装饰模式(包装模式)
模式动机
一般有两种方式可以实现给一个类或对象增加行为:
• 继承机制,使用继承机制是给现有类添加功能的一种有效途径,通过继承一个现有类可以使得子类在拥有自身方法的同时还拥有父类的方法。但是这种方法是静态的,用户不能控制增加行为的方式和时机。
• 关联机制,即将一个类的对象嵌入另一个对象中,由另一个对象来决定是否调用嵌入对象的行为以便扩展自己的行为,我们称这个嵌入的对象为装饰器(Decorator)。
装饰模式以对客户透明的方式动态地给一个对象附加上更多的责任,换言之,客户端并不会觉得对象在装饰前和装饰后有什么不同。装饰模式可以在不需要创造更多子类的情况下,将对象的功能加以扩展。这就是装饰模式的模式动机。
模式定义
装饰模式(Decorator Pattern) :动态地给一个对象增加一些额外的职责(Responsibility),就增加对象功能来说,装饰模式比生成子类实现更为灵活。其别名也可以称为包装器(Wrapper),与适配器模式的别名相同,但它们适用于不同的场合。根据翻译的不同,装饰模式也有人称之为“油漆工模式”,它是一种对象结构型模式。
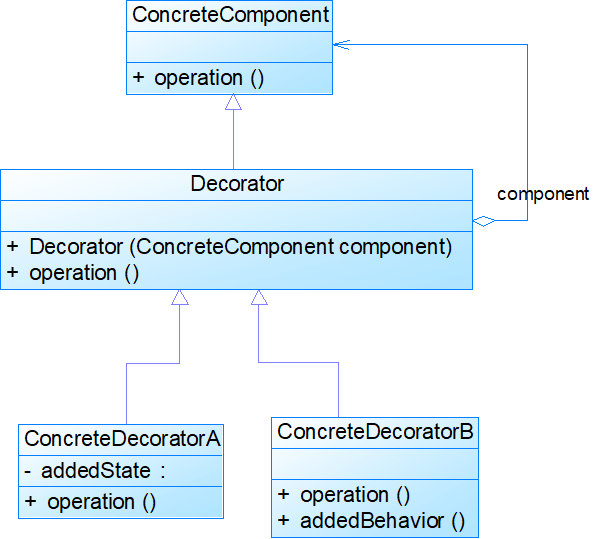
模式结构
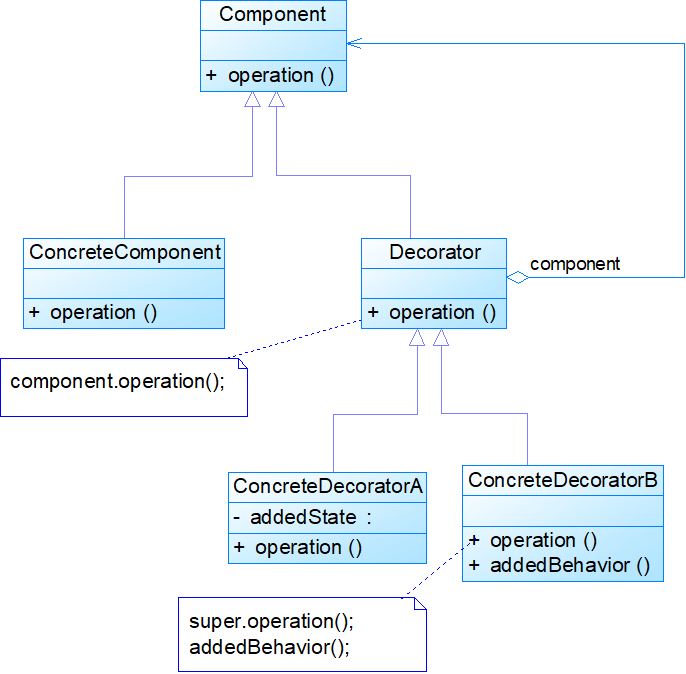
装饰模式包含如下角色:
• Component: 抽象构件
• ConcreteComponent: 具体构件
• Decorator: 抽象装饰类
• ConcreteDecorator: 具体装饰类
模式分析
与继承关系相比,关联关系的主要优势在于不会破坏类的封装性,而且继承是一种耦合度较大的静态关系,无法在程序运行时动态扩展。在软件开发阶段,关联关系虽然不会比继承关系减少编码量,但是到了软件维护阶段,由于关联关系使系统具有较好的松耦合性,因此使得系统更加容易维护。当然,关联关系的缺点是比继承关系要创建更多的对象。
使用装饰模式来实现扩展比继承更加灵活,它以对客户透明的方式动态地给一个对象附加更多的责任。装饰模式可以在不需要创造更多子类的情况下,将对象的功能加以扩展。
典型的抽象装饰类代码:
1 public class Decorator extends Component 2 { 3 private Component component; 4 public Decorator(Component component) 5 { 6 this.component=component; 7 } 8 public void operation() 9 { 10 component.operation(); 11 } 12 }
典型的具体装饰类代码:
1 public class ConcreteDecorator extends Decorator 2 { 3 public ConcreteDecorator(Component component) 4 { 5 super(component); 6 } 7 public void operation() //在子类的operation方法中增加一个方法 8 { 9 super.operation(); 10 addedBehavior(); 11 } 12 public void addedBehavior() 13 { 14 //新增方法 15 } 16 }
实例与解析
实例一:变形金刚
• 变形金刚在变形之前是一辆汽车,它可以在陆地上移动。当它变成机器人之后除了能够在陆地上移动之外,还可以说话;如果需要,它还可以变成飞机,除了在陆地上移动还可以在天空中飞翔。

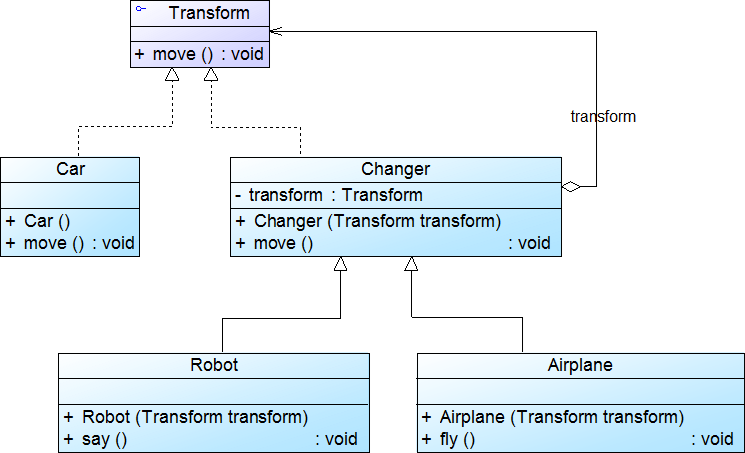
1 //抽象构建 2 public interface Transform 3 { 4 public void move(); 5 } 6 7 //具体构建 8 public final class Car implements Transform 9 { 10 public Car() 11 { 12 System.out.println("变形金刚是一辆车!"); 13 } 14 15 public void move() 16 { 17 System.out.println("在陆地上移动!"); 18 } 19 } 20 21 //抽象装饰类 22 public class Changer implements Transform 23 { 24 private Transform transform; 25 26 public Changer(Transform transform) 27 { 28 this.transform=transform; 29 } 30 31 public void move() 32 { 33 transform.move(); 34 } 35 } 36 37 //具体装饰类 38 public class Robot extends Changer 39 { 40 public Robot(Transform transform) 41 { 42 super(transform); 43 System.out.println("变成机器人!"); 44 } 45 46 public void say() 47 { 48 System.out.println("说话!"); 49 } 50 } 51 52 //具体装饰类 53 public class Airplane extends Changer 54 { 55 public Airplane(Transform transform) 56 { 57 super(transform); 58 System.out.println("变成飞机!"); 59 } 60 61 public void fly() 62 { 63 System.out.println("在天空飞翔!"); 64 } 65 } 66 67 //客户端 68 public class Client 69 { 70 public static void main(String args[]) 71 { 72 Transform camaro; 73 camaro=new Car(); 74 camaro.move(); 75 System.out.println("-----------------------------"); 76 77 Airplane bumblebee=new Airplane(camaro); 78 bumblebee.move(); 79 bumblebee.fly(); 80 } 81 }
实例二:多重加密系统
• 某系统提供了一个数据加密功能,可以对字符串进行加密。最简单的加密算法通过对字母进行移位来实现,同时还提供了稍复杂的逆向输出加密,还提供了更为高级的求模加密。用户先使用最简单的加密算法对字符串进行加密,如果觉得还不够可以对加密之后的结果使用其他加密算法进行二次加密,当然也可以进行第三次加密。现使用装饰模式设计该多重加密系统。
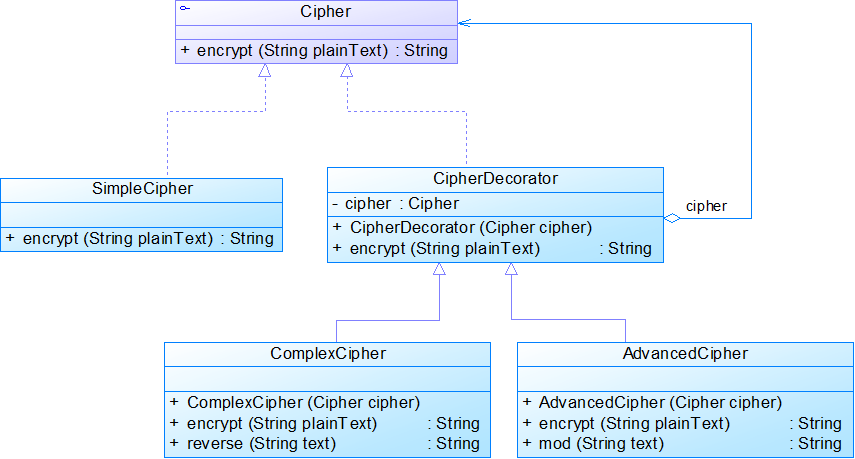
1 //抽象构建 2 public interface Cipher 3 { 4 public String encrypt(String plainText); 5 } 6 7 //具体构建 8 public class SimpleCipher implements Cipher 9 { 10 public String encrypt(String plainText) 11 { 12 String str=""; 13 for(int i=0;i<plainText.length();i++) 14 { 15 char c=plainText.charAt(i); 16 if(c>='a'&&c<='z') 17 { 18 c+=6; 19 if(c>'z') c-=26; 20 if(c<'a') c+=26; 21 } 22 if(c>='A'&&c<='Z') 23 { 24 c+=6; 25 if(c>'Z') c-=26; 26 if(c<'A') c+=26; 27 } 28 str+=c; 29 } 30 return str; 31 } 32 } 33 34 //抽象装饰类 35 public class CipherDecorator implements Cipher 36 { 37 private Cipher cipher; 38 39 public CipherDecorator(Cipher cipher) 40 { 41 this.cipher=cipher; 42 } 43 44 public String encrypt(String plainText) 45 { 46 return cipher.encrypt(plainText); 47 } 48 } 49 //具体装饰类 50 public class ComplexCipher extends CipherDecorator 51 { 52 public ComplexCipher(Cipher cipher) 53 { 54 super(cipher); 55 } 56 57 public String encrypt(String plainText) 58 { 59 String result=super.encrypt(plainText); 60 result=reverse(result); 61 return result; 62 } 63 64 public String reverse(String text) 65 { 66 String str=""; 67 for(int i=text.length();i>0;i--) 68 { 69 str+=text.substring(i-1,i); 70 } 71 return str; 72 } 73 } 74 75 //具体装饰类 76 public class AdvancedCipher extends CipherDecorator 77 { 78 public AdvancedCipher(Cipher cipher) 79 { 80 super(cipher); 81 } 82 83 public String encrypt(String plainText) 84 { 85 String result=super.encrypt(plainText); 86 result=mod(result); 87 return result; 88 } 89 90 public String mod(String text) 91 { 92 String str=""; 93 for(int i=0;i<text.length();i++) 94 { 95 String c=String.valueOf(text.charAt(i)%6); 96 str+=c; 97 } 98 return str; 99 } 100 } 101 102 //客户端 103 public class Client 104 { 105 public static void main(String args[]) 106 { 107 String password="sunnyLiu"; //明文 108 String cpassword; //密文 109 Cipher sc,cc; 110 111 sc=new SimpleCipher(); 112 cpassword=sc.encrypt(password); 113 System.out.println(cpassword); 114 System.out.println("---------------------"); 115 116 cc=new ComplexCipher(sc); 117 cpassword=cc.encrypt(password); 118 System.out.println(cpassword); 119 System.out.println("---------------------"); 120 121 /* 122 ac=new AdvancedCipher(cc); 123 cpassword=ac.encrypt(password); 124 System.out.println(cpassword); 125 System.out.println("---------------------"); 126 */ 127 } 128 }
模式优缺点
优点
• 装饰模式与继承关系的目的都是要扩展对象的功能,但是装饰模式可以提供比继承更多的灵活性。
• 可以通过一种动态的方式来扩展一个对象的功能,通过配置文件可以在运行时选择不同的装饰器,从而实现不同的行为。
• 通过使用不同的具体装饰类以及这些装饰类的排列组合,可以创造出很多不同行为的组合。可以使用多个具体装饰类来装饰同一对象,得到功能更为强大的对象。
• 具体构件类与具体装饰类可以独立变化,用户可以根据需要增加新的具体构件类和具体装饰类,在使用时再对其进行组合,原有代码无须改变,符合“开闭原则”。
缺点
• 使用装饰模式进行系统设计时将产生很多小对象,这些对象的区别在于它们之间相互连接的方式有所不同,而不是它们的类或者属性值有所不同,同时还将产生很多具体装饰类。这些装饰类和小对象的产生将增加系统的复杂度,加大学习与理解的难度。
• 这种比继承更加灵活机动的特性,也同时意味着装饰模式比继承更加易于出错,排错也很困难,对于多次装饰的对象,调试时寻找错误可能需要逐级排查,较为烦琐。
模式适用环境
在以下情况下可以使用装饰模式:
• 在不影响其他对象的情况下,以动态、透明的方式给单个对象添加职责。
• 需要动态地给一个对象增加功能,这些功能也可以动态地被撤销。
• 当不能采用继承的方式对系统进行扩充或者采用继承不利于系统扩展和维护时。不能采用继承的情况主要有两类:第一类是系统中存在大量独立的扩展,为支持每一种组合将产生大量的子类,使得子类数目呈爆炸性增长;第二类是因为类定义不能继承(如final类)。
模式应用
(1) 在javax.swing包中,可以通过装饰模式动态给一些构件增加新的行为或改善其外观显示。
• 如JList构件本身并不支持直接滚动,即没有滚动条,要创建可以滚动的列表,可以使用如下代码实现:
1 JList list = new JList(); 2 JScrollPane sp = new JScrollPane(list);
(2) 装饰模式在JDK中最经典的实例是Java IO。
• 以InputStream为例:
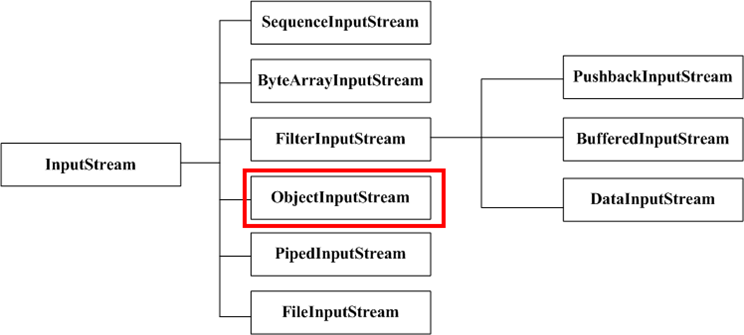
抽象装饰类:FilterInputStream
1 …… 2 protected volatile InputStream in; 3 protected FilterInputStream(InputStream in) { 4 this.in = in; 5 } 6 ……
角色分配:
• 抽象构件类:InputStream
• 具体构件类:FileInputStream、ByteArrayInputStream等
• 抽象装饰类:FilterInputStream
• 具体装饰类:BufferedInputStream、DataInputStream等
客户端使用:
1 …… 2 FileInputStream inFS=new FileInputStream("temp/fileSrc.txt"); 3 BufferedInputStream inBS=new BufferedInputStream(inFS); 4 //定义一个字节数组,用于存放缓冲数据 5 byte[] data = new byte[1024]; 6 inBS.read(data); 7 ……
模式扩展
装饰模式的简化-需要注意的问题
• 一个装饰类的接口必须与被装饰类的接口保持相同,对于客户端来说无论是装饰之前的对象还是装饰之后的对象都可以一致对待。
• 尽量保持具体构件类Component作为一个“轻”类,也就是说不要把太多的逻辑和状态放在具体构件类中,可以通过装饰类对其进行扩展。
• 如果只有一个具体构件类而没有抽象构件类,那么抽象装饰类可以作为具体构件类的直接子类。
装饰模式的简化
透明装饰模式(多重加密系统)
• 在透明装饰模式中,要求客户端完全针对抽象编程,装饰模式的透明性要求客户端程序不应该声明具体构件类型和具体装饰类型,而应该全部声明为抽象构件类型。
1 Cipher sc,cc,ac; 2 sc=new SimpleCipher(); 3 cc=new ComplexCipher(sc); 4 ac=new AdvancedCipher(cc);
半透明装饰模式(变形金刚)
• 大多数装饰模式都是半透明(semi-transparent)的装饰模式,而不是完全透明(transparent)的。即允许用户在客户端声明具体装饰者类型的对象,调用在具体装饰者中新增的方法。
1 Transform camaro; 2 camaro=new Car(); 3 camaro.move(); 4 Robot bumblebee=new Robot(camaro); 5 bumblebee.move(); 6 bumblebee.say();


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号