手写数字识别记录
独热编码
是一种稀疏向量
其中一个元素为1,其余元素均为0
常用于表示有有限个可能值的字符串或标识符
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNST_data/", one_hot = True) mnist.train.labels[1] # 值为3 #则输出为 array([0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.])
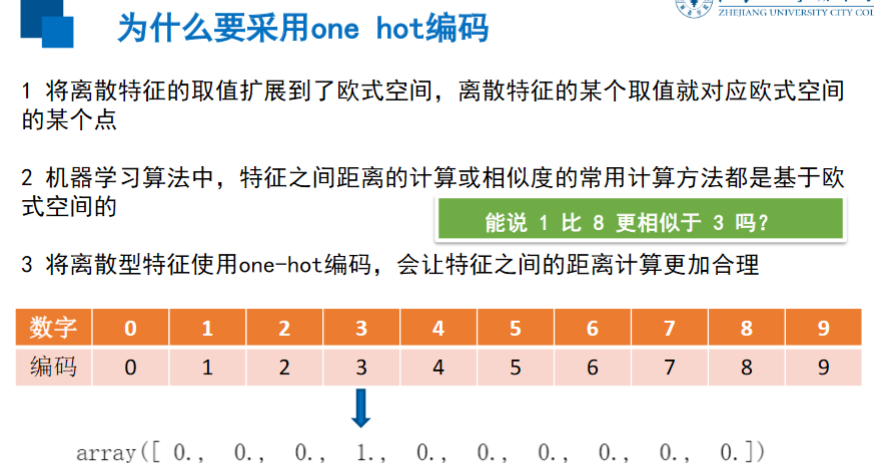
如果直接用阿拉伯数字,则1的距离更近于3,然而其实8更相似与3

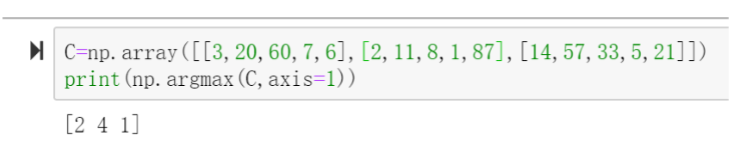
argmax
#argmax返回最大值的下标 A = tf.constant([3, 20, 60, 7, 6]) print(tf.argmax(A).numpy()) #输出为3
#numpy中也提供了argmax,可对numpy.array 数据使用
argmax第二个参数为0时,取每列中最大,为1时取每行中最大
Softmax

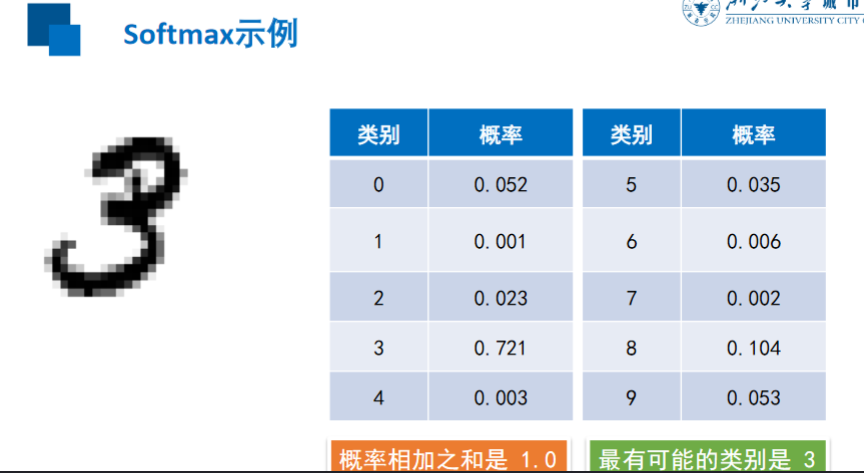
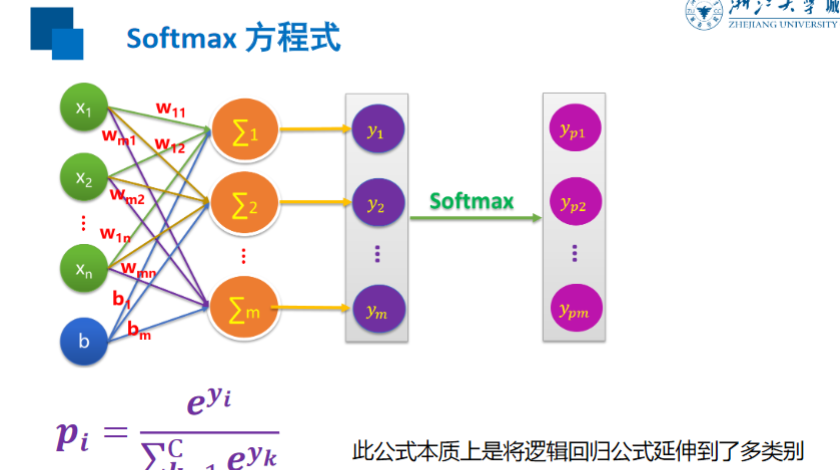
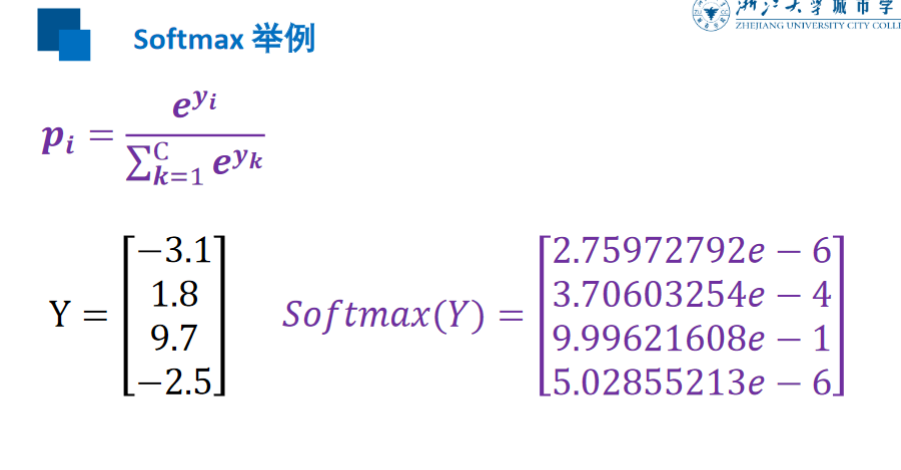
交叉熵损失



code:
%matplotlib inline from matplotlib import pyplot as plt import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np from sklearn.preprocessing import scale mnist = tf.keras.datasets.mnist (train_image, train_label), (test_image, test_label) = mnist.load_data() train_image = train_image.reshape(-1, 784) test_image = test_image.reshape(-1, 784) train_image = tf.cast(train_image / 255.0, dtype = tf.float32) test_image = tf.cast(test_image / 255.0, dtype = tf.float32) train_label = tf.one_hot(train_label, depth = 10) #test_label = tf.one_hot(test_label, depth = 10) w = tf.Variable(tf.random.normal([784, 10], mean = 0.0, stddev = 1.0, dtype = tf.float32)) b = tf.Variable(tf.random.normal([10], dtype = tf.float32)) def model(x, w, b): ret = tf.matmul(x, w) + b return tf.nn.softmax(ret) def loss_fun(x, y, w, b): return tf.reduce_mean(tf.keras.losses.categorical_crossentropy(y_true = y, y_pred = model(x, w, b))) def grad(x, y, w, b): with tf.GradientTape() as tap: loss_ = loss_fun(x, y, w, b) return tap.gradient(loss_, [w, b]) optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate = learn_rate) learn_rate = 0.001 batch = 30 total = train_image.shape[0] n = int(total / batch) for i in range(20): for j in range(n): xs = train_image[j * batch : (j + 1) * batch] ys = train_label[j * batch : (j + 1) * batch] grads = grad(xs, ys, w, b) optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, [w, b])) loss_ = loss_fun(train_image, train_label, w, b) print("Train: ", i + 1, "loss: ", loss_) plt.imshow(tf.reshape(test_image[1], (28, 28)), cmap = "binary") plt.show() print("pred:", tf.argmax(model(tf.reshape(test_image[1], (-1, 784)), w, b), 1).numpy(), "True:", test_label[1])
cifar100:
import tensorflow as tf import numpy from tensorflow.python.keras.datasets import cifar100 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt if __name__ == "__main__" : (train_x, train_y), (test_x, test_y) = cifar100.load_data() model = tf.keras.models.Sequential() model.add(tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(32, (3, 3), input_shape = (32, 32, 3), padding = 'same', activation = 'relu')) model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.3)) model.add(tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2))) model.add(tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), padding = 'same', activation = 'relu')) model.add(tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2))) model.add(tf.keras.layers.Flatten()) model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(1024, activation = 'relu')) model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(100, activation = 'softmax')) model.compile(optimizer = 'adam', loss = 'sparse_categorical_crossentropy', metrics = 'accuracy') model.h = model.fit(train_x, train_y, epochs = 5, validation_split = 0.2, batch_size = 100, verbose = 2) test_pred = model.predict_classes(test_x) print(test_pred[0]) plt.imshow(test_x[0]) plt.show()
自己选择的路,跪着也要走完。朋友们,虽然这个世界日益浮躁起来,只要能够为了当时纯粹的梦想和感动坚持努力下去,不管其它人怎么样,我们也能够保持自己的本色走下去。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号