YOLOV3目标检测模型训练实例
YOLOV3目标检测
从零开始学习使用keras-yolov3进行图片的目标检测,比较详细地记录了准备以及训练过程,提供一个信号灯的目标检测模型训练实例,并提供相关代码与训练集。
DEMO测试
YOLO提供了模型以及源码,首先使用YOLO训练好的权重文件进行快速测试,首先下载权重文件
https://pjreddie.com/media/files/yolov3.weights
将yolo3的版本库clone到本地,本次测试的commit id为e6598d1
git clone git@github.com:qqwweee/keras-yolo3.git
安装各种依赖,缺啥就安啥,注意依赖版本对应,以下版本仅供参考
Keras==2.2.4
numpy==1.16.0
tensorflow==1.12.0
...
执行convert.py文件,将darknet的yolo转换为可以用于keras的h5文件,生成的文件被保存在model_data下,此外convert.py和yolov3.vfg在git clone后的根目录已经给出,不需要单独下载。
python convert.py yolov3.cfg yolov3.weights model_data/yolo.h5
使用python yolo_video.py -h获取help内容
usage: yolo_video.py [-h] [--model MODEL] [--anchors ANCHORS]
[--classes CLASSES] [--gpu_num GPU_NUM] [--image]
[--input [INPUT]] [--output [OUTPUT]]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--model MODEL path to model weight file, default model_data/yolo.h5
--anchors ANCHORS path to anchor definitions, default
model_data/yolo_anchors.txt
--classes CLASSES path to class definitions, default
model_data/coco_classes.txt
--gpu_num GPU_NUM Number of GPU to use, default 1
--image Image detection mode, will ignore all positional
arguments
--input [INPUT] Video input path
--output [OUTPUT] [Optional] Video output path
本次测试是进行图片的目标检测,注意当参数为--image时会忽略所有位置参数,也就是说当进行图片检测时每次都需要手动输入位置,当然这可以以后通过自行构建代码修改
python yolo_video.py --image
之后会出现Input image filename:我是放到./img/3.jpg下,于是就直接将路径输入

稍等一会就可以识别完成
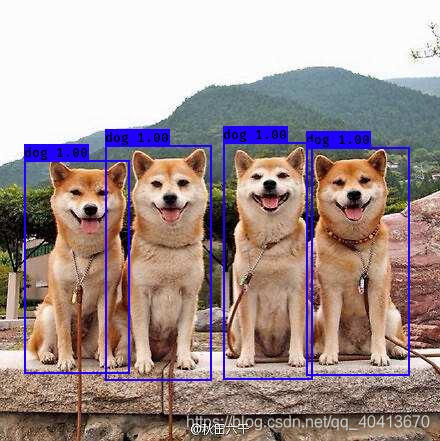
模型训练
准备数据集
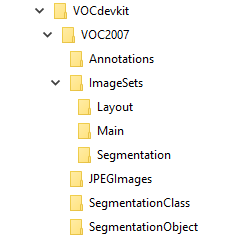
首先需要准备好目录结构,可以在 http://host.robots.ox.ac.uk/pascal/VOC/voc2007/ 中下载VOC2007数据集,然后删除其中所有的文件,仅保留目录结构,也可以手动建立如下目录结构
然后将所有的图片放置在JPEGImages目录下,然后在
https://github.com/tzutalin/labelImg 下载labelImg标注工具,此工具是为了将图片框选标注后生成XML文件,使用labelImg打开图片,标注好后将图片生成的XML文件放置于Annotations文件夹内,保存的名字就是图片的名字。
准备训练文件
在VOCdevkit/VOC2007下建立一个python文件,将代码写入并运行,即会在VOCdevkit/VOC2007/ImageSets/Main下生成四个txt文件
import os
import random
trainval_percent = 0
train_percent = 1 # 全部划分为训练集,因为yolo3在训练时依旧会划分训练集与测试集,不需要在此划分
xmlfilepath = 'Annotations'
txtsavepath = 'ImageSets/Main'
total_xml = os.listdir(xmlfilepath)
num = len(total_xml)
list = range(num)
tv = int(num * trainval_percent)
tr = int(tv * train_percent)
trainval = random.sample(list, tv)
train = random.sample(trainval, tr)
ftrainval = open('ImageSets/Main/trainval.txt', 'w')
ftest = open('ImageSets/Main/test.txt', 'w')
ftrain = open('ImageSets/Main/train.txt', 'w')
fval = open('ImageSets/Main/val.txt', 'w')
for i in list:
name = total_xml[i][:-4] + '\n'
if i in trainval:
ftrainval.write(name)
if i in train:
ftest.write(name)
else:
fval.write(name)
else:
ftrain.write(name)
ftrainval.close()
ftrain.close()
fval.close()
ftest.close()
在VOCdevkit的上层目录,我目前的目录结构为Train下,建立python文件并运行,生成三个txt文件,注意,此处代码需要将classes更改成需要训练的类别,我只需要训练person一类,所以此处数组中只有person类别

import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
from os import getcwd
sets=[('2007', 'train'), ('2007', 'val'), ('2007', 'test')]
classes = ["person"]
def convert_annotation(year, image_id, list_file):
in_file = open('VOCdevkit/VOC%s/Annotations/%s.xml'%(year, image_id),'rb')
tree=ET.parse(in_file)
root = tree.getroot()
for obj in root.iter('object'):
difficult = obj.find('difficult').text
cls = obj.find('name').text
if cls not in classes or int(difficult)==1:
continue
cls_id = classes.index(cls)
xmlbox = obj.find('bndbox')
b = (int(xmlbox.find('xmin').text), int(xmlbox.find('ymin').text), int(xmlbox.find('xmax').text), int(xmlbox.find('ymax').text))
list_file.write(" " + ",".join([str(a) for a in b]) + ',' + str(cls_id))
wd = getcwd()
for year, image_set in sets:
image_ids = open('VOCdevkit/VOC%s/ImageSets/Main/%s.txt'%(year, image_set)).read().strip().split()
list_file = open('%s.txt'%(image_set), 'w')
for image_id in image_ids:
list_file.write('VOCdevkit/VOC%s/JPEGImages/%s.jpg'%(year, image_id))
convert_annotation(year, image_id, list_file)
list_file.write('\n')
list_file.close()
接下来将Train目录下所有的文件复制到git clone后的目录下,此时的文件目录结构是这样的
修改参数
此时需要修改model_data/coco_classes.txt与voc_classes.txt文件,这两个文件都是需要存放训练类别的,同样我只是训练person类别,此处只有一行person。
接下来修改yolov3.cfg,假如你不需要加载预训练的权重,那么此文件是没有必要修改的,此文件是为生成yolo_weights.h5作配置的,在此文件中搜索yolo,会有三处匹配,都是相同的更改方式,以第一次匹配举例,三处注释位置,也就是共需改动9行
...
[convolutional]
size=1
stride=1
pad=1
filters=18 # 3*(5+len(classes)) # 我训练一种类别 即 3*(5+1) = 18
activation=linear
[yolo]
mask = 6,7,8
anchors = 10,13, 16,30, 33,23, 30,61, 62,45, 59,119, 116,90, 156,198, 373,326
classes=1 # 一种类别
num=9
jitter=.3
ignore_thresh = .5
truth_thresh = 1
random=1 # 显存小就改为0
...
运行python convert.py -w yolov3.cfg yolov3.weights model_data/yolo_weights.h5生成model_data / yolo_weights.h5用于加载预训练的权重。
训练模型
之后就可以开始训练了,因为我一开始暂时没有数据,就随便找了几张图片标注后试了一下,因为不足十张,外加我在构建VOC数据集时又划分了一下数据集与训练集,而train.py又默认将数据划分了0.1的训练集,不足十张乘0.1取整就是0,导致我一直报错,此处一定要注意,一定要有验证集,也就是至少需要有两张图片,一张作为训练集一张作为验证集,否则运行train.py时会报错KeyError: 'val_loss',运行train_bottleneck.py会报错IndexError: list index out of range,此外还需要注意的是需要手动建立logs/000/目录,防止保存模型时无法找到目录而抛出异常。训练一般使用train.py就可以了,对于出现的问题多多去看看github的issue与README,很多问题都会有讨论与解决,对于train.py我略微做了一些更改以适应我的训练目的,对于一些更改的地方有注释
"""
Retrain the YOLO model for your own dataset.
"""
import numpy as np
import keras.backend as K
from keras.layers import Input, Lambda
from keras.models import Model
from keras.optimizers import Adam
from keras.callbacks import TensorBoard, ModelCheckpoint, ReduceLROnPlateau, EarlyStopping
from yolo3.model import preprocess_true_boxes, yolo_body, tiny_yolo_body, yolo_loss
from yolo3.utils import get_random_data
def _main():
annotation_path = 'train.txt'
log_dir = 'logs/000/'
classes_path = 'model_data/voc_classes.txt'
anchors_path = 'model_data/yolo_anchors.txt'
class_names = get_classes(classes_path)
num_classes = len(class_names)
anchors = get_anchors(anchors_path)
input_shape = (416,416) # multiple of 32, hw
# 此处去掉了 create_tiny_model 的判断 # load_pretrained 为False即不加载预训练的权重,为True则加载预训练的权重
model = create_model(input_shape, anchors, num_classes,load_pretrained=False,
freeze_body=2, weights_path='model_data/yolo_weights.h5') # make sure you know what you freeze
logging = TensorBoard(log_dir=log_dir)
# ModelCheckpoint 回调检查模型周期 更改为每10次检查
checkpoint = ModelCheckpoint(log_dir + 'ep{epoch:03d}-loss{loss:.3f}-val_loss{val_loss:.3f}.h5',
monitor='val_loss', save_weights_only=True, save_best_only=True, period=10)
reduce_lr = ReduceLROnPlateau(monitor='val_loss', factor=0.1, patience=3, verbose=1)
early_stopping = EarlyStopping(monitor='val_loss', min_delta=0, patience=6000, verbose=1)
# 对输入划分训练集与测试集的比重
val_split = 0.3
with open(annotation_path) as f:
lines = f.readlines()
np.random.seed(10101)
np.random.shuffle(lines)
np.random.seed(None)
num_val = int(len(lines)*val_split)
num_train = len(lines) - num_val
# Train with frozen layers first, to get a stable loss.
# Adjust num epochs to your dataset. This step is enough to obtain a not bad model.
if True:
model.compile(optimizer=Adam(lr=1e-3), loss={
# use custom yolo_loss Lambda layer.
'yolo_loss': lambda y_true, y_pred: y_pred})
# batch_size 需要针对显存更改数量
batch_size = 10
print('Train on {} samples, val on {} samples, with batch size {}.'.format(num_train, num_val, batch_size))
# epochs 即训练次数
model.fit_generator(data_generator_wrapper(lines[:num_train], batch_size, input_shape, anchors, num_classes),
steps_per_epoch=max(1, num_train//batch_size),
validation_data=data_generator_wrapper(lines[num_train:], batch_size, input_shape, anchors, num_classes),
validation_steps=max(1, num_val//batch_size),
epochs=50,
initial_epoch=0,
callbacks=[logging, checkpoint])
model.save_weights(log_dir + 'trained_weights_stage_1.h5')
# Unfreeze and continue training, to fine-tune.
# Train longer if the result is not good.
if True:
for i in range(len(model.layers)):
model.layers[i].trainable = True
model.compile(optimizer=Adam(lr=1e-4), loss={'yolo_loss': lambda y_true, y_pred: y_pred}) # recompile to apply the change
print('Unfreeze all of the layers.')
# batch_size 需要针对显存更改数量
batch_size = 10 # note that more GPU memory is required after unfreezing the body
print('Train on {} samples, val on {} samples, with batch size {}.'.format(num_train, num_val, batch_size))
# epochs即训练次数
model.fit_generator(data_generator_wrapper(lines[:num_train], batch_size, input_shape, anchors, num_classes),
steps_per_epoch=max(1, num_train//batch_size),
validation_data=data_generator_wrapper(lines[num_train:], batch_size, input_shape, anchors, num_classes),
validation_steps=max(1, num_val//batch_size),
epochs=50,
initial_epoch=50)
model.save_weights(log_dir + 'trained_weights_final.h5')
# Further training if needed.
def get_classes(classes_path):
'''loads the classes'''
with open(classes_path) as f:
class_names = f.readlines()
class_names = [c.strip() for c in class_names]
return class_names
def get_anchors(anchors_path):
'''loads the anchors from a file'''
with open(anchors_path) as f:
anchors = f.readline()
anchors = [float(x) for x in anchors.split(',')]
return np.array(anchors).reshape(-1, 2)
def create_model(input_shape, anchors, num_classes, load_pretrained=True, freeze_body=2,
weights_path='model_data/yolo_weights.h5'):
'''create the training model'''
K.clear_session() # get a new session
image_input = Input(shape=(None, None, 3))
h, w = input_shape
num_anchors = len(anchors)
y_true = [Input(shape=(h//{0:32, 1:16, 2:8}[l], w//{0:32, 1:16, 2:8}[l], \
num_anchors//3, num_classes+5)) for l in range(3)]
model_body = yolo_body(image_input, num_anchors//3, num_classes)
print('Create YOLOv3 model with {} anchors and {} classes.'.format(num_anchors, num_classes))
if load_pretrained:
model_body.load_weights(weights_path, by_name=True, skip_mismatch=True)
print('Load weights {}.'.format(weights_path))
if freeze_body in [1, 2]:
# Freeze darknet53 body or freeze all but 3 output layers.
num = (185, len(model_body.layers)-3)[freeze_body-1]
for i in range(num): model_body.layers[i].trainable = False
print('Freeze the first {} layers of total {} layers.'.format(num, len(model_body.layers)))
model_loss = Lambda(yolo_loss, output_shape=(1,), name='yolo_loss',
arguments={'anchors': anchors, 'num_classes': num_classes, 'ignore_thresh': 0.5})(
[*model_body.output, *y_true])
model = Model([model_body.input, *y_true], model_loss)
return model
def create_tiny_model(input_shape, anchors, num_classes, load_pretrained=True, freeze_body=2,
weights_path='model_data/tiny_yolo_weights.h5'):
'''create the training model, for Tiny YOLOv3'''
K.clear_session() # get a new session
image_input = Input(shape=(None, None, 3))
h, w = input_shape
num_anchors = len(anchors)
y_true = [Input(shape=(h//{0:32, 1:16}[l], w//{0:32, 1:16}[l], \
num_anchors//2, num_classes+5)) for l in range(2)]
model_body = tiny_yolo_body(image_input, num_anchors//2, num_classes)
print('Create Tiny YOLOv3 model with {} anchors and {} classes.'.format(num_anchors, num_classes))
if load_pretrained:
model_body.load_weights(weights_path, by_name=True, skip_mismatch=True)
print('Load weights {}.'.format(weights_path))
if freeze_body in [1, 2]:
# Freeze the darknet body or freeze all but 2 output layers.
num = (20, len(model_body.layers)-2)[freeze_body-1]
for i in range(num): model_body.layers[i].trainable = False
print('Freeze the first {} layers of total {} layers.'.format(num, len(model_body.layers)))
model_loss = Lambda(yolo_loss, output_shape=(1,), name='yolo_loss',
arguments={'anchors': anchors, 'num_classes': num_classes, 'ignore_thresh': 0.5})(
[*model_body.output, *y_true])
model = Model([model_body.input, *y_true], model_loss)
return model
def data_generator(annotation_lines, batch_size, input_shape, anchors, num_classes):
'''data generator for fit_generator'''
n = len(annotation_lines)
i = 0
while True:
image_data = []
box_data = []
for b in range(batch_size):
if i==0:
np.random.shuffle(annotation_lines)
image, box = get_random_data(annotation_lines[i], input_shape, random=True)
image_data.append(image)
box_data.append(box)
i = (i+1) % n
image_data = np.array(image_data)
box_data = np.array(box_data)
y_true = preprocess_true_boxes(box_data, input_shape, anchors, num_classes)
yield [image_data, *y_true], np.zeros(batch_size)
def data_generator_wrapper(annotation_lines, batch_size, input_shape, anchors, num_classes):
n = len(annotation_lines)
if n==0 or batch_size<=0: return None
return data_generator(annotation_lines, batch_size, input_shape, anchors, num_classes)
if __name__ == '__main__':
_main()
测试模型
当模型训练完成后,就可以加载模型进行图片测试了
import sys
import argparse
from yolo import YOLO, detect_video
from PIL import Image
if __name__ == '__main__':
config = {
"model_path": "logs/000/trained_weights_final.h5", # 加载模型
"score": 0.1, # 超出这个值的预测才会被显示
"iou": 0.5, # 交并比
}
yolo = YOLO(**config)
image = Image.open("./img/1.jpg")
r_image = yolo.detect_image(image)
r_image.save("./img/2.jpg")
此后就需要不断开始优化参数并训练了,其实在目录中有很多文件是用不到的或者是使用一次后就一般不会再用到了,可以备份一下代码后适当精简目录结构。
模型训练实例
从百度下载了50张信号灯的图片作训练集,实例仅为模型训练的Demo,数据集比较小,相关信息仅供参考。
运行环境
cuda 8.0
python 3.6
keras 2.1.5
tensorflow-gpu 1.4.0
相关配置
val_split = 0.1 # 训练集与测试集划分比例
batch_size = 5 # 每次训练选择样本数
epochs = 300 # 训练三百次
运行结果
数据集中的红灯比较多,所以训练结果中红灯的置信度为0.60和0.72,绿灯样本较少,识别的绿灯的置信度为0.38,整体效果还算可以。
loss: 25.8876 - val_loss: 38.1282
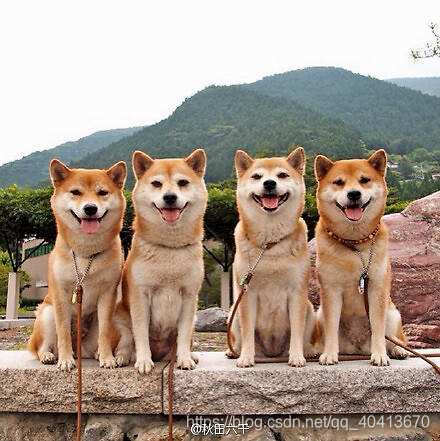
原图

识别

实例代码
如果觉得不错,点个star吧 😃
https://github.com/WindrunnerMax/Example


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号