【Spring】学习笔记06-Bean作用域
Spring官方,Beans作用域类型
| Scope | Description |
|---|---|
|
(Default) Scopes a single bean definition to a single object instance for each Spring IoC container. |
|
|
Scopes a single bean definition to any number of object instances. |
|
|
Scopes a single bean definition to the lifecycle of a single HTTP request. That is, each HTTP request has its own instance of a bean created off the back of a single bean definition. Only valid in the context of a web-aware Spring |
|
|
Scopes a single bean definition to the lifecycle of an HTTP |
|
|
Scopes a single bean definition to the lifecycle of a |
|
|
Scopes a single bean definition to the lifecycle of a |
The Singleton Scope
这一点,Spring官网说明的很详细,
Only one shared instance of a singleton bean is managed, and all requests for beans with an ID or IDs that match that bean definition result in that one specific bean instance being returned by the Spring container.
To put it another way, when you define a bean definition and it is scoped as a singleton, the Spring IoC container creates exactly one instance of the object defined by that bean definition.
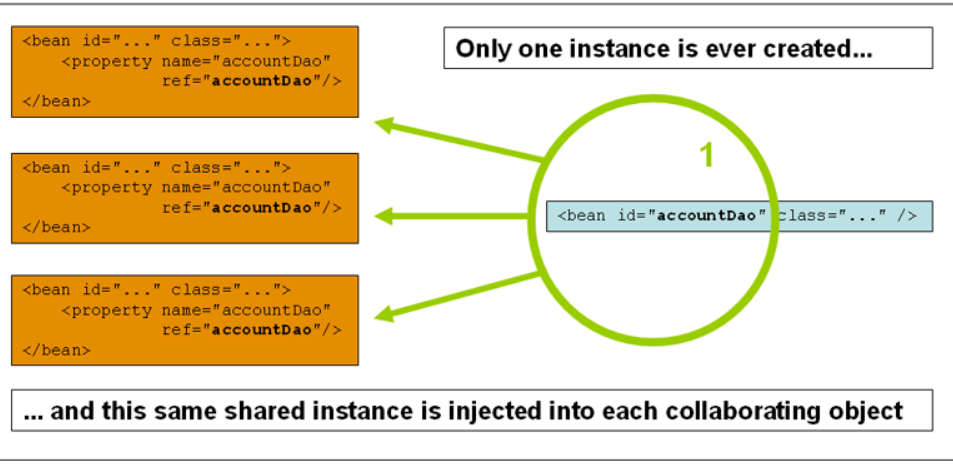
This single instance is stored in a cache of such singleton beans, and all subsequent requests and references for that named bean return the cached object. The following image shows how the singleton scope works:
他说我们对当前单例作用域的bean的所有请求,都是有Spring容器返回的特殊bean实例(同一个),而且这个单例实例是存储在这些单例bean的一个缓存中
然后就是
<bean id="accountService" class="com.something.DefaultAccountService"/> <!-- the following is equivalent, though redundant (singleton scope is the default) --> <bean id="accountService" class="com.something.DefaultAccountService" scope="singleton"/>
以上这两种都是单例作用域bean的注册,也就是说我们默认注册的bean的作用域就是“singleton”单例的
实例测试:
ApplicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <import resource="UserBean.xml"/> <import resource="UserBean_c_namespace.xml"/> <bean id="address_bean" class="com.wang.pojo.Address"> <constructor-arg index="0" value="北京市海淀区"/> </bean> <bean id="student" class="com.wang.pojo.Student"> <!-- 普通值注入,value--> <property name="name" value="王广元"/> <!-- Bean注入,ref--> <property name="address" ref="address_bean"/> <!-- 数组注入--> <property name="books"> <array> <value>你的名字</value> <value>我的天才女友</value> <value>万历十五年</value> </array> </property> <!-- list注入--> <property name="hobbys"> <list> <value>jungle</value> <value>yoga</value> <value>music</value> </list> </property> <!-- map注入--> <property name="card"> <map> <entry key="学生卡" value="200"></entry> <entry key="洗澡卡" value="20"></entry> <entry key="剪发卡" value="200"></entry> </map> </property> <!-- set注入--> <property name="games"> <set> <value>LOL</value> <value>Dota</value> </set> </property> <!-- null值注入--> <property name="wife"> <null></null> </property> <!-- Properties注入--> <property name="info"> <props> <prop key="学号">11223344</prop> <prop key="大学">新加坡国立大学</prop> <prop key="专业">计算机科学与技术</prop> </props> </property> </bean> </beans>
在上述bean的注册中,我们没有声明它的作用域,所以默认是单例的
单元测试
@Test public void test04(){ ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("ApplicationContext.xml"); Student student1= (Student) context.getBean("student"); Student student2= (Student) context.getBean("student"); System.out.println(student1 == student2); } //结果 true
The Prototype Scope
The non-singleton prototype scope of bean deployment results in the creation of a new bean instance every time a request for that specific bean is made.
That is, the bean is injected into another bean or you request it through a getBean() method call on the container.
As a rule, you should use the prototype scope for all stateful beans and the singleton scope for stateless beans.
Spring官方文档说,当对所有非单例模式的原型作用域的注册bean的的部署的请求,都会导致一个新的实例的创建,无论我们是将这个bean注入到其他bean当中,或者使用getBean()获取这个bean
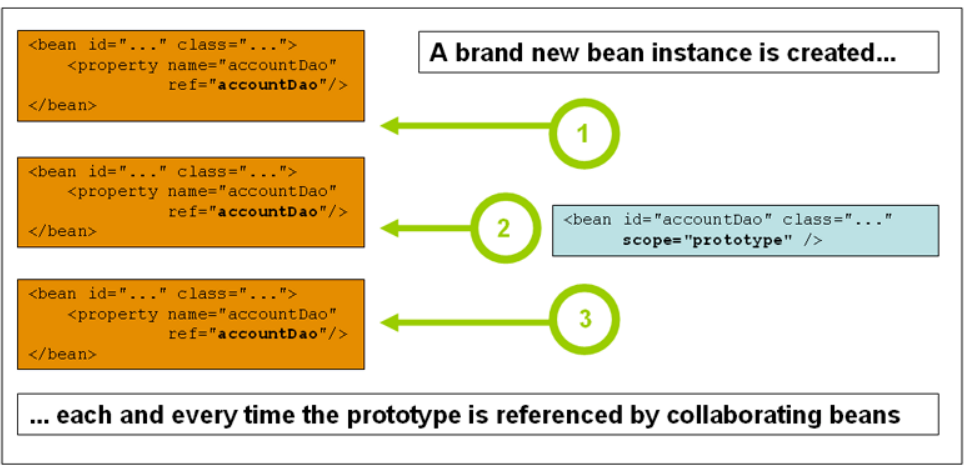
实例测试
bean.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> </bean> <bean id="user_c1" class="com.wang.pojo.User" c:_0="user_c_0" c:_1="18" scope="prototype"/> </beans>
单元测试
@Test public void test05(){ ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("UserBean_c_namespace.xml"); User user1 = (User) context.getBean("user_c1"); User user2 = (User) context.getBean("user_c1"); System.out.println(user1 == user2); } //false




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列01:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 25岁的心里话
· 按钮权限的设计及实现