ABC 273 ABCD
https://atcoder.jp/contests/abc273
A - A Recursive Function
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<LL,LL> PII;
const LL N=500200,M=2002;
LL f[N];
int main()
{
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0); ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
LL T=1;
//cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
LL n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++)
{
if(i==0) f[i]=1;
else f[i]=i*f[i-1];
}
cout<<f[n]<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
B - Broken Rounding
题目大意:
给定一个数字,找和10^i离得最近的数字。
Sample Input 1
2048 2
Sample Output 1
2100
好像前几天刚写了一个cf长得极其相似的题目。
学学佬儿的写法
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<LL,LL> PII;
const LL MAXN=1e18;
const LL N=500200,M=2002;
LL f[N];
int main()
{
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0); ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
LL T=1;
//cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
LL n,k;
cin>>n>>k;
for(int i=0;i<=15;i++)
{
if(i==0) f[i]=1;
else f[i]=f[i-1]*10;
//cout<<f[i]<<" ";
}
//cout<<endl;
for(int i=1;i<=k;i++)
{
LL mod=n%f[i];
if(mod<f[i]/2) n-=mod;
else n+=(-mod)+f[i];
}
cout<<n<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
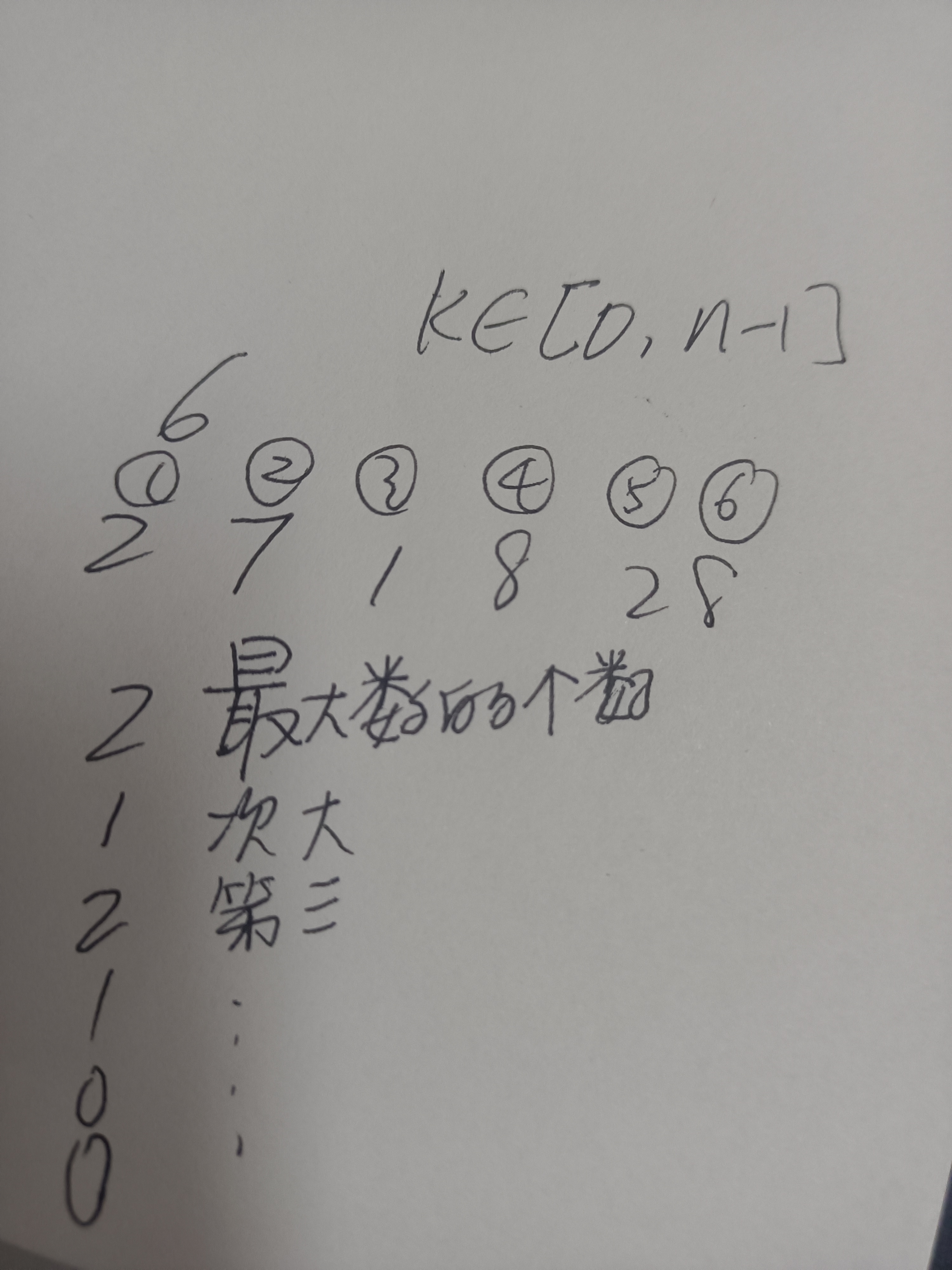
C - (K+1)-th Largest Number
题目大意:
看得懂的自己看吧,看不懂的看图描述。
(反正我是服了这出题人,读题读了两天,还是找的别人的题解才看懂的意思)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<LL,LL> PII;
const LL N=500200,M=2002;
LL a[N];
int main()
{
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0); ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
LL T=1;
//cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
LL n;
cin>>n;
set<LL> s;
map<LL,LL> mp;
for(LL i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
LL x;
cin>>x;
mp[x]++;//记录个数
s.insert(x);//自动排列
}
LL len=s.size();
LL k=0;
for(auto i:s)
{
k++;
a[len-k]=mp[i];//因为是从第0个位置开始放置最大值的个数
}
for(LL i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cout<<a[i]<<endl;//按照从0到n的顺序输出。其实1到n也行(上面改一下)
}
}
return 0;
}
D - LRUD Instructions
题目大意:
给定一个h*w的矩阵,再给定初始位置(rs,cs)
有n个障碍物,障碍物不可以进入也不可以跨越;
有q条指令:指令每次都有LRUD四个方向,然后还有行进的步数。
当碰到障碍物时即可停止,问我们每一步操作后到达的位置是在哪里?
Sample Input 2
6 6 6 3
7
3 1
4 3
2 6
3 4
5 5
1 1
3 2
10
D 3
U 3
L 2
D 2
U 3
D 3
U 3
R 3
L 3
D 1
Sample Output 2
6 3
5 3
5 1
6 1
4 1
6 1
4 1
4 2
4 1
5 1
(模拟题) 题目意思倒是不难,难的是如何省时判断以及移动,写法如何优化
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<LL,LL> PII;
const LL MAXN=1e18;
const LL N=5000200,M=2002;
LL h,w,rs,cs,n,q;
set<LL>::iterator it;
map<LL,set<LL>> row,col;
int main()
{
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0); ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int T=1;
//cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
cin>>h>>w>>rs>>cs;
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
LL r,c;
cin>>r>>c;
row[r].insert(c);
col[c].insert(r);
}
cin>>q;
while(q--)
{
char op;
int x;
cin>>op>>x;
if(op=='L')//不改变x,左移y
{
//插入左右边界
row[rs].insert(0);
row[rs].insert(w+1);
it=row[rs].upper_bound(cs);//因为找的是比当前x第一大的数字,所以就找到了后面的大的第一个,但是我们想要的是左边的最后一个(也就是和cs挨的最近的)
it--;//所以--就找到啦!
cs=max(cs-x,(*it)+1);//因为有可能还是在0的位置上,要保证不出界
}
else if(op=='R')//不改变x,右移y
{
//插入左右边界
row[rs].insert(0);
row[rs].insert(w+1);
it=row[rs].upper_bound(cs);//这里就是正常的找的比cs大一丢丢的最近的数字
cs=min(cs+x,(*it)-1);//但是也是不可以出界o
}
else if(op=='U')//不改变y,上移x
{
//插入上下边界
col[cs].insert(0);
col[cs].insert(h+1);
//与第一个if情况类似,因为我们找的是比rs小一丢丢的数字,但是找到了比它大一丢丢的数字,所以直接--
it=col[cs].upper_bound(rs);
it--;//这样就可以直接找到这个数字的位置
rs=max(rs-x,(*it)+1);
}
else if(op=='D')//不改变y,下移x
{
//插入上下边界
col[cs].insert(0);
col[cs].insert(h+1);
it=col[cs].upper_bound(rs);//正常比它大一丢丢的数字
rs=min(rs+x,(*it)-1);//但是以防出界,还是得--一个位置
}
cout<<rs<<" "<<cs<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
好好学学写法
本文作者:Vivian-0918
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/Vivian-0918/p/16859201.html
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步