solution-p7372
一道非常有意思的题。
考虑构造出一堆环,使得每次大操作后每个环内数都沿着环走一步。
这样子最后重新回到初始状态的步数是所有环长的最小公倍数。
先来钦定一下环长,考虑 \(k = \prod p_i^{c_i}\),那我们不加证明地猜测最优方案时环长 \(len_i = p_i^{c_i}\)。
考虑一个类似于 S 形填数。
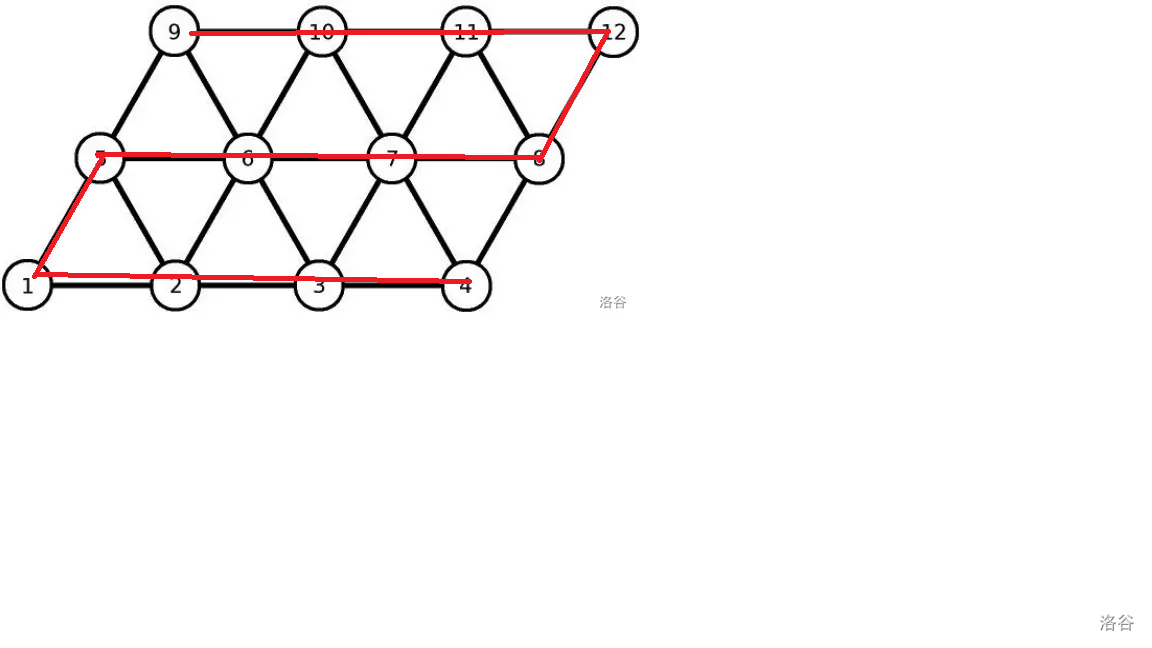
如图,这是这个图中存在的最大的一个可能的环。
接着,我们把这个环分成若干段。
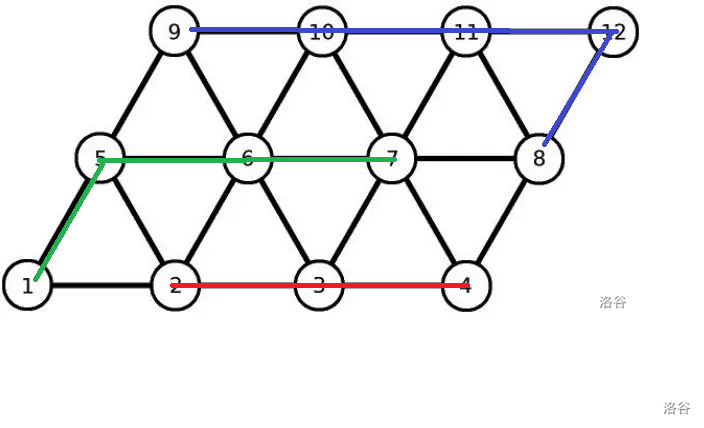
如图是在 \(k=60\) 时的一种划分方式。接下来我们只需要找到一种构造方式使得每一此只交换边上的两个点就做完了。
下面是其中一种方案:
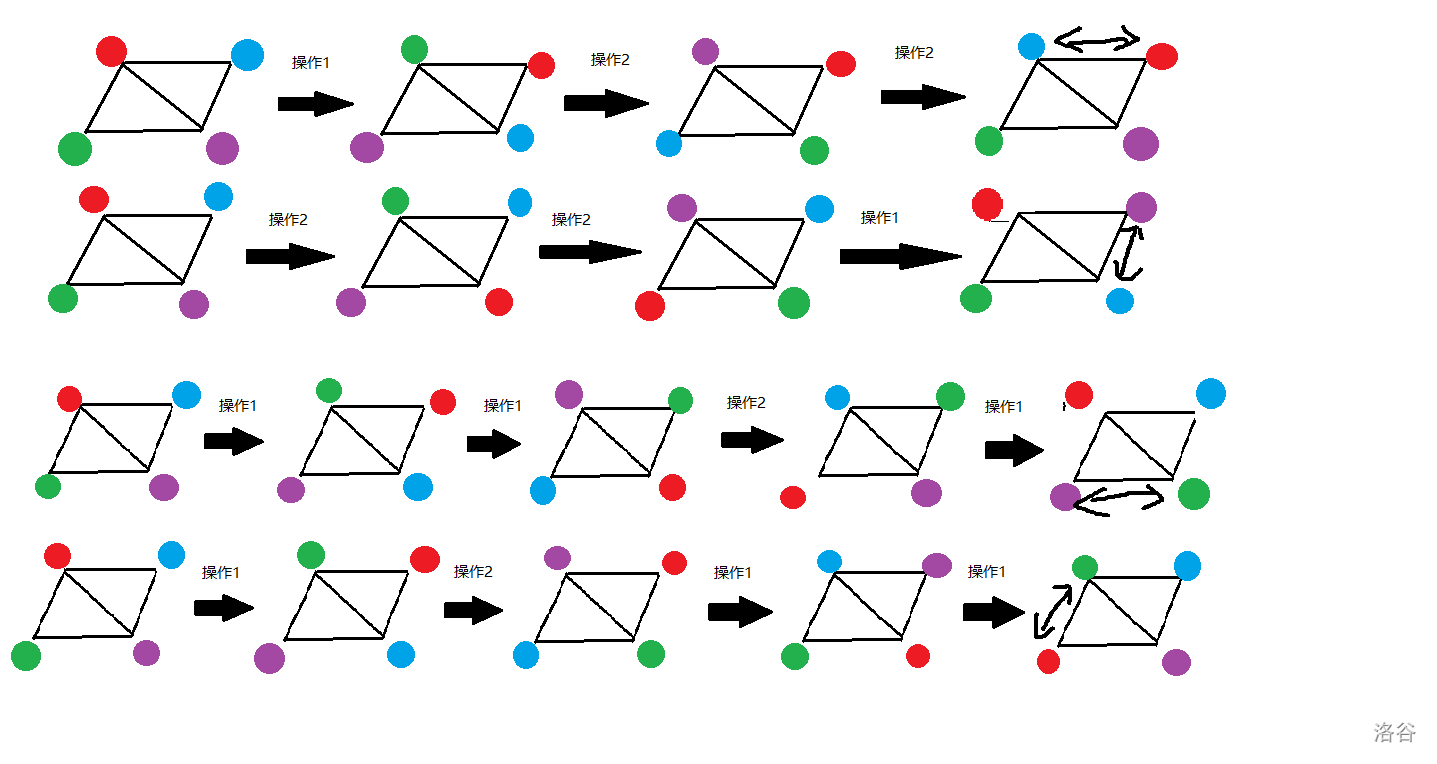
至此,我们做完了整道题。
点击查看代码
// Problem: P7372 [COCI2018-2019#4] Slagalica
// Contest: Luogu
// URL: https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P7372
// Memory Limit: 64 MB
// Time Limit: 1000 ms
//
// Powered by CP Editor (https://cpeditor.org)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const long long inf = 1e18;
const int mininf = 1e9 + 7;
#define int long long
#define pb emplace_back
inline int read(){int x=0,f=1;char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')f=-1;ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){x=(x<<1)+(x<<3)+(ch^48);ch=getchar();}return x*f;}
inline void write(int x){if(x<0){x=~(x-1);putchar('-');}if(x>9)write(x/10);putchar(x%10+'0');}
#define put() putchar(' ')
#define endl puts("")
const int MAX = 1e2 + 10;
struct node{
int x, y, op;
}; vector <node> ans;
void up1(int x, int y){
ans.pb(node{x, y, 2});
ans.pb(node{x, y, 2});
ans.pb(node{x, y, 1});
// puts("u1");
// write(x), put(), write(y), endl;
}
void up2(int x, int y){
ans.pb(node{x, y, 1});
ans.pb(node{x, y, 2});
ans.pb(node{x, y, 1});
ans.pb(node{x, y, 1});
// puts("u2");
// write(x), put(), write(y), endl;
}
void across2(int x, int y){
ans.pb(node{x, y, 1});
ans.pb(node{x, y, 2});
ans.pb(node{x, y, 2});
// puts("a1");
// write(x), put(), write(y), endl;
}
void across1(int x, int y){
ans.pb(node{x, y, 1});
ans.pb(node{x, y, 1});
ans.pb(node{x, y, 2});
ans.pb(node{x, y, 1});
// puts("a2");
// write(x), put(), write(y), endl;
}
int n, m, k;
int nowx = 1, nowy = 1;
int id[MAX][MAX];
bool tonxt(){
if(nowx % 2) nowy++;
else nowy--;
if(nowy <= 0) nowx++, nowy = 1;
if(nowy > m) nowy = m, nowx++;
if(nowx > n) return false;
return true;
}
void work(int x){
// write(x), endl;
if(nowx > n){
puts("-1");
exit(0);
}
x--;
int prex = nowx, prey = nowy;
while(x--){
if(!tonxt()){
puts("-1");
exit(0);
}
if(prex == nowx){
if(prex == n){
across2(prex, min(prey, nowy));
}else{
across1(prex + 1, min(prey, nowy));
}
}else{
if(nowy == m){
up1(nowx, m - 1);
}else{
up2(nowx, 1);
}
}
prex = nowx, prey = nowy;
}
tonxt();
// endl;
}
void solve(){
n = read(), m = read(), k = read();
int psz = 0;
for(int i = 2; i * i <= k; i++){
int cnt = 1;
while(k % i == 0){
cnt *= i;
k /= i;
}
if(cnt > 1) work(cnt);
}
if(k > 1) work(k);
write(ans.size()), endl;
for(int i = 0; i < ans.size(); i++){
putchar(ans[i].op == 1 ? 'R' : 'T'), put();
write(ans[i].x - 1), put(), write(ans[i].y), endl;
}
}
signed main(){
int t = 1;
while(t--) solve();
return 0;
}



