OpenCv 028---图像积分图算法
1 前备知识
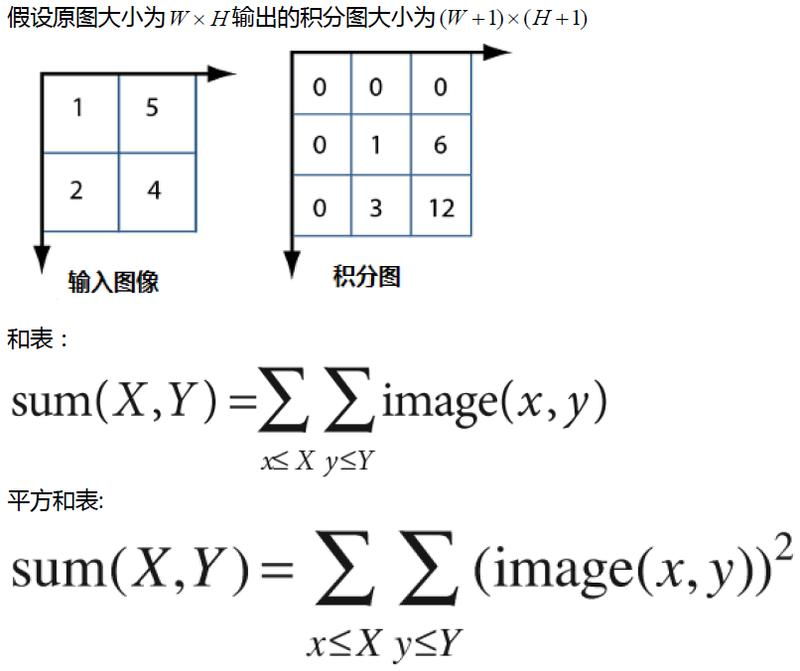
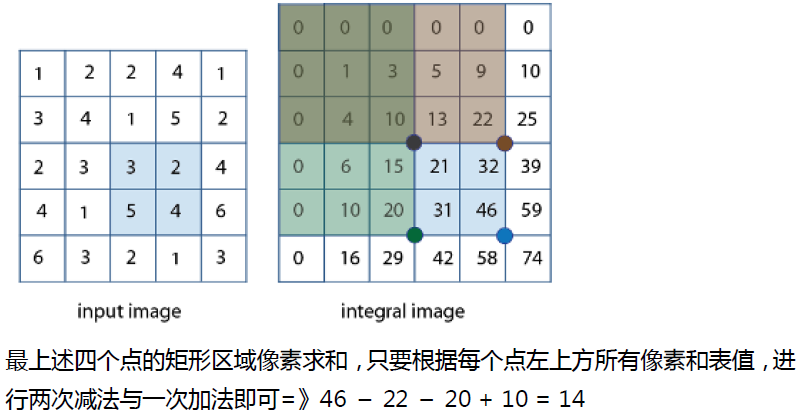
积分图像是Crow在1984年首次提出,是为了在多尺度透视投影中提高渲染速度,是一种快速计算图像区域和与平方和的算法。其核心思想是对每个图像建立自己的积分图查找表,在图像积分处理计算阶段根据预先建立的积分图查找表,直接查找从而实现对均值卷积线性时间计算,做到了卷积执行的时间与半径窗口大小的无关联。图像积分图在图像特征提取HAAR/SURF、二值图像分析、图像相似相关性NCC计算、图像卷积快速计算等方面均有应用,是图像处理中的经典算法之一。 图像积分图建立与查找 在积分图像(Integral Image - ii)上任意位置(x, y)处的ii(x, y)表示该点左上角所有像素之和, 其中(x,y)是图像像素点坐标。
2 所用到的主要OpenCv API
*
3 程序代码
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp> #include <iostream> using namespace cv; using namespace std; void blur_demo(Mat &image, Mat &sum); void edge_demo(Mat &image, Mat &sum); int getblockSum(Mat &sum, int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int i); int main(int argc, char** argv) { Mat src = imread("images/lena.png"); if (src.empty()) { printf("could not load image...\n"); return -1; } namedWindow("input", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE); imshow("input", src); namedWindow("output", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE); // 计算积分图 Mat sum, sqrsum; integral(src, sum, sqrsum, CV_32S, CV_32F); // 积分图应用 int type = 0; while (true) { char c = waitKey(100); if (c > 0) { type = (int)c; printf("c : %d\n", type); } if (c == 27) { break; // ESC } if (type == 49) { // 数字键 1 blur_demo(src, sum); } else if (type == 50) { // 数字键 2 edge_demo(src, sum); } else { blur_demo(src, sum); } } waitKey(0); return 0; } void blur_demo(Mat &image, Mat &sum) { int w = image.cols; int h = image.rows; Mat result = Mat::zeros(image.size(), image.type()); int x2 = 0, y2 = 0; int x1 = 0, y1 = 0; int ksize = 5; int radius = ksize / 2; int ch = image.channels(); int cx = 0, cy = 0; for (int row = 0; row < h + radius; row++) { y2 = (row + 1)>h ? h : (row + 1); y1 = (row - ksize) < 0 ? 0 : (row - ksize); for (int col = 0; col < w + radius; col++) { x2 = (col + 1)>w ? w : (col + 1); x1 = (col - ksize) < 0 ? 0 : (col - ksize); cx = (col - radius) < 0 ? 0 : col - radius; cy = (row - radius) < 0 ? 0 : row - radius; int num = (x2 - x1)*(y2 - y1); for (int i = 0; i < ch; i++) { // 积分图查找和表,计算卷积 int s = getblockSum(sum, x1, y1, x2, y2, i); result.at<Vec3b>(cy, cx)[i] = saturate_cast<uchar>(s / num); } } } imshow("output", result); imwrite("D:/result.png", result); } /** * 3x3 sobel 垂直边缘检测演示 */ void edge_demo(Mat &image, Mat &sum) { int w = image.cols; int h = image.rows; Mat result = Mat::zeros(image.size(), CV_32SC3); int x2 = 0, y2 = 0; int x1 = 0, y1 = 0; int ksize = 3; // 算子大小,可以修改,越大边缘效应越明显 int radius = ksize / 2; int ch = image.channels(); int cx = 0, cy = 0; for (int row = 0; row < h + radius; row++) { y2 = (row + 1)>h ? h : (row + 1); y1 = (row - ksize) < 0 ? 0 : (row - ksize); for (int col = 0; col < w + radius; col++) { x2 = (col + 1)>w ? w : (col + 1); x1 = (col - ksize) < 0 ? 0 : (col - ksize); cx = (col - radius) < 0 ? 0 : col - radius; cy = (row - radius) < 0 ? 0 : row - radius; int num = (x2 - x1)*(y2 - y1); for (int i = 0; i < ch; i++) { // 积分图查找和表,计算卷积 int s1 = getblockSum(sum, x1, y1, cx, y2, i); int s2 = getblockSum(sum, cx, y1, x2, y2, i); result.at<Vec3i>(cy, cx)[i] = saturate_cast<int>(s2 - s1); } } } Mat dst, gray; convertScaleAbs(result, dst); normalize(dst, dst, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX); cvtColor(dst, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY); imshow("output", gray); imwrite("D:/edge_result.png", gray); } int getblockSum(Mat &sum, int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int i) { int tl = sum.at<Vec3i>(y1, x1)[i]; int tr = sum.at<Vec3i>(y2, x1)[i]; int bl = sum.at<Vec3i>(y1, x2)[i]; int br = sum.at<Vec3i>(y2, x2)[i]; int s = (br - bl - tr + tl); return s; }
4 运行结果
5 扩展及注意事项
6*目前只做大概了解,知道有这一算法,后续具体使用再做具体分析
One day,I will say
"I did it"



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号