Java 流程控制
Java 流程控制
用户交互Scanner
- java.util.Scanner是Java5的特征
- Scanner类是用于获取用户的输入
- 通过Scanner类的next()和nextLine()方法获取输入的字符串
- 读取前需要使用hasNext()和hasNextLine()判断是否还有输入的数据
-
Scanner对象
next():
- 读到有效字符后才可以结束(因此直接Enter也无法结束输入)
- 当读到有效字符后,可以将后续输入的空格作为结束符
- next()无法得到带有空格的字符串
package proCess;//包名需注意自身的包名 import java.util.Scanner;//使用Scanner需要注意导入包 public class DemoScanner {//注意文件名和类名 public static void main(String[] args) { //创建一个扫描器对象,用来接收键盘数据 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("使用next方法接收"); System.out.println("使用hasNext方法判断是否还有字符串"); System.out.println("请输入: "); //判断用户是否输入了字符串 if (scanner.hasNext()) { //使用next方法接收 String str = scanner.next(); //键盘: Hello world //输出结果只有Hello没有world System.out.println("输出内容: " + str); } /* String str = scanner.next(); System.out.println("输出内容: " + str); 这个注释的写法同样可以替代上述用if语句 */ //凡是属于IO流的类,如果不关闭,会一直占用资源 scanner.close(); } }

nextLine():
- Enter作为结束符(可以获取带有空格的字符串)
- nextLine() 方法可以返回输入Enter前的所有字符串(用的比较多)
package proCess;//包名需注意自身的包名 import java.util.Scanner; public class DemoScanner {//注意文件名和类名 public static void main(String[] args) { //创建一个扫描器对象,用来接收键盘数据 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("Please Input: "); String str = scanner.nextLine();//等待接收字符串 System.out.println("Output : " + str); /* System.out.println("使用nextLine方法接收"); System.out.println("使用hasNextLine方法判断是否还有字符串"); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); if (scanner.hasNextLine()) { String str_1 = scanner.nextLine();//等待用户输入 System.out.println("输出内容: " + str_1); } 与上述代码一样效果 */ //凡是属于IO流的类,如果不关闭,会一直占用资源 scanner.close(); } }

hasnextInt()/hasnextFloat()/hasnextDouble()等
hasnextInt()可以用来判断输入是否为整数(同样Float和Double等,可与判断输入的值是否相对应要求类型)
package proCess;//需以自身的环境的包名 import java.util.Scanner; public class ImproveScanner {//注意自己设定的类名和文件名 public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); int i = 0; System.out.println("Please input(整数): "); if (scanner.hasNextInt()) { //判断输入的数字是否为整数类型 //Int是个可以更改为double或float等等 i = scanner.nextInt(); System.out.println("Output: " + i); } else { System.out.println("输入的不是整数"); } System.out.println("============================="); //关闭scanner类,避免占用资源 scanner.close(); } }
写一段小代码
要求:
- 可以输入多个数字, 求和与求平均数, 每输入一个数字用回车确认, 通过输入非数字来结束输入
- 其中有循环语句,在后续会介绍,如今只需要知道while()括号中的条件被满足即可执行,不满足括号中的条件就不执行
package proCess;//需以自身的环境的包名 import java.util.Scanner; public class DemoSum {//注意自己设定的类名和文件名 public static void main(String[] args) { //可以输入多个数字, 求和与求平均数, 每输入一个数字用回车确认, 通过输入非数字来结束输入 //创建输入类 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); //和 double sum = 0; //输入多少个数字 int m = 0; System.out.println("请输入数字: "); //通过循环判断是否还能输入, 并在循环内进行求和与统计 while (scanner.hasNextDouble()) { //sum += scanner.nextDouble(); double x = scanner.nextDouble(); m++; sum += x; System.out.println("你输入第" + m + "当前sum结果: " + sum); System.out.println("==================================="); } System.out.println("==================================="); System.out.println("共输入了" + m + "数字"); System.out.println(m + "个数字的总和: " + sum); System.out.println(m + "个数字的平均数: " + (sum / m)); } }

顺序结构
- Java基本结构就是顺序结构(一句一句执行)
- 最为简单的算法结构
- 语句与语句之间是按照上到下的顺序执行
选择结构
单选结构
判断一个东西是否可行,然后才去执行
//语法格式 if(布尔表达式){ //如果布尔表达式为true就执行该语句 }
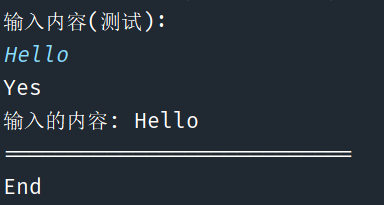
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ChoiceStructure {//注意类名
public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("输入内容(测试): "); String str = scanner.nextLine(); //equals()判断字符串是否相等 if (str.equals("Hello")) { System.out.println("Yes"); System.out.println("输入的内容: " + str); System.out.println("==========================="); } System.out.println("End"); scanner.close(); }}
双选结构
两种判断,就需要使用双选结构
//语法格式 if(布尔表达式){ //如果布尔表达式为true就执行该语句 }else{ //如果布尔表达式为false就执行该语句 }package Structure;//注意包名 import java.util.Scanner; public class ChoiceStructure {//注意类名 public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("输入的分数大于等于60则输出及格,小于60就不及格"); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("输入分数(测试): "); int score = scanner.nextInt(); if (score >= 60) { System.out.println("恭喜你取得 " + score + "分, 及格!!!"); } else { System.out.println("非常遗憾你取得 " + score + "分, 不及格!!!"); } System.out.println("==========================="); scanner.close(); } }

多选结构
在现实生活,肯定不止于二元问题,因此有多选结构
//语法格式 if(布尔表达式_1){ //如果布尔表达式_1为true就执行该语句 }else if(布尔表达式_2){ //如果布尔表达式_2为true就执行该语句 }else if(布尔表达式_3){ //如果布尔表达式_3为true就执行该语句 }else{ //如果以上的布尔表达式都不为true就执行该语句 }package Structure;//注意包名 import java.util.Scanner; public class ChoiceStructure {//注意类名 public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("输入的成绩进行多级判断"); Scanner scanner_2 = new Scanner(System.in);//接收键盘输入 System.out.println("输入分数(测试): "); int score_1 = scanner_2.nextInt(); if (score_1 == 100) { System.out.println("恭喜你取得 " + score_1 + "分, 是S级!!!"); } else if (score_1 < 100 && score_1 >= 80) { System.out.println("恭喜你取得 " + score_1 + "分, 是A级!!!"); } else if (score_1 < 80 && score_1 >= 60) { System.out.println("恭喜你取得 " + score_1 + "分, 是B级!!!"); } else if (score_1 < 60) { System.out.println("非常遗憾你取得 " + score_1 + "分, 是C级!!!"); } else { System.out.println("麻烦输入(0~100)!!!"); } System.out.println("==================================="); scanner.close(); } }

*
嵌套if结构
使用嵌套的 if…else 语句是合法的。也就是说你可以在另一个 if 或者 else if 语句中使用 if 或者 else if 语句。
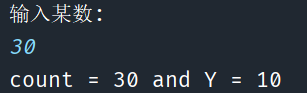
if(布尔表达式_1){ //如果布尔表达式_1为true就执行该语句 if(布尔表达式_2){ //如果布尔表达式_2为true就执行该语句 } }package Structure;//注意包名 import java.util.Scanner; public class ChoiceStructure {//注意类名 public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("输入某数: "); int count = sc.nextInt();//输入的数用nextInt方法接收住 int y = 10; //输入的count==30和y==10共同达成才可输出 if (count == 30) { if (y == 10) { System.out.print("count = 30 and Y = 10"); } } sc.close(); } }
switch多选择结构
判断一个变量与一系列值中某个值是否相等,每个值称为一个分支(变量类型基本都可以使用)
switch 语句可以包含一个 default 分支,该分支一般是 switch 语句的最后一个分支(可以在任何位置,但建议在最后一个)。default 在没有 case 语句的值和变量值相等的时候执行。default 分支不需要 break 语句。
//语法格式 switch(expression){ case value : //语句 break; //可选 case value : //语句 break; //可选 //你可以有任意数量的case语句 default : //可选 //语句 }
case(穿透)和switch(匹配一个具体的值)
- 当case语句中没有break的话,而后续case语句中(没有break)都会输出
- case语句要是有break,就不会输出后续case语句
- switch语句就是用于匹配
package Structure; import java.util.Scanner; public class SwitchStructure { public static void main(String[] args) { //char grade = args[0].charAt(0); System.out.println("输入内容(测试): "); Scanner test = new Scanner(System.in); String str = test.nextLine(); //switch case 执行时,一定会先进行匹配 // 匹配成功返回当前 case 的值, // 再根据是否有 break,判断是否继续输出,或是跳出判断。 switch (str) { case "Hello World": System.out.println("初学者"); break; case "大佬": System.out.println("王者"); break; default: System.out.println("未知内容"); } System.out.println("你的等级是 " + str); } }

循环结构
- while循环
- 最基本的循环结构
while( 布尔表达式 ) { //循环内容 }
- 只要布尔表达式为true,循环就会一直执行
- while(true)死循环用于等待客户端连接, 定时检查等(需要尽量避免)
package ForWhile; public class DemoWhile { public static void main(String[] args) { //用while循环输出1+...+100 int i = 0; int sum = 0; while (i < 100) { i++; sum += i; } System.out.println("1+...+100 = " + sum); } } /* 1+...+100 = 5050 */
- do...while循环
- 与while循环基本一致, 但do...while即使布尔表达式不成立,仍然会执行一次
do { //代码语句 }while(布尔表达式);package ForWhile;//注意包名 public class DemoWhile {//注意自己的类名 public static void main(String[] args) { //用do...while循环输出1+...+100 int i = 0; int sum = 0; do { //这里要解释下为何i++和sum+=i不对调 //因为当执行到i=99;sum=4950,当进行到这里的i++时,i=100,再加上sum,结果就是5050的 //上述用while也是 //假设将i=++放前,sum+=i后面,当执行到i=99;sum=4851(98已经加上了),再sum+99=4950,但后面i++了,i=100不再执行循环了 //但其实i++放sum前面,sum就是从1开始加 //但要是i++放sum后面,sum就是从0开始加,第二次i++才是有意义的,也就是当i=98;sum=4851(98加上了),然后i++;i=99,sum=4950(99加上了),然后i++;i=100就跳出了,少加上100 //其实就是i++放后面影响循环while(i<100)即(0~99),要是while(i<=99)就可以,但也导致了i会加1变成101 i++; sum += i; } while (i < 100); System.out.println("i: = " + i); System.out.println("1+...+100 = " + sum); } } ```
while和do..while区别
- while是先判断后执行; do.while是先执行一次后判断
- for循环
- 使得一些循环结构变得简单
for(初始化; 布尔表达式; 更新) { //代码语句 }
- for循环执行的次数是在执行前就确定的
- 执行初始化步骤。可以声明一种类型,但可初始化一个或多个循环控制变量,也可以是空语句
增强型for循环(Java5引入了一种用于数组的增强型for循环)
//语法格式 for(声明语句 : 表达式){ //代码句子 }**声明语句: ** 声明新的局部变量, 该变量的类型必须和数组元素的类型相匹配, 局部变量的作用域限定在循环语句块中, 其值与此时数组元素的值相等。
表达式:表达式是要访问的数组名,或者是返回值为数组的方法。
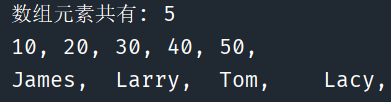
package ForWhile; public class ArryFor { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] numbers = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50}; //定义数组 //输出数组元素 // System.out.println(Arrays.toString(numbers)); //输出数组共有多少元素; 这里的数组是真的共有5个, 不用特别从0开始数,数到4 System.out.println("数组元素共有: " + numbers.length); /* for(int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++){ System.out.println(numbers[i]); //数组下标由0开始 } */ //遍历数组元素 //将数组元素赋于x,然后再循环体中执行 for (int x : numbers) { System.out.print(x); System.out.print(",\t"); } System.out.print("\n"); String[] names = {"James", "Larry", "Tom", "Lacy"}; //定义字符串数组 for (String name : names) { System.out.print(name); System.out.print(",\t"); } } }
Break和Continue
- break用于强行退出循环,不会执行循环中余下的语句(switch中也会用到)
- break可以理解为辞职
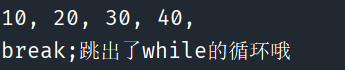
package ForWhile; public class JumpFor { public static void main(String[] args) { //输出10, 20, 30,...100的数字,但一遇上50就不输出了(连50都不用输出) int a = 10; while (a <= 100) { System.out.print(a); System.out.print(",\t"); a += 10; if (a == 50) { break;//跳出了while的循环;后续的60~100都没有输出 } } System.out.println(); System.out.println("break;跳出了while的循环哦"); System.out.println("======================================="); } }
- continue用于终止某次循环,就是跳过循环体中尚未执行的语句,接着进行下一次的循环执行判定
- continue适用于任何循环控制结构中。作用是让程序立刻跳转到下一次循环的迭代
- continue可以理解为请假
在 for 循环中,continue 语句使程序立即跳转到更新语句。
在 while 或者 do…while 循环中,程序立即跳转到布尔表达式的判断语句。
package ForWhile; public class JumpFor { public static void main(String[] args) { //输出1~100的数字(遇到10,20...100不输出) int i = 0; while (i < 100) { i++; if (i % 10 == 0) {//当遇到10的倍数立马执行continue; System.out.println(); continue;//立马回到while循环,再执行循环 } System.out.print(i); System.out.print(",\t"); } } }
package ForWhile; public class TestTra { public static void main(String[] args) { //打印三角形(5行) for (int i = 0; i <= 5; i++) { for (int j = 5; j >= i; j--) { System.out.print(" ");//打印空格;第一行5个空格,依次递减 } for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {//这个是左半部的*号 System.out.print("*");//打印*号,第一行1个*;第二行2个;第三行3个... } for (int j = 1; j < i; j++) {//这个是右半部的*号(这里是<符号哦) System.out.print("*");//打印*号,第一行0个*;第二行1个;第三行2个... } System.out.println(); } System.out.println("或许有更好的做法, 但用刚开始思路来写仍然需要拆分"); } }
小结
这次关于流程控制的学习很多,但也是真正感受到代码的应用, 真的写出来程序有种能使用的成就感,虽然我知道我还有很长的路要走,但我希望各位不要被多所击败
掌握好Scanner的应用, 固定搭配即可, 这真的是你想有程序交互的基础; 一定要掌握循环结构和选择结构,这是我们未来写代码的基础中的基础,但也不算很难,主要难在缕清思路
本文来自博客园,作者:Wo_OD,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/WoOD-outPut/articles/17035925.html



