[模板]虚树
虚树,顾名思义就是不存在的树。
1. 虚树是什么?
虚树常常被使用在树形 $\operatorname{DP}$ 中。
当一次询问仅涉及到整棵树中少量节点时,对整棵树进行 $\operatorname{DP}$ 在时间上无法接受
此时我们可以建立一棵仅包含部分关键节点的树(也就是虚树),将非关键边构成的链简化,在虚树上进行 $\operatorname{DP}$
虚树包含的节点为所有的询问点以及它们两两的LCA
比如下面的图片,如果我要询问的点是红色的点
那么虚树中包含的点就是红色的点(询问点)和蓝色的点( $\operatorname{LCA}$ )
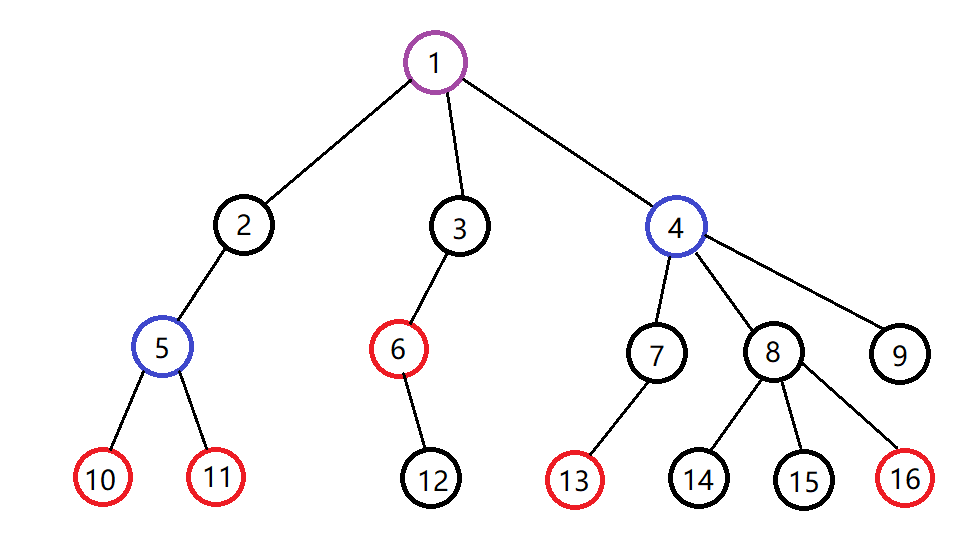
可以发现一号节点是紫色的,这是因为它既是询问点又是 $\operatorname{LCA}$
建立出来的虚树是这样的
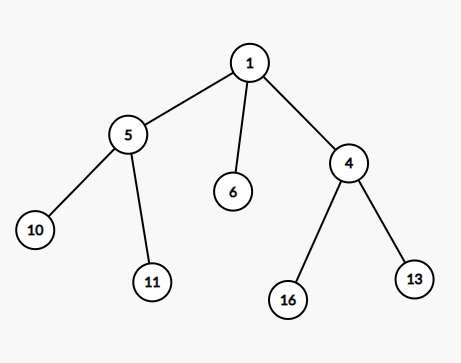
显然虚树的叶子节点必定是询问点,因此对于一个大小为 $k$ 的询问,叶子节点至多有 $k$ 个,整棵树最多有 $2k-1$ 个节点
在实际操作中,我们一般选定一个点作为树的根(我一般是选 $1$ 号点)
这样可以避免很多麻烦
2. 准备工作
- 预处理出原树的 $\operatorname{DFS}$ 序
- 将询问点按照 $\operatorname{DFS}$ 序排序
- 高效的在线 $\operatorname{LCA}$ 算法(比如倍增,比如树链剖分)
说句闲话:其实倍增法没有树链剖分快
倍增法建立的复杂度是 $\Theta(n\log n)$ ,查询是 $\Theta(\log n)$
而树链剖分的复杂度是 $\Theta(n)$ ,查询也是 $\Theta(\log n)$
看上去貌似树剖更快,但 @Jijidawang 大佬指出在某些情况下ST表更优
我个人喜欢树剖,但有时候树剖写起来麻烦

struct Edge{ int pre,to,val; }; struct Tree_Cut{ Edge edge[WR]; int head[WR],tot=0; int sze[WR],fa[WR],son[WR],dpt[WR]; int top[WR],rnk[WR],ipt[WR],cnt=0; void add(int u,int v,int val){ edge[++tot].pre=head[u]; edge[tot].to=v; edge[tot].val=val; head[u]=tot; } void dfs1(int u,int root){ fa[u]=root,dpt[u]=dpt[root]+1,sze[u]=1; for(int i=head[u];i;i=edge[i].pre){ int v=edge[i].to; if(v==root) continue; dfs1(v,u); sze[u]+=sze[v]; if(sze[v]>sze[son[u]]) son[u]=v; } } void dfs2(int u,int tp){ top[u]=tp,ipt[u]=++cnt,rnk[cnt]=u; if(son[u]) dfs2(son[u],tp); for(int i=head[u];i;i=edge[i].pre){ int v=edge[i].to; if(v!=son[u]&&v!=fa[u]) dfs2(v,v); } } int LCA(int x,int y){ while(top[x]!=top[y]){ if(dpt[top[x]]<dpt[top[y]]) swap(x,y); x=fa[top[x]]; } if(dpt[x]>dpt[y]) return y; else return x; } }tree;

void dfs(int u,int root){ dpt[u]=dpt[root]+1; for(int i=1;i<=17;i++){ fa[u][i]=fa[fa[u][i-1]][i-1]; } ipt[u]=++cnt,rnk[cnt]=u; for(int i=head[u];i;i=edge[i].pre){ int v=edge[i].to; if(v==root) continue; fa[v][0]=u; dfs(v,u); } } int LCA(int x,int y){ if(dpt[x]<dpt[y]) swap(x,y); for(int i=17;i>=0;i--){ if(dpt[fa[x][i]]>=dpt[y]){ x=fa[x][i]; } } if(x==y) return res; for(int i=17;i>=0;i--){ if(fa[x][i]!=fa[y][i]){ x=fa[x][i],y=fa[y][i]; } } return fa[x][0]; }
3. 建树
非常有趣的工作
引入一个概念:最右链
最右链的意思是在目前这条链的左边(不包括这条链)的虚树已经建设完毕
注意到最右链并没有被并入虚树里,这是因为还会不断地有求出的 $LCA$ 插进最右链中
在建树的最后一步我们将会清空栈,将最右链并入虚树
初始无条件将树根并入栈中(这里建议数组模拟栈,否则可能会比较麻烦)
然后将所有询问点顺次加入,同时加入当前询问点 $now$ 和栈顶元素 $stk[top]$ 的最近公共祖先 $lca$
这里要大力分类讨论:
Case 1:lca=stk[top]
这种情况的意思是 $now$ 在 $stk[top]$ 的子树中
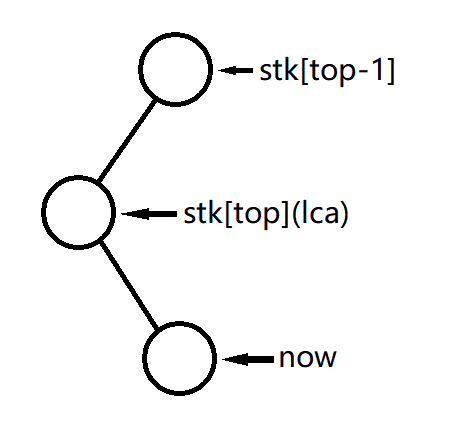
对于这种情况,直接把 $now$ 加到栈顶就好
Case 2:lca在stk[top]和stk[top-1]之间
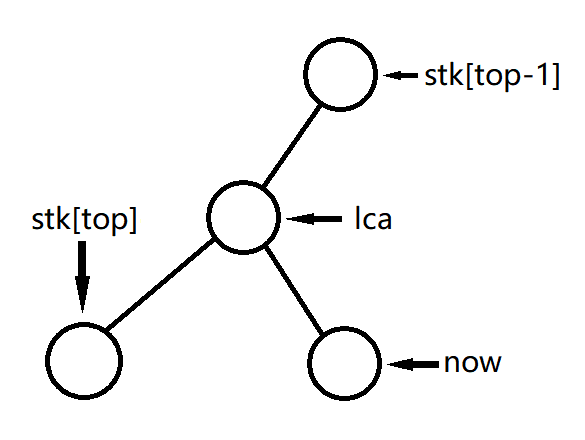
此时最右链末端从 $stk[top-1] \to stk[top]$ 变为 $stk[top-1] \to lca \to now$
也就是说我们先让 $stk[top]$ 出栈,再让 $lca$ 和 $now$ 入栈即可
注意弹栈后要将 $lc$ 和 $stk[top]$ 连边
Case 3:lca=stk[top−1]
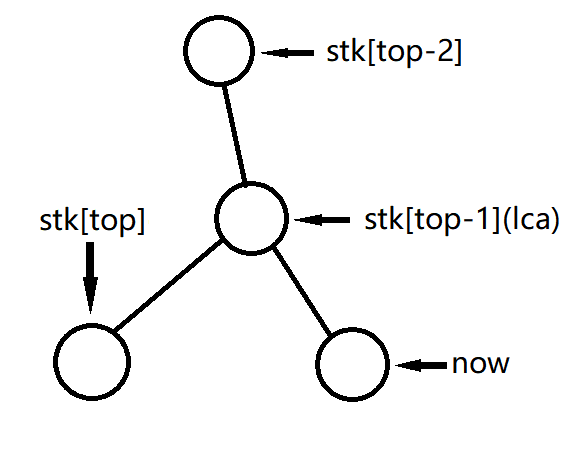
和 $Case 2$ 基本相同,只不过不用再让 $lca$ 入栈,直接入栈 $now$ 即可
Case 4:dpt[lca]<dpt[stk[top]-1]
此时 $lca$ 已经不在 $stk[top-1]$ 的子树里了,甚至也可能不在 $$stk[top-2],stk[top-3]\cdots$ 的子树中
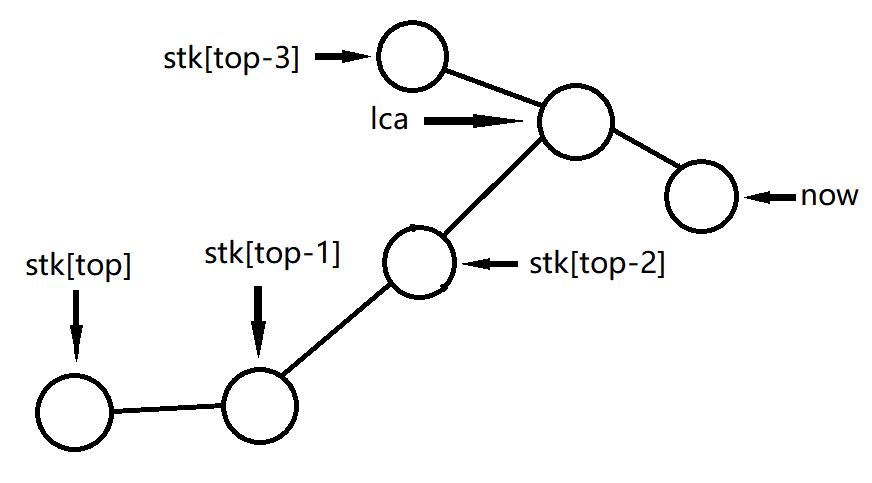
如图,我们进行两次操作
第一次操作:循环将最右链顶端弹出,剪下的边加入虚树,直到不再是 $Case 4$
第二次操作:根据实际情况将 $now$ 入栈
在建树的最后,我们清空栈,将栈中元素连边

bool cmp(int x,int y){ return tree.ipt[x]<tree.ipt[y]; } void build(){ sort(a+1,a+1+k,cmp);//按照DFS序大小排序 top=1;stk[top]=1; tot=0;//清空 for(int i=1;i<=k;i++){ if(a[i]==1) continue; int lca=tree.LCA(a[i],stk[top]); if(lca!=stk[top]){//-------------------------------如果是Case 1直接跳过 while(tree.dpt[lca]<tree.dpt[stk[top-1]]){//---Case 4 int u=stk[top],v=stk[top-1]; add(u,v);add(v,u); top--; } if(tree.dpt[lca]>tree.dpt[stk[top-1]]){//------Case 2 int u=lca,v=stk[top]; add(u,v);add(v,u); stk[top]=lca; }else{//---------------------------------------Case 3 int u=lca,v=stk[top]; add(u,v);add(v,u); top--; } } stk[++top]=a[i]; } for(int i=1;i<top;i++){//最后统一清空栈进行连边 int u=stk[i],v=stk[i+1]; add(u,v);add(v,u); } } 建树
4. 清空
这里要注意的是我们不能在最后统一清空 $head$ 等数组,$\Theta(n)$ 的时间复杂度无法承受
所以我们在树形 $\operatorname{DP}$ 的末尾进行清空
然后我们会发现模板中只需要清空 $head$ 和 $vis$ 两个数组就好了
整个模板放一下
#include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> #include<string> #define int long long #define WR WinterRain using namespace std; const int WR=1001000,INF=2147483647; struct Edge{ int pre,to; }; struct Tree_Cut{ Edge edge[WR]; int head[WR],tot=0; int sze[WR],fa[WR],son[WR],dpt[WR]; int top[WR],rnk[WR],ipt[WR],cnt=0; void add(int u,int v){ edge[++tot].pre=head[u]; edge[tot].to=v; head[u]=tot; } void dfs1(int u,int root){ fa[u]=root,dpt[u]=dpt[root]+1,sze[u]=1; for(int i=head[u];i;i=edge[i].pre){ int v=edge[i].to; if(v==root) continue; dfs1(v,u); sze[u]+=sze[v]; if(sze[v]>sze[son[u]]) son[u]=v; } } void dfs2(int u,int tp){ top[u]=tp,ipt[u]=++cnt,rnk[cnt]=u; if(son[u]) dfs2(son[u],tp); for(int i=head[u];i;i=edge[i].pre){ int v=edge[i].to; if(v!=son[u]&&v!=fa[u]) dfs2(v,v); } } int LCA(int x,int y){ while(top[x]!=top[y]){ if(dpt[top[x]]<dpt[top[y]]) swap(x,y); x=fa[top[x]]; } if(dpt[x]>dpt[y]) return y; else return x; } }tree; Edge edge[WR]; int n,m,k; int a[WR],stk[WR],top; int head[WR],tot; bool vis[WR]; int read(){ int sze=0,w=1; char ch=getchar(); while(ch>'9'||ch<'0'){ if(ch=='-') w=-1; ch=getchar(); } while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){ sze=(sze<<3)+(sze<<1)+ch-48; ch=getchar(); } return sze*w; } bool cmp(int x,int y){ return tree.ipt[x]<tree.ipt[y]; } void add(int u,int v){ edge[++tot].pre=head[u]; edge[tot].to=v; head[u]=tot; } void build(){ sort(a+1,a+1+k,cmp); top=1;stk[top]=1; tot=0; for(int i=1;i<=k;i++){ if(a[i]==1) continue; int lca=tree.LCA(a[i],stk[top]); if(lca!=stk[top]){ while(tree.dpt[lca]<tree.dpt[stk[top-1]]){ int u=stk[top],v=stk[top-1]; add(u,v);add(v,u); top--; } if(tree.dpt[lca]>tree.dpt[stk[top-1]]){ int u=lca,v=stk[top]; add(u,v);add(v,u); stk[top]=lca; }else{ int u=lca,v=stk[top]; add(u,v);add(v,u); top--; } } stk[++top]=a[i]; } for(int i=1;i<top;i++){ int u=stk[i],v=stk[i+1]; add(u,v);add(v,u); } } int dp(int u,int root){ int res=0; //这里写普通的树形DP vis[u]=0,head[u]=0; return res; } signed main(){ n=read(); for(int i=1;i<n;i++){ int u=read(),v=read(); tree.add(u,v); tree.add(v,u); } tree.dfs1(1,0); tree.dfs2(1,1); m=read(); while(m--){ k=read(); for(int i=1;i<=k;i++) a[i]=read(),vis[a[i]]=true; build(); printf("%lld\n",dp(1,0)); } return 0; }
本文来自博客园,作者:冬天的雨WR,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/WintersRain/p/16498718.html
为了一切不改变的理想,为了改变不理想的一切


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号