //生成JavaDoc文档 //javadoc后续是编码格式IDEA可以利用"工具栏"中生成JavaDoc文档
标识符
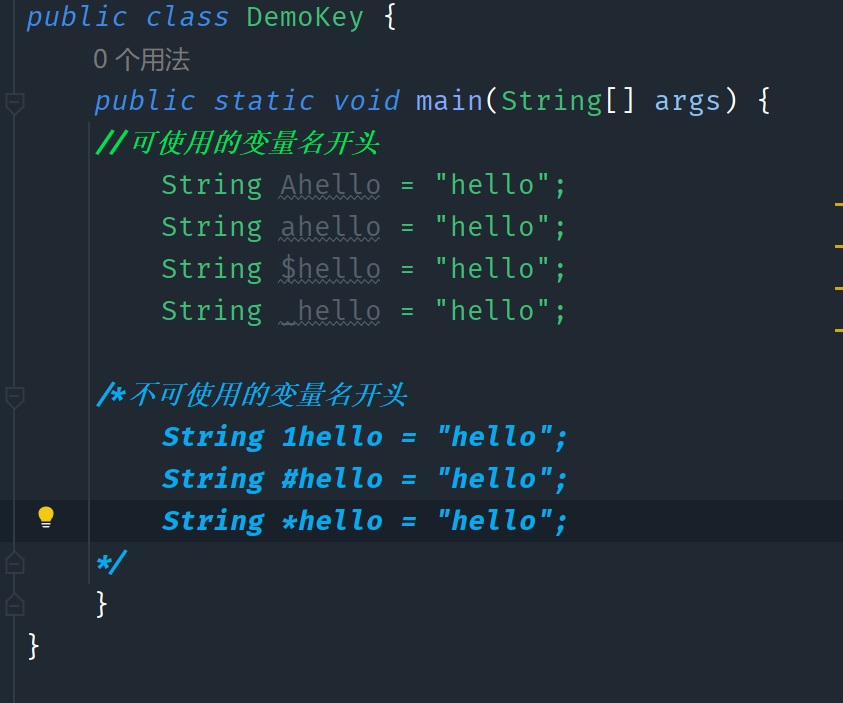
- 不建议使用中文作变量名
标识符是大小写敏感
String Man = "Hello"; String man = "Hello"; //二者是完全不同的
数据类型
-
强类型语言
- 变量使用需要严格符合规定,需要定义后才可使用
-
变量
- 数据类型 变量名 = 值;
-
数值类型
- 整数类型
- 浮点类型
//八大类型 //整数类型 byte num1 = 20;//-128~12 int num2 = 10;//常用 占4字节 short num3 = 30;// 占2字节 long num4 = 40L;//long类型 //小数、浮点数 float num5 = 40.1F;//flo double num6 = 3.1415926; -
Boolean类型
- 占1位的True和False
//布尔类型: 是 非 boolean flag_1 = true; boolean flag_2 = false; -
字符类型
- char_字符(一个字如:'X')需要用单引号括住
- String_字符串(属于引用类型)
//字符:就一个 char Str_char = 'W'; //字符串: 不是关键字,是类 String Name = "Hello"; -
引用类型
- 类
- 接口
- 数组
-
类型转换
- (类型)变量名
- 低位转高位随意(自动转换); 高位转低位需要注意(强制转换)
- 避免内存溢出和精度问题
- 无法对布尔类型转换
-
类型拓展
//整数拓展 int i = 10; int i_1 = 0b10;//二进制 int i_2 = 010;//八进制0开头 int i_3 = 0x10;//十六进制0x开头 System.out.println(i_1); System.out.println(i_2); System.out.println(i_3); //浮点数拓展 //舍入误差,结果都是大约 //最好完全避免使用浮点数进行比较 float f = 0.1F; double f_2 = 1.0/10; System.out.println(f == f_2);//false float d = 23123232331231F; float d_2 = 23123232331231F + 1; System.out.println(d == d_2);//true System.out.println("==========================="); //字符拓展: Unicode //字符本质是数字 char c_1 = 'a';//97:a; 65:A char c_2 = '国'; System.out.println(c_1); System.out.println((int) c_1); System.out.println(c_2); System.out.println((int) c_2); System.out.println("==========================="); //转义字符:制表符 // \t; \n等 System.out.println("Hello\tWorld!!!"); System.out.println("==========================="); //boolean flag = true; //if (flag==true) {}不推荐 //if (flag) {}
变量
- 使用规范: 数据类型 变量名 = 值
- 变量需要类型,类型可分为基本类型和引用类型(String)
- 变量名需要是合法标识符
- 变量声明是一条完整语句,最后以分号";"结束
- 不可int a=1, b=2;(不推荐这样写)
-
类变量
-
命名规则: 驼峰原则 lastNmae
-
//类变量:static static double value = 3500; -
作用域: 整个类内都可使用(从属类)
-
-
实例变量
-
命名规则: 驼峰原则 lastNmae
-
//实例变量:从属于对象,若不自行初始化,则有个默认值替代NULL //布尔值:默认值false String name = "WoOD"; public static void main(String[] args) { //实例变量 System.out.println("实例变量"); DemovarName varName = new DemovarName(); System.out.println(varName.name); } -
作用域: 从属对象
-
-
局部变量
-
命名规则: 驼峰原则 lastNmae
-
public static void main(String[] args) { //局部变量 System.out.println("局部变量"); int a = 1; int b = 2; char x = 'X'; double pi = 3.14; System.out.println(a + b); } -
作用域: 仅在方法内
-
-
常量
-
命名规则: 全部大写字母和下划线 MAX_VALUE
-
//常量final: 初始化后不可更改 static final int finalValue = 10000;
-
-
代码整合
public class DemovarName {//注意class类名和文件名 //实例变量 String name = "WoOD"; //类变量:static static double value = 3500; //常量final static final int finalValue = 10000; public static void main(String[] args) { //局部变量 System.out.println("局部变量"); int a = 1; int b = 2; char x = 'X'; double pi = 3.14; System.out.println(a + b); System.out.println("==================="); //实例变量 System.out.println("实例变量"); DemovarName varName = new DemovarName(); System.out.println(varName.name); System.out.println("==================="); //类变量 System.out.println("类变量"); System.out.println(value); System.out.println("==================="); //常量 System.out.println("常量"); System.out.println(finalValue); /* public class DemovarName { static int a = 1;//类变量 String name = "WoOD";//实例变量 public void method() { int i = 10;//局部变量(方法内) } } */ } }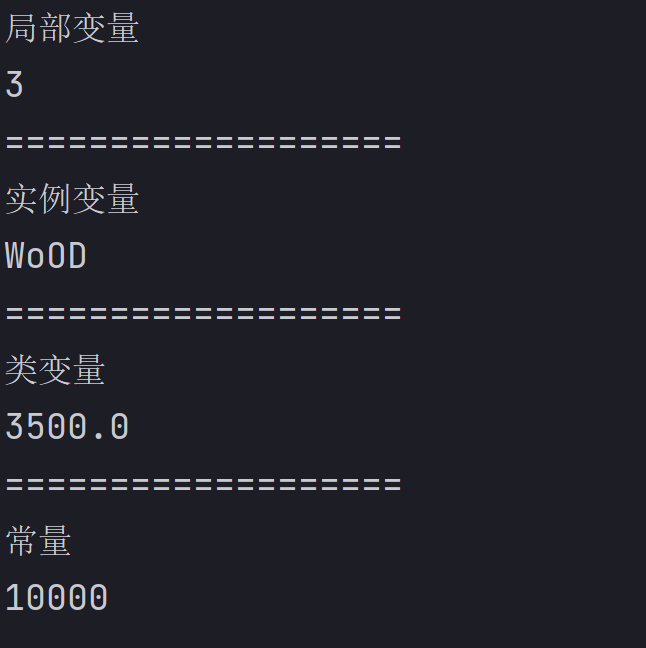
运算符
-
算数运算符
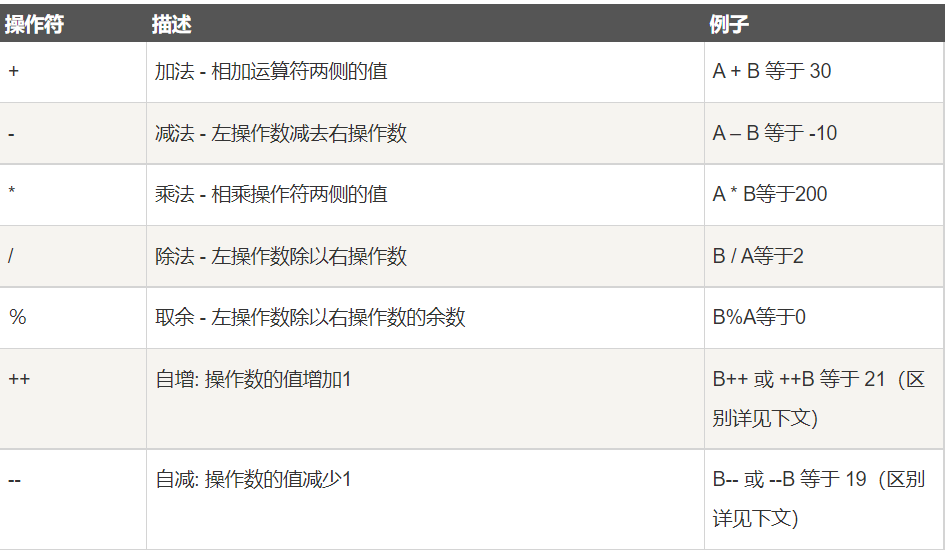
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { int a = 10; int b = 20; int c = 25; int d_0 = 25; int d_1 = 25; System.out.println("a + b = " + (a + b) ); System.out.println("a - b = " + (a - b) ); System.out.println("a * b = " + (a * b) ); System.out.println("b / a = " + (b / a) ); System.out.println("b % a = " + (b % a) ); System.out.println("c % a = " + (c % a) ); System.out.println("a++ = " + (a++) ); System.out.println("a-- = " + (a--) ); // 查看 d_0++ 与 ++d 的不同 System.out.println("d_0++ = " + (d_0++) ); System.out.println("++d_1 = " + (++d_1) ); } } /*结果: a + b = 30 a - b = -10 a * b = 200 b / a = 2 b % a = 0 c % a = 5 a++ = 10 a-- = 11 d_0++ = 25 ++d_1 = 26 */-
++(自增)和--(自减)
- a++ 是先对a进行提取运算,此时b=3,但同时a的值a+1=4=a
- ++a 是先对a进行a+1=6=a的运算,然后才将a=6赋值给c
-
int a = 10; long b = 223232012L; System.out.println("a + b = " + (String) (a + b));//错误语句 //查看结果的数据类型 -
两个不同数据进行运算,最终结果向高位的数据类型转换
-
-
赋值运算符
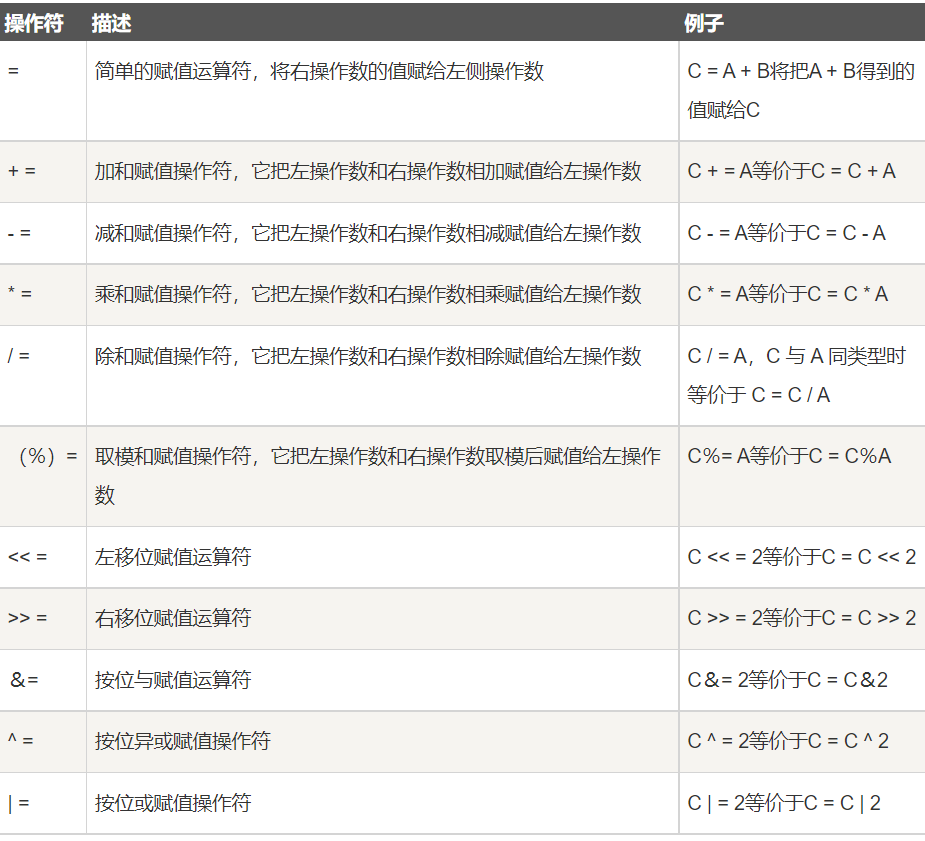
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { int a = 10; int b = 20; int c = 0; c = a + b; System.out.println("c = a + b = " + c ); c += a ; System.out.println("c += a = " + c ); c -= a ; System.out.println("c -= a = " + c ); c *= a ; System.out.println("c *= a = " + c ); a = 10; c = 15; c /= a ; System.out.println("c /= a = " + c ); a = 10; c = 15; c %= a ; System.out.println("c %= a = " + c ); c <<= 2 ; System.out.println("c <<= 2 = " + c ); c >>= 2 ; System.out.println("c >>= 2 = " + c ); c >>= 2 ; System.out.println("c >>= 2 = " + c ); c &= a ; System.out.println("c &= a = " + c ); c ^= a ; System.out.println("c ^= a = " + c ); c |= a ; System.out.println("c |= a = " + c ); } } /* 结果 c = a + b = 30 c += a = 40 c -= a = 30 c *= a = 300 c /= a = 1 c %= a = 5 c <<= 2 = 20 c >>= 2 = 5 c >>= 2 = 1 c &= a = 0 c ^= a = 10 c |= a = 10 */ -
关系运算符
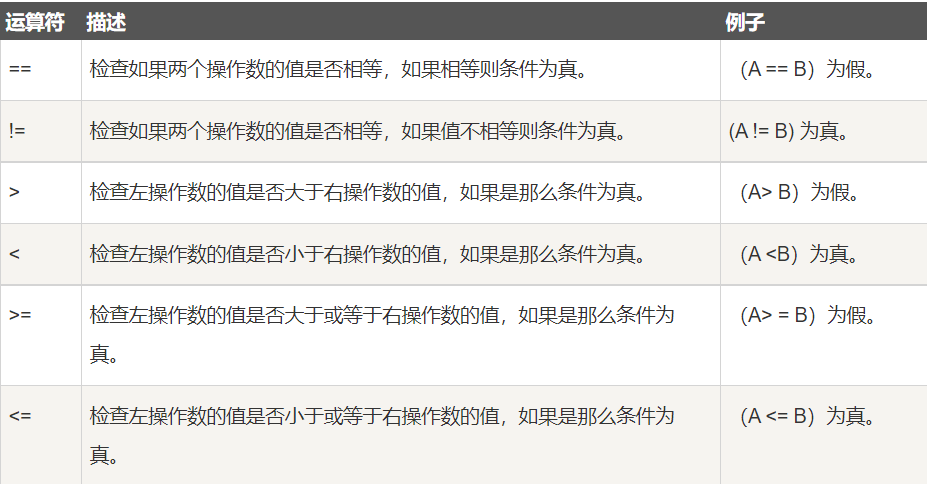
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { int a = 10; int b = 20; System.out.println("a == b = " + (a == b) ); System.out.println("a != b = " + (a != b) ); System.out.println("a > b = " + (a > b) ); System.out.println("a < b = " + (a < b) ); System.out.println("b >= a = " + (b >= a) ); System.out.println("b <= a = " + (b <= a) ); } } /* 结果 a == b = false a != b = true a > b = false a < b = true b >= a = true b <= a = false */- if大量使用
-
逻辑运算符
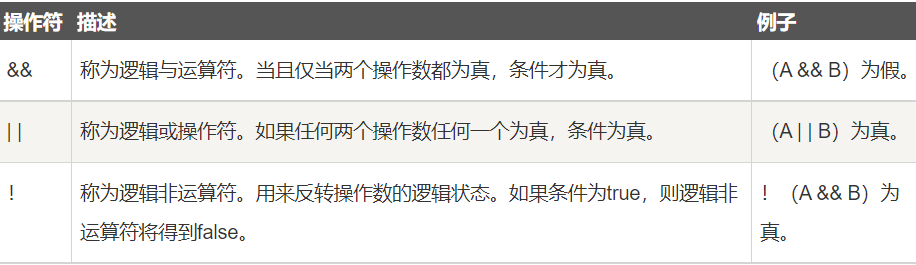
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { boolean a = true; boolean b = false; System.out.println("a && b = " + (a&&b)); System.out.println("a || b = " + (a||b) ); System.out.println("!(a && b) = " + !(a && b)); } } /* a && b = false a || b = true !(a && b) = true */-
短路运算
//短路运算 int c = 5; int d = 5; System.out.println("c: " + c); boolean d_0 = (c < 4) && (c++ > 4); //当d_0遇上(c<4)的false直接返回给d_0,不用执行(c++>4) System.out.println("d_0: " + d_0); System.out.println("c: " + c); System.out.println("================="); System.out.println("d: " + d); boolean d_1 = (d > 4) && (d++ > 4); //当d_1遇上(d>4)的true直接返回给d_1,需要执行执行(d++>4) //所以d+1=6 System.out.println("d_1: " + d_1); System.out.println("d: " + d); System.out.println("==========================="); /* 结果 c: 5 d_0: false c: 5 ================= d: 5 d_1: true d: 6 */
-
-
位运算符(可忽略)
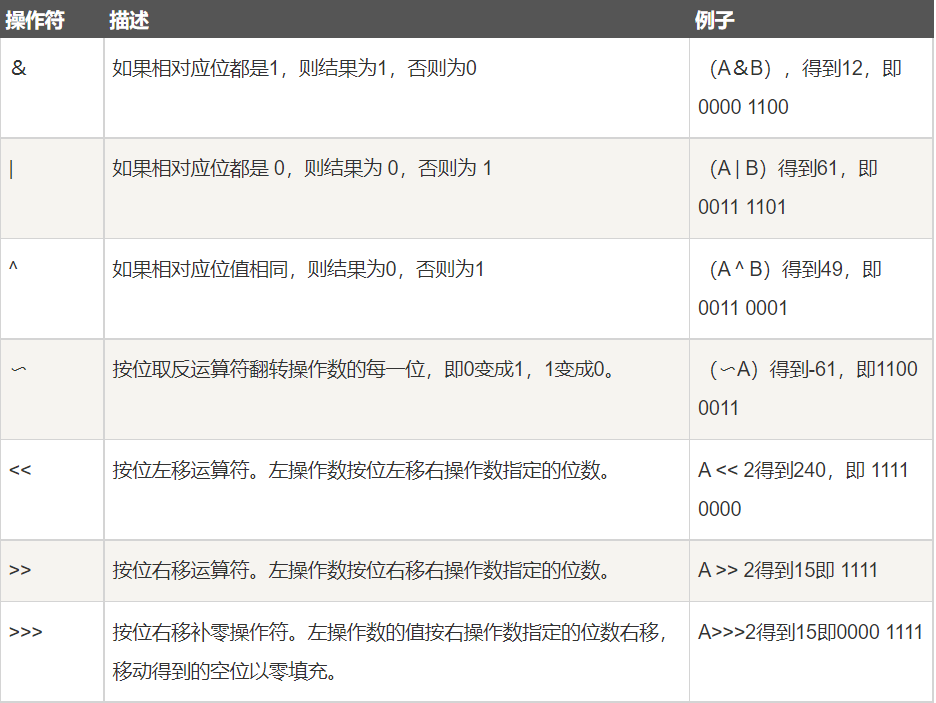
/* A = 0011 1100; B = 0000 1101; ============================= A&B = 0000 1100;与 A|B = 0011 1101;或 A^B = 0011 0001;异或 ~B = 1111 0010;取反码 ============================== <<左移 >>右移 >>: 左移1位=乘2 <<: 右移1位=除2 */ System.out.println(2 << 3);public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { int a = 60; /* 60 = 0011 1100 */ int b = 13; /* 13 = 0000 1101 */ int c = 0; c = a & b; /* 12 = 0000 1100 */ System.out.println("a & b = " + c ); c = a | b; /* 61 = 0011 1101 */ System.out.println("a | b = " + c ); c = a ^ b; /* 49 = 0011 0001 */ System.out.println("a ^ b = " + c ); c = ~a; /*-61 = 1100 0011 */ System.out.println("~a = " + c ); c = a << 2; /* 240 = 1111 0000 */ System.out.println("a << 2 = " + c ); c = a >> 2; /* 15 = 1111 */ System.out.println("a >> 2 = " + c ); c = a >>> 2; /* 15 = 0000 1111 */ System.out.println("a >>> 2 = " + c ); } } /* 结果 a & b = 12 a | b = 61 a ^ b = 49 ~a = -61 a << 2 = 240 a >> 2 = 15 a >>> 2 = 15 */ -
条件运算符(要会)
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args){ int a , b; a = 10; // 如果 a 等于 1 成立,则设置 b 为 20,否则为 30 b = (a == 1) ? 20 : 30; System.out.println( "Value of b is : " + b ); // 如果 a 等于 10 成立,则设置 b 为 20,否则为 30 b = (a == 10) ? 20 : 30; System.out.println( "Value of b is : " + b ); } } /* Value of b is : 30 Value of b is : 20 */ System.out.println("x ? y : z"); //if x==true output y, else output z int score_0 = 100; int score_00 = 97; String score_1 = score_0 == 100 ? "满分" : "仍需努力"; String score_2 = score_00 == 100 ? "满分" : "仍需努力"; System.out.println("score_0: " + score_1); System.out.println("score_00: " + score_2); /* 满分 仍需努力 */ -
instanceof 运算符(可忽略)
-
检查该对象是否是一个特定类型(类类型或接口类型)
-
/* String name = "James"; boolean result = name instanceof String; // 由于 name 是 String 类型,所以返回真 如果被比较的对象兼容于右侧类型,该运算符仍然返回 true。 */ //看下面的例子: class Vehicle {} public class Car extends Vehicle { public static void main(String[] args){ Vehicle a = new Car(); boolean result = a instanceof Car; System.out.println( result); } } //结果 //true
-
-
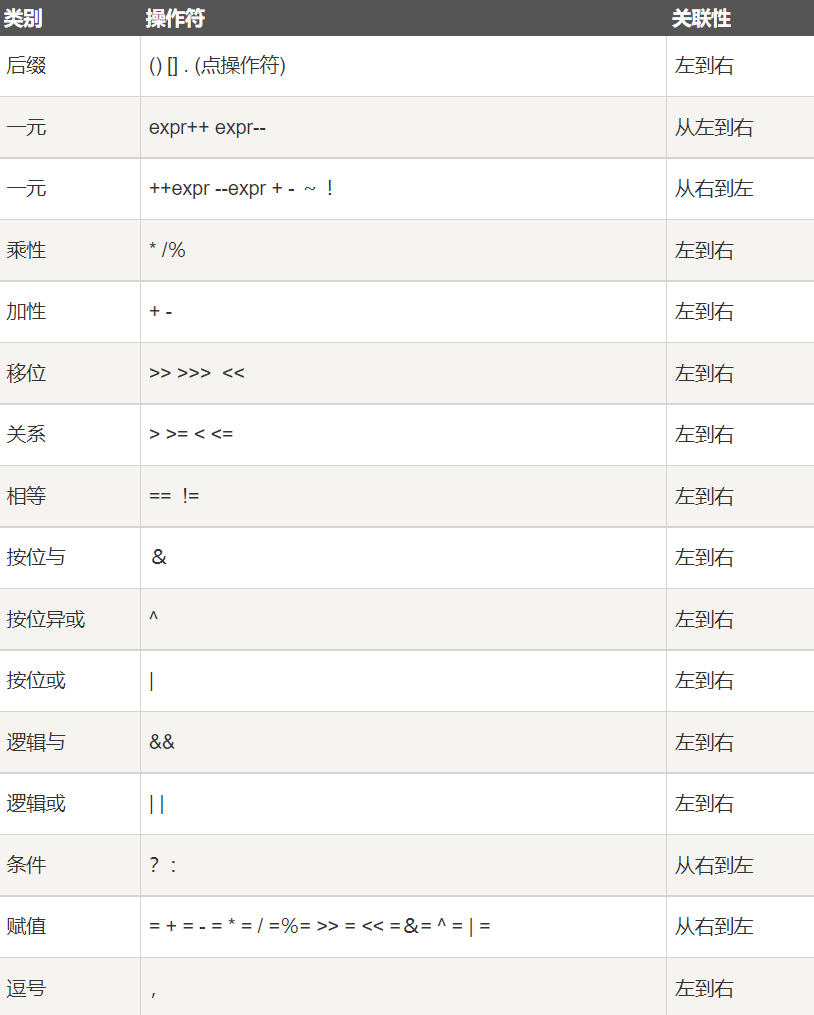
优先级(不需特别去记)
包机制
更好组织类
语法格式
package pkg1[.pkg2[.pkg3...]];包的本质就是文件夹
使用import语句可以导入其他包的类
包与包之间的类名不要重复
需要规范包名
package com.WoOD.www // com包内的WoOD包内的www类或者包 import com.WoOD.www.*; //这个包内的类全部导入
小结
基础语法是需要牢固的,未来使用最多就是这些基础语法,在这章节里最难受的应该是运算符的使用,但不用特别害怕,里面标题(可忽略)基本就是日常很少使用的,不用特别去记忆,但需要会,不会太难的。
或许有很多在a++和++a有很多疑问,但这并不是什么太难的点,记住当b=a++;时,a(未加1)原本的值赋值给b,但当b=a++;语句执行完,a也会随之加1,但b获取的值是未加1的a。反之亦然,b=++a;就是首先将a+1然后赋值给b, a的值也在执行的过程中加了1。
本文来自博客园,作者:Wo_OD,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/WoOD-outPut/p/17028948.html