JavaWeb学习:OGNL
一、OGNL:Object-Graph Navigation Language(对象导航图语言)的缩写,是应用于Java中的一个开源的表达式语言
二、OGNL的优势:
- 支持对象方法调用
- 支持静态方法调用和值访问(表达式:@[类全名(包括包路径)]@[方法名 | 值名])
- 支持赋值操作和表达式串联
- 访问OGNL上下文
- 操作集合
- 可以new 一个对象
三、Java环境
①、对象方法调用
@Test public void demo1() throws OgnlException { OgnlContext context = new OgnlContext(); Object root = context.getRoot(); Object object = Ognl.getValue("'hellow ognl'.length()", context, root); System.out.println(object); }
②、静态方法调用和值访问
@Test public void demo2() throws OgnlException { OgnlContext context = new OgnlContext(); Object root = context.getRoot(); Object object = Ognl.getValue("@java.lang.Math@random()", context, root); System.out.println(object); }
③、赋值操作和表达式串联
@Test public void demo3() throws OgnlException { OgnlContext context = new OgnlContext(); Object root = context.getRoot(); Object object = Ognl.getValue("price=100, discount=0.8, price*discount", context, root); System.out.println(object); }
出现异常:ognl.OgnlException: target is null for setProperty(null, "price", 100),不知道怎么解决
④、访问OGNL上下文(OgnlContext)
public class User { private String userName; private String passWord; public String getUserName() { return userName; } public void setUserName(String userName) { this.userName = userName; } public String getPassWord() { return passWord; } public void setPassWord(String passWord) { this.passWord = passWord; } public User(String userName, String passWord) { this.userName = userName; this.passWord = passWord; } public User() { } }
4.1、访问Root中的数据
@Test public void demo4() throws OgnlException { OgnlContext context = new OgnlContext(); context.setRoot(new User("zhangsan","123")); Object root = context.getRoot(); Object username = Ognl.getValue("userName", context, root); Object password = Ognl.getValue("passWord", context, root); System.out.println(username+":"+password); }
4.2、访问context中的数据,需要加#
@Test public void demo5() throws OgnlException { OgnlContext context = new OgnlContext(); Object root = context.getRoot(); context.put("name", "zhangsan"); Object name=Ognl.getValue("#name", context, root); System.out.println(name); }
四、Struts2环境
①、对象方法调用、静态方法调用
<!-- 调用对象方法 --> <s:property value="'hello struts ognl'.length()"/> <!-- 在struts2中静态方法访问默认式禁止访问的, 需要设置一个常量(struts.ognl.allowStaticMethodAccess=true)开启访问权限 --> <s:property value="@java.lang.Math@random()"/> <!-- 赋值操作和表达式串联(无法正常显示,不知道为什么) --> <s:property value="price=100, discount=0.8, price*discount"/>
②、访问ognl上下文(OgnlContext)需要使用ValueStack存储数据
2.1、在Struts2环境中使用OGNL语法,主要作用:数据库传输(Struts2的框架中的数据都存储到ValueStack中)
-
-
- ValueStack接口,实现类OgnlValueStack对象
- ValueStack贯穿整个Action的生命周期
-
2.2、ValueStack中有两个主要区域:
root:其实就是一个ArrayList,主要存储对象
context:其实就是一个Map,主要存储web开发常用对象数据库的引用

操作值栈是指操作ValueStack的root区域,而操作request、session、application、就相当于操作context区域
可以通过Debug方式查看(debug在页面上看不到,配置常量<constant name="struts.devMode" value="true" />),具体代码
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <%@ taglib uri="/struts-tags" prefix="s"%> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <h3>Success</h3> <s:debug></s:debug> </body> </html>
root区域的内容

context区域
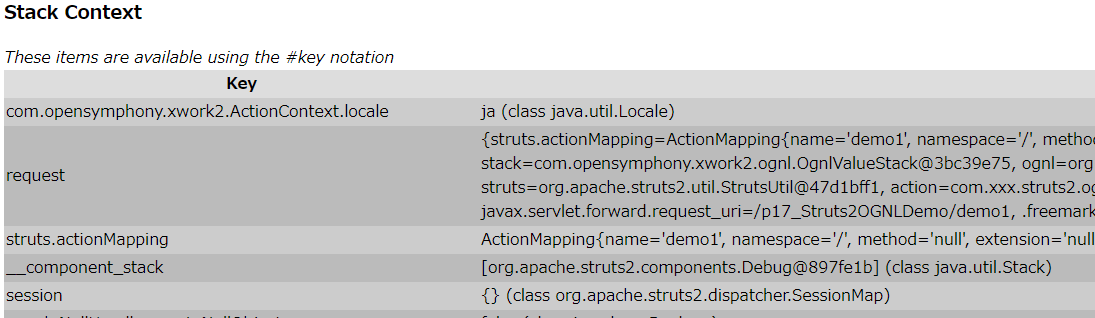
2.3、值栈与ActionContext的关系
ActionContext:Action的上下文,当有请求时,执行过滤器中的doFilter方法,此方法会创建ActionContext,在创建ActionContext过程中创建ValueStack对象,并将ValueStack对象存储在ActionContext中,所以可以通过ActionContext获取值栈对象(ActionContext.getContext().getValueStack())
ActionContext对象可以访问Servlet的API(访问的是域对象的数据),因为其内部有值栈的引用。
2.4、ValueStack的获取
1、通过ActionContext对象获取值栈
ActionContext.getContext().getValueStack()
2、在Struts2内部将值栈存入request对象中
ServletActionContext.getRequest().getAttribute(ServletActionContext.STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY)
2.5、ValueStack的操作(实际操作的root区域)
操作的方式一:因为root区域是存储了当前Action对象的,所以把操作数据存储在Action对象中(存储数据存放在Action对象的属性)
public class Demo1Action extends ActionSupport { private User user; public User getUser() { return user; } @Override public String execute() throws Exception { user = new User("zhangsan","123"); return SUCCESS; } }
查看ognl debug,可以看到User对象数据存储到Demo1Action的user属性上
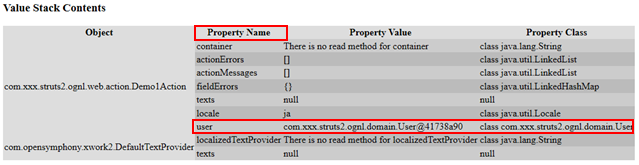
页面读取root中的数据,根据上图中Property Name中值进行读取操作的。
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <%@ taglib uri="/struts-tags" prefix="s"%> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <h3>Success</h3> <s:debug></s:debug><br /> <s:property value="user.userName"/> <s:property value="user.passWord"/> </body> </html>
操作的方式二:操作ValueStack对象(通过push(Object obj) 、set(String key,Object obj)两个方法操作ValueStack对象)
push(Object obj) 方法
public class Demo2Action extends ActionSupport { @Override public String execute() throws Exception { ValueStack valueStack=ActionContext.getContext().getValueStack(); valueStack.push(new User("lisi", "456")); return super.execute(); } }
通过下图,push方法把存储数据对象压入栈内。避免Property Name中的值重复,否则数据会冲突
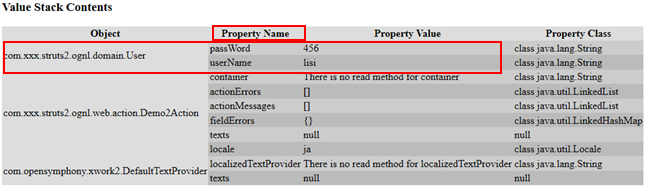
根据Property Name获取数据
<s:property value="userName"/> <s:property value="passWord"/>
set(String key,Object obj)方法
public class Demo2Action extends ActionSupport { @Override public String execute() throws Exception { ValueStack valueStack=ActionContext.getContext().getValueStack(); List<User> list=new ArrayList<User>(); list.add(new User("aaa", "111")); list.add(new User("bbb", "222")); list.add(new User("ccc", "333")); valueStack.set("list",list); valueStack.set("name", "zhangsan"); return super.execute(); } }
通过下图,set方法把存储数据存储在Map集合中并压入栈内
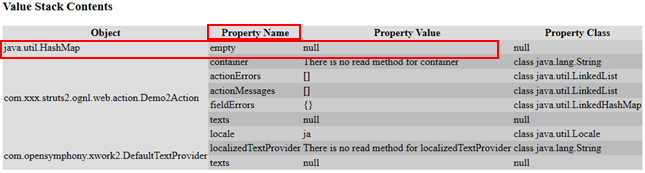
根据Property Name获取数据,但是Property Name没值,可以根据set方法中的key值获取数据
<s:property value="list[0].userName"/><br /> <s:property value="list[0].passWord"/><br /> <s:property value="list[1].userName"/><br /> <s:property value="list[1].passWord"/><br /> <s:property value="list[2].userName"/><br /> <s:property value="list[2].passWord"/><br /> <s:property value="name"/>
总结:在ognl表达式中action传值给jsp页面,有两种方式:操作root(就是操作ValueStack)、操作context(操作request、session、application)
-
- 操作ValueStack:获取ValueStack、读写ValueStack
- 获取ValueStack有两种方式:ActionContext、Request
- 写ValueStack:
- 一、通过当前Action对象属性
- 二、通过ValueStack的push(Object obj)、set(String key,Object)方法
- push(Object obj)、set(String key,Object obj)都会把数据从栈顶压入,这样的话,最后执行的方法会在栈顶。
- push存储对象,set存储集合或字符串
- 读ValueStack:
- 一、ognl表达式 二、EL表达式(${name} ):访问request对象中的getAttribute方法
- 可以使用EL表达式的原因:Struts2框架对request.getAttribute(String key)方法进行增强,在getAttribute方法中,先去获取request查找对应key的数据,如果没有找到的话,再去ValueStack中查找对应key的数据(stack.findValue(key);),
- 操作context:获取request、session、application,读写request、session、application
- 获取request、session、application两种方式:一、ServletActionContext 二、ActionContext
- 写request、session、application
-
ServletActionContext.getRequest().setAttribute("name", "request"); ServletActionContext.getRequest().getSession().setAttribute("name", "session"); ServletActionContext.getServletContext().setAttribute("name", "application"); ActionContext.getContext().put("reqName", "reqValue"); ActionContext.getContext().getSession().put("sessName", "sessValue"); ActionContext.getContext().getApplication().put("appName", "appValue"); - 读request、session、application:jsp页面通过ognl表达式,读取context中的数据需要加#
-
<s:property value="#request.name"/> <s:property value="#request.reqName"/> <s:property value="#session.name"/> <s:property value="#session.sessName"/> <s:property value="#application.name"/> <s:property value="#application.appName"/>
- #attr.name:逐级查找request、session、application中的数据,
- 如果request中没数据,就查看session,session没有数据就查看application
- 如果request中有数据,就不会查看session。
- #parameters.id:获取参数信息
- 获取request、session、application两种方式:一、ServletActionContext 二、ActionContext



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号