简单的四则运算(JAVA版) 201571030129
简单的四则运算(JAVA版)
GitHub项目地址:https://github.com/wangshenghai/wsh.git
1、需求分析
- 每个练习题至少要包含2种运算符;
- 随机产生的练习题在运算过程中不得出现负数与非整数,比如不能出 3/5+2=2.6,2-5+10=7等算式;
- 练习题生成好后,将你的学号
- 每个练习题至少要包含1种运算符。
- 随机产生的算术题在运算过程中不得出现负数与非整数,比如不能出 3/5+2=2.6,2-5+10=7等算式。
- 练习题生成好后,将你的学号
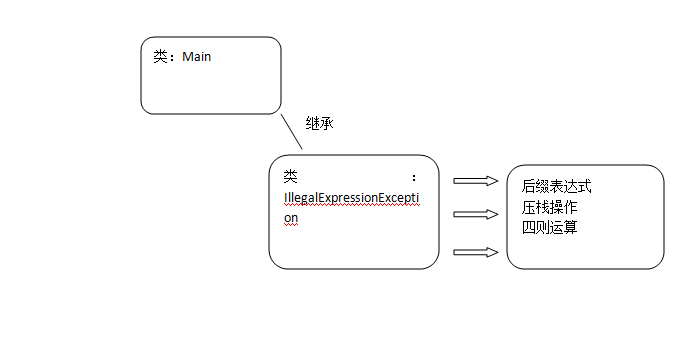
public class Main { public int eval(String exp) throws IllegalExpressionException{ List<String> list = infixExpToPostExp(exp);//转化成后缀表达式 return doEval(list);//真正求值 } //遇到操作符压栈,遇到表达式从后缀表达式中弹出两个数,计算出结果,压入堆栈 private int doEval(List<String> list) throws IllegalExpressionException { Stack<String> stack = new Stack<String>(); String element; int n1,n2,result; try{ for(int i = 0; i < list.size();i++){ element = list.get(i); if(isOperator(element)){ n1 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop()); n2 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop()); result = doOperate(n1,n2,element); stack.push(new Integer(result).toString()); }else{ stack.push(element); } } return Integer.parseInt(stack.pop()); }catch(RuntimeException e){ throw new IllegalExpressionException(e.getMessage()); } } private int doOperate(int n1, int n2, String operator) { if(operator.equals("+")) return n1 + n2; else if(operator.equals("-")) return n1 - n2; else if(operator.equals("*")) return n1 * n2; else return n1 / n2; } private boolean isOperator(String str){ return str.equals("+") || str.equals("-") || str.equals("*") || str.equals("/"); } private List<String> infixExpToPostExp(String exp) throws IllegalExpressionException{//将中缀表达式转化成为后缀表达式 List<String> postExp = new ArrayList<String>();//存放转化的后缀表达式的链表 StringBuffer numBuffer = new StringBuffer();//用来保存一个数的 Stack<Character> opStack = new Stack<Character>();//操作符栈 char ch,preChar; opStack.push('#'); try{ for(int i = 0; i < exp.length();){ ch = exp.charAt(i); switch(ch){ case '+': case '-': case '*': case '/': preChar = opStack.peek(); // 如果栈里面的操作符优先级比当前的大,则把栈中优先级大的都添加到后缀表达式列表中 while(priority(preChar) >= priority(ch)){ postExp.add(""+preChar); opStack.pop(); preChar = opStack.peek(); } opStack.push(ch); i++; break; case '(': // 左括号直接压栈 opStack.push(ch); i++; break; case ')': // 右括号则直接把栈中左括号前面的弹出,并加入后缀表达式链表中 char c = opStack.pop(); while(c != '('){ postExp.add("" + c); c = opStack.pop(); } i++; break; // #号,代表表达式结束,可以直接把操作符栈中剩余的操作符全部弹出,并加入后缀表达式链表中 case '#': char c1; while(!opStack.isEmpty()){ c1 = opStack.pop(); if(c1 != '#') postExp.add("" + c1); } i++; break; //过滤空白符 case ' ': case '\t': i++; break; // 数字则凑成一个整数,加入后缀表达式链表中 default: if(Character.isDigit(ch)){ while(Character.isDigit(ch)){ numBuffer.append(ch); ch = exp.charAt(++i); } postExp.add(numBuffer.toString()); numBuffer = new StringBuffer(); }else{ throw new IllegalExpressionException("illegal operator"); } } } }catch(RuntimeException e){ throw new IllegalExpressionException(e.getMessage()); } return postExp; }
public static void main(String[] args) throws IllegalExpressionException
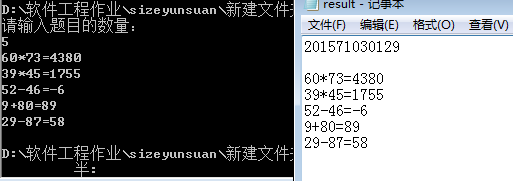
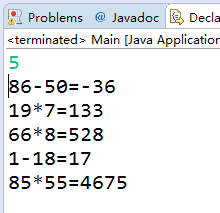
{ Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入题目的数量:"); int s = scan.nextInt(); ArrayList<String> ex= new ArrayList<String>(); String[] operate=new String[]{"+","-","*","/"}; Random r=new Random(); ScriptEngineManager manager = new ScriptEngineManager(); ScriptEngine se = manager.getEngineByName("js"); for(int i=0;i<s;i++) { int a=(int)(Math.random()*100); int b=(int)(Math.random()*100); int c=(int)(Math.random()*100); int q=(int)(Math.random()*2); String cz=operate[r.nextInt(4)]; String cz1=operate[r.nextInt(4)]; //if(q==0){ String AX=String.valueOf(a)+String.valueOf(cz)+String.valueOf(b); Main eval=new Main(); int result = eval.eval(AX+"#"); System.out.println(a+cz+b+"="+result); ex.add(AX+"="+result); }
try { File f = new File("result.txt"); FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(f); PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(fw); pw.println("201571030129"); pw.println(); for(String con:ex) { pw.println(con); } fw.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); }
6、总结
做本次设计令我影响最深刻的是,做设计的时候困难重重,第一JAVA语言的基础很薄弱,没有很好的掌握语言以至于应用,第二做项目的时候盲目的开始写导致在写的过程中没有思路,丢失的内容很多,然后改起来很麻烦,设计中没能按要求完成,在以后的学习中继续努力,加油!
7、PSP展示
|
PSP2.1 |
任务内容 |
计划完成需要的时间(min) |
实际完成需要的时间(min) |
|
Planning |
计划 |
15 |
8 |
|
· Estimate |
· 估计这个任务需要多少时间,并规划大致工作步骤 |
15 |
8 |
|
Development |
开发 |
485 |
600 |
|
·· Analysis |
需求分析 (包括学习新技术) |
10 |
10 |
|
· Design Spec |
· 生成设计文档 |
5 |
6 |
|
· Design Review |
· 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) |
5 |
4 |
|
· Coding Standard |
代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) |
10 |
10 |
|
· Design |
具体设计 |
35 |
20 |
|
· Coding |
具体编码 |
240 |
330 |
|
· Code Review |
· 代码复审 |
120 |
100 |
|
· Test |
· 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
60 |
80 |
|
Reporting |
报告 |
20 |
30 |
|
·· Test Report |
· 测试报告 |
3 |
3 |
|
· Size Measurement |
计算工作量 |
2 |
2 |
|
· Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
· 事后总结 ,并提出过程改进计划 |
15 |
25 |



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号