【慢慢学Android】:1.Activity之间的转换以及数据的传递(Intent)
2012-05-25 11:24 ATP_ 阅读(2060) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报当作自己的笔记,参考引用了一些大神文章:
http://www.cnblogs.com/halzhang/archive/2010/05/28/1746592.html
http://developer.android.com/reference/android/os/Bundle.html
Intent简介:
在一个Android应用中,主要由四种组件组成(四种组件分别为:Activity、Broadcast、Service、ContentProvider),而这四种组件是独立的,它们之间可以互相调用,协调工作,最终组成一个真正的Android应用。在这些组件之间的通讯中,主要是由Intent协助完成的。
Intent负责对应用中一次操作的动作、动作涉及数据、附加数据进行描述,Android则根据此Intent的描述,负责找到对应的组件,将Intent传递给调用的组件,并完成组件的调用。因此,Intent在这里起着一个媒体中介的作用,专门提供组件互相调用的相关信息,实现调用者与被调用者之间的解耦。
Intent来实现Activity之间的跳转:
1.无数据的简单跳转
通常在button的setOnClickListener中,通过构造一个新的intent实例,然后通过startActivity(Intent实例)来实现:
open.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, FileBrowser.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
});
为什么需要指定两个活动呢?因为在Android中有一个活动栈,这样的构造方式才能确保正确的将前一个活动压入栈中,才能在触发返回键的时候活动能够正确出栈。
2.所有Activity都必须在AndroidManifest.xml中声明:
<activity android:name="SecondActivity"></activity>
3.Intent常用的构造函数:
A.Intent(String action) 指定action类型的构造函数
B.Intent(String action, Uri uri) 指定Action类型和Uri的构造函数,URI主要是结合程序之间的数据共享ContentProvider
C.Intent(Context packageContext, Class<?> cls) 传入组件的构造函数(示例一中提到的Activity之间的转换)
D.Intent(String action, Uri uri, Context packageContext, Class<?> cls) 前两种结合体
Intent(String action, Uri uri) 的action就是对应在AndroidMainfest.xml中的action节点的name属性值。在Intent类中定义了很多的Action和Category常量。
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_EDIT, null);
startActivity(intent);
该示例所使用的是构造函数B,Intent.ACTION_EDIT表示的是一个Action,执行此代码的时候,程序就会在AndroidManifest.xml中寻找相应的URI下所属的Activity;
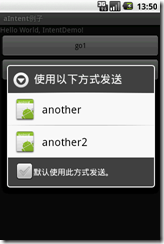
<action android:name="android.intent.action.EDIT" />对应的Activity,如果对应为多个activity具有<action android:name="android.intent.action.EDIT" />此时就会弹出一个dailog选择Activity,如下图:
Activity之间数据的传递:
首先需要使用到的是Bundle
String path = file.getAbsolutePath();
String name = file.getName();
Intent intent = new Intent(FileBrowser.this,MainActivity.class);
Bundle bundle=new Bundle();
bundle.putString("path",path );
bundle.putString("name", name);
intent.putExtras(bundle);
startActivity(intent);
首先,示例中创建了一个Intent的实例,用于转换Activity,同时,从该Activity中的变量获取了需要传递的数据;
其次是bundle.putXXX()方法的调用,向bundle中填充数据
| void | putInt(String key, int value)
Inserts an int value into the mapping of this Bundle, replacing any existing value for the given key.
|
| void | putIntArray(String key, int[] value)
Inserts an int array value into the mapping of this Bundle, replacing any existing value for the given key.
|
| void | putLong(String key, long value)
Inserts a long value into the mapping of this Bundle, replacing any existing value for the given key.
|
| void | putBoolean(String key, boolean value)
Inserts a Boolean value into the mapping of this Bundle, replacing any existing value for the given key.
|
| void | putBooleanArray(String key, boolean[] value)
Inserts a boolean array value into the mapping of this Bundle, replacing any existing value for the given key.
|
| void | putAll(Bundle map)
Inserts all mappings from the given Bundle into this Bundle.
|
| void | putString(String key, String value)
Inserts a String value into the mapping of this Bundle, replacing any existing value for the given key.
|
| void | putStringArray(String key, String[] value)
Inserts a String array value into the mapping of this Bundle, replacing any existing value for the given key.
|
| void | putStringArrayList(String key, ArrayList<String> value)
Inserts an ArrayList value into the mapping of this Bundle, replacing any existing value for the given key.
|
然后调用intent.putExtras(bundle),将bundle绑定在intent上,最后startActivity();
数据的接收:
Bundle bd = intent.getExtras();
String str_path = bd.getString("path");
String str_name = bd.getString("name");
text = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.tv_address);
name = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.tv_name);
text.setText(str_path);
name.setText(str_name);