现代软件工程个人作业——词频统计(字符数、行数、单词数、高频单词和词组)
现代软件工程课的第一次个人作业博主做的相当差劲,让我清楚地意识到自己与他人的差距。
通过这篇博客博主将展示自己是如何走上事倍功半的歧路,认真分析错误原因,希望大家不要重蹈我的覆辙。
首先让我们来看一下作业要求:详细要求在邓宏平老师的博客:第一次个人作业——词频统计
这次词频统计的主要功能有:
1. 统计文件的字符数(只需要统计Ascii码,汉字不用考虑,换行符不用考虑,'\0'不用考虑)(ascii码大小在[32,126]之间)
2. 统计文件的单词总数
3. 统计文件的总行数(任何字符构成的行,都需要统计)(不要只看换行符的数量,要小心最后一行没有换行符的情形)(空行算一行)
4. 统计文件中各单词的出现次数,对给定文件夹及其递归子文件夹下的所有文件进行统计
6. 统计两个单词(词组)在一起的频率,输出频率最高的前10个。
注意:
a) 空格,水平制表符,换行符,均算字符
b) 单词的定义:至少以4个英文字母开头,跟上字母数字符号,单词以分隔符分割,不区分大小写。
英文字母:A-Z,a-z
字母数字符号:A-Z,a-z,0-9
分割符:空格,非字母数字符号
例如:”file123”是一个单词,”123file”不是一个单词。file,File和FILE是同一个单词。
如果两个单词只有最后的数字结尾不同,则认为是同一个单词,例如,windows,windows95和windows7是同一个单词,iPhone4和IPhone5是同一个单词,但是,windows和windows32a是不同的单词,因为他们不是仅有数字结尾不同。输出按字典顺序,例如,windows95,windows98和windows2000同时出现时,输出windows2000。单词长度只需要考虑[4, 1024],超出此范围的不用统计。
c)词组的定义:windows95 good, windows2000 good123,可以算是同一种词组。按照词典顺序输出。三词相同的情形,比如good123 good456 good789,根据定义,则是 good123 good123 这个词组出现了两次。
good123 good456 good789这种情况,由于这三个单词与good123都是同一个词,最终统计结果是good123 good123这个词组出现了2次。
两个单词分属两行,也可以直接组成一个词组。统计词组,只看顺序上,是否相邻。
d) 输入文件名以命令行参数传入。需要遍历整个文件夹时,则要输入文件夹的路径。
e) 输出文件result.txt
characters: number
words: number
lines: number
<word>: number
<word>为文件中真实出现的单词大小写格式,例如,如果文件中只出现了File和file,程序不应当输出FILE,且<word>按字典顺序(基于ASCII)排列,上例中程序应该输出File: 2
f) 根据命令行参数判断是否为目录
g) 将所有文件中的词汇,进行统计,最终只输出一个整体的词频统计结果。
评分标准
1. 统计文件的字符数(1分)
2. 统计文件的单词总数(1分)
3. 统计文件的总行数(1分)
4. 统计文件中各单词的出现次数(1分)
5. 对给定文件夹及其递归子文件夹下的所有文件进行统计(2分)
6. 统计两个单词(词组)在一起的频率,输出频率最高的前10个(2分)
以上六个结果输出错误则对应子任务得-1分,全部输出正确则按运行时间确定排名(用时按升序前30%得满分8分,30%-70%得7.5分,后30%得7分)。
7. 博客撰写(代码实现过程,性能分析、优化报告等)(2分)
8. 在Linux系统下,进行性能分析,过程写到blog中(附加题,2分)
完成时间:一周之内
需求分析:
1.统计字符数和行数容易实现。
2.统计单词总数:作业要求中对单词的定义,是4个英文字母开头,后跟零个或多个英文字母或数字,单词长度在[4,1024]之间。一般来说匹配一定格式的字符串都用正则表达式和迭代器来实现。
3.统计统计文件中各单词的出现次数,并输出出现频率最高的10个:单词存放于容器中,没出现一个新单词需要查找它是不是已经存在了,如果存在的话单词频率 加一,否则将单词加入容器。如何实现判断单词相等和不等是重要的一点。将所有单词收集到容器后需要根据出现频率对单词进行排序,并输出频率最高的10个。
4.输出出现频率最高的10个词组:相邻的两个单词组成一个词组,也需要查重和依频率排序。
5.对给定文件夹及其递归子文件夹下的所有文件进行统计:判断是目录还是文件,如果是目录,需要获取目录下文件的名字再对文件进行处理。
接下来博主就走上了错误的第一步:选择了不熟悉的编程语言
一般来说,要在短时间内完成复杂和难度较高的工程,应该选择你熟悉的编程语言。
博主会 对C比较熟悉但是没有系统学过C++,希望通过这门课的实践可以把C++学起来。结果博主天真地看了一整天的Primer C++(╯°Д°)╯,第二天就急躁躁地开始编程了。相信很多人都知道这本经典有多么晦涩难懂,可想而知一天下来我能吸收多少知识。事实上,更多的时间应该用来进一步分析需求,有针对性地查找解决方法,综合功能和性能的考虑设计多个方案,在比较、测试过后筛选出合理的方案。对于这个作业我还是推荐用C++写的,只是日程这么紧张的情况下,时间应该多分配给需求分析和前期构建的工作,C++上面的新知识可以现查现学。
结果,博主又走错了路:选择了不合理的数据结构
数据结构是重中之重,要慎之又慎
博主在没有事先了解数据量的情况下选择了vector作为容器,因为它有find函数和sort函数。这种偷懒的行为是极其不可取的。
构建工作应该优先考虑需求,而不是你目前的编程水平或者工作量。
事实上博主考虑过map,但是为什么没有选择它呢,原因主要是我一开始的思路是为单词和词组各定义一个类,在类中存放单词和频率,重构==运算符以便判断是否相等,另外如果相等的单词字典序先于目前这个单词,就修改目前这个单词,如果用map,单词做key,频率作value,可是map不支持修改key值,因为map会自动根据key排序,key是它排序的基础。然后博主就这么把它抛弃了。
其实,可以建立两个map,以单词的简写作为共同的key,一个map的value是单词的完整形式,另一个map的value是单词的频率。(助教的思路)
另外,C++11还支持unordered_map, 它以哈希表为基础,查找时间复杂度只有O(1),而且不会自动根据Key值进行排序,但是占的空间相对较大。不过,对map类进行按值排序,一般需要将map中的数据以pair的形式传递给顺序容器(如我选择的vector)再用sort进行排序。顺序容器可用的sort排序效率都非常高, vector使用的是快速排序。
如果让博主再有一次机会,博主会选什么呢?答案是map。虽然将map中的数据转移到vector中也需要耗费较多地时间,但只需要操作一次,也就是O(n)的复杂度但是vector中的find用的是线性探查,每得到一个新单词都得查重,时间复杂度已经是O(n*n)了。后面博主自己写了hash查找函数,和实时申请内存结合起来就会非常复杂(时间限制博主没有实现(ಥ_ಥ))。综合来看还是用map或unordered map比较合理。
接下来分享代码。
先上第一版,使用了vector可用的stl函数find和sort.
说明:1.这一版程序里面可能还有一些小bug和比较写得比较生涉的地方,欢迎大家指出。05.txt是一份用于测试的文本文件。
2. 将文件里的所有内容读作一个字符串,用来统计字符总数和收集新单词、新词组。
3.从str里面获取新单词是用正则表达式匹配的,具体在getNewExpr函数里。
4.使用sort之前需要定义compare方式或者重构>、<运算符,博主采用前者。
5.getAllFiles函数用于判断路径是目录还是文件,如果是目录的话获取所有文件名并放入一个string类的vector中。
6.阅读源码建议先读类定义然后从main函数开始依照线程阅读。
#include<iostream> #include<fstream> #include<string> #include<sstream> #include<vector> #include<algorithm> #include<cctype> #include<regex> #include<io.h> using namespace std; int begFlag = 1; typedef struct { unsigned int charNum; unsigned int lineNum; unsigned int wordNum; }amount; class word { private: string wordStr; unsigned int freq; public: word() = default; word(string str) { wordStr = str; freq = 1; } string getWordStr() { return wordStr; } unsigned int getFreq() { return freq; } void addFreq() { freq++; } void resetWordStr(string str) { if (str < wordStr) { wordStr = str; } } bool operator == (const word &obj) const { string word1 = this->wordStr, word2 = obj.wordStr; int i = word1.length() - 1; int j = word2.length() - 1; while (i >= 0) { if (word1[i] >= '0'&&word1[i] <= '9') word1[i] = '\0'; else break; i--; } while (j >= 0) { if (word2[j] >= '0'&&word2[j] <= '9') word2[j] = '\0'; else break; j--; } if (i == j) { for (int t = 0; t <= i; t++) { if (word1[t] != word2[t] && abs(word1[t] - word2[t]) != 32) return false; } } else return false; return true; } void printWord(ofstream &output) { output << wordStr << "\t" << freq << endl; } }; class phrase { private: //string phrStr; unsigned int freq; word part1, part2; public: //lack a default constructor phrase(word part1, word part2) { this->part1 = part1; this->part2 = part2; //phrStr = str; freq = 1; } /* string getPhrStr() { return phrStr; } */ word getPart1() { return part1; } word getPart2() { return part2; } unsigned int getFreq() { return freq; } void addFreq() { freq++; } void resetPhrase(phrase &obj) { //string objStr = obj.getPhrStr(); word objPart1 = obj.getPart1(); word objPart2 = obj.getPart2(); // '||' is a short circuit operator if (objPart1.getWordStr() < this->part1.getWordStr() || objPart2.getWordStr() < this->part2.getWordStr()) { this->part1 = objPart1; this->part2 = objPart2; } } bool operator == (const phrase &obj) const { word objPart1 = obj.part1, objPart2 = obj.part2; return (part1 == objPart1 && part2 == objPart2); } void printPhrase(ofstream &output) { string word1 = part1.getWordStr(), word2 = part2.getWordStr(); word1 < word2 ? output << word1 + " " + word2 << "\t" << freq << endl : output << word2 + " " + word1 << "\t" << freq << endl; } }; bool wordCompare(word former, word latter) { return former.getFreq() > latter.getFreq(); } bool phraseCompare(phrase former, phrase latter) { return former.getFreq() > latter.getFreq(); } void examineNewWord(vector<word> &wvec, word &newWord) { vector<word>::iterator beg = wvec.begin(), end = wvec.end(), itr; itr = find(beg, end, newWord); //is there any repition? if (itr != end) { // this word already exists in wvec itr->resetWordStr(newWord.getWordStr()); itr->addFreq(); } else { wvec.push_back(newWord); } } void examineNewPhr(vector<phrase> &pvec, phrase &newPhrase) { vector<phrase>::iterator beg = pvec.begin(), end = pvec.end(), itr; itr = find(beg, end, newPhrase); ////is there any repition? if (itr != end) { itr->resetPhrase(newPhrase); itr->addFreq(); } else { pvec.push_back(newPhrase); } } /* collect all expressions that match the definition of word in the parameter string */ void getNewExpr(string &str, vector<word> &wvec, vector<phrase> &pvec, amount &result) { word newWord; string wordPattern("[[:alpha:]]{4}[[:alnum:]]{0,1020}"); regex reg(wordPattern); //intermediate variables in generating a new phrase //string::size_type pos1, pos2; string newPhrStr = "\0"; word part1("\0"), part2("\0"); phrase newPhrase( part1, part2); /* collect a word in advance, then combine two words and the substring between them into a phrase */ for (sregex_iterator it(str.begin(), str.end(), reg), end_it; it != end_it; it++) { result.wordNum++; newWord = word(it->str()); examineNewWord(wvec, newWord); if (begFlag) { begFlag = 0; part1 = newWord; } else { part2 = newWord; newPhrase = phrase(part1, part2); examineNewPhr(pvec, newPhrase); //pos1 = pos2; part1 = part2; } } } /* calculate the amount of characters with ASCII code within [32,126]*/ unsigned long getCharNum(string &str) { unsigned long charNum = 0; string::iterator end = str.end(), citr; for (citr = str.begin(); citr != end; citr++) { if (*citr >= 32 && *citr <= 126) charNum++; } return charNum; } /* calculate the number of lines in one file */ unsigned long getLineNum(string filename) { ifstream input(filename); unsigned long lines = 0; string str; while (!input.eof()) { getline(input, str); lines++; } return lines; } /* process one file, update the amount of characters and the amount of lines, collect all expressions that match the word definition into wvec. */ void fileProcess(string filename, amount &result, vector<word> &wvec, vector<phrase> &pvec) { ifstream input; stringstream buffer; string srcStr; try { input.open(filename); if (!input.is_open()) { throw runtime_error("cannot open the file"); } } catch (runtime_error err) { cout << err.what(); return ; } if (input.eof()) return; buffer << input.rdbuf(); srcStr = buffer.str(); // update the amount of characters result.charNum += getCharNum(srcStr); //update the amount of lines result.lineNum += getLineNum(filename); //update the wvec getNewExpr(srcStr, wvec, pvec,result); input.close(); } /* print the results in the required format*/ void getResult(const char* resfile, amount &result, vector<word> &wvec, vector<phrase> &pvec) { auto wvecSize = wvec.size(); auto pvecSize = pvec.size(); ofstream output(resfile); output << "char_number :" << result.charNum << endl; output << "line_number :" << result.lineNum << endl; output << "word_number :" << result.wordNum << endl; //sort wvec in descending frequency order vector<word>::iterator wbeg = wvec.begin(), wend = wvec.end(), witr; sort(wbeg, wend, wordCompare); output << " " << endl; output << "the top ten frequency of words" << endl; if(wvecSize){ if (wvecSize < 10) { for (witr = wbeg; witr != wend; witr++) { witr->printWord(output); } } else { vector<word>::iterator wlast = wbeg + 10; for (witr = wbeg; witr != wlast; witr++) { witr->printWord(output); } } } //sort pvec in descending frequency order vector<phrase>::iterator pbeg = pvec.begin(), pend = pvec.end(), pitr; sort(pbeg, pend, phraseCompare); output << " " << endl; output << "the top ten frequency of phrases" << endl; if (pvecSize) { if (pvecSize < 10) { for (pitr = pbeg; pitr != pend; pitr++) { pitr->printPhrase(output); } } else { vector<phrase>::iterator plast = pbeg + 10; for (pitr = pbeg; pitr != plast; pitr++) { pitr->printPhrase(output); } } } } /* determine whether the given path is a directory or a file, if it is a directory, push names of all the files in the directory into fvec*/ int getAllFiles(string path, vector<string> &files) { long hFile = 0; int flag = -1; struct _finddata_t fileinfo; string p; if ((hFile = _findfirst(p.assign(path).append("\\*").c_str(), &fileinfo)) != -1) { flag = 0; while (_findnext(hFile, &fileinfo) == 0) { if ((fileinfo.attrib & _A_SUBDIR)) //if it is a folder { if (strcmp(fileinfo.name, ".") != 0 && strcmp(fileinfo.name, "..") != 0) { //files.push_back(p.assign(path).append("/").append(fileinfo.name));//save filename getAllFiles(p.assign(path).append("/").append(fileinfo.name), files); } } else //it is a file { files.push_back(p.assign(path).append("/").append(fileinfo.name));//文件名 } } _findclose(hFile); } return flag; } int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { amount result; result.charNum = 0; result.lineNum = 0; result.wordNum = 0; vector<word> wvec; vector<phrase> pvec; int dirFlag; vector<string> fvec; string path = "05.txt"; const char* resFile = "AllFiles.txt"; dirFlag = getAllFiles(path, fvec); if (dirFlag == 0) { vector<string>::iterator end = fvec.end(), it; for (it = fvec.begin(); it != end; it++) { fileProcess(*it, result, wvec, pvec); } } else { fileProcess(path, result, wvec, pvec); } getResult(resFile, result, wvec, pvec); system("pause"); }
输出结果:
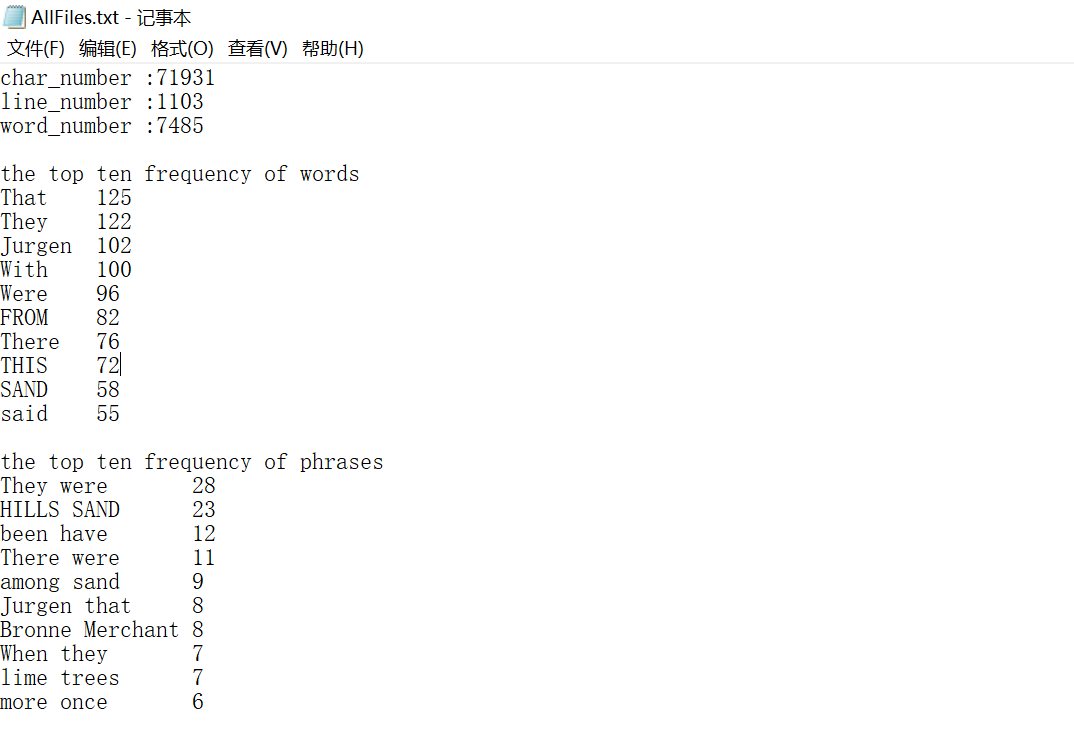
VS性能向导给出的结果:
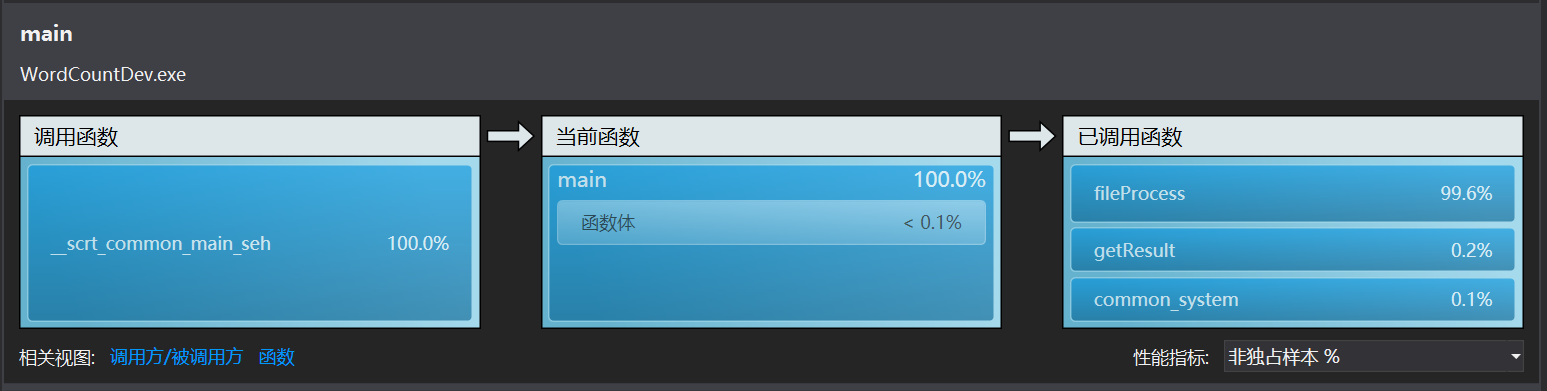
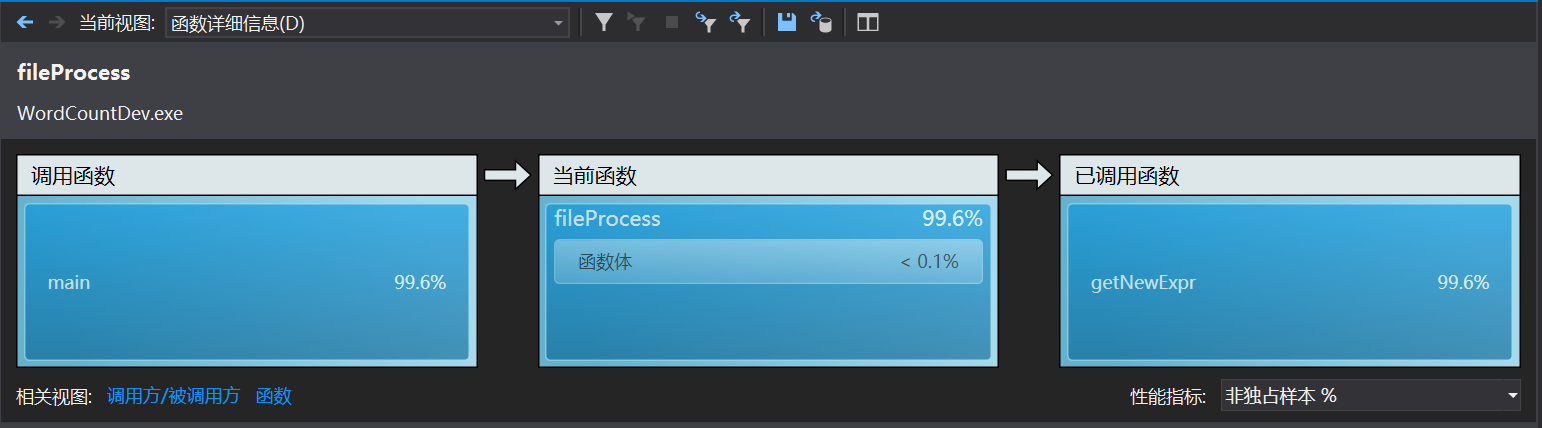
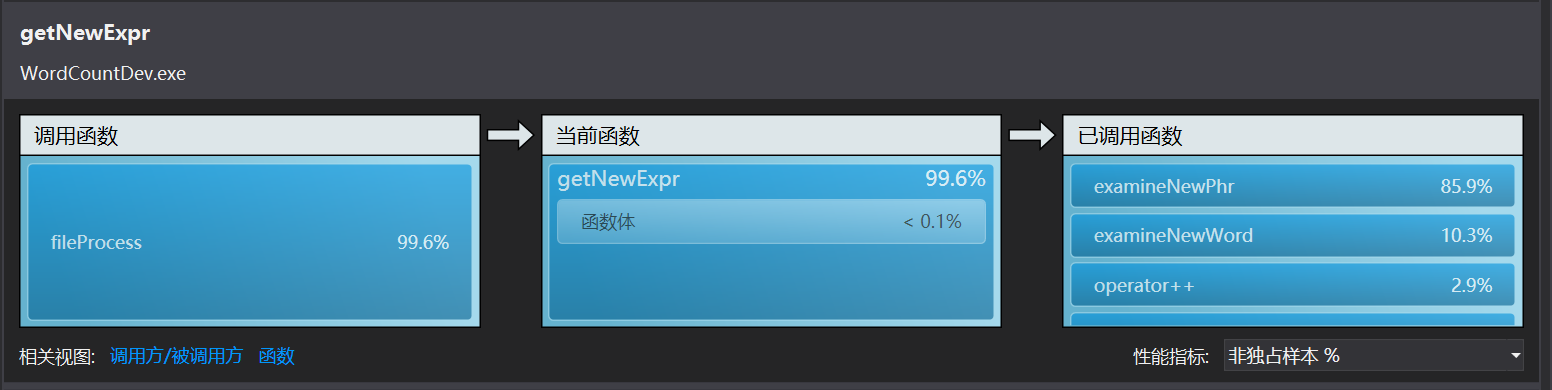
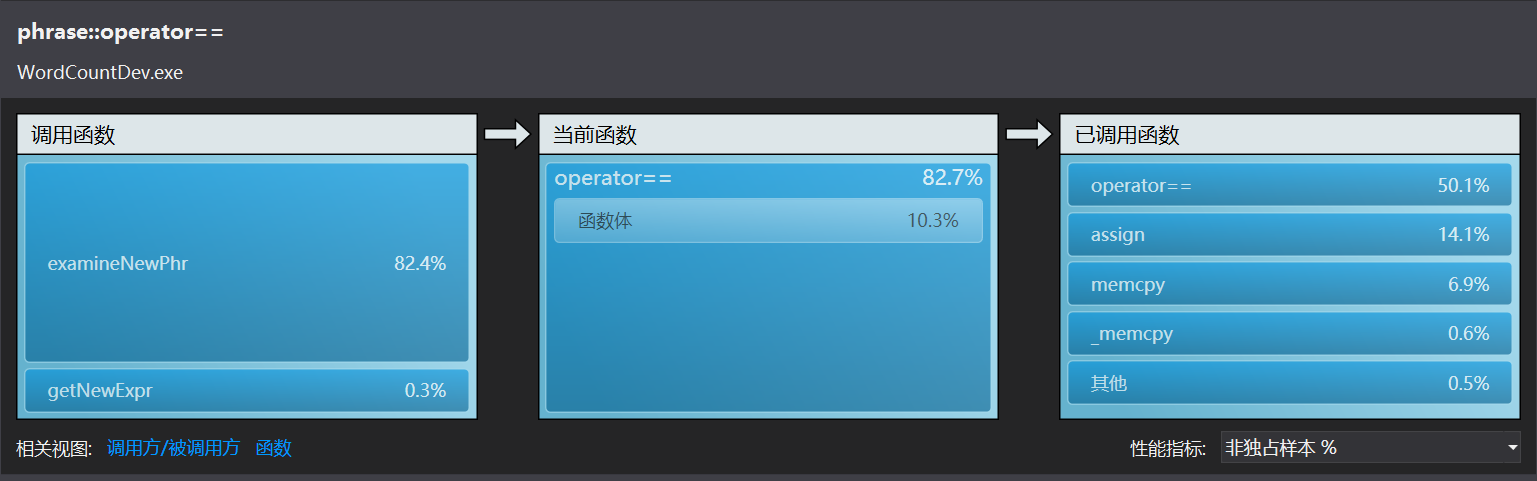
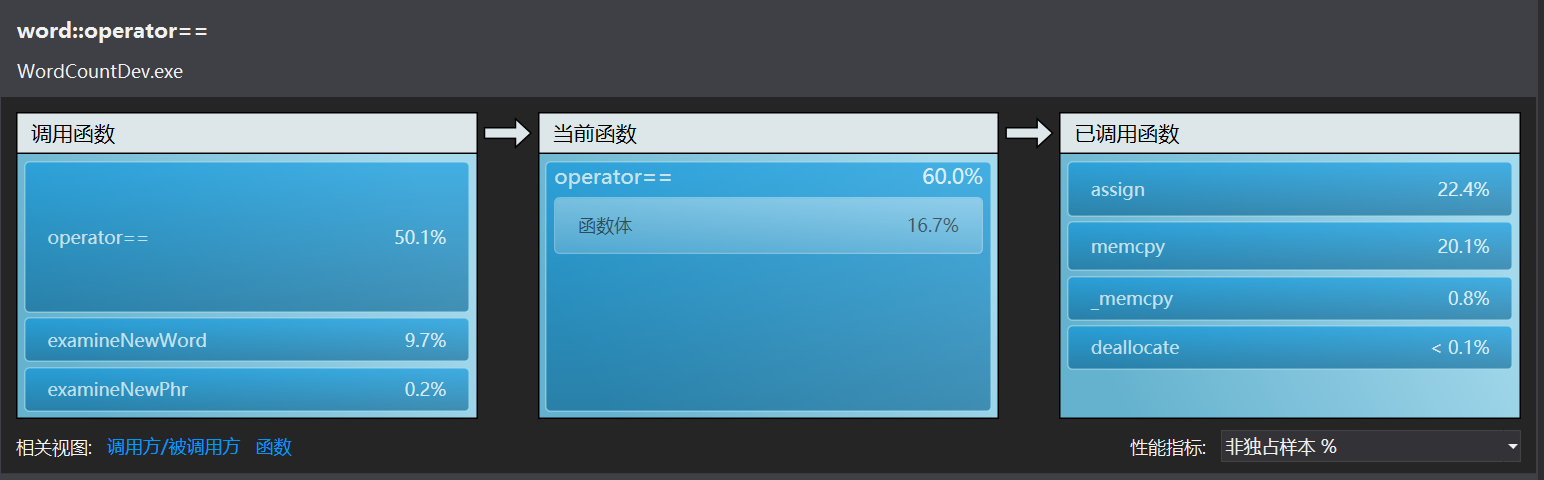
由此可以确定examineNewPhr里的查找过程find非常耗时间,因为find是根据这个重构的运算符来判断是否相等的。
为此,博主决定在vector里面存放一个哈希表。
第二版代码如下:
说明:这一版只实现了单词统计没有实现词组统计。除了word类定义、examineNewWord函数被修改,增加了hash函数外,其他基本没太大的变化。newsample是我们这次作业的测试集,数据量大概175M字节。用上面第一版根本跑不起来。
#include<iostream> #include<fstream> #include<string> #include<sstream> #include<vector> #include<algorithm> #include<cctype> #include<regex> #include<io.h> using namespace std; #define WORD_POOL_SIZE 18000000; #define MAX_FIGURES 20; int begFlag = 1; typedef struct { unsigned int charNum; unsigned int lineNum; unsigned int wordNum; }amount; class word{ public: string wordStr; unsigned int freq; word(string str, unsigned int fre) { wordStr = str; freq = fre; } void resetWordStr(string str) { if (str < wordStr) { wordStr = str; } } bool operator == (const word &obj) const { string word1 = this->wordStr, word2 = obj.wordStr; int i = word1.length() - 1; int j = word2.length() - 1; while (i >= 0) { if (word1[i] >= '0'&&word1[i] <= '9') word1[i] = '\0'; else break; i--; } while (j >= 0) { if (word2[j] >= '0'&&word2[j] <= '9') word2[j] = '\0'; else break; j--; } if (i == j) { for (int t = 0; t <= i; t++) { if (word1[t] != word2[t] && abs(word1[t] - word2[t]) != 32) return false; } } else return false; return true; } void printWord(ofstream &output) { output << wordStr << "\t" << freq << endl; } }; bool wordCompare(word former, word latter) { return former.freq > latter.freq; } unsigned int Hash(string str) { const char *p = str.c_str(); unsigned int seed = 7, key; unsigned long long hash = 0; int figures=0; while (*p!='\0'&& figures<= 20) { hash = hash*seed + (*p); p++; figures++; } key = hash%WORD_POOL_SIZE; return(key); } void examineNewWord(vector<word> &wvec, word &newWord) { string str = newWord.wordStr; int i = str.length() - 1; while (i >= 0) { if (str[i] >= '0'&&str[i] <= '9') { str[i] = '\0'; } else if (str[i]>=97&&str[i]<=122) { str[i] = str[i] - 32; } i--; } unsigned int key = Hash(str); int outOfSlot = 1; int open = 0; vector<word>::iterator beg = wvec.begin(); vector<word>::iterator itr = beg + key; while (outOfSlot) { itr = beg + (itr - beg + open * 13)%WORD_POOL_SIZE; if (itr->wordStr == "\0") { itr->wordStr = newWord.wordStr; itr->freq++; outOfSlot = 0; } else if (*itr == newWord) { itr->resetWordStr(newWord.wordStr); itr->freq++; outOfSlot = 0; } open++; } } void getNewExpr(string &str, vector<word> &wvec, unsigned int &wordNum) { word newWord("\0",1); string wordPattern("[[:alpha:]]{4}[[:alnum:]]{0,1020}"); regex reg(wordPattern); for (sregex_iterator it(str.begin(), str.end(), reg), end_it; it != end_it; it++) { wordNum++; newWord.wordStr = it->str(); examineNewWord(wvec, newWord); } } /* calculate the amount of characters with ASCII code within [32,126]*/ unsigned long getCharNum(string &str) { unsigned long charNum = 0; string::iterator end = str.end(), citr; for (citr = str.begin(); citr != end; citr++) { if (*citr >= 32 && *citr <= 126) charNum++; } return charNum; } /* calculate the number of lines in one file */ unsigned long getLineNum(string filename) { ifstream input(filename); unsigned long lines = 0; string str; while (!input.eof()) { /* if (getline(input, str)) { lines++; }*/ getline(input, str); lines++; } return lines; } void fileProcess(const char* filename, amount &result, vector<word> &wvec) { ifstream input; stringstream buffer; string srcStr; try { input.open(filename); if (!input.is_open()) { throw runtime_error("cannot open the file"); } } catch (runtime_error err) { cout << err.what(); return; } if (input.eof()) return; buffer << input.rdbuf(); srcStr = buffer.str(); // update the amount of characters result.charNum += getCharNum(srcStr); //update the amount of lines result.lineNum += getLineNum(filename); //update the wvec getNewExpr(srcStr, wvec, result.wordNum); input.close(); } /* print the results in the required format*/ void getResult(const char* resfile, amount &result, vector<word> &wvec) { auto wvecSize = wvec.size(); //auto pvecSize = pvec.size(); ofstream output(resfile); output << "char_number :" << result.charNum << endl; output << "line_number :" << result.lineNum << endl; output << "word_number :" << result.wordNum << endl; //sort wvec in descending frequency order vector<word>::iterator wbeg = wvec.begin(), wend = wvec.end(), witr; sort(wbeg, wend, wordCompare); output << " " << endl; output << "the top ten frequency of words" << endl; if (wvecSize) { if (wvecSize < 10) { for (witr = wbeg; witr != wend; witr++) { witr->printWord(output); } } else { vector<word>::iterator wlast = wbeg + 10; for (witr = wbeg; witr != wlast; witr++) { witr->printWord(output); } } } } /* determine whether the given path is a directory or a file, if it is a directory, push names of all the files in the directory into fvec*/ int getAllFiles(string path, vector<string> &files) { long hFile = 0; int flag = -1; struct _finddata_t fileinfo; string p; if ((hFile = _findfirst(p.assign(path).append("\\*").c_str(), &fileinfo)) != -1) { flag = 0; while (_findnext(hFile, &fileinfo) == 0) { if ((fileinfo.attrib & _A_SUBDIR)) //if it is a folder { if (strcmp(fileinfo.name, ".") != 0 && strcmp(fileinfo.name, "..") != 0) { //files.push_back(p.assign(path).append("/").append(fileinfo.name));//save filename getAllFiles(p.assign(path).append("/").append(fileinfo.name), files); } } else //it is a file { files.push_back(p.assign(path).append("/").append(fileinfo.name));//文件名 } } _findclose(hFile); } return flag; } int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { amount result; result.charNum = 0; result.lineNum = 0; result.wordNum = 0; vector<word> wvec(18000000,word("\0",0)); int dirFlag; vector<string> fvec; const char* path = "D:/Visual Studio/newsample"; const char* resFile = "AllFiles.txt"; dirFlag = getAllFiles(path, fvec); if (dirFlag == 0) { vector<string>::iterator end = fvec.end(), it; for (it = fvec.begin(); it != end; it++) { fileProcess(it->c_str(), result, wvec); } } else { fileProcess(path, result, wvec); } getResult(resFile, result, wvec); //system("pause"); }
在来看看VS给出的性能向导报告:
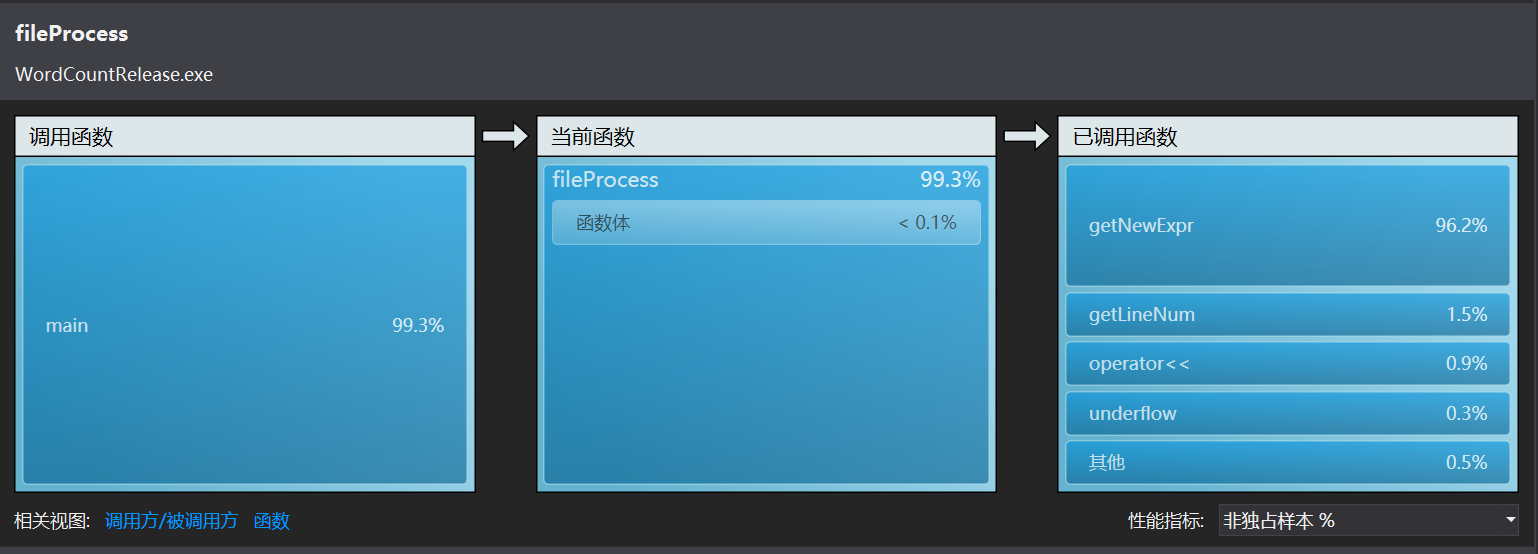
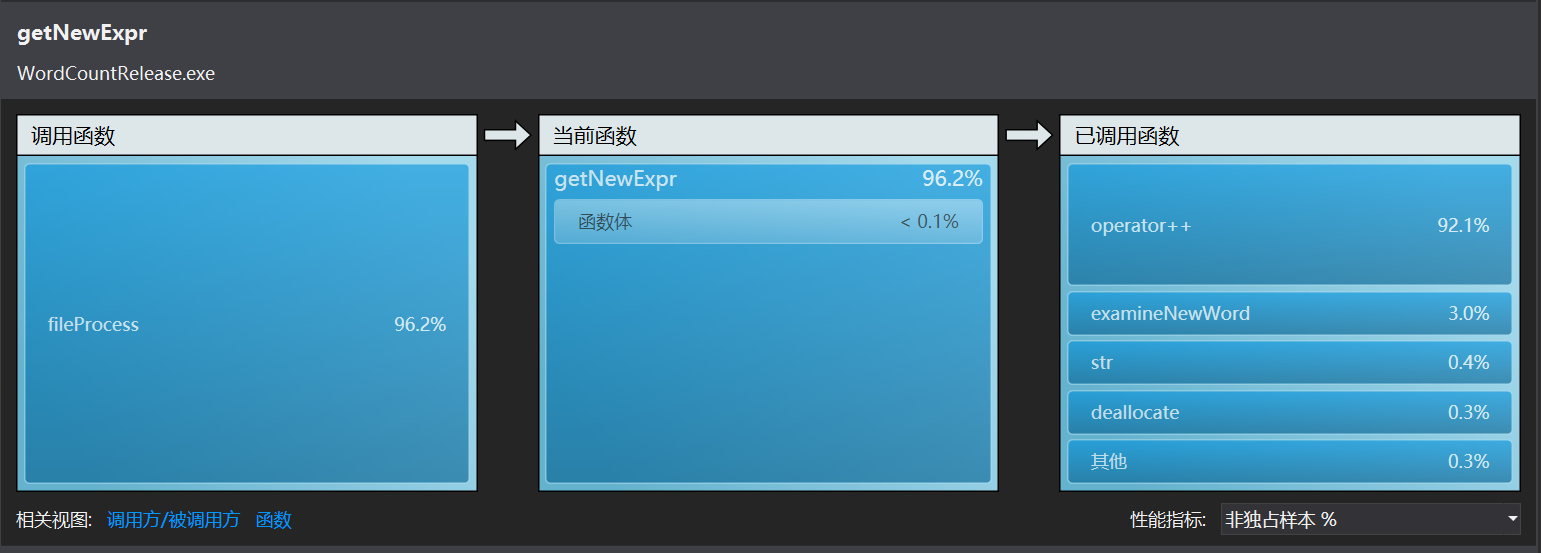
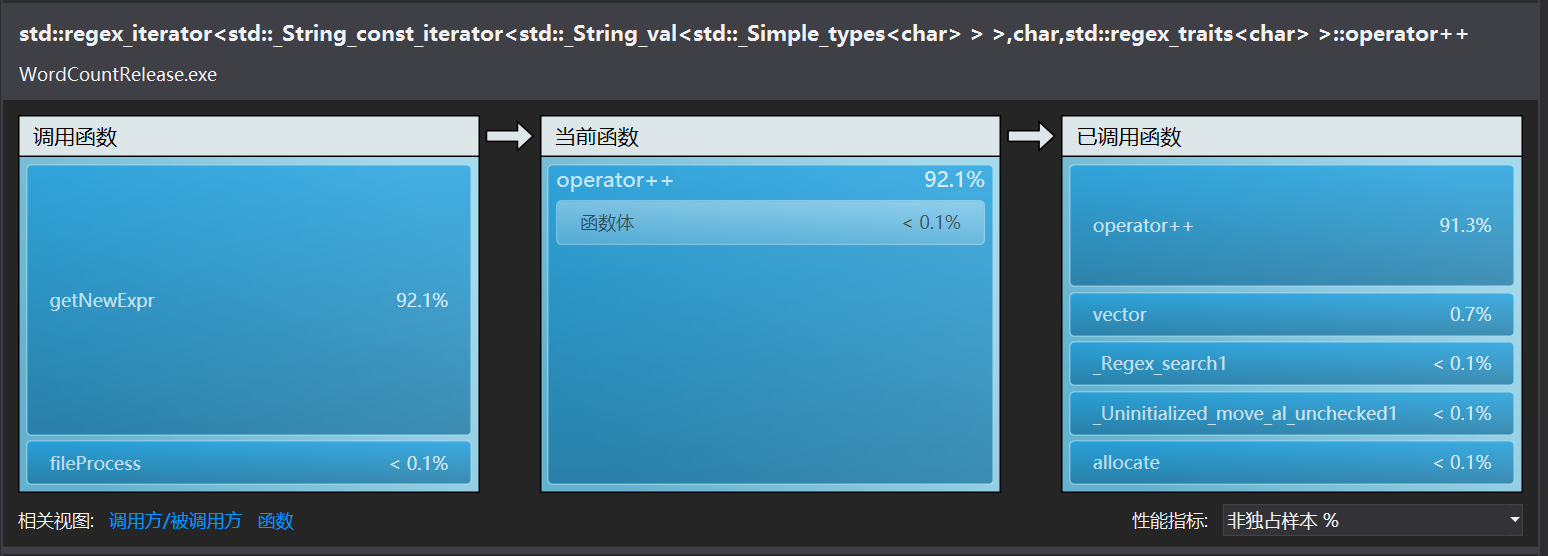
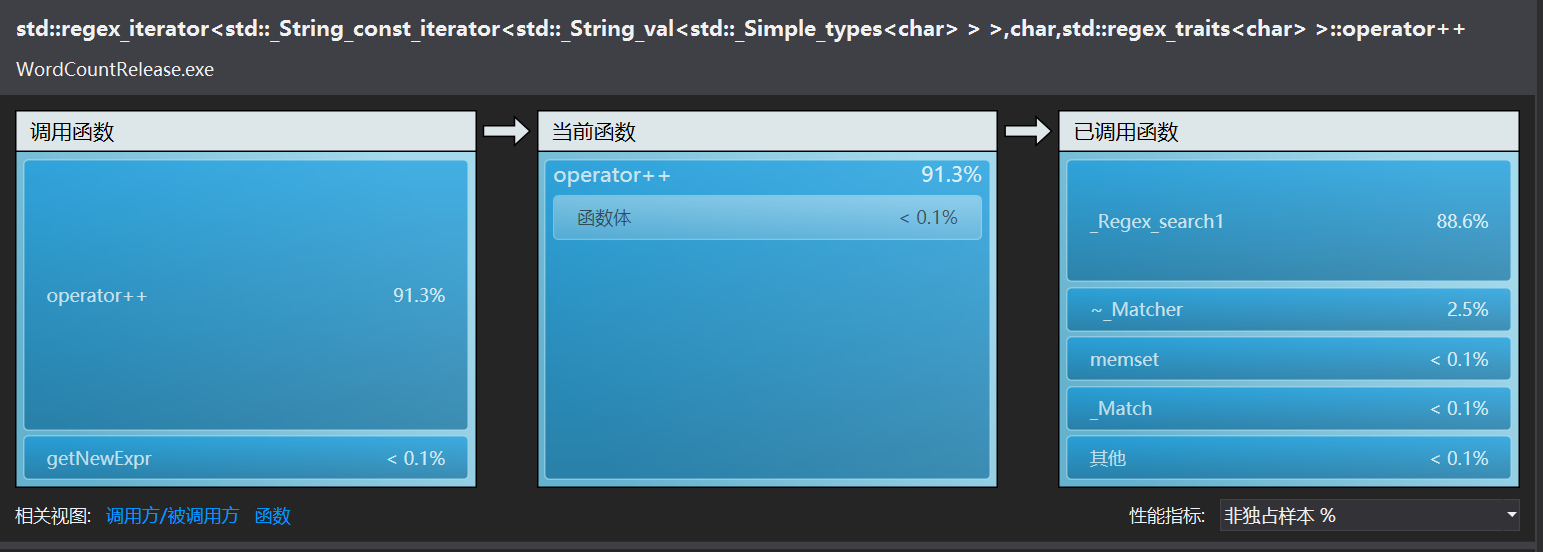
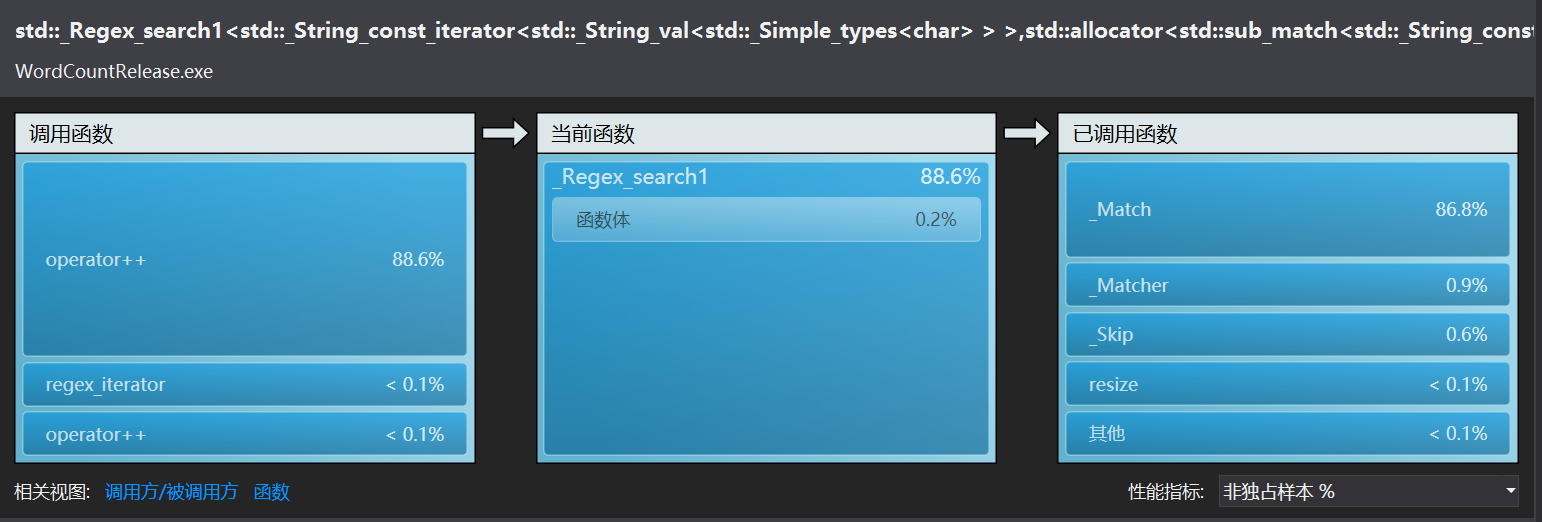
显然查找的效率变高了很多,新的冤大头转移到到了正则表达式匹配上面。
这个问题如何优化,博主暂时还没有进行调查。另外,这一版程序有一个突出的问题就是空间的浪费,即在main函数中直接开size为18000000的vector,这种做法对栈的占用率非常高,由于词组的数目至少是单词的两倍,就需要把vector的空间开到35000000(因为实际结果是33000000多),会导致Stack Overflow问题。这说明我的哈希冲突解决策略不合理,应该选择可以动态申请内存、对空间利用比较合理的冲突解决方法。
看到这里,你大概能理解博主后悔的心情。要说错误的起始点在哪里,那还是前期需求分析和构建工作做的太仓促了。应老师要求,我们使用Teambition制作PSP(Personal Software Process (PSP, 个人开发流程,或称个体软件过程)。但是博主找不到导出的功能键在哪里,(ಠ_ಠ),所以先上截图再临时做个表格吧
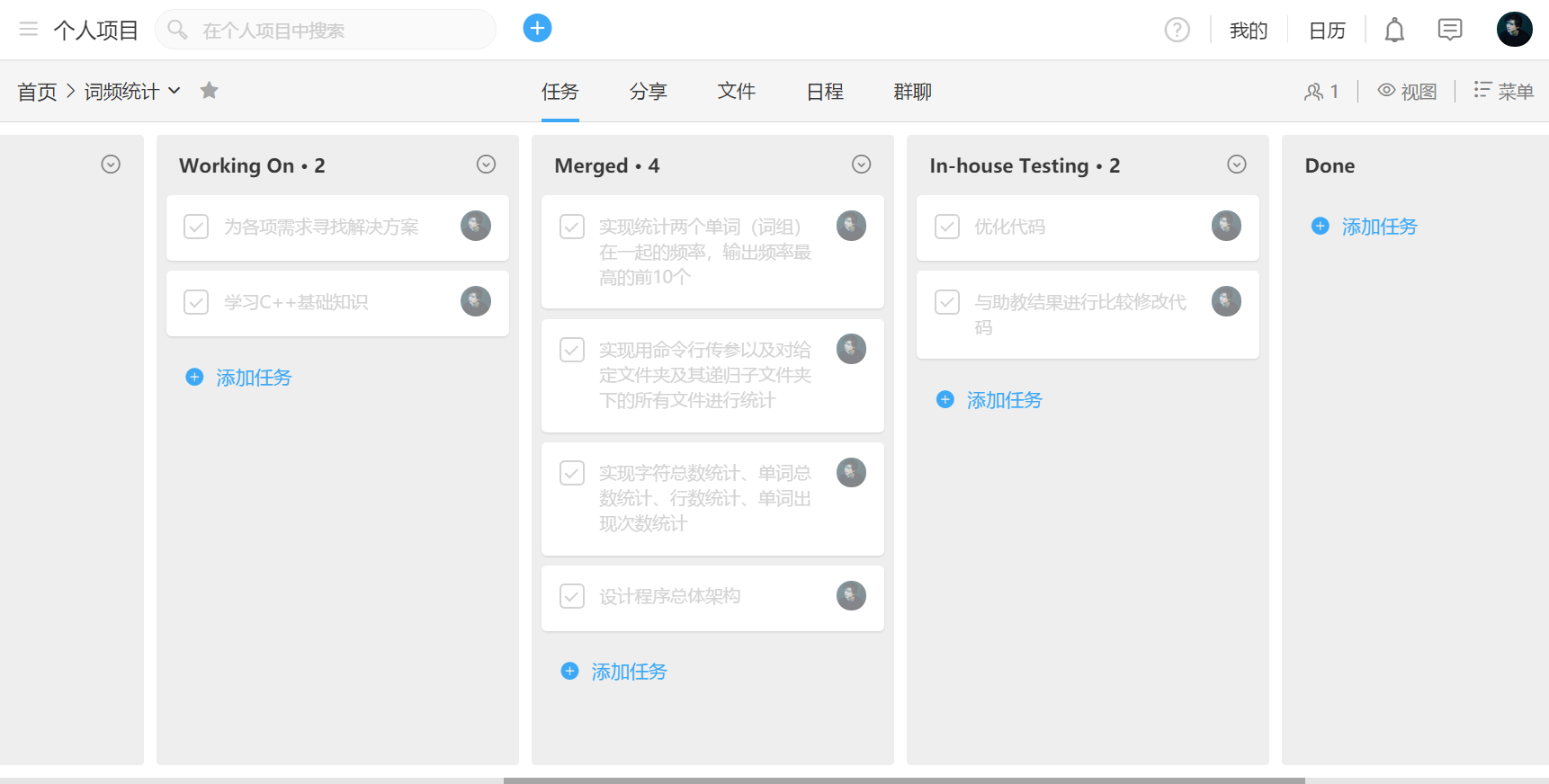
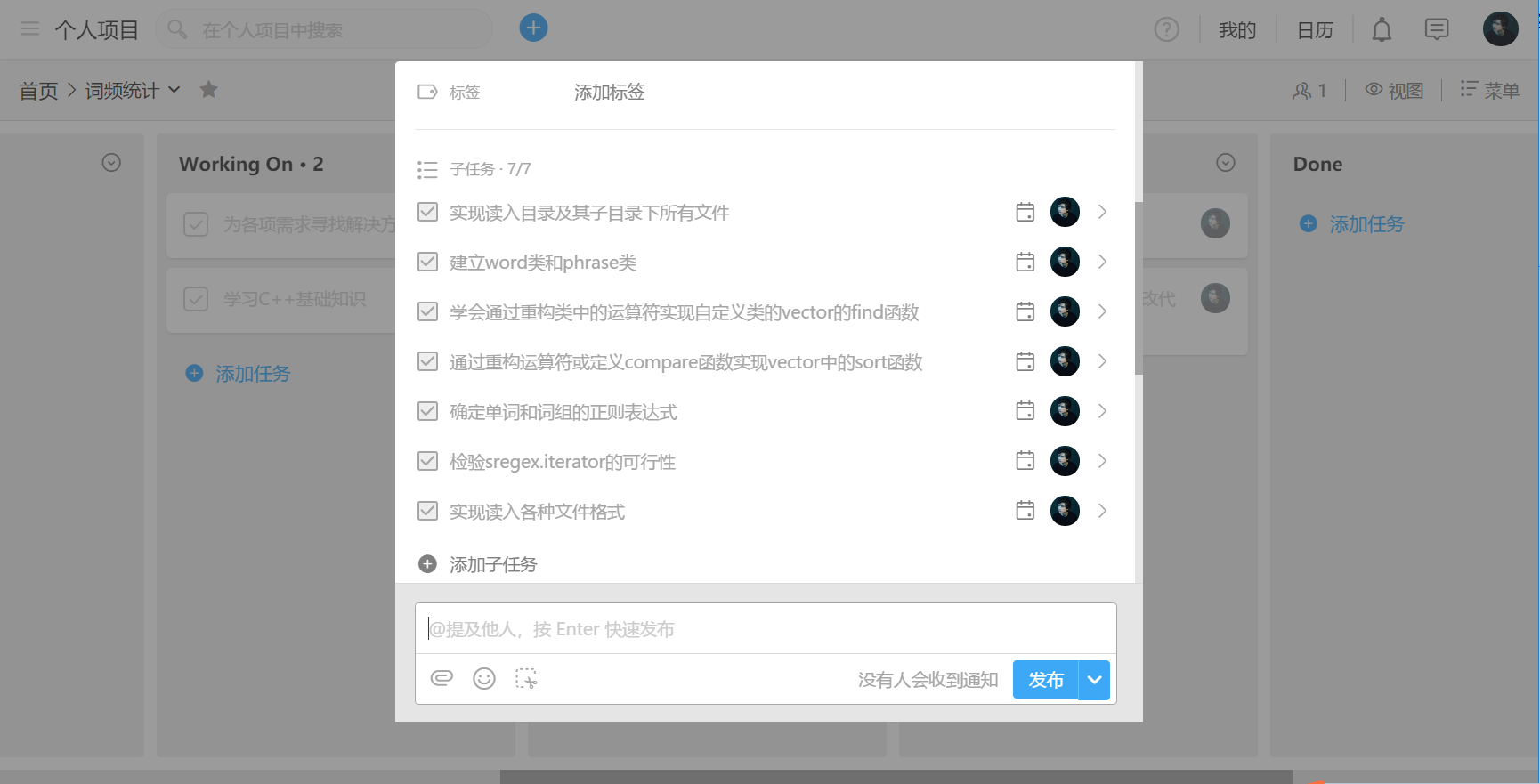
| 任务 | 预计完成时间 | 实际用时 | |||
| 学习C++基础知识 | 6h | 10h | |||
| 为各项功能实现解决方案 | 6h | 8h | |||
| 设计程序总架构 | 30min | 25min | |||
|
1h | 2.5h | |||
| 实现统计词组出现次数,输出最高10个 | 2h | 2h | |||
| 实现对文件夹内所有文件进行统计 | 1h | 1.5h | |||
| 和标准结果进行对比,优化代码 | 12h |
∞ |
博主该去补一补其他科的作业了......
之后有时间的话会更新班里面词频统计做的比较优秀的方案。Σ(・ω・ノ)ノ


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号