react生命周期
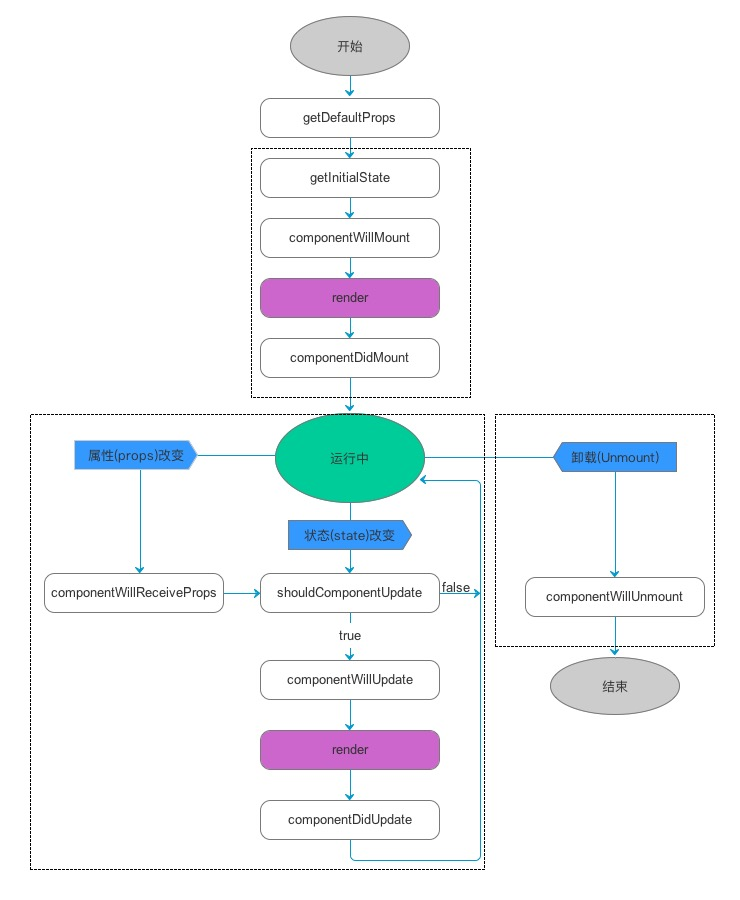
react生命周期分为三种状态
1. 初始化
2. 更新
3. 销毁
初始化
1.getDefaultProps()
设置默认的props,也可以用dufaultProps设置组件的默认属性。
2.getInitialState()
在使用es6的class语法时是没有这个钩子函数的,可以直接在constructor中定义this.state。此时可以访问this.props
3.componentWillMount()
组件初始化时只调用,以后组件更新不调用,整个生命周期只调用一次,此时可以修改state。
在渲染前调用,在客户端也在服务端。
4.render()
react最重要的步骤,创建虚拟dom,进行diff算法,更新dom树都在此进行。此时就不能更改state了。
5.componentDidMount()
组件渲染之后调用,只调用一次。
在第一次渲染后调用,只在客户端。之后组件已经生成了对应的DOM结构,可以通过this.getDOMNode()来进行访问。
如果你想和其他js框架一起使用,可以在这个方法中调用setTimeout,setInterval或者发送AJAX请求等操作(防止异步操作阻塞UI)
更新
6.componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps)
组件初始化时不调用,组件接受新的props时调用。
使用componentWillReceiveProps的时候,不要去向上分发,调用父组件的相关setState方法,否则会成为死循环
在组件接收到一个新的prop(更新后)时被调用,这个方法在初始化render时不会被调用。
7.shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps)
react性能优化非常重要的一环。组件接受新的state或者props时调用,我们可以设置在此对比前后两个props和state是否相同,
如果相同则返回false阻止更新,因为相同的属性状态一定会生成相同的dom树,这样就不需要创造新的dom树和旧的dom树进行diff算法对比,
节省大量性能,尤其是在dom结构复杂的时候
返回一个布尔值,在组件接收到新的props或者state时被调用。
在初始化时或者使用forceUpdate时不被调用。
可以在你确认不需要更新组件时使用
8.componentWillUpdata(nextProps, nextState)
组件初始化时不调用,只有在组件将要更新时才调用,此时可以修改state
9.render()
组件渲染
10.componentDidUpdate()
组件初始化时不调用,组件更新完成后调用,此时可以获取dom节点。
卸载
11.componentWillUnmount()
组件将要卸载时调用,一些事件监听和定时器需要在此时清除
二.组件生命周期的执行次数是什么样子的
只执行一次: constructor、componentWillMount、componentDidMount
执行多次:render 、子组件的componentWillReceiveProps、componentWillUpdate、componentDidUpdate
有条件的执行:componentWillUnmount(页面离开,组件销毁时)
不执行的:根组件(ReactDOM.render在DOM上的组件)的componentWillReceiveProps(因为压根没有父组件给传递props)
三、React生命周期执行顺序
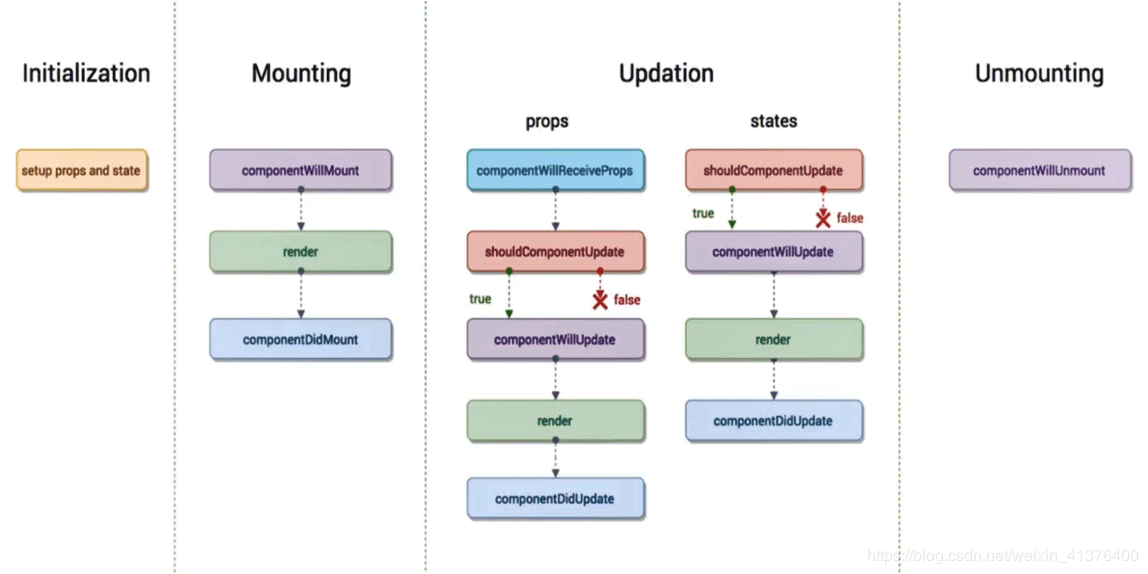
Mounting中为组件的挂载过程
componentWillMount组件挂载之前
render组件的渲染方法
componentDidMount组件挂载完成执行
Updation中为组件数据发生变化的过程
props独有
componentWillReceiveProps
触发条件
- 当一个组件从父组件接收了参数。
2.如果这个组件第一次被父组件加载的时候不会被执行。
3.这个组件之前已经存在于父组件中,并且接收的数据发生变动这时此方法才会被触发。
props和states共有
shouldComponentUpdata:是否要更新数据?需要一个返回值true继续执行下面的生命周期,false就会终止当前组件数
componentWillUpdate:组件将要更新
render:组件的重新渲染
componentDidUpdata:组件完成更新
Unmounting组件卸载##
componentWillUnmount:组件销毁的时候触发


