DS博客作业02--栈和队列
| 这个作业属于哪个班级 | 数据结构--网络2011/2012 |
|---|---|
| 这个作业的地址 | DS博客作业02--栈和队列 |
| 这个作业的目标 | 学习栈和队列的结构设计及运算操作 |
| 姓名 | 王博 |
0.PTA得分截图
栈和队列题目集总得分,请截图,截图中必须有自己名字。题目至少完成2/3(不包括选择题),否则本次作业最高分5分。

1.本周学习总结(0-5分)
1.1 栈
画一个栈的图形,介绍如下内容。
-
顺序栈的结构、操作函数
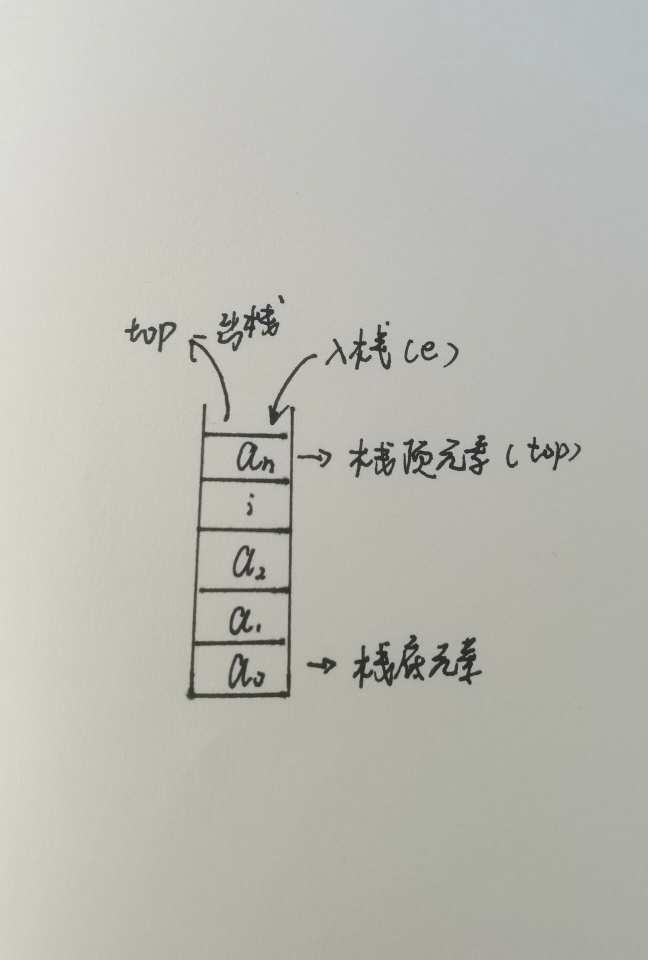
操作函数
-
结构体
struct SNode { ElementType* Data; /* 存储元素的数组 */ Position Top; /* 栈顶指针 */ int MaxSize; }; -
入栈
void PushStack(Stack S, ElementType x) { if (S->Top == S->MaxSize) { printf("Stack Full\n"); return; } S->Top++; S->Data[S->Top] = x; }- 出栈
ElementType PopStack(Stack S) { if (S->Top == -1) { printf("Stack Empty\n"); return 0; } return S->Data[S->Top--]; }- 栈空
int StackEmpty(Stack S) { if (S->Top == -1) return 1; else return 0; } -
-
链栈的结构、操作函数
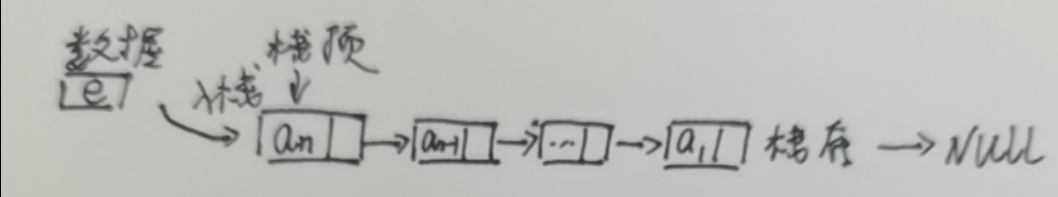
操作函数
- 结构体定义:
typedef int Elmetype; struct SNode { Elmetype data; struct SNode* next; }; typedef struct SNode* LinkStack;- 进栈:
void Push(LinkStack& S, Elmetype X) { LinkStack NewS = new SNode; /*数据载入*/ NewS->data = X; /*头插法插入新数据*/ NewS->next = S->next; S->next = NewS; }- 出栈:
bool Pop(LinkStack& S, Elmetype& e) { /*首先要判断栈顶是否为空*/ if (S->next == NULL) { return false; } e = S->next->data; LinkStack delSNode = S->next; S->next = delSNode->next; delete delSNode; return true; }- 取栈顶元素:
void DestoryLinkStack(LinkStack& S) { LinkStack delS = S; while (S != NULL) { S = S->next; delete delS; delS = S; } }
1.2 栈的应用
- 表达式求值
- 表达式转换
- 符号的配对(创建一个栈,在读入字符的过程中,如果是左括号,则直接入栈,等待相匹配的同类右括号;如果是右括号,且与当前栈顶左括号匹配,则将栈顶左括号出栈)
- 迷宫问题
1.3 队列
画一个队列的图形,介绍如下内容。
队列是一种特殊的线性表,特殊之处在于它只允许在表的前端进行删除操作,而在表的后端进行插入操作,和栈一样,队列是一种操作受限制的线性表。进行插入操作的端称为队尾,进行删除操作的端称为队头.
-
顺序队列的结构、操作函数
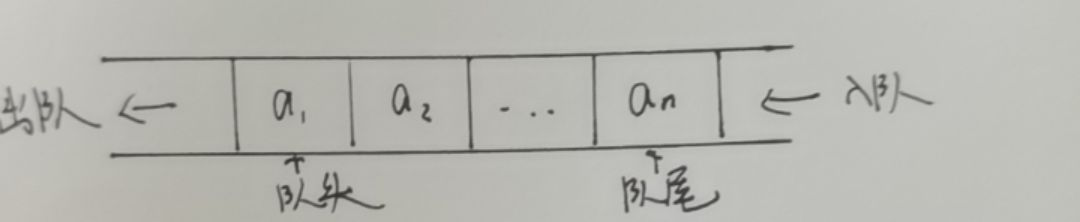
- 结构体定义
typedef struct { ElemType data[MaxSize]; int front, rear; }SqQueue; typedef SqQueue* Queue;- 初始化队列
void InitQueue(Queue Q) { Q = (Queue)malloc(sizeof(SqQueue)*Max); Q->front = Q->rear = 0; }- 销毁队列
void DestroyQueue(Queue Q) { free(Q); }- 判断队列是否为空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue Q) { return (Q->front == Q->rear); }- 入队
bool EnQueue(Queue Q,ElemType e) { if(Q->rear == MaxSize) return false; Q->data[Q->rear++] = e; return true; }- 出队
bool DeQueue(Queue Q,ElemType &e) { if(Q->front == Q->rear) return false; e = Q->data[Q->front++]; return true; } -
环形队列的结构、操作函数
-
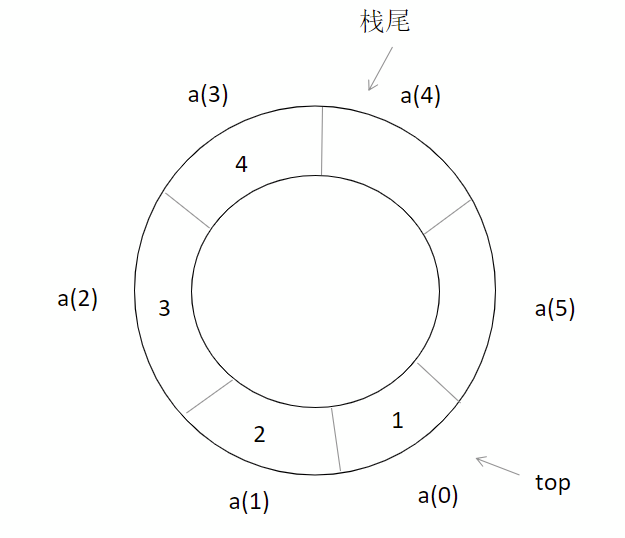
- 结构体定义
typedef struct { ElemType data[MaxSize]; int front, rear; }SqQueue; typedef SqQueue* Queue;- 初始化队列
void InitQueue(Queue Q) { Q = (Queue)malloc(sizeof(SqQueue)*Max); Q->front = Q->rear = 0; }- 销毁队列
void DestroyQueue(Queue Q) { free(Q); }- 判断队列是否为空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue Q) { return (Q->front == Q->rear); }- 入队
bool EnQueue(Queue Q,ElemType e) { if((Q->rear +1) % MaxSize == Q->front) return false; Q->data[Q->rear] = e; Q->rear = (Q->rear + 1) % MaxSize; return true; }- 出队
bool DeQueue(Queue Q,ElemType &e) { if(Q->front == Q->rear) return false; e = Q->data[Q->front]; Q->front = (Q->front + 1) % MaxSize; return true; } -
链队列的结构、操作函数
- 结构体定义
typedef struct QNode /* 声明链式队列的结点 */ { int data; struct QNode *next; }Node; typedef struct QueuePoint /* 声明链式队列的首尾指针 */ { Node *front; Node *rear; }; typedef QueuePoint* Queue;- 初始化队列
Queue InitQueue (Queue Q) { Q = (Queue)malloc(sizeof(QueuePoint)); Q->front = Q->rear = NULL; return Q; }- 销毁队列
void DestroyQueue(Queue Q) { Node* pre = Q->front,* p; if(pre != NULL) { p = pre->next; while(p != NULL) { free(pre); pre = p;p = p->next; } free(pre); } free(Q); }- 判断队列是否为空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue Q) { return (Q->rear == NULL); }- 入队
void EnQueue(Queue Q,ElemType e) { Node* p; p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node)); p->data = e; p->next = NULL; if(Q->rear == NULL) Q->front = Q->rear = p; else { Q->rear->next = p; Q->rear = p; } }- 出队
bool DeQueue(Queue Q,ElemType &e) { Node* p; if(Q->rear == NULL) return false; p = Q->front; if(Q->front == Q->rear) Q->front = Q->rear = NULL; else Q->front = Q->front->next; e = p->data; free(p); return true; } -
队列应用,要有具体代码操作。
舞伴问题
int QueueLen(SqQueue Q){//队列长度 return (Q->rear -Q->front + MAXQSIZE ) % MAXQSIZE; } int EnQueue(SqQueue &Q, Person e){//入队 Q->rear = (Q->rear + 1) %MAXQSIZE; Q->data[Q->rear] = e; return 0; } int QueueEmpty(SqQueue &Q){//判空 if(Q->front==Q->rear){ return 1; }else{ return 0; } } int DeQueue(SqQueue &Q, Person &e){//出队 //就很神奇,把出队那个存到e中 Q->front=(Q->front+1)%MAXQSIZE; e=Q->data[Q->front]; return 0; } void DancePartner(Person dancer[], int num){ /* *函数作用: *1.将Person里存的人分到Mdancers, Fdancers两个队列 *2.Mdancers, Fdancers一比一配队出列 */ //Mdancers, Fdancers for(int i=0;i<num;i++){ if(dancer[i].sex=='M'){ EnQueue(Mdancers,dancer[i]); }else{ EnQueue(Fdancers,dancer[i]); } } while(QueueEmpty(Mdancers)!=1&&QueueEmpty(Fdancers)!=1){ Person x,y; DeQueue(Mdancers, x); DeQueue(Fdancers, y); cout<<y.name<<" "<<x.name<<endl; } }
2.PTA实验作业(4分)
此处请放置下面2题代码所在码云地址(markdown插入代码所在的链接)。如何上传VS代码到码云
2.1 符号配对
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string s;
char b[7];
b[1] = '('; b[2] = ')'; b[3] = '['; b[4] = ']'; b[5] = '{'; b[6] = '}';//用来存储括号,省掉三分之二的代码量。如果你代码超过100行了,那很有可能是因为用了6个if而不是2个。
int find = 0;
bool isasimple = false;
stack<char> bracket;//特地百度了一下括号的英文单词,就用他做栈名字吧。
while (1) {
getline(cin, s);
if (s==".") goto zoulou;//当结束时,直接“zoulou”(走咯)
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {//*/是两个字符比较特殊,单独讨论
if (s[i] == '/' && 1 + i < s.length())
if (s[i + 1] == '*') {
bracket.push(s[i]);//我们将两个字符以/的形式保存,这样方便
i++;//因为这时候是两个字符
continue;
}
if (s[i] == '*' && 1 + i < s.length())
if (s[i + 1] == '/')
{
if (bracket.empty()) {
cout << "NO" << endl << "?-*/" << endl;
return 0;
}
else {
if (bracket.top() != '/') {
cout << "NO" << endl << bracket.top() << "-?" << endl;
return 0;
}
else {
bracket.pop();
i++;//弹栈是弹一个,但是让栈弹的却是两个字符
continue;
}
}
}
isasimple = false;
for (find = 1; find <= 6; find++) {
if (b[find] == s[i]) {//找一下是不是剩余的六个字符
isasimple = true; break;
}
}
if (isasimple) {
if (find % 2 == 1) {
bracket.push(s[i]);
continue;
}
else {
if (bracket.empty()) {
cout << "NO" << endl << "?-" << b[find] << endl;
return 0;
}
else {
if (bracket.top() == '/') {
cout << "NO" << endl <<"/*-?" << endl;
return 0;
}
else if (bracket.top() != b[find - 1]) {
cout << "NO" << endl << bracket.top() << "-?" << endl;
return 0;
}
else {
bracket.pop();
continue;
}
}
}
}
}
}
zoulou:
if (bracket.empty()) {//走咯之后还没完,如果栈不是空的,也还会出错。
cout << "YES" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "NO" << endl << bracket.top() << "-?" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
2.1.1 解题思路及伪代码
- 当左边一堆左括号时,右边出现一个右括号,此右括号与离他最近的一个左括号匹配。 就是我们一直以右括号为标准,当右括号出现时,我们就要找他左边的括号。 所以我们要保存左括号,由于这个性质,我们可以用栈保存左括号。
- 思路:我们一直把左括号压入栈中,当找到有个右括号时,我们把它和栈顶元素比较。
但是比较的时候,要看栈是否为空。非空的话我们可以比较。如果为空,那我们就保存这个右符号,同时设置一个flag变量。
最终还要看一看栈里面是不是空的,如果是空的,且flag也没问题,那我们输出yes
如果栈为空,但是flag标记了,那我们输出那个右符号
如果栈不是空的,输出栈顶即可。
2.1.2 总结解题所用的知识点
-
顺序栈的结构
-
顺序栈的出栈入栈操作
-
递归函数的调用
-
标准输入输出流的运用
-
使用了hash表的知识,用hash表来存储会用到的符号。
-
使用了STL库的string类。
-
学会了利用string类的特点对多行元素进行有指定结束标志的读取。
2.2 银行业务队列简单模拟
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a[1010], b[1010]; //数组a,b用来存放A,B窗口的顾客
int ca = 0,cb = 0; //ca,cb分别代表窗口A、窗口B的人数
int n; //n为顾客总数
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int temp; //顾客编号
scanf("%d", &temp);
//编号为偶数的去A窗口 ,否则去B窗口
if (temp % 2)
a[++ca] = temp;
else
b[++cb] = temp;
}
int f = 0;//控制空格的输出
int x = 1, y = 1; //x,y为a[],b[]下标,从1开始遍历(模拟队列,先进先出)
//A优先输出,A出两个,B出一个
while (x <= ca || y <= cb)
{
if (x <= ca)
{
if (f++)
printf(" ");
printf("%d", a[x++]);
}
if (x <= ca)
{
if (f++)
printf(" ");
printf("%d", a[x++]);
}
if (y <= cb)
{
if (f++)
printf(" ");
printf("%d", b[y++]);
}
}
return 0;
}
2.2.1 解题思路及伪代码
emm,很尴尬没有用队列和栈QwQ
2.2.2 总结解题所用的知识点
3.阅读代码(0--1分)
找1份优秀代码,理解代码功能,并讲出你所选代码优点及可以学习地方。主要找以下类型代码:
注意:不能选教师布置在PTA的题目。完成内容如下。
3.1 题目及解题代码
可截图,或复制代码,需要用代码符号渲染。
#include<iostream>
#include <stack>
char s[4] = { 'q','a','b','c' };
std::stack<int> a[4];
bool move(int before, int after) {
if (a[before].empty())
return false;
if (!a[after].empty())
if ((a[after].top() - a[before].top()) < 0)
return false;
a[after].push(a[before].top());
a[before].pop();
printf("%c -> %c\n", s[before], s[after]);//faster than cout
return true;
}
int main() {
int N, count = 0;
std::cin >> N;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
a[1].push(N - i);
if (N % 2 == 1) {
s[2] = 'c'; s[3] = 'b';
}
while (++count) {
move((count - 1) % 3 + 1, (count) % 3 + 1);
if (!move((count - 1) % 3 + 1, (count + 1) % 3 + 1)&&!move((count + 1) % 3 + 1, (count - 1) % 3 + 1))
break;
}
}
3.2 该题的设计思路及伪代码
链表题目,请用图形方式展示解决方法。同时分析该题的算法时间复杂度和空间复杂度。
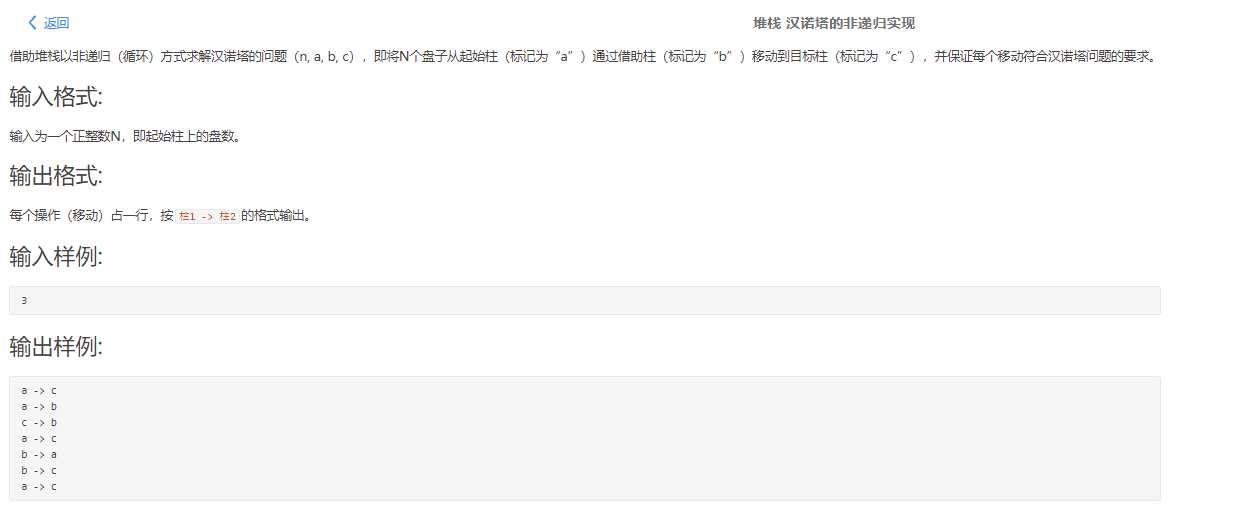
所有的汉诺塔移动可以总结为重复的两步,我们假设现在最小的圆盘在a柱子上,柱子为a,b,c
第一步:将最小圆盘移动到下一个柱子上,也就是b
第二步:对a柱子和c柱子进行顶上最小的元素进行判断,把小一点的那个圆盘移动到大一点的那个圆盘(有空则摞在空柱子上)。
重复上述两步就可以得到答案。
注意:这样得到的最后的答案不一定是摞在c上,如果N是偶数将摞在b上,所以如果N是偶数我们就令第二个柱子为c,第三个柱子为b,这样就一定最后是摞在c上的。
3.3 分析该题目解题优势及难点。
真的有毒




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人