1. 概念
跳表是在数据结构为链表的基础上加入二分的思想产生的,是一个增删改查皆为logn时间复杂度的数据结构,它的效率和红黑树以及 AVL 树不相上下,但实现起来容易得多
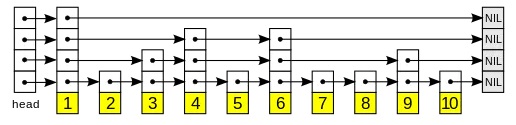
2. 应用
最典型的应用是redis中的zset有序队列
3. 代码
首先需要定义跳表每一个节点的数据结构
public int key;
public T value;
public SkipListNode<T> up,down,left,right; // 上下左右四个指针
然后是跳表的主类
private SkipListNode<T> head, tail;
private int nodes; // 节点总数
private int listLevel; // 层数
private Random random; // 用于投掷硬币
private static final double PROBABILITY = 0.5; // 向上提升一个的概率
public SkipList() {
random = new Random();
clear();
}
/**
* 清空跳跃表
*/
public void clear() {
head = new SkipListNode<T>(Integer.MIN_VALUE, null);
tail = new SkipListNode<T>(Integer.MAX_VALUE, null);// 保证插入时永远会插入到头尾节点的中间
horizontalLink(head, tail);
listLevel = 0;
nodes = 0;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return nodes == 0;
}
public int size() {
return nodes;
}
/**
* 在最下面一层,找到要插入的位置前面的那个key
* @param key
* @return
*/
private SkipListNode<T> findNode(int key) {
SkipListNode<T> p = head;
while (true) {
while (p.right != tail && p.right.key <= key) {
p = p.right;
}
if (p.down != null) {
p = p.down;
} else {
break;
}
}
return p;
}
/**
* 查找是否存储key,存在则返回该节点,否则返回null
*/
public SkipListNode<T> search(int key) {
SkipListNode<T> p = findNode(key);
if (key == p.getKey()) {
return p;
} else {
return null;
}
}
/**
* 向跳跃表中添加key-value
*/
public void put(int k, T v) {
SkipListNode<T> p = findNode(k);
// 如果key值相同,替换原来的value即可结束
if (k == p.getKey()) {
p.value = v;
return;
}
SkipListNode<T> q = new SkipListNode<T>(k, v);
backLink(p, q); // 在p后面插入q
int currentLevel = 0; // 当前所在的层级是0
// 抛硬币
while (random.nextDouble() < PROBABILITY) {
if (currentLevel >= listLevel) {
listLevel++;
SkipListNode<T> p1 = new SkipListNode<T>(Integer.MIN_VALUE, null);
SkipListNode<T> p2 = new SkipListNode<T>(Integer.MAX_VALUE, null);
horizontalLink(p1, p2);
verticalLink(p1, head);
verticalLink(p2, tail);
head = p1;
tail = p2;
}
// 将p移动到上一层
while (p.up == null) {
p = p.left;
}
p = p.up;
SkipListNode<T> e = new SkipListNode<T>(k, null);
backLink(p, e); // 将e插入到p的后面
verticalLink(e, q); // 将e和q上下连接
q = e;
currentLevel++;
}
nodes++; // 层数递增
}
private void backLink(SkipListNode<T> node1, SkipListNode<T> node2) {
node2.left = node1;
node2.right = node1.right;
node1.right.left = node2;
node1.right = node2;
}
private void horizontalLink(SkipListNode<T> node1, SkipListNode<T> node2) {
node1.right = node2;
node2.left = node1;
}
private void verticalLink(SkipListNode<T> node1, SkipListNode<T> node2) {
node1.down = node2;
node2.up = node1;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return "跳跃表为空!";
}
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
SkipListNode<T> p = head;
while (p.down != null) {
p = p.down;
}
while (p.left != null) {
p = p.left;
}
if (p.right != null) {
p = p.right;
}
while (p.right != null) {
builder.append(p);
builder.append("\n");
p = p.right;
}
return builder.toString();
}
}
最后是测试用例及结果
public static void main(String[] args) {
SkipList<String> list = new SkipList<String>();
System.out.println(list);
list.put(2, "yan");
list.put(1, "co");
list.put(3, "feng");
list.put(1, "cao");
list.put(4, "曹");
list.put(6, "丰");
list.put(5, "艳");
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println(list.size());
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号