2024.6 -> 做题记录与方法总结
2024/6/15
P4363 [九省联考 2018] 一双木棋 chess
经典轮廓线dp
使用的关键在于发现状态数并不多,用 \(n\) 进制数来表现轮廓的状态
\(dp\) 的 转移 和 轮廓线 息息相关
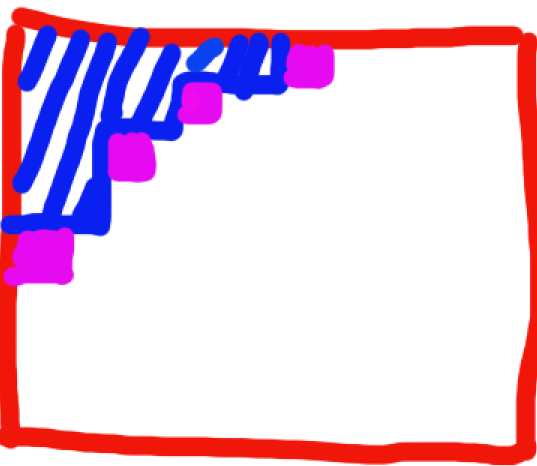
如图,蓝色轮廓线状态只能转移到含一个紫色的状态
因为 $ 1 \leq n,m \leq 10$ 用 \(11\) 进制压缩状态就可以了
轮廓线状态压缩:
ll zip(int *now){
ll res = 0;
for(int i = n;i>=1;i--) res = res * 11 + now[i];
return res;
}
void unzip(ll S,int *now) {
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++) {
now[i] = S % 11;
S /= 11;
}
}
AC-Code:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int rd() {
int x = 0, w = 1;
char ch = 0;
while (ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
if (ch == '-') w = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
x = x * 10 + (ch - '0');
ch = getchar();
}
return x * w;
}
void wt(int x) {
static int sta[35];
int f = 1;
if(x < 0) f = -1,x *= f;
int top = 0;
do {
sta[top++] = x % 10, x /= 10;
} while (x);
if(f == -1) putchar('-');
while (top) putchar(sta[--top] + 48);
}
typedef long long ll;
int n,m;
int a[11][11],b[11][11];
unordered_map<ll,ll> dp;
ll zip(int *now){
ll res = 0;
for(int i = n;i>=1;i--) res = res * 11 + now[i];
return res;
}
void unzip(ll S,int *now) {
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++) {
now[i] = S % 11;
S /= 11;
}
}
const ll inf = 1e9;
ll dfs(ll S){
if(dp.count(S)) return dp[S];
int size = 0;
int *now = new int[11];
unzip(S,now);
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++) size += now[i];
int re = (size & 1) ? inf:-inf;
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++) {
if((i == 1 && now[i] < m) || (i != 1 && now[i] < now[i-1])) {
now[i]++;
if((size & 1)) re = min((ll)re,dfs(zip(now)) - b[i][now[i]]);
else re = max((ll)re,dfs(zip(now)) + a[i][now[i]]);
now[i]--;
}
}
delete now;
return dp[S] = re;
}
signed main() {
n = rd(),m = rd();
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++)
for(int j = 1;j<=m;j++)
a[i][j] = rd();
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++)
for(int j = 1;j<=m;j++)
b[i][j] = rd();
ll ed = 0;
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++) ed = ed * 11 + m;
dp[ed] = 0;
ll ans = dfs(0);
wt(ans);
return 0;
}
2024/6/16
codeforces Round 953 Div.2
A.Alice and Books
分成两堆,其中一堆编号最大一定是 \(n\)
只需要在 \(1 \rightarrow (n - 1)\) 中找到最大值 \(a_i\)
答案为 \(a_i + a_n\)
AC-Code:
#define useLL
#include<C:\Users\Ming\Desktop\workplace\head_file\all_function.h>
using namespace AllRangeApply_Define;
using namespace Atomic::fastSTD;
namespace my{
void solve() {
int n = read();
vector<int> a(n);
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++) a[i] = read();
int maxn = 0;
for(int i = 0;i<n-1;i++) maxn = max(maxn,a[i]);
write(a[n-1] + maxn);
putchar('\n');
}
signed main(){
int t = read();
while(t--) solve();
return 0;
}
}
signed main(){
return my::main();
}
B.New Bakery
题面:
鲍勃决定开一家面包店。开业当天,他烤出了 \(n\) 个可以出售的包子。通常一个包子的价格是 \(a\) 个金币,但为了吸引顾客,鲍勃组织了以下促销活动:
- 鲍勃选择某个整数 \(k\) ( \(0 \le k \le \min(n, b)\) )。
- 鲍勃以修改后的价格出售第一批 \(k\) 个小面包。在这种情况下,售出的 \(i\) ( \(1 \le i \le k\) )个馒头的价格是 \((b - i + 1)\) 个硬币。
- 剩下的 \((n - k)\) 个馒头以每个 \(a\) 个硬币的价格出售。
注意 \(k\) 可以等于 \(0\) 。在这种情况下,鲍勃将以每个 \(a\) 个硬币的价格出售所有馒头。
帮助鲍勃确定出售所有 \(n\) 个馒头所能获得的最大利润。
不难计算出利润表达式
展开表达式
开口向下,\(k = (b + \frac{1}{2} - a)\) 时取最大值
计算出 \(k\) 后,因为 $0 \le k \le \min(n, b) 且 k \in N $,判断一下最大值在何处取即可
AC-Code:
#define useLL
#include<C:\Users\Ming\Desktop\workplace\head_file\all_function.h>
using namespace AllRangeApply_Define;
using namespace Atomic::fastSTD;
namespace my{
void solve() {
int n = read(),a = read(),b = read();
double k = b - a + 0.5;
if(k < 0) k = 0;
else if(k > min(n,b)) k = min(n,b);
int ans = 0;
double t = k;
k = (int)k;
ans = -0.5 * k * k + (b + 0.5 - a) * k + n * a;
if((int)k < t && t < k + 1) {
k = k + 1;
ans = max(ans,(int)(-0.5 * k * k + (b + 0.5 - a) * k + n * a));
}
write(ans);
putchar('\n');
}
signed main(){
int t = read();
while(t--) solve();
return 0;
}
}
signed main(){
return my::main();
}
2024/6/17
codeforces round 953 Div.2
C.Manhattan Permutations
注意到 \(k \in even\) 故 \(k \in odd\) 的情况一定是 NO
然后将其反向排列,得到最大值
取得最大值
让我们来考虑一下,如果我们将同位排列中的 \(x\) 和 \(1\) 互换会发生什么。这种排列的曼哈顿值等于 \(|x - 1| + |x - 1| = 2 \cdot |x - 1|\) 。那么从 \(0\) 到 \(2 \cdot (n - 1)\) 的任何偶数 \(k\) 都可以得到。如果是 \(k > 2 \cdot (n - 1)\) ,那么让我们交换 \(1\) 和 \(n\) 元素。请注意,我们已经将问题缩小到了更小的 \((n - 2)\) ,只是现在的索引是从 \(2\) 开始,而不是 \(1\) 。现在我们可以像处理同位排列一样,将 \(2\) 与某个 \(x\) (\(x > 1\)和 \(x < n\) )互换。排列的值会发生 \(|x - 2| \cdot 2\) 的变化,因此可以得到从 \(0\) 到 \(2 \cdot (n - 1) + 2 \cdot (n - 3)\) 的任意偶数 \(k\) 。请注意,如果我们继续这样做,最终将得到排列 \([n, n - 1, ..., 1]\) ,而我们已经证明了从 \(0\) 到 \(max_k\) 的任何偶数 \(k\) 都是可以实现的。因此,如何在 \(O(n)\) 时间内重构排列本身是显而易见的。
然后构造
AC-Code:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void solve() {
int n;
long long k;
cin>>n>>k;
long long sum = 0;
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++) sum += abs(n - 1 - 2 * i);
if(k & 1 || sum < k) {
puts("NO");
return;
}
puts("Yes");
vector<int> p(n);
k /= 2;
iota(p.begin(),p.end(),0);
for(int i = 0;k > 0;i++) {
if(k >= n - 1 - 2 * i) {
swap(p[i],p[n - 1 - i]);
k -= n - 1 - 2 * i;
}else {
swap(p[i],p[i + k]);
k = 0;
}
}
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++) cout<<p[i] + 1<<' ';
cout<<'\n';
}
signed main() {
int t = 1;
cin>>t;
while(t--) solve();
return 0;
}
2024/06/23
codeforces round 953 Div.2
D.Elections
难绷,赛时想的差不多了,然后偏到数据结构
如果候选人 \(i\) 最初没有获胜(当没有人被剔除时),那么为了使他们获胜,我们必须剔除所有 \(id\) 小于 \(i\) 的候选人。因为如果仍然有人的 \(id\) 小于 \(i\) ,那么候选人 \(i\) 的票数就不会增加,而其他人的最大票数也不会减少。
让我们先找出选举的获胜者,对于他们来说,答案是 \(0\) ,对于所有其他候选人,我们需要删除所有 \(id\) 小于 \(i\) 的人。
但有时仅仅删除这些人可能还不够,因此我们需要额外删除几名候选人,这样他们的粉丝就会把票投给我们。
请注意,此时只需删除一个最大值为 \(a_i\) 的候选人,那么我们就一定会赢,因此候选人 \(i\) 的答案要么是 \(0\) ,要么是 \(i\) ,要么是 \(i + 1\) 。
因此,我们最终得到了一个在 \(O(n)\) 中有效的解。
AC-code:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void solve() {
int n,c;
cin>>n>>c;
vector<int> a(n);
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++) cin>>a[i];
if(n == 1) {
cout<<0<<'\n';
return;
}
int mx = *max_element(a.begin() + 1,a.end());
int mxc = max(a[0] + c,mx);
int winer = mxc == a[0] + c ? 0:find(a.begin() + 1,a.end(),mx) - a.begin();
long long sum = c;
for(int i = 0;i<n;sum += a[i],i++) {
int ans = 0;
if(i == winer) ans = 0;
else if(sum + a[i] >= mx) ans = i;
else ans = i + 1;
cout<<ans<<" \n"[i == n-1];
}
}
signed main() {
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--) solve();
return 0;
}
2024/06/28
北京时间:0:46
不得不感慨codeforce的阴间比赛时间
---还有 jiangly 太强了---
Educational Codeforces Round 167 (Rated for Div. 2)
A. Catch the Coin
赛时稀里糊涂就过了
注意到我们是先手
所以,\(y\) 掉到 \(-2\) 就无药可救了
否则,一定可以赶得上
AC-code:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int rd() {
int x = 0, w = 1;
char ch = 0;
while (ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
if (ch == '-') w = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
x = x * 10 + (ch - '0');
ch = getchar();
}
return x * w;
}
void wt(int x) {
static int sta[35];
int f = 1;
if(x < 0) f = -1,x *= f;
int top = 0;
do {
sta[top++] = x % 10, x /= 10;
} while (x);
if(f == -1) putchar('-');
while (top) putchar(sta[--top] + 48);
}
signed main() {
int n = rd();
while(n--) {
int x = rd(),y = rd();
if(y < -1) {
puts("NO");
continue;
}
puts("YES");
}
return 0;
}
B - Substring and Subsequence
赛时没过,想复杂了
其实暴力就可以了
AC-code:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void solve() {
string a,b;
cin>>a>>b;
int ans = b.size();
for(int i = 0;i<b.size();i++) {
int k = i;
for(int j = 0;j<a.size();j++) {
if(k < b.size() && a[j] == b[k]) k++;
}
ans = min(ans,i + (int)b.size() - k);
}
cout<<ans + a.size()<<'\n';
}
signed main() {
int T;
cin>>T;
while(T--) solve();
return 0;
}
C - Two Movies
这个赛时想的很快
求一种选择,使得最小值最大
因为当 一个人对两个评价为 一个不坏和一个坏,我们必然贪心的选择不坏的那个
没有人会给自己找别扭,不是吗
所以对于 \(\{1,-1\},\{0,-1\},\{0,0\},\{1,0\}\) 评价都可以无脑判断
那么 对于 \(\{1,1\}\) 和 \(\{-1,-1\}\) 呢?
维护最小值最大,肯定是贪心让大的多付出
哪个是大的呢?
因为
所以对于 \(\{1,-1\},\{0,-1\},\{0,0\},\{1,0\}\) 评价都可以无脑判断
我们可以先将所以的正面评价都累加起来,后面再考虑有舍有得
回到 对于 \(\{1,1\}\) 和 \(\{-1,-1\}\)
从 \(\sum a\) 和 \(\sum b\) 中较大的一个里面去扣,就结束了
AC-code:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int rd() {
int x = 0, w = 1;
char ch = 0;
while (ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
if (ch == '-') w = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
x = x * 10 + (ch - '0');
ch = getchar();
}
return x * w;
}
void wt(int x) {
static int sta[35];
int f = 1;
if(x < 0) f = -1,x *= f;
int top = 0;
do {
sta[top++] = x % 10, x /= 10;
} while (x);
if(f == -1) putchar('-');
while (top) putchar(sta[--top] + 48);
}
void solve() {
int n = rd();
vector<int> a(n);
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++) a[i] = rd();
vector<int> b(n);
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++) b[i] = rd();
int maxn = 0,sa = 0,sb = 0;
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++) if(a[i] == 1) sa++;
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++) if(b[i] == 1) sb++;
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++) {
if(a[i] == -1 && b[i] == -1) {
if(sa >= sb) sa--;
else sb--;
}
if(a[i] == 1 && b[i] == 1) {
if(sa >= sb) sa--;
else sb--;
}
}
wt(min(sa,sb));
putchar('\n');
}
signed main() {
int t = rd();
while(t--) solve();
return 0;
}
CF708E Student's Camp
显然,我们不难找到
\[\large f_{i,l,r} = g_{l-1} g_{m - r} \sum_{\max(l,l^{\prime}) \leq \min(r,r^{\prime})} f_{i-1,l^{\prime},r^{\prime}} \]其中 \(g_i\) 代表着 \(k\) 天正好消失 \(i\) 个格子,
\[g_i = \dbinom{k}{i}p^i(1-p)^{k-i} \]\(f_{i,l,r}\) 是第 \(i\) 行恰保留了 \(l,r\) 后 \(0\sim i\) 行还连通的概率
但是,\(f\) 数组达到了 \(O(nm^2)\) 的规模
显然不可接受
这个时候就需要 正难则反
我们考虑扣掉不连通的情况
令 \(f_{i,r}\) 为 第 \(i\) 行右端点为 \(r\),第 \(0\) 行到 第 \(i\) 行都连通的概率
在转移的时候,枚举左端点 \(l\),计算与之相交的区间和
因为网格是对称的,那么 \(f_{i,r}\) 也可以指 第 \(i\) 行的左端点是 \(m - r + 1\),右端点为 \(m\),连通的概率
得到转移:
当然,这一堆的求和符号暗示我们,用 前缀和 的时候,到了
令 \(p_{i}\) 前缀和为 \(a_i\),\(p_ih_i\) 的前缀和为 \(b_i\)
那么有:
这样,转移式简单多了,时间复杂度优化到了 \(O(nm)\)
AC-code:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int rd() {
int x = 0, w = 1;
char ch = 0;
while (ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
if (ch == '-') w = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
x = x * 10 + (ch - '0');
ch = getchar();
}
return x * w;
}
void wt(int x) {
static int sta[35];
int f = 1;
if(x < 0) f = -1,x *= f;
int top = 0;
do {
sta[top++] = x % 10, x /= 10;
} while (x);
if(f == -1) putchar('-');
while (top) putchar(sta[--top] + 48);
}
const int mod = 1e9+7;
const int N = 1.5e3+10;
const int S = 1e5+10;
#define int long long
void reduce(int &x){x += x >> 31 & mod;}
int mul(int a,int b){
return a * b % mod;
}
int pow(int x,int k,int res = 1){
while(k){
if(k & 1) res = (res * x) % mod;
x = (x * x) % mod;
k >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
void fma(int &x,int y,int z) {
x = (y * z + x) % mod;
}
int n,m,k;
int fac[S],inv[S];
int ps[N],pre[N];
int f[N][N];
int C(int a,int b){
return fac[a] * inv[b] % mod * inv[a - b] % mod;
}
signed main() {
fac[0] = fac[1] = inv[0] = inv[1] = 1;
for(int i = 2;i<S;i++) {
fac[i] = mul(fac[i-1],i);
inv[i] = mul(inv[mod % i],mod - mod/i);
}
for(int i = 2;i<S;i++) inv[i] = mul(inv[i-1],inv[i]);
int a,b;
n = rd(),m = rd(),a = rd(),b = rd(),k = rd();
int P = pow(b,mod - 2,a);
for(int i = 0;i <= m && i <= k;i++) ps[i] = pow(P,i,pow(1 + mod - P,k - i,C(k,i)));
pre[0] = ps[0];
for(int i = 1;i<=m;i++) reduce(pre[i] = ps[i] + pre[i-1] - mod);
f[0][m] = 1;
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++) {
static int tp[N],ts[N];
for(int j = 1;j<=m;j++) {
reduce(tp[j] = tp[j-1] + f[i-1][j] - mod);
fma(ts[j] = ts[j-1],ps[j],tp[j]);
}
for(int r = 1;r<=m;r++) {
int sm = mul(pre[r-1],tp[m] - tp[m-r] + mod);
reduce(sm -= ts[r-1]);
f[i][r] = mul(sm,ps[m-r]);
}
}
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 1;i<=m;i++) reduce(ans += f[n][i] - mod);
wt(ans);
return 0;
}
这个题还有一点容斥的思想
当我们发现三维存不下的时候,就需要想一想用容斥能不能省掉一维的空间
这个题就是这样,我们会惊讶的发现 \(l,r\) 太大,所以 \(l,r\) 是我们重点关照的对象
那么,我们能不能想出砍掉一个端点,以至于去使用 正难则反 的思想呢?
就算我们推出了式子,我们能否有清晰的逻辑去实现前缀和呢?
P3648 [APIO2014] 序列分割
题面:
题目描述
你正在玩一个关于长度为 \(n\) 的非负整数序列的游戏。这个游戏中你需要把序列分成 \(k + 1\) 个非空的>块。为了得到 \(k + 1\) 块,你需要重复下面的操作 \(k\) 次:
选择一个有超过一个元素的块(初始时你只有一块,即整个序列)
选择两个相邻元素把这个块从中间分开,得到两个非空的块。
每次操作后你将获得那两个新产生的块的元素和的乘积的分数。你想要最大化最后的总得分。
输入格式
第一行包含两个整数 \(n\) 和 \(k\)。保证 \(k + 1 \leq n\)。
第二行包含 \(n\) 个非负整数 \(a_1, a_2, \cdots, a_n\) \((0 \leq a_i \leq 10^4)\),表示前文所述的序列。
输出格式
第一行输出你能获得的最大总得分。
第二行输出 \(k\) 个介于 \(1\) 到 \(n - 1\) 之间的整数,表示为了使得总得分最大,你每次操作中分开两个块的位置。第 \(i\) 个整数 \(s_i\) 表示第 \(i\) 次操作将在 \(s_i\) 和 \(s_{i + 1}\) 之间把块分开。
如果有多种方案使得总得分最大,输出任意一种方案即可。
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
7 3 4 1 3 4 0 2 3样例输出 #1
108 1 3 5提示
你可以通过下面这些操作获得 \(108\) 分:
初始时你有一块 \((4, 1, 3, 4, 0, 2, 3)\)。在第 \(1\) 个元素后面分开,获得 \(4 \times (1 + 3 + 4 + 0 + 2 + 3) = 52\) 分。
你现在有两块 \((4), (1, 3, 4, 0, 2, 3)\)。在第 \(3\) 个元素后面分开,获得 \((1 + 3) \times (4 + 0 + 2 + 3) = 36\) 分。
你现在有三块 \((4), (1, 3), (4, 0, 2, 3)\)。在第 \(5\) 个元素后面分开,获得 \((4 + 0) \times (2 + 3) = 20\) 分。
所以,经过这些操作后你可以获得四块 \((4), (1, 3), (4, 0), (2, 3)\) 并获得 \(52 + 36 + 20 = 108\) 分。
不难看出,明显的斜率优化典题
首先,通过乘法结合律,分块的顺序不会改变分值
因为,对于 块 \(abc\),\(a(b + c) + bc = ab + (a + b)c = ab + ac + bc\)
那么,通过一个 \(dp\),做一个内嵌套 (每次分的位置都为最优策略中第一次分开的位置)
得到转移式:
其中 \(s_i\) 为 序列 \(0 \sim i\) 的前缀和
一看 \(k \rightarrow k + 1\),滚动数组少不了
这样,式子变成了
那么对于 \(i\) 的最优决策点 \(j\) 和不优决策点 \(k\)(默认 \(j < k\))
即:
是一个 \(y = \frac{f_i - s_i ^ 2}{s_i}\ \& \ x = -s_i\) 的函数
我们看到决定优决策点的斜率是大于 \(1\) 的
我们可将每个点看做 \(P(-s_i,f_i - s_k ^ 2)\),维护一个横坐标单增的下凸包 ()
此题就解决了!
AC-code:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
int rd() {
int x = 0, w = 1;
char ch = 0;
while (ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
if (ch == '-') w = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
x = x * 10 + (ch - '0');
ch = getchar();
}
return x * w;
}
void wt(int x) {
static int sta[35];
int f = 1;
if(x < 0) f = -1,x *= f;
int top = 0;
do {
sta[top++] = x % 10, x /= 10;
} while (x);
if(f == -1) putchar('-');
while (top) putchar(sta[--top] + 48);
}
const int N = 100005;
int f[N],g[N],n,k,s[N],pre[205][N];
double slope(int a,int b){
int x1 = -s[a],x2 = -s[b];
int y1 = g[a] - s[a] * s[a],y2 = g[b] - s[b] * s[b];
if(x1 == x2) return -1e18;
return (double)(y1 - y2) / (double)(x1 - x2);
}
signed main() {
n = rd(),k = rd();
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++) {
s[i] = rd();
s[i] += s[i - 1];
}
static int q[N],head = 0,tail = 0; //[head,tail)
for(int d = 1;d<=k;d++){
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++) g[i] = f[i];
head = 0,tail = 0;
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++) {
while(tail - head >= 2 && slope(q[head],q[head + 1]) <= s[i]) head++;
if(tail > head) {
int &j = q[head];
pre[d][i] = j;
f[i] = g[j] + (s[i] - s[j]) * s[j];
}
while(tail - head >= 2 && slope(q[tail - 1],q[tail - 2]) >= slope(q[tail - 1],i)) tail--;
q[tail++] = i;
}
}
wt(f[n]);putchar('\n');
for(int x = pre[k][n];k;x = pre[--k][x]) wt(x),putchar(' ');
return 0;
}
这里也附上 《深入浅出提高版》的向量维护凸包
code:
#define useLL
#include <C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\workspace\head_file\all_function.h>
using namespace Atomic::fastSTD;
using namespace AllRangeApply_Define;
namespace my{
const int N = 1e5+5;
typedef long long ll;
ll f[2][N],pre[210][N];
int a[N],n,k,head,tail;
struct vec
{
int id,x;
ll y;
ll operator ()(int v){
return (ll)x * v + y;
}
}q[N];
ll cross(vec a,vec b,vec c) {
a.x -= b.x;
a.y -= b.y;
b.x -= c.x;
b.y -= c.y;
return b.x * a.y - a.x * b.y;
}
signed main() {
n = rd(),k = rd();
for(int i= 1;i<=n;i++) a[i] = rd();
for(int i= 1;i<=n;i++) a[i] += a[i-1];
for(int T = 1;T<=k;T++) {
head = tail = 0;
q[0] = (vec) {0,0,0};
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++) {
while(head < tail && q[head](a[i]) <= q[head + 1](a[i])) ++head;
f[T & 1][i] = q[head](a[i]);
pre[T][i] = q[head].id;
vec x = (vec) {i,a[i],f[T&1^1][i] - (ll)a[i] * a[i]};
while(head < tail && cross(q[tail-1],q[tail],x) <= 0) --tail;
q[++tail] = x;
}
}
wt(f[k & 1][n]);
putchar('\n');
int now = n;
for(int i = k;i>=1;i--) {
wt(pre[i][now]);
putchar(' ');
now = pre[i][now];
}
return 0;
}
}
signed main() {
return my::main();
}



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· .NET周刊【3月第1期 2025-03-02】