Spring-SpringBoot(Environment&@Value源码解析&Application)
Spring-SpringBoot(Environment&@Value源码解析&Application)
前面聊了SpringBoot的自动装配的启动流程,这一篇我想聊聊他的配置文件的解析,因为我们看见我们平常的配置文件,并没有看见它在哪里被解析的。但是我们就是能够拿到配置文件中的内容,SpringBoot到底是怎么实现的呢?这个和前面的自动装配是否有关,答案是肯定的。下面聊聊它的具体细节。
Environment:存储所有配置源的集合
我们可以通过 applicationContext.getEnvironment().getProperty("配置文件中key的名称");去获取我们配置文件中的数值。我们是从environment中获取的,那么下来就先分析一下它。
因为约定大于配置,所以自动装配了一个PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer,Spring初始化的时候会去调用#postProcessBeanFactory,在这个方法中把所有的配置文件都变成了一个个propertysource对象,同时把environment对象也包装成了一个propertysource对象,并且一个个propertysource对象存储在了MutablePropertySources中。
【源码解析】
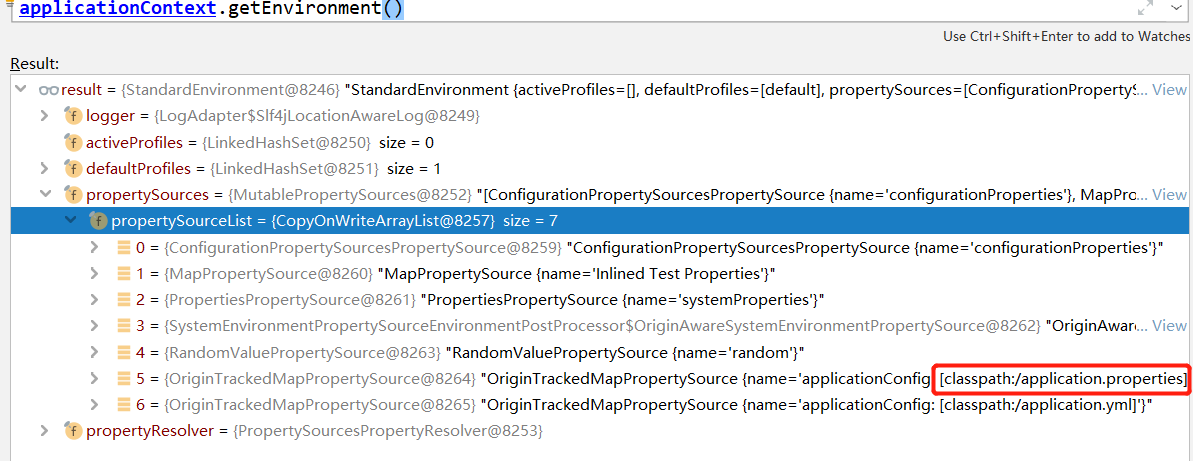
我们看见,其实获取到的environment中就包装了我们的配置文件,点开里面的propertySourceList发现里面就都是我们在配置文件中配置的属性值。也就是说【environment】的【propertySources】中装的就是很多种【propertysource】对象,而我们传递过去的名称就是某个property对象中的属性值
那么这里就有个问题,我们【application.properties】对应的【propertysource】对象,是如何被加载到【environment】对象中的?实际上他还是和前面说的一样,约定大于配置,他里面是有一个配置文件的解析的一个自动配置类,通过spi的形式被加载了。我们去看【EnableAutoConfiguration】中装配了一个【PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration】,在这个类中实例化了一个【PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer】,那毫无疑问,他就是加载配置文件的核心所在了。
他继承了【BeanFactoryPostProcessor】,并且重写了#postProcessBeanFactory,而Spring会调用这个方法去执行。所以我们看看这个方法。
整体流程&源码解析:
- new一个MutablePropertySources,这个对象中维护了一个list集合,集合里面存储的是所有的属性源对象(例如配置文件,环境变量等等),换言之这个对象维护存储的是所有的配置文件对象
- 然后获取到environment对象(这个对象在SpringBoot启动Spring容器的时候,已经初始化了,所以这里就不为空),并且这个对象中已经有一些基本信息了,比如环境变量等。
- 把environment包装成一个【propertysource】并且存储在【MutablePropertySources】中
![]() View Codepublic void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException { if (this.propertySources == null) { //这里有一个MutablePropertySources,在它的内部维护了一个list存储的是所有的propertysource对象(Spring中会把所有的属性源对象放在这里的MutablePropertySources中的对象中) this.propertySources = new MutablePropertySources(); //这里的environment对象不为空的原因是,我们在对Spring容器初始化的时候,已经把这个environment对象进行初始化了 if (this.environment != null) { //然后拿到了environment并且把它也包装成了一个propertysource对象 this.propertySources.addLast( new PropertySource<Environment>(ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, this.environment) { @Override @Nullable public String getProperty(String key) { return this.source.getProperty(key); } } ); } try { PropertySource<?> localPropertySource = new PropertiesPropertySource(LOCAL_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, mergeProperties()); if (this.localOverride) { this.propertySources.addFirst(localPropertySource); } else { this.propertySources.addLast(localPropertySource); } } catch (IOException ex) { throw new BeanInitializationException("Could not load properties", ex); } } // 把包含了environment对象的MutablePropertySources拿到PropertySourcesPropertyResolver中进行解析 processProperties(beanFactory, new PropertySourcesPropertyResolver(this.propertySources)); this.appliedPropertySources = this.propertySources; }
View Codepublic void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException { if (this.propertySources == null) { //这里有一个MutablePropertySources,在它的内部维护了一个list存储的是所有的propertysource对象(Spring中会把所有的属性源对象放在这里的MutablePropertySources中的对象中) this.propertySources = new MutablePropertySources(); //这里的environment对象不为空的原因是,我们在对Spring容器初始化的时候,已经把这个environment对象进行初始化了 if (this.environment != null) { //然后拿到了environment并且把它也包装成了一个propertysource对象 this.propertySources.addLast( new PropertySource<Environment>(ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, this.environment) { @Override @Nullable public String getProperty(String key) { return this.source.getProperty(key); } } ); } try { PropertySource<?> localPropertySource = new PropertiesPropertySource(LOCAL_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, mergeProperties()); if (this.localOverride) { this.propertySources.addFirst(localPropertySource); } else { this.propertySources.addLast(localPropertySource); } } catch (IOException ex) { throw new BeanInitializationException("Could not load properties", ex); } } // 把包含了environment对象的MutablePropertySources拿到PropertySourcesPropertyResolver中进行解析 processProperties(beanFactory, new PropertySourcesPropertyResolver(this.propertySources)); this.appliedPropertySources = this.propertySources; }- 把【MutablePropertySources】去解析,例如:${xx.xx.name}解析成真正的配置属性值
- 解析完成后,把解析后的对象放在BeanFactory中,因为@Value的注解还没有解析呢
![]() View Codeprotected void processProperties(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactoryToProcess, final ConfigurablePropertyResolver propertyResolver) throws BeansException { //设置占位符的前后缀已经我们的分隔符(平常我们会在@Value的注解中用到的东西) propertyResolver.setPlaceholderPrefix(this.placeholderPrefix); propertyResolver.setPlaceholderSuffix(this.placeholderSuffix); propertyResolver.setValueSeparator(this.valueSeparator); //这是一个String类型的解析器,在这个解析器中持有了咱们包含了environment对象的propertyResolver StringValueResolver valueResolver = strVal -> { String resolved = (this.ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders ? propertyResolver.resolvePlaceholders(strVal) : propertyResolver.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(strVal)); if (this.trimValues) { resolved = resolved.trim(); } return (resolved.equals(this.nullValue) ? null : resolved); }; //把beanDefinition中属性的值,例如:${xx.xx.name}解析成真正的配置属性值 doProcessProperties(beanFactoryToProcess, valueResolver); }
View Codeprotected void processProperties(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactoryToProcess, final ConfigurablePropertyResolver propertyResolver) throws BeansException { //设置占位符的前后缀已经我们的分隔符(平常我们会在@Value的注解中用到的东西) propertyResolver.setPlaceholderPrefix(this.placeholderPrefix); propertyResolver.setPlaceholderSuffix(this.placeholderSuffix); propertyResolver.setValueSeparator(this.valueSeparator); //这是一个String类型的解析器,在这个解析器中持有了咱们包含了environment对象的propertyResolver StringValueResolver valueResolver = strVal -> { String resolved = (this.ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders ? propertyResolver.resolvePlaceholders(strVal) : propertyResolver.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(strVal)); if (this.trimValues) { resolved = resolved.trim(); } return (resolved.equals(this.nullValue) ? null : resolved); }; //把beanDefinition中属性的值,例如:${xx.xx.name}解析成真正的配置属性值 doProcessProperties(beanFactoryToProcess, valueResolver); }
@Value的收集和属性赋值
【注解收集】:
当Spring初始化的时候执行到org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#finishBeanFactoryInitialization的时候开始进行注解的收集以及对相关属性进行赋值。
循环收集有@Value的属性的类,然后把类进行包装成AutowiredFieldElement对象。
【流程】:
- 收集哪些类上有@Value的注解(执行一个【MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor】的实现【AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#postProcessMergedBeanDefinition】),这这个里面有对@Value和@Autowird的操作,
- 这个方法会把有这个注解的类包装成一个AutowiredFieldElement对象,key为类名,value就是相关属性。
【源码解析】:
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition#postProcessingLock
View Code
进行包装
View Code
【属性赋值】:
【流程】:实际上就是对类上的value后面的属性值进行解析,然后拿到解析的数据和配置文件中的数据进行对比。如果对比成功,则通过反射,把相关的属性进行赋值。而配置文件的数据我们在上面加载environment文件的时候,已经把内容存储了起来。
主要代码在:org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#populateBean
application.properties加载到environment中
【流程】:
- 通过spi的形式加载了11个监听类,
- 加载Spring的时候循环执行了他们的onApplicationEvent方法
- 其中一个监听类【ConfifigFileApplicationListener】是主要加载的监听类。
- 执行了这个监听类的【onApplicationEvent】去加载了我们的application类。
- 加载的时候,把文件使用流的方式读取出来,并且变成了【OriginTrackedMapPropertySource】对象,存储在了environment中。
【代码解析】
入口就在SpringApplication.run方法中的这行代码
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
在方法prepareEnvironment中加载了application.properties文件【listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);】
- 加载监听器:
![]() View Code//通过spi的形式加载了EventPublishingRunListener并且执行了他的方法 void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) { for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners) { listener.environmentPrepared(environment); } }
View Code//通过spi的形式加载了EventPublishingRunListener并且执行了他的方法 void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) { for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners) { listener.environmentPrepared(environment); } }- 循环调用监听器的方法
![]() View Code//initialMulticaster这里存储的是11个监听器,他们的key是ApplicationListener,也是通过spi的形式导入进来了,然后在multicastEvent中循环调用每个监听器的的onApplicationEvent方法 @Override public void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) { this.initialMulticaster .multicastEvent(new ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(this.application, this.args, environment)); }
View Code//initialMulticaster这里存储的是11个监听器,他们的key是ApplicationListener,也是通过spi的形式导入进来了,然后在multicastEvent中循环调用每个监听器的的onApplicationEvent方法 @Override public void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) { this.initialMulticaster .multicastEvent(new ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(this.application, this.args, environment)); }- ConfifigFileApplicationListener中的onApplicationEvent中的核心方法,加载application文件,并且存储在environment中
![]() View Codevoid load() { FilteredPropertySource.apply(this.environment, DEFAULT_PROPERTIES, LOAD_FILTERED_PROPERTY, (defaultProperties) -> { this.profiles = new LinkedList<>(); this.processedProfiles = new LinkedList<>(); this.activatedProfiles = false; this.loaded = new LinkedHashMap<>(); initializeProfiles(); while (!this.profiles.isEmpty()) { Profile profile = this.profiles.poll(); if (isDefaultProfile(profile)) { addProfileToEnvironment(profile.getName()); } //加载application文件,并且把文件读取出来,变成OriginTrackedMapPropertySource load(profile, this::getPositiveProfileFilter, addToLoaded(MutablePropertySources::addLast, false)); this.processedProfiles.add(profile); } load(null, this::getNegativeProfileFilter, addToLoaded(MutablePropertySources::addFirst, true)); //把OriginTrackedMapPropertySource放在environment中 addLoadedPropertySources(); applyActiveProfiles(defaultProperties); }); }
View Codevoid load() { FilteredPropertySource.apply(this.environment, DEFAULT_PROPERTIES, LOAD_FILTERED_PROPERTY, (defaultProperties) -> { this.profiles = new LinkedList<>(); this.processedProfiles = new LinkedList<>(); this.activatedProfiles = false; this.loaded = new LinkedHashMap<>(); initializeProfiles(); while (!this.profiles.isEmpty()) { Profile profile = this.profiles.poll(); if (isDefaultProfile(profile)) { addProfileToEnvironment(profile.getName()); } //加载application文件,并且把文件读取出来,变成OriginTrackedMapPropertySource load(profile, this::getPositiveProfileFilter, addToLoaded(MutablePropertySources::addLast, false)); this.processedProfiles.add(profile); } load(null, this::getNegativeProfileFilter, addToLoaded(MutablePropertySources::addFirst, true)); //把OriginTrackedMapPropertySource放在environment中 addLoadedPropertySources(); applyActiveProfiles(defaultProperties); }); }- 配置前缀默认路径
![]() View Codeprivate void load(Profile profile, DocumentFilterFactory filterFactory, DocumentConsumer consumer) { //"classpath:/,classpath:/config/,file:./,file:./config/*/,file:./config/";默认的加载路径 getSearchLocations().forEach((location) -> { boolean isDirectory = location.endsWith("/"); //这里返回application的文件名称(写死了) Set<String> names = isDirectory ? getSearchNames() : NO_SEARCH_NAMES; names.forEach((name) -> load(location, name, profile, filterFactory, consumer)); }); }
View Codeprivate void load(Profile profile, DocumentFilterFactory filterFactory, DocumentConsumer consumer) { //"classpath:/,classpath:/config/,file:./,file:./config/*/,file:./config/";默认的加载路径 getSearchLocations().forEach((location) -> { boolean isDirectory = location.endsWith("/"); //这里返回application的文件名称(写死了) Set<String> names = isDirectory ? getSearchNames() : NO_SEARCH_NAMES; names.forEach((name) -> load(location, name, profile, filterFactory, consumer)); }); }- 循环路径并且添加application去寻找文件
![]() View Code//循环上面的文件路径去找application文件 private void load(String location, String name, Profile profile, DocumentFilterFactory filterFactory, DocumentConsumer consumer) { if (!StringUtils.hasText(name)) { for (PropertySourceLoader loader : this.propertySourceLoaders) { if (canLoadFileExtension(loader, location)) { load(loader, location, profile, filterFactory.getDocumentFilter(profile), consumer); return; } } throw new IllegalStateException("File extension of config file location '" + location + "' is not known to any PropertySourceLoader. If the location is meant to reference " + "a directory, it must end in '/'"); } Set<String> processed = new HashSet<>(); for (PropertySourceLoader loader : this.propertySourceLoaders) { for (String fileExtension : loader.getFileExtensions()) { if (processed.add(fileExtension)) { loadForFileExtension(loader, location + name, "." + fileExtension, profile, filterFactory, consumer); } } } }
View Code//循环上面的文件路径去找application文件 private void load(String location, String name, Profile profile, DocumentFilterFactory filterFactory, DocumentConsumer consumer) { if (!StringUtils.hasText(name)) { for (PropertySourceLoader loader : this.propertySourceLoaders) { if (canLoadFileExtension(loader, location)) { load(loader, location, profile, filterFactory.getDocumentFilter(profile), consumer); return; } } throw new IllegalStateException("File extension of config file location '" + location + "' is not known to any PropertySourceLoader. If the location is meant to reference " + "a directory, it must end in '/'"); } Set<String> processed = new HashSet<>(); for (PropertySourceLoader loader : this.propertySourceLoaders) { for (String fileExtension : loader.getFileExtensions()) { if (processed.add(fileExtension)) { loadForFileExtension(loader, location + name, "." + fileExtension, profile, filterFactory, consumer); } } } }- 拼接完整名称,如果有多余的名称,比如dev,那就把dev这个路径拼上去
![]() View Code//循环上面的文件路径去找application文件 private void load(String location, String name, Profile profile, DocumentFilterFactory filterFactory, DocumentConsumer consumer) { if (!StringUtils.hasText(name)) { for (PropertySourceLoader loader : this.propertySourceLoaders) { if (canLoadFileExtension(loader, location)) { load(loader, location, profile, filterFactory.getDocumentFilter(profile), consumer); return; } } throw new IllegalStateException("File extension of config file location '" + location + "' is not known to any PropertySourceLoader. If the location is meant to reference " + "a directory, it must end in '/'"); } Set<String> processed = new HashSet<>(); for (PropertySourceLoader loader : this.propertySourceLoaders) { for (String fileExtension : loader.getFileExtensions()) { if (processed.add(fileExtension)) { loadForFileExtension(loader, location + name, "." + fileExtension, profile, filterFactory, consumer); } } } }
View Code//循环上面的文件路径去找application文件 private void load(String location, String name, Profile profile, DocumentFilterFactory filterFactory, DocumentConsumer consumer) { if (!StringUtils.hasText(name)) { for (PropertySourceLoader loader : this.propertySourceLoaders) { if (canLoadFileExtension(loader, location)) { load(loader, location, profile, filterFactory.getDocumentFilter(profile), consumer); return; } } throw new IllegalStateException("File extension of config file location '" + location + "' is not known to any PropertySourceLoader. If the location is meant to reference " + "a directory, it must end in '/'"); } Set<String> processed = new HashSet<>(); for (PropertySourceLoader loader : this.propertySourceLoaders) { for (String fileExtension : loader.getFileExtensions()) { if (processed.add(fileExtension)) { loadForFileExtension(loader, location + name, "." + fileExtension, profile, filterFactory, consumer); } } } }![]() View Codeprivate void loadForFileExtension(PropertySourceLoader loader, String prefix, String fileExtension, Profile profile, DocumentFilterFactory filterFactory, DocumentConsumer consumer) { DocumentFilter defaultFilter = filterFactory.getDocumentFilter(null); DocumentFilter profileFiter = filterFactory.getDocumentFilter(profile); //这个profile指的是,如果我们在application中的active的属性中有内容,则把这个内容加在文件的路径下面 比如 application-dev if (profile != null) { String profileSpecificFile = prefix + "-" + profile + fileExtension; load(loader, profileSpecificFile, profile, defaultFilter, consumer); load(loader, profileSpecificFile, profile, profileFilter, consumer); // Try profile specific sections in files we've already processed for (Profile processedProfile : this.processedProfiles) { if (processedProfile != null) { String previouslyLoaded = prefix + "-" + processedProfile + fileExtension; load(loader, previouslyLoaded, profile, profileFilter, consumer); } } } //如果没有附加值 load(loader, prefix + fileExtension, profile, profileFilter, consumer); }
View Codeprivate void loadForFileExtension(PropertySourceLoader loader, String prefix, String fileExtension, Profile profile, DocumentFilterFactory filterFactory, DocumentConsumer consumer) { DocumentFilter defaultFilter = filterFactory.getDocumentFilter(null); DocumentFilter profileFiter = filterFactory.getDocumentFilter(profile); //这个profile指的是,如果我们在application中的active的属性中有内容,则把这个内容加在文件的路径下面 比如 application-dev if (profile != null) { String profileSpecificFile = prefix + "-" + profile + fileExtension; load(loader, profileSpecificFile, profile, defaultFilter, consumer); load(loader, profileSpecificFile, profile, profileFilter, consumer); // Try profile specific sections in files we've already processed for (Profile processedProfile : this.processedProfiles) { if (processedProfile != null) { String previouslyLoaded = prefix + "-" + processedProfile + fileExtension; load(loader, previouslyLoaded, profile, profileFilter, consumer); } } } //如果没有附加值 load(loader, prefix + fileExtension, profile, profileFilter, consumer); }- 读取application文件,通过流读取,并且把它变成一个propertysource对象
![]() View Codeprivate void load(PropertySourceLoader loader, String location, Profile profile, DocumentFilter filter, DocumentConsumer consumer) { Resource[] resources = getResources(location); for (Resource resource : resources) { try { if (resource == null || !resource.exists()) { if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) { StringBuilder description = getDescription("Skipped missing config ", location, resource, profile); this.logger.trace(description); } continue; } if (!StringUtils.hasText(StringUtils.getFilenameExtension(resource.getFilename()))) { if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) { StringBuilder description = getDescription("Skipped empty config extension ", location, resource, profile); this.logger.trace(description); } continue; } //这里最终拼接文件的全路径,这里也就是我们在environment中看到的那个路径 String name = "applicationConfig: [" + getLocationName(location, resource) + "]"; //通过流的方式,把他的属性加载成Document文件,并且在这里把它变成了一个对象OriginTrackedMapPropertySource List<Document> documents = loadDocuments(loader, name, resource); if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(documents)) { if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) { StringBuilder description = getDescription("Skipped unloaded config ", location, resource, profile); this.logger.trace(description); } continue; } List<Document> loaded = new ArrayList<>(); for (Document document : documents) { if (filter.match(document)) { addActiveProfiles(document.getActiveProfiles()); addIncludedProfiles(document.getIncludeProfiles()); loaded.add(document); } } Collections.reverse(loaded); if (!loaded.isEmpty()) { loaded.forEach((document) -> consumer.accept(profile, document)); if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) { StringBuilder description = getDescription("Loaded config file ", location, resource, profile); this.logger.debug(description); } } } catch (Exception ex) { StringBuilder description = getDescription("Failed to load property source from ", location, resource, profile); throw new IllegalStateException(description.toString(), ex); } } }
View Codeprivate void load(PropertySourceLoader loader, String location, Profile profile, DocumentFilter filter, DocumentConsumer consumer) { Resource[] resources = getResources(location); for (Resource resource : resources) { try { if (resource == null || !resource.exists()) { if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) { StringBuilder description = getDescription("Skipped missing config ", location, resource, profile); this.logger.trace(description); } continue; } if (!StringUtils.hasText(StringUtils.getFilenameExtension(resource.getFilename()))) { if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) { StringBuilder description = getDescription("Skipped empty config extension ", location, resource, profile); this.logger.trace(description); } continue; } //这里最终拼接文件的全路径,这里也就是我们在environment中看到的那个路径 String name = "applicationConfig: [" + getLocationName(location, resource) + "]"; //通过流的方式,把他的属性加载成Document文件,并且在这里把它变成了一个对象OriginTrackedMapPropertySource List<Document> documents = loadDocuments(loader, name, resource); if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(documents)) { if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) { StringBuilder description = getDescription("Skipped unloaded config ", location, resource, profile); this.logger.trace(description); } continue; } List<Document> loaded = new ArrayList<>(); for (Document document : documents) { if (filter.match(document)) { addActiveProfiles(document.getActiveProfiles()); addIncludedProfiles(document.getIncludeProfiles()); loaded.add(document); } } Collections.reverse(loaded); if (!loaded.isEmpty()) { loaded.forEach((document) -> consumer.accept(profile, document)); if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) { StringBuilder description = getDescription("Loaded config file ", location, resource, profile); this.logger.debug(description); } } } catch (Exception ex) { StringBuilder description = getDescription("Failed to load property source from ", location, resource, profile); throw new IllegalStateException(description.toString(), ex); } } }- 把对象放进environment中。
![]() View Codeprivate void addLoadedPropertySources() { MutablePropertySources destination = this.environment.getPropertySources(); List<MutablePropertySources> loaded = new ArrayList<>(this.loaded.values()); Collections.reverse(loaded); String lastAdded = null; Set<String> added = new HashSet<>(); for (MutablePropertySources sources : loaded) { for (PropertySource<?> source : sources) { if (added.add(source.getName())) { //最终在这里把application存入了environment中 addLoadedPropertySource(destination, lastAdded, source); lastAdded = source.getName(); } } } }
View Codeprivate void addLoadedPropertySources() { MutablePropertySources destination = this.environment.getPropertySources(); List<MutablePropertySources> loaded = new ArrayList<>(this.loaded.values()); Collections.reverse(loaded); String lastAdded = null; Set<String> added = new HashSet<>(); for (MutablePropertySources sources : loaded) { for (PropertySource<?> source : sources) { if (added.add(source.getName())) { //最终在这里把application存入了environment中 addLoadedPropertySource(destination, lastAdded, source); lastAdded = source.getName(); } } } }【问题】:
yml和application那个优先级高?
application,因为在源码中application结尾的文件首先进行了读取,但是他们都会被包装成environment,因为在源码中是循环读取和包装以他们结尾的文件。
- 既然他们都可以被包装成environment文件,如果在两个文件中都存储了相同的key那个会被读取?
- application,因为在使用getProperty方法的时候,一旦获取到,代码就返回了,所以即使yml的配置也被加载了,但是不是被读取到。
- 是否可以通过修改自己的配置文件名?
- 可以的,因为spring在加载environment的时候,也加载了环境变量,那我们就可以把我们的文件名称放在环境变量中,甚至我们可以自己包装一个property,给他塞在propertsources中。比如说要进行动态配置,然后定时刷新。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号