Java学习之ServletContext
一、ServletContext的特点
Web工程中只有一个ServletContext对象(所有的Servlet获取ServletContext对象都是同一个)
二、ServletContext的用法
①、获取全局配置参数
②、获取Web工程中的资源
③、根据其特点,servlet间共享数据
三、验证用法
①、获取全局配置参数
Ⅰ、配置参数

Ⅱ、获取配置的参数
ServletContext context = getServletContext(); String address=context.getInitParameter("address"); System.out.println(address);
Ⅲ、结果

注意: getInitParameter获取值为NULL,可能有以下几个原因
1、xml文件中<context-param>节点有误
2、xml文件的正确路径(WEB-INF/Web.xml)
②、获取工程资源
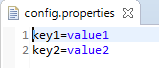
资源文件内容
Ⅰ、根据路径先获取绝对路径,再转成流对象
1、通过ServletContext对象获取绝对路径
ServletContext context = getServletContext(); // Web项目在tomcat里面的根目录 System.out.println(context.getRealPath("/"));//结果: D:\workspace\apache-tomcat-9.0.30\webapps\p03_HelloHttpServlet\ // Web项目在tomcat的根目录中file/config.properties资源路径 System.out.println(context.getRealPath("file/config.properties"));//结果: D:\workspace\apache-tomcat-9.0.30\webapps\p03_HelloHttpServlet\file\config.properties
2、通过this.getClass().getClassLoader()对象获取路径
// 当前类文件(HellowHttpServlet)的字节码文件(HellowHttpServlet.class)所在tomcat中的根目录(/WEB-INF/classes/)URL对象 System.out.println(this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource("/"));//结果:file:/D:/workspace/apache-tomcat-9.0.30/webapps/p03_HelloHttpServlet/WEB-INF/classes/ // 根据当前类文件(HellowHttpServlet)的字节码文件(HellowHttpServlet.class)所在tomcat中的根目录(/WEB-INF/classes/)URL对象的getPath()方法获取路径 System.out.println(this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource("../../file/config.properties").getPath());//结果:/D:/workspace/apache-tomcat-9.0.30/webapps/p03_HelloHttpServlet/file/config.properties
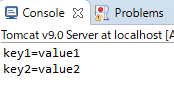
实例:打印文件内容
ServletContext context = getServletContext(); //InputStream is = new FileInputStream(this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource("../../file/config.properties").getPath());//这样做也是可以的 InputStream is = new FileInputStream(context.getRealPath("file/config.properties")); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is)); String s; while ((s = br.readLine()) != null) { System.out.println(s); }
结果:
Ⅱ、根据路径获取流对象
1、通过ServletContext对象获取流对象
ServletContext context = getServletContext(); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(context.getResourceAsStream("file/config.properties"))); String s; while ((s = br.readLine()) != null) { System.out.println(s); }
2、通过this.getClass().getClassLoader()对象获取流对象
InputStream is=this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("../../file/config.properties"); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is)); String s; while ((s = br.readLine()) != null) { System.out.println(s); }
③、servlet间共享数据
这里就做两个servlet共享数据,一个servlet设置servletcontext,一个servlet获取servletcontext
1、设置ServletContext
ServletContext context = getServletContext(); context.setAttribute("Key", "value"); /*重定向 resp.setStatus(302); resp.setHeader("Location", "GetServletContextValue");*/ /*重定向写法: 重新定位方向 参数即跳转的位置 resp.sendRedirect("GetServletContextValue");*/ /*请求转发的写法: 参数即跳转的位置*/ req.getRequestDispatcher("GetServletContextValue").forward(req, resp);
2、获取ServletContext
System.out.println(getServletContext().getAttribute("Key"));
ServletContext大概就这样了。
补充:页面跳转
通过上面代码发现页面跳转有两种形式:一、重定向 二、请求转发
***重定向
resp.sendRedirect("GetServletContextValue");
就相当于
resp.setStatus(302);
resp.setHeader("Location", "GetServletContextValue");
其特点:
1、 地址上显示的是最后的那个资源的路径地址
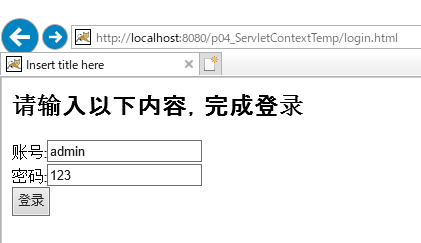
1.1、请求页面地址
点击登录按钮后地址
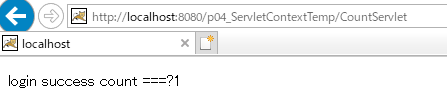
2、 请求次数最少有两次, 服务器在第一次请求后,会返回302 以及一个地址, 浏览器在根据这个地址,执行第二次访问。
3、 可以跳转到任意路径。 不是自己的工程也可以跳。
4、 效率稍微低一点, 执行两次请求。
5、 后续的请求,没法使用上一次的request存储的数据,或者 没法使用上一次的request对象,因为这是两次不同的请求。
***请求转发
req.getRequestDispatcher("GetServletContextValue").forward(req, resp);
其特点:
1、地址上显示的是请求servlet的地址。 返回200 ok
1.1、请求页面地址

点击登录按钮后地址
2、请求次数只有一次, 因为是服务器内部帮客户端执行了后续的工作。
3、只能跳转自己项目的资源路径 。
4、效率上稍微高一点,因为只执行一次请求。
5、可以使用上一次的request对象。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号