给定一个链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。
要求返回这个链表的 深拷贝。
我们用一个由 n 个节点组成的链表来表示输入/输出中的链表。每个节点用一个 [val, random_index] 表示:
val:一个表示 Node.val 的整数。
random_index:随机指针指向的节点索引(范围从 0 到 n-1);如果不指向任何节点,则为 null 。
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer。
自己的题解:
思路:整两个MAP,一个用来存放原始的list中每个节点的地址对应的位置;一个用来存放第二个新的节点链表的每个位置(下标),对应的地址。
和这个视频的思路大致是一样的
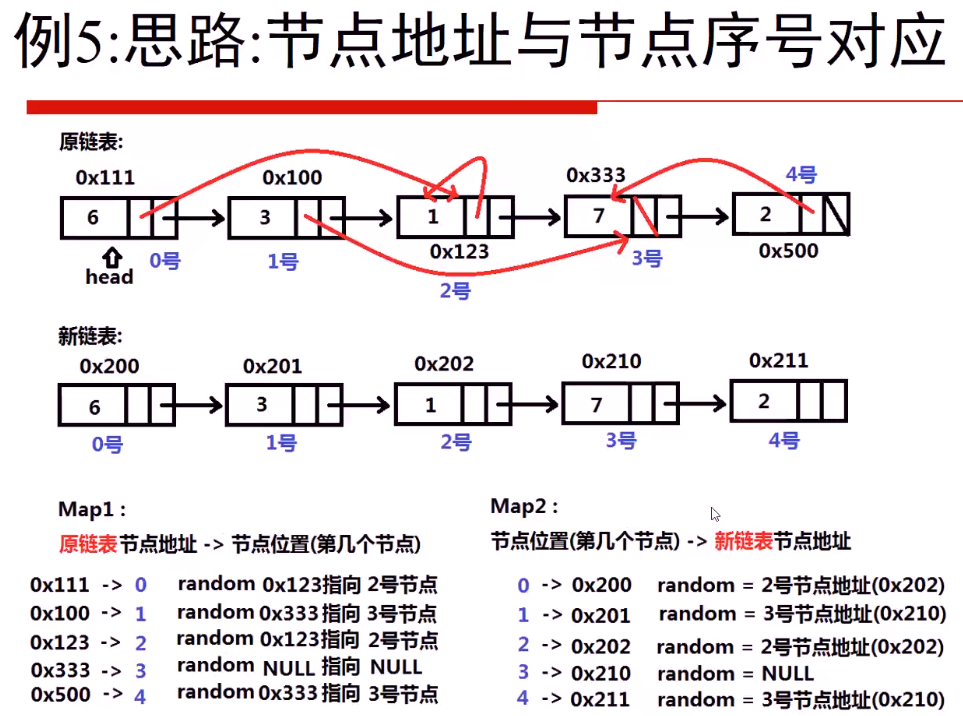
然后,我自己的代码:
/* // Definition for a Node. class Node { int val; Node next; Node random; public Node(int val) { this.val = val; this.next = null; this.random = null; } } */ import java.util.*; class Solution { public Node copyRandomList(Node head) { Node HeadTemp=head; Node NodeList2Head=new Node(-1); Node NodeList2_ptr=NodeList2Head; int count=0; HashMap<Node, Integer> Map_ListNode_1 = new HashMap<>();//node 对应的第几个数 HashMap<Integer,Node> Map_ListNode_2 = new HashMap<>();//第二个链表中用数 对应地址 while(HeadTemp!=null) { Node NodeList2Temp=new Node(HeadTemp.val); // System.out.println(NodeList2Temp.val); NodeList2_ptr.next=NodeList2Temp; NodeList2_ptr=NodeList2_ptr.next; Map_ListNode_1.put(HeadTemp,count); Map_ListNode_2.put(count,NodeList2Temp); HeadTemp=HeadTemp.next; count++; } NodeList2_ptr.next=null; int count2=0; HeadTemp=head; NodeList2_ptr=NodeList2Head.next; while(HeadTemp!=null) { Integer pos_random_ptr=Map_ListNode_1.get(HeadTemp.random); // System.out.println("pos_random_ptr:"+pos_random_ptr); Node pos_node_adress=Map_ListNode_2.get(pos_random_ptr); // if(pos_node_adress!=null) // { // System.out.println(pos_node_adress.val); // } NodeList2_ptr.random=pos_node_adress; // System.out.println("pos_node_adress val:"+pos_node_adress.val); // System.out.println(Map_ListNode_2.get(count2).val); NodeList2_ptr=NodeList2_ptr.next; HeadTemp=HeadTemp.next; count2++; } return NodeList2Head.next; } }
Leetcode的题解(自己喜欢的):
方法 2: O(N)O(N) 空间的迭代
想法
迭代算法不需要将链表视为一个图。当我们在迭代链表时,我们只需要为 random 指针和 next 指针指向的未访问过节点创造新的节点并赋值即可。
算法
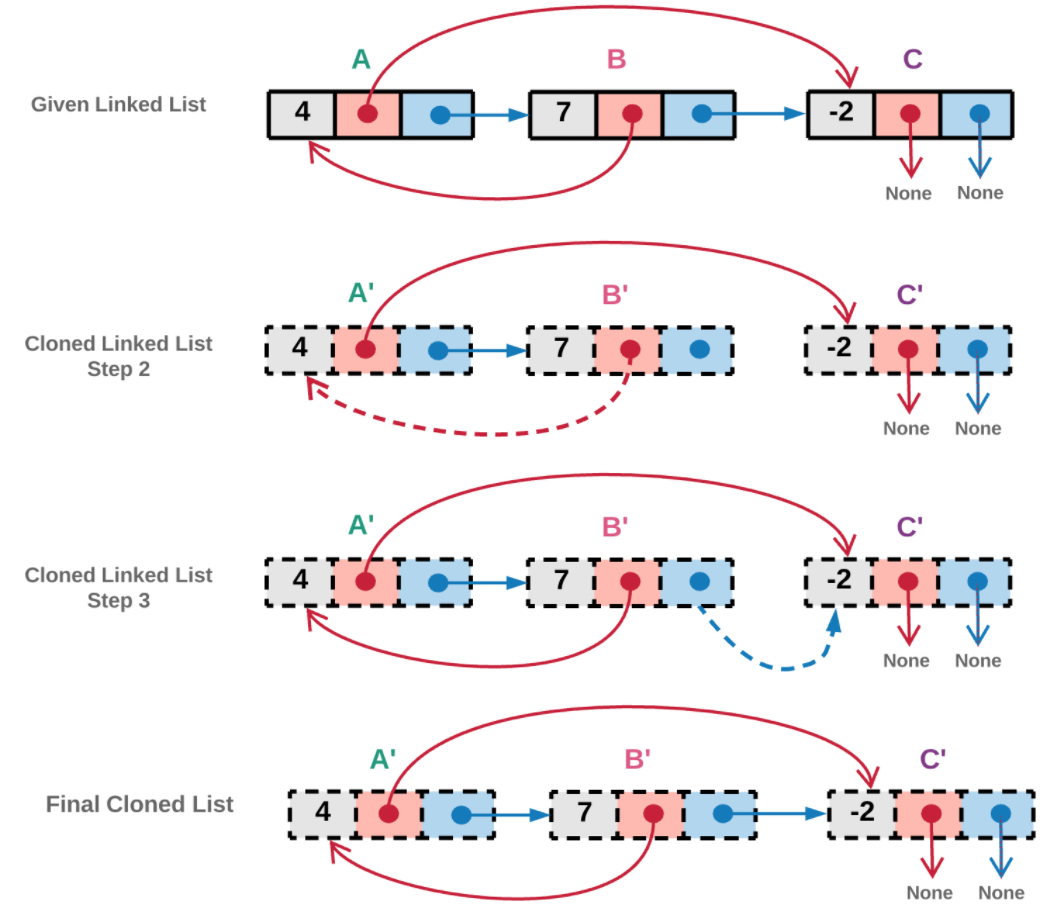
1.从 head 节点开始遍历链表。下图中,我们首先创造新的 head 拷贝节点。拷贝的节点如下图虚线所示。实现中,我们将该新建节点的引用也放入已访问字典中。
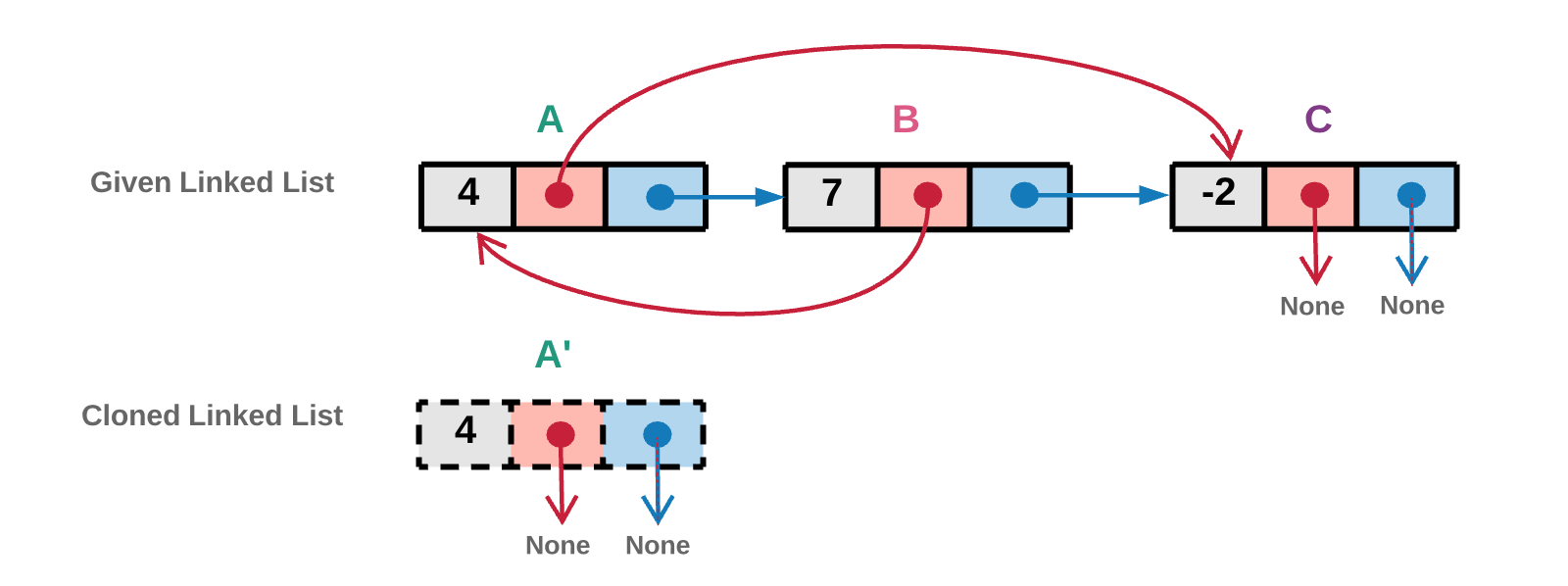
2.random 指针
如果当前节点 ii 的 random 指针指向一个节点 jj 且节点 jj 已经被拷贝过,我们将直接使用已访问字典中该节点的引用而不会新建节点。
如果当前节点 ii 的 random 指针指向的节点 jj 还没有被拷贝过,我们就对 jj 节点创建对应的新节点,并把它放入已访问节点字典中。
下图中, AA 的 random 指针指向的节点 CC 。前图中可以看出,节点 CC 还没有被访问过,所以我们创造一个拷贝的 C'C ′节点与之对应,并将它添加到已访问字典中。
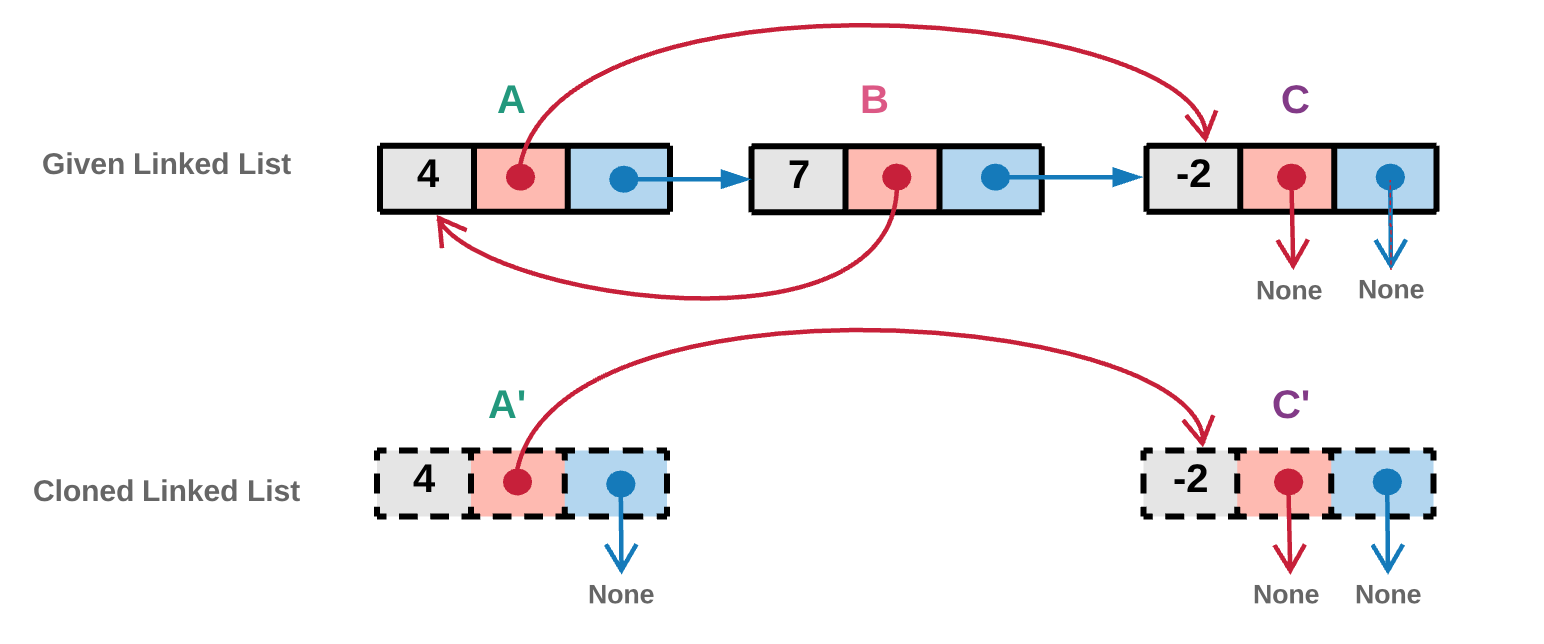
3.next 指针
如果当前节点 ii 的 next 指针指向的节点 jj 在已访问字典中已有拷贝,我们直接使用它的拷贝节点。
如果当前节点 ii 的next 指针指向的节点 jj 还没有被访问过,我们创建一个对应节点的拷贝,并放入已访问字典。
下图中,AA 节点的 next 指针指向节点 BB 。节点 BB 在前面的图中还没有被访问过,因此我们创造一个新的拷贝 B'B 节点,并放入已访问字典中。
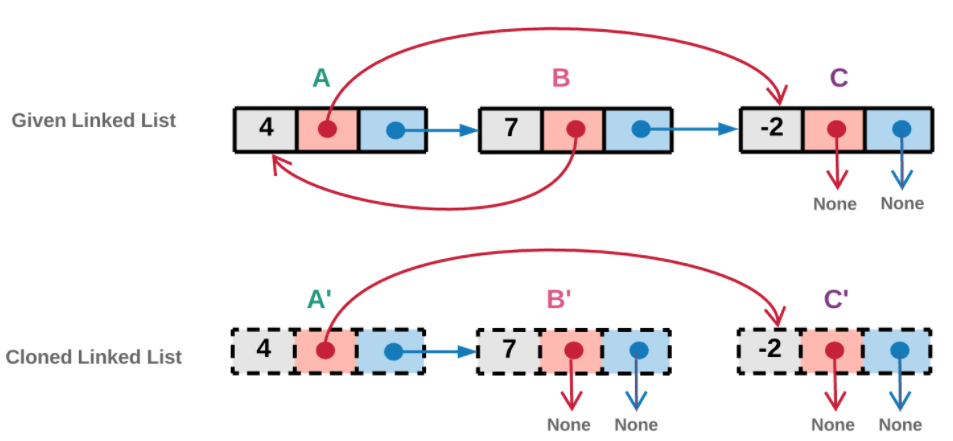
4.我们重复步骤 2 和步骤 3 ,直到我们到达链表的结尾。
下图中, 节点 BB 的 random 指针指向的节点 AA 已经被访问过了,因此在步骤 2 中,我们不会创建新的拷贝,将节点 B'B ′的 random 指针指向克隆节点 A'A 同样的, 节点 BB 的 next 指针指向的节点 CC 已经访问过,因此在步骤 3 中,我们不会创建新的拷贝,而直接将 B'B ′的 next 指针指向已经存在的拷贝节点 C'C ′。
/* // Definition for a Node. class Node { public int val; public Node next; public Node random; public Node() {} public Node(int _val,Node _next,Node _random) { val = _val; next = _next; random = _random; } }; */ public class Solution { // Visited dictionary to hold old node reference as "key" and new node reference as the "value" HashMap<Node, Node> visited = new HashMap<Node, Node>(); public Node getClonedNode(Node node) { // If the node exists then if (node != null) { // Check if the node is in the visited dictionary if (this.visited.containsKey(node)) { // If its in the visited dictionary then return the new node reference from the dictionary return this.visited.get(node); } else { // Otherwise create a new node, add to the dictionary and return it this.visited.put(node, new Node(node.val, null, null)); return this.visited.get(node); } } return null; } public Node copyRandomList(Node head) { if (head == null) { return null; } Node oldNode = head; // Creating the new head node. Node newNode = new Node(oldNode.val); this.visited.put(oldNode, newNode); // Iterate on the linked list until all nodes are cloned. while (oldNode != null) { // Get the clones of the nodes referenced by random and next pointers. newNode.random = this.getClonedNode(oldNode.random); newNode.next = this.getClonedNode(oldNode.next); // Move one step ahead in the linked list. oldNode = oldNode.next; newNode = newNode.next; } return this.visited.get(head); } } 作者:LeetCode 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer/solution/fu-zhi-dai-sui-ji-zhi-zhen-de-lian-biao-by-leetcod/ 来源:力扣(LeetCode)


