open read write lseek stat lstat
/* 打开一个已经存在的文件 #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> int open(const char *pathname, int flags); 参数: pathname: 文件路径 flags: 文件的操作权限设置 必选项:O_RDONLY, O_WRONLY, O_RDWR 可选项:O_CREAT等 用|连接 返回值: 返回文件描述符,调用失败返回-1 有错误号时,如何打印错误描述? #include <stdio.h> void perror(const char *s); s为用户描述错误 输出 "s:实际错误描述" perror会自动捕捉当前错误 创建一个新的文件 int open(const char *pathname, int flags, mode_t mode); mode: 八进制的数,表示创建出的新文件的操作权限 三种权限:读写执行 因此是8进制 三种用户:此用户,用户所在组,其它用户,因此3个八进制数,加一个符号位,如0777,表示三种用户均可读可写可执行 最终的权限:mode & ~umask umask的作用是操作系统抹去某些权限,保证安全 关闭文件 #include <unistd.h> int close(int fd); */ #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <unistd.h> int main() { // 打开一个文件 // int fd = open("a.txt", O_RDONLY); int fd = open("a.txt", O_RDONLY | O_CREAT, 0777); if(fd == -1) { perror("hello"); } close(fd); return 0; }
read write
/* 读文件 #include <unistd.h> ssize_t read(int fd, void *buf, size_t count); 参数: fd:文件描述符,open得到 buf:缓冲区,读取数据需要存放的地址 count:请求读取的字节数 返回值: 成功: >0:读取到的字节数 =0:文件已经读取完 失败:-1,并设置errno 写文件 #include <unistd.h> ssize_t write(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count); 参数: fd:文件描述符,由open得到 buf:要往磁盘写入的数据 count:写入数据的字节数 返回值: 成功:实际写入的字节数 失败:-1,并设置errno */ // 数据拷贝 #include <stdio.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main() { int fd1 = open("a.txt", O_RDWR); if(fd1 == -1) { perror("fd1 open"); return -1; } int fd2 = open("b.txt", O_WRONLY | O_CREAT, 0777); if(fd2 == -1) { perror("fd2 open"); return -1; } char str[1024]; int total_len = 0; int len = 0; while((len = read(fd1, str, sizeof(str))) > 0) { write(fd2, str, len); total_len += len; } close(fd1); close(fd2); printf("%d, length word copy finished\n", total_len); return 0; }
lseek
/* 重定向读写文件的偏移 标准C库 #include <stdio.h> int fseek(FILE *stream, long offset, int whence); Linux系统函数 #include <sys/types.h> #include <unistd.h> off_t lseek(int fd, off_t offset, int whence); 参数: fd:文件描述符,通过open得到 offset:偏移量 whence: SEEK_SET 设置文件指针的偏移量 SEEK_CUR 设置偏移量:当前位置 + 第二个参数offset的值 SEEK_END 设置偏移量:文件大小 + 第二个参数offset的值 返回值: 最终文件指针的位置 使用: 1、移动文件指针到首地址 lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_SET); 2、获取当前地址 lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_CUR); 3、获取文件大小 lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_END); 4、拓展文件长度,如对文件增加100B lseek(fd, 100, SEEK_END); */ #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <stdio.h> int main() { int fd = open("a.txt", O_RDWR | O_CREAT, 0777); if(fd == -1) { perror("fd open"); return -1; } off_t off = lseek(fd, 100, SEEK_END); // 写入数据才会变 write(fd, " ", 1); close(fd); return 0; }
stat lstat
/* #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <unistd.h> int stat(const char *pathname, struct stat *statbuf); 作用:获取一个文件的相关信息 参数: pathname:操作文件的路径 statbuf:结构体变量,传出参数,用于保存获取到的文件信息 返回值: 成功:0 失败:-1,并设置errno int lstat(const char *pathname, struct stat *statbuf); 作用:获取软连接文件的信息,而不是具体文件 */ #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <stdio.h> int main() { int fd = open("a.txt", O_RDWR | O_CREAT, 0777); if(fd == -1) { perror("fd open"); return -1; } write(fd, "123", 3); close(fd); struct stat statbuf; int status = stat("a.txt", &statbuf); printf("%ld, size of file\n", statbuf.st_size); return 0; }
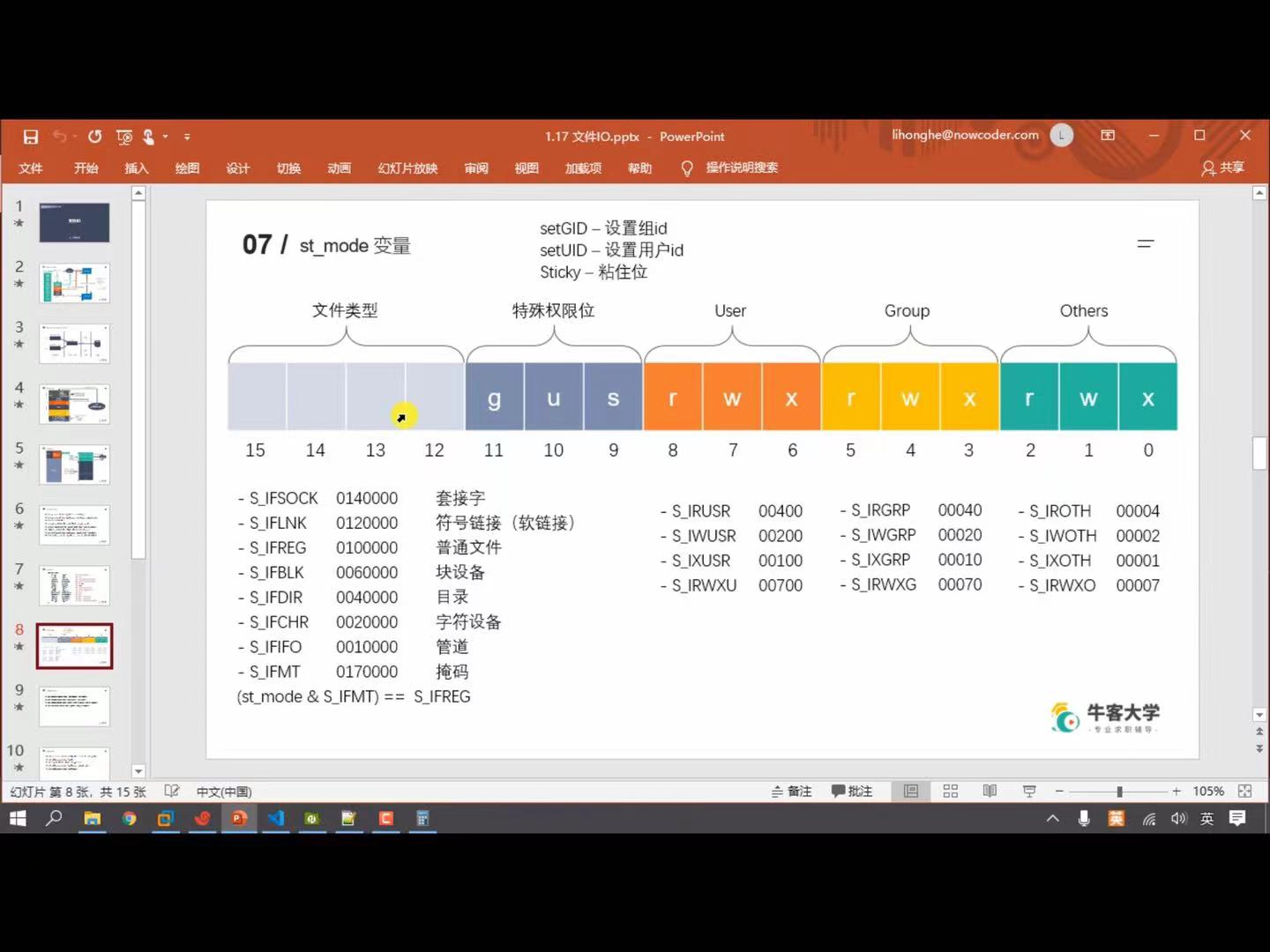
如下,st_mode变量与右三列按位与,可以判断是否有相应权限
最左边一列为文件类型,先于掩码按位与,然后判断结果是否与某个类型相等
因为文件类型是通过两个位设置的,不是4个2进制位的变换
练习
// 练习:实现获取文件的一些信息 #include <stdio.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <string.h> #include <pwd.h> #include <grp.h> #include <time.h> int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { char file_path_name[1024]; if(argc < 2) { strcpy(file_path_name, "a.txt"); } else if(argc == 2) strcpy(file_path_name, argv[1]); else { printf("argv error!\n"); return -1; } struct stat statbuf; int flag = stat("a.txt", &statbuf); if(flag == -1) { perror("stat error"); return -1; } // 获取文件所有者 char *fileUser = getpwuid(statbuf.st_uid)->pw_name; // 获取文件所在组 char *fileGroup = getgrgid(statbuf.st_gid)->gr_name; // 文件大小 int file_size = statbuf.st_size; // 获取修改时间 char *mtime = ctime(&statbuf.st_mtime); printf("%s %s %s %d %s\n", file_path_name, fileUser, fileGroup, file_size, mtime); return 0; }
自己选择的路,跪着也要走完。朋友们,虽然这个世界日益浮躁起来,只要能够为了当时纯粹的梦想和感动坚持努力下去,不管其它人怎么样,我们也能够保持自己的本色走下去。






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
2021-04-23 [每日一题]LintCode1861 老鼠跳跃