使用Collections 将自定义对象进行排序
对象排序或比较的场合均需要Comparable接口
public class User implements Comparable<User>{ private String name; private int phone; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getPhone() { return phone; } public void setPhone(int phone) { this.phone = phone; } public String toString() { return name+" "+phone; } User(String name ,int phone) { this.name=name; this.phone=phone; } public int compareTo(User anotherString) { int len1 = this.getName().length(); int len2 = anotherString.getName().length(); int lim = Math.min(len1, len2); char v1[] = this.getName().toCharArray(); char v2[] = anotherString.getName().toCharArray(); int k = 0; while (k < lim) { char c1 = v1[k]; char c2 = v2[k]; if (c1 != c2) { return c1 - c2; } k++; } return len1 - len2; } }
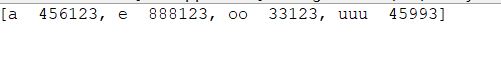
import java.util.*; public class Test{ public static void main(String[] args){ List l =new ArrayList(); l.add(new User("a",456123)); l.add(new User("e",888123)); l.add(new User("uuu",45993)); l.add(new User("oo",33123)); Collections.sort(l); System.out.println(l); } }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号