【Vue】基础(虚拟DOM & 响应式原理)
虚拟 DOM
Vue 通过建立一个虚拟 DOM 来追踪自己要如何改变真实 DOM
在Vue中定义虚拟节点(VNode)描述节点信息
export default class VNode { tag: string | void; data: VNodeData | void; children: ?Array<VNode>; text: string | void; elm: Node | void; ns: string | void; context: Component | void; // rendered in this component's scope key: string | number | void; componentOptions: VNodeComponentOptions | void; componentInstance: Component | void; // component instance parent: VNode | void; // component placeholder node
这里描述节点文本,标签信息(tag),真实Dom节点(elm),节点的data信息,子节点,父节点等信息
“虚拟 DOM”是我们对由 Vue 组件树建立起来的整个 VNode 树的称呼
从结构可以看到根节点(parent为空)就可以表示整个树
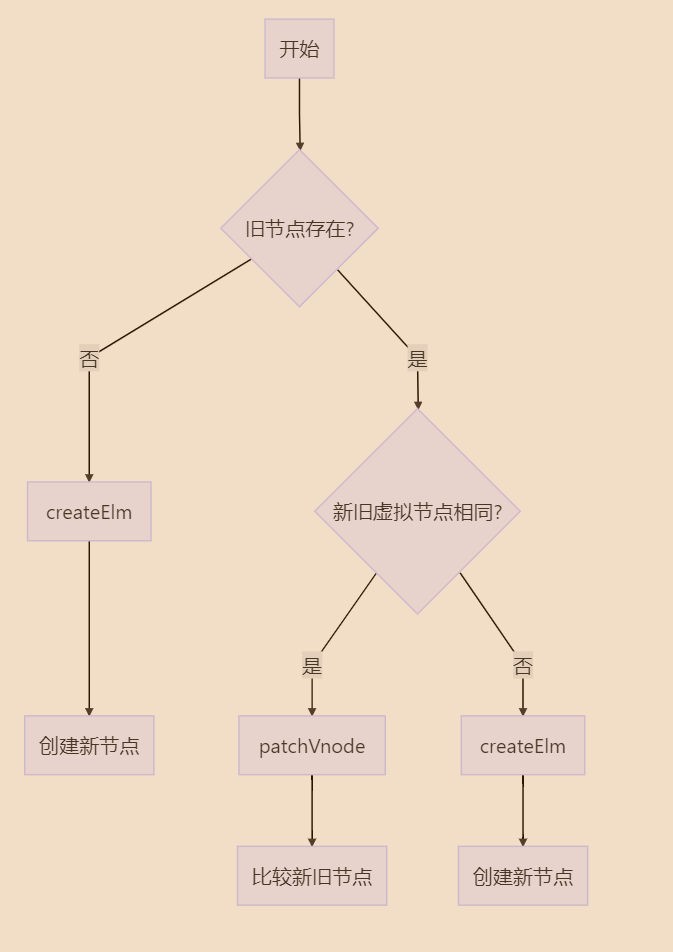
有了虚拟 DOM ,Vue就会比较差异,更新真实DOM
比较差异是在patch.js里面的patch方法(补丁)
响应式原理
Vue的响应式大概会经过下面几个阶段
1. 使用 Object.defineProperty 把属性全部转为getter/setter
2. 属性变更时通知观察者(watcher)变更
3. watcher触发重新渲染生成虚拟 DOM
4. Vue框架遍历计算新旧虚拟 DOM差异
4.1 由于 JavaScript 的限制,Vue 不能检测数组和对象的变化
5. 加载操作,将差异局部修改到真实 DOM
从源码解读Vue响应式(部分代码有截取)
//截取部分代码 Object.defineProperty(obj, key, { get: function reactiveGetter () { const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val return value }, set: function reactiveSetter (newVal) { const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val /* eslint-disable no-self-compare */ if (newVal === value || (newVal !== newVal && value !== value)) { return } /* eslint-enable no-self-compare */ if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && customSetter) { customSetter() } // #7981: for accessor properties without setter if (getter && !setter) return if (setter) { setter.call(obj, newVal) } else { val = newVal } childOb = !shallow && observe(newVal) dep.notify() } })
setter前面的都是赋值的判断,
1. 值是否相等,
2. 是否自定义setter函数,
3. 是否只读
4. 最后一句dep.notify(),dep是什么类型,这里看都猜到是通知,具体定义
const dep = new Dep()
export default class Dep { static target: ?Watcher; id: number; subs: Array<Watcher>; constructor () { this.id = uid++ this.subs = [] } addSub (sub: Watcher) { this.subs.push(sub) } removeSub (sub: Watcher) { remove(this.subs, sub) } depend () { if (Dep.target) { Dep.target.addDep(this) } } notify () { // stabilize the subscriber list first const subs = this.subs.slice() if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !config.async) { // subs aren't sorted in scheduler if not running async // we need to sort them now to make sure they fire in correct // order subs.sort((a, b) => a.id - b.id) } for (let i = 0, l = subs.length; i < l; i++) { subs[i].update() } } }
可以看到,Dep类 提供一个订阅,通知的功能
最后我们看一下订阅的目标Watcher是做什么
Watcher最重要的一个方法update
update () { /* istanbul ignore else */ if (this.lazy) { this.dirty = true } else if (this.sync) { this.run() } else { queueWatcher(this) } }
转发请标明出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/WilsonPan/p/12744695.html

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号