凸包
定义
在二维欧几里得空间中,凸包可想象为一条刚好包着所有点的橡皮圈。
用不严谨的话来讲,给定二维平面上的点集,凸包就是将最外层的点连接起来构成的凸多边形,它能包含点集中所有的点。

实现
graham (葛立恒)扫描法
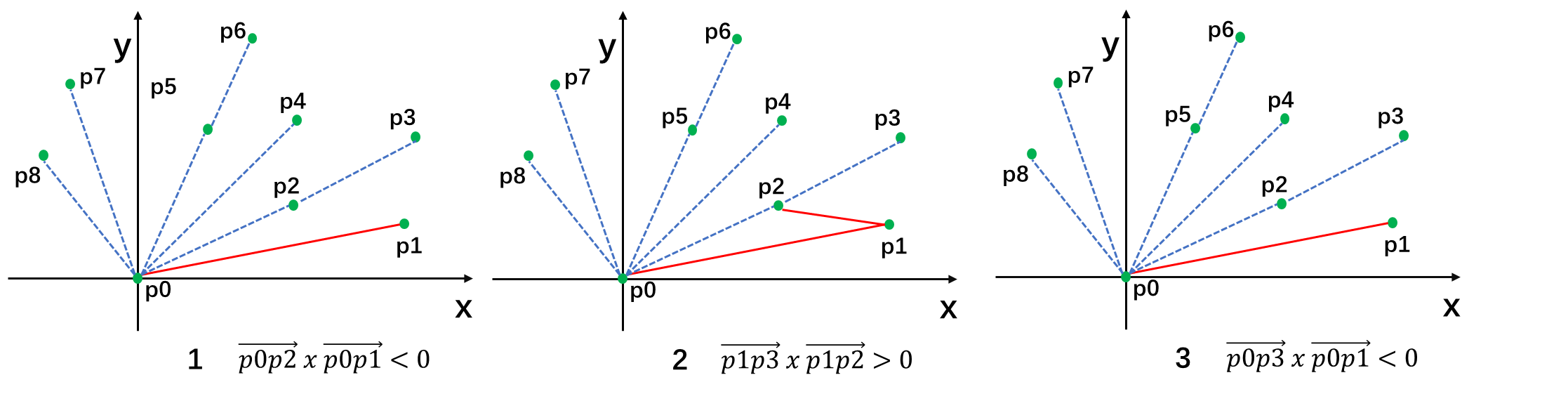
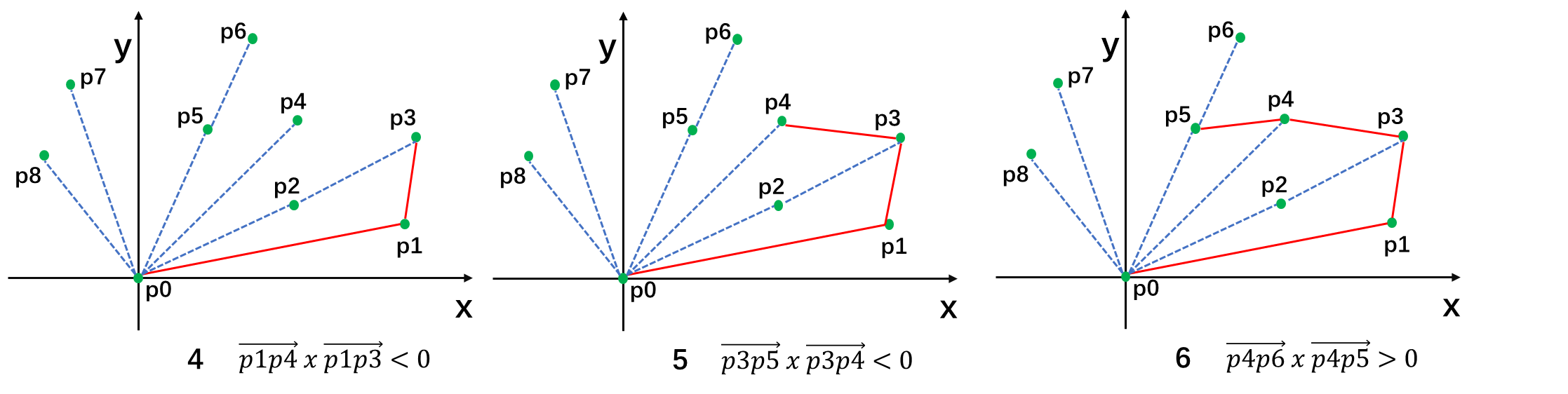
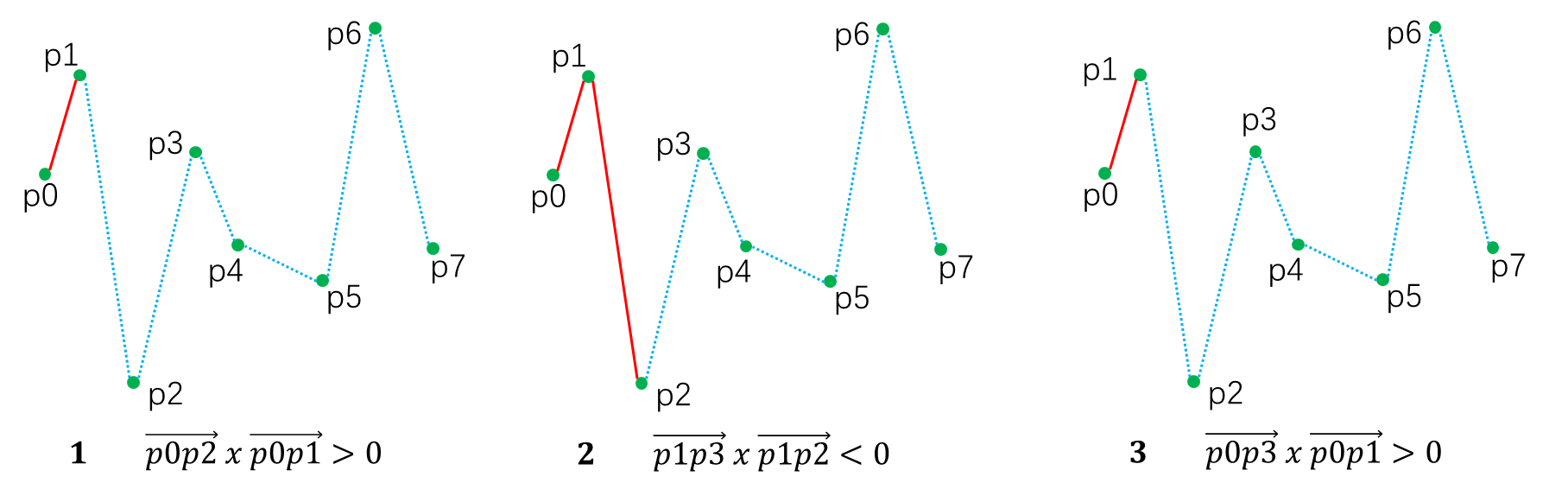
① 找到所有点中最左下角的点 p0。(按 x 升序排列,如果 x 相同,则按 y 升序排列)
② 以 p0 为基准求所有点的极角,并按照极角排序 (按极角升序排列,若极角相同,则按 x 升序排列),设这些点为p1,p2,……,pn-1 。
③ 建立一个栈,p0、p1 进栈,对于 P[2..n-1]的每个点,利用叉积判断,若栈顶的两个点与它不构成"向左转"的关系,则将栈顶的点出栈,直至没有点需要出栈以后,将当前点进栈。
④ 所有点处理完之后栈中保存的点就是凸包了。

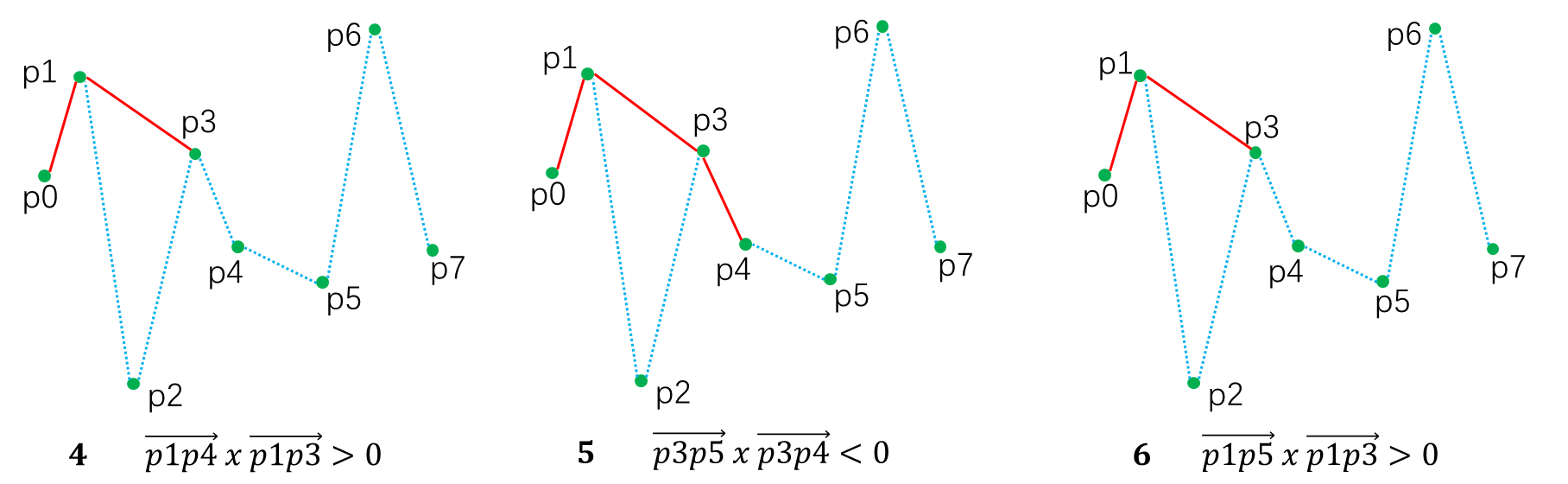
Andrew算法 (安德鲁)
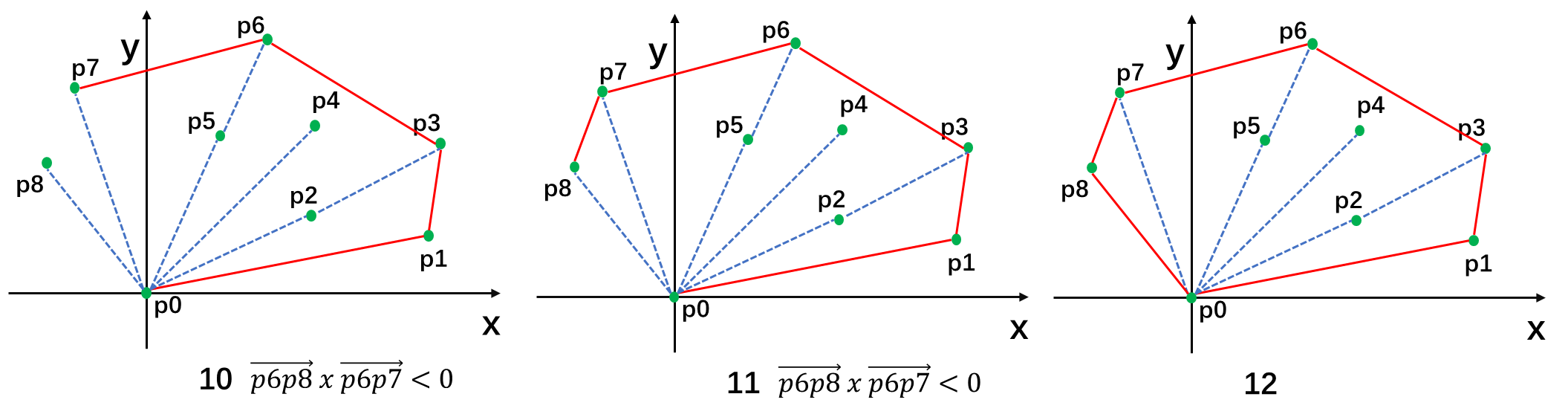
① 将给定集的点按 x 坐标升序排列。x 相同的按 y 坐标升序排列。
② 按下述流程创建凸包的上部。
🔰 将排序后的点按照 x 坐标从小到大顺序加入凸包 U 中。
若新加入的点使得 U 不再是凸多边形,则逆序删除之前加入 U 的点,直至 U 重新成为凸多边形为止。
③ 按下述流程创建凸包的下部。
🔰 将排序后的点按照 x 坐标从大到小顺序加入凸包 L 中。
若新加入的点使得 L 不再是凸多边形,则逆序删除之前加入 L 的点,直至 L 重新成为凸多边形为止。
👍 上凸包和下凸包即为凸包(注意处理重复点)
Andrew算法为Graham扫描法的一种变体,两种算法都是对所有的点进行扫描得到凸包,但是在扫描之前做了不同的处理。

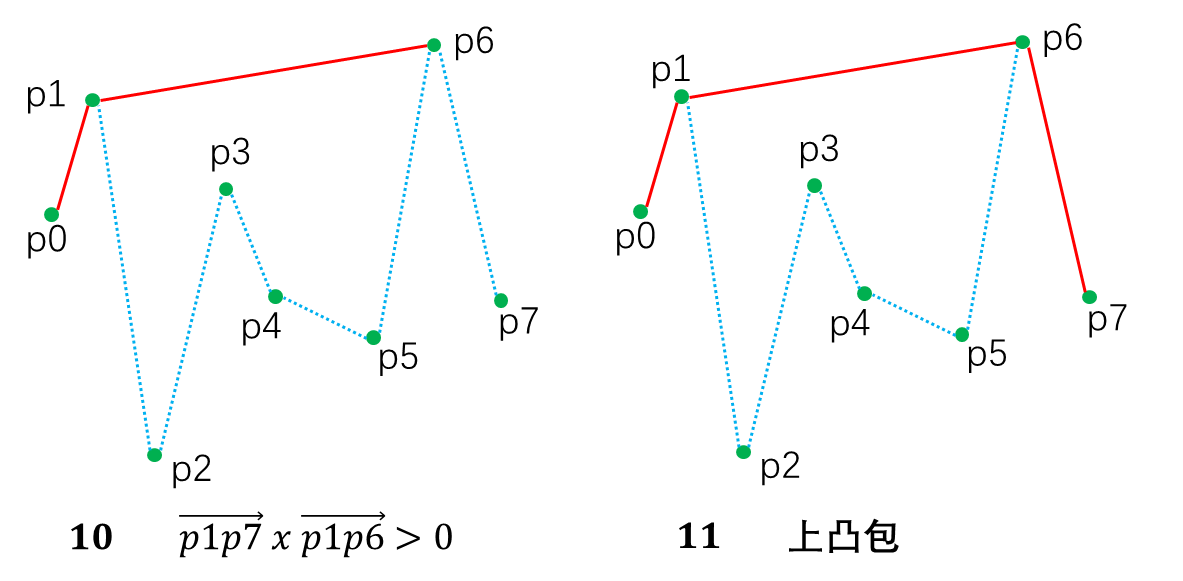
下凸包从p7,p5开始,从右往左扫描。
下凸包与上凸包类似,不在赘述。
graham 扫描法
//graham
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int x,y;
node(){}
node(int a,int b) {x=a;y=b;}
bool operator <(const node &n) const
{
if(x!=n.x) return x<n.x;
else return y<n.y;
}
};
vector<node> P;
node sta[150];
int n,top;
bool cmp(node a,node b);
void Convex_Hull();
int cross(node a,node b, node c);
double cal();
double dis(node a,node b);
int main()
{
int i,x,y;
while(~scanf("%d",&n)&&n)
{
P.clear();
if(n<=1) printf("%.2lf",0.0);
else
{
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
P.push_back(node(x,y));
}
Convex_Hull();
printf("%.2lf\n",cal());
}
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
bool cmp(node a,node b)
{
double A,B;
A=atan2(a.y-P[0].y,a.x-P[0].x);
B=atan2(b.y-P[0].y,b.x-P[0].x);
if(A!=B) return A<B;
else return a.x<b.x;
}
int cross(node a, node b, node c)
{return (b.x-a.x)*(c.y-a.y)-(b.y-a.y)*(c.x-a.x);}
double dis(node a,node b)
{return sqrt((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)+(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y));}
void Convex_Hull()
{
top=-1;
sort(P.begin(),P.end());
sort(P.begin()+1,P.end(),cmp);
sta[++top]=P[0]; sta[++top]=P[1];
for(int i=2;i<n;)
{
if(top&&cross(sta[top-1],P[i],sta[top])>=0) top--;
else sta[++top]=P[i++];
}
}
double cal()
{
if(top==1) return dis(sta[0],sta[1]);
double ans=0;
sta[++top]=sta[0];
for(int i=1;i<=top;i++) ans+=dis(sta[i],sta[i-1]);
return ans;
}
Andrew算法
//Andrew
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int x,y;
node(){}
node(int a,int b) {x=a;y=b;}
bool operator <(const node &n) const
{
if(x!=n.x) return x<n.x;
else return y<n.y;
}
};
vector<node> P;
node sta[150];
int n,top;
void Convex_Hull();
int cross(node a,node b, node c);
double cal();
double dis(node a,node b);
int main()
{
int i,x,y;
while(~scanf("%d",&n)&&n)
{
P.clear();
if(n<=1) printf("%.2lf",0.0);
else
{
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
P.push_back(node(x,y));
}
Convex_Hull();
printf("%.2lf\n",cal());
}
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
int cross(node a, node b, node c)
{return (b.x-a.x)*(c.y-a.y)-(b.y-a.y)*(c.x-a.x);}
double dis(node a,node b)
{return sqrt((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)+(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y));}
void Convex_Hull()
{
sort(P.begin(),P.end());
int i,s;
top=-1;
for(i=0;i<n;)
{
if(top>0&&cross(sta[top-1],P[i],sta[top])<=0) top--;
else sta[++top]=P[i++];
}
s=top;
for(i=n-2;i>=0;)
{
if(top>s&&cross(sta[top-1],P[i],sta[top])<=0) top--;
else sta[++top]=P[i--];
}
top--;
}
double cal()
{
if(top==1) return dis(sta[0],sta[1]);
double ans=0;
sta[++top]=sta[0];
for(int i=1;i<=top;i++) ans+=dis(sta[i],sta[i-1]);
return ans;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号