(三)语音合成器实例
这篇距离上次更新已经过去很久了。所幸阅读的人并不多,因为该教程还未更完,估计只看了之前那个粗糙案例的人要沮丧了。这里使用一个完整的实例来弥补之前留下的坑。
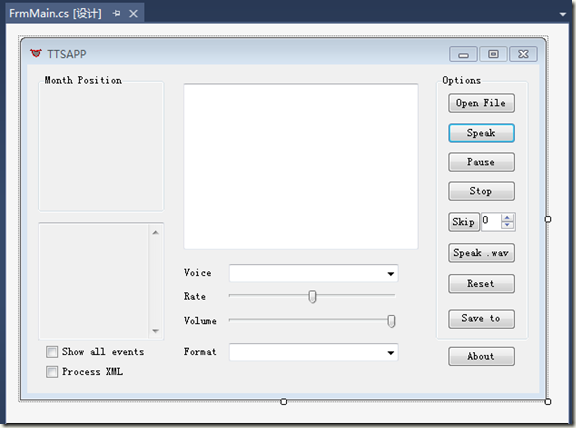
首先创建一个窗体程序TTSApp,界面布局如下:
相应的素材可以在对应的源码中找到。这里就不具体介绍了。下面看程序的详细代码:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Data; using System.Drawing; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Windows.Forms; using System.Speech.Synthesis; using System.Speech.AudioFormat; using System.IO; namespace TTSApp { public partial class FrmMain : Form { private List<AudioFormatInfo> formatList = new List<AudioFormatInfo>(); //音频格式列表 private SpeechSynthesizer speechSynthesizer = new SpeechSynthesizer(); //语音合成器 private PictureBox pic1 = new PictureBox(); //用于显示嘴型动画 private PictureBox pic2 = new PictureBox(); private AudioFormatInfo formatInfo; private string text; private bool showEvents; /// <summary> /// 窗体构造 /// </summary> public FrmMain() { InitializeComponent(); speechSynthesizer.SpeakProgress += new EventHandler<SpeakProgressEventArgs>(speechSynthesizer_SpeakProgress); //朗读进度监视 speechSynthesizer.VisemeReached += new EventHandler<VisemeReachedEventArgs>(speechSynthesizer_VisemeReached); //嘴型动画事件 speechSynthesizer.SpeakCompleted += new EventHandler<SpeakCompletedEventArgs>(speechSynthesizer_SpeakCompleted); //朗读完成时触发 speechSynthesizer.Rate = this.tbRate.Value; //默认语速 speechSynthesizer.Volume = this.tbVolume.Value; //默认音量 //初始化视位到达用于显示嘴型动画的PictureBox pic1.Size = new Size(128, 128); pic1.BackgroundImage = imageList.Images[14]; pic2.Size = new Size(128, 128); pic2.BackColor = Color.Transparent; pic1.Controls.Add(pic2); pic1.Location = new Point(5, 15); this.gbMouth.Controls.Add(pic1); this.showEvents = this.chkAllEvent.Checked; } /// <summary> /// 窗体加载 /// </summary> private void FrmMain_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) { BindVoiceList(); BindFormatList(); } /// <summary> /// 绑定语音库列表 /// </summary> private void BindVoiceList() { this.cbVoive.DataSource = (from item in speechSynthesizer.GetInstalledVoices() select item.VoiceInfo.Name).ToList(); } /// <summary> /// 绑定音频格式列表 /// </summary> private void BindFormatList() { formatList.Add(new AudioFormatInfo("8kHz 8Bit Mono", 8000, AudioBitsPerSample.Eight, AudioChannel.Mono)); formatList.Add(new AudioFormatInfo("8kHz 8Bit Stereo", 8000, AudioBitsPerSample.Eight, AudioChannel.Stereo)); formatList.Add(new AudioFormatInfo("8kHz 16Bit Mono", 8000, AudioBitsPerSample.Sixteen, AudioChannel.Mono)); formatList.Add(new AudioFormatInfo("8kHz 16Bit Stereo", 8000, AudioBitsPerSample.Sixteen, AudioChannel.Stereo)); formatList.Add(new AudioFormatInfo("11kHz 8Bit Mono", 11000, AudioBitsPerSample.Eight, AudioChannel.Mono)); formatList.Add(new AudioFormatInfo("11kHz 8Bit Stereo", 11000, AudioBitsPerSample.Eight, AudioChannel.Stereo)); formatList.Add(new AudioFormatInfo("11kHz 16Bit Mono", 11000, AudioBitsPerSample.Sixteen, AudioChannel.Mono)); formatList.Add(new AudioFormatInfo("11kHz 16Bit Stereo", 11000, AudioBitsPerSample.Sixteen, AudioChannel.Stereo)); formatList.Add(new AudioFormatInfo("12kHz 8Bit Mono", 12000, AudioBitsPerSample.Eight, AudioChannel.Mono)); formatList.Add(new AudioFormatInfo("12kHz 8Bit Stereo", 12000, AudioBitsPerSample.Eight, AudioChannel.Stereo)); formatList.Add(new AudioFormatInfo("12kHz 16Bit Mono", 12000, AudioBitsPerSample.Sixteen, AudioChannel.Mono)); formatList.Add(new AudioFormatInfo("12kHz 16Bit Stereo", 12000, AudioBitsPerSample.Sixteen, AudioChannel.Stereo)); formatList.Add(new AudioFormatInfo("16kHz 8Bit Mono", 16000, AudioBitsPerSample.Eight, AudioChannel.Mono)); formatList.Add(new AudioFormatInfo("16kHz 8Bit Stereo", 16000, AudioBitsPerSample.Eight, AudioChannel.Stereo)); formatList.Add(new AudioFormatInfo("16kHz 16Bit Mono", 16000, AudioBitsPerSample.Sixteen, AudioChannel.Mono)); formatList.Add(new AudioFormatInfo("16kHz 16Bit Stereo", 16000, AudioBitsPerSample.Sixteen, AudioChannel.Stereo)); formatList.Add(new AudioFormatInfo("22kHz 8Bit Mono", 22000, AudioBitsPerSample.Eight, AudioChannel.Mono)); formatList.Add(new AudioFormatInfo("22kHz 8Bit Stereo", 22000, AudioBitsPerSample.Eight, AudioChannel.Stereo)); formatList.Add(new AudioFormatInfo("22kHz 16Bit Mono", 22000, AudioBitsPerSample.Sixteen, AudioChannel.Mono)); formatList.Add(new AudioFormatInfo("22kHz 16Bit Stereo", 22000, AudioBitsPerSample.Sixteen, AudioChannel.Stereo)); formatList.Add(new AudioFormatInfo("24kHz 8Bit Mono", 24000, AudioBitsPerSample.Eight, AudioChannel.Mono)); formatList.Add(new AudioFormatInfo("24kHz 8Bit Stereo", 24000, AudioBitsPerSample.Eight, AudioChannel.Stereo)); formatList.Add(new AudioFormatInfo("24kHz 16Bit Mono", 24000, AudioBitsPerSample.Sixteen, AudioChannel.Mono)); formatList.Add(new AudioFormatInfo("24kHz 16Bit Stereo", 24000, AudioBitsPerSample.Sixteen, AudioChannel.Stereo)); formatList.Add(new AudioFormatInfo("32kHz 8Bit Mono", 32000, AudioBitsPerSample.Eight, AudioChannel.Mono)); formatList.Add(new AudioFormatInfo("32kHz 8Bit Stereo", 32000, AudioBitsPerSample.Eight, AudioChannel.Mono)); formatList.Add(new AudioFormatInfo("32kHz 16Bit Mono", 32000, AudioBitsPerSample.Sixteen, AudioChannel.Mono)); formatList.Add(new AudioFormatInfo("32kHz 16Bit Stereo", 32000, AudioBitsPerSample.Sixteen, AudioChannel.Mono)); formatList.Add(new AudioFormatInfo("44kHz 8Bit Mono", 44000, AudioBitsPerSample.Eight, AudioChannel.Mono)); formatList.Add(new AudioFormatInfo("44kHz 8Bit Stereo", 44000, AudioBitsPerSample.Eight, AudioChannel.Stereo)); formatList.Add(new AudioFormatInfo("44kHz 16Bit Mono", 44000, AudioBitsPerSample.Sixteen, AudioChannel.Mono)); formatList.Add(new AudioFormatInfo("44kHz 16Bit Stereo", 44000, AudioBitsPerSample.Sixteen, AudioChannel.Stereo)); formatList.Add(new AudioFormatInfo("48kHz 8Bit Mono", 48000, AudioBitsPerSample.Eight, AudioChannel.Mono)); formatList.Add(new AudioFormatInfo("48kHz 8Bit Stereo", 48000, AudioBitsPerSample.Eight, AudioChannel.Stereo)); formatList.Add(new AudioFormatInfo("48kHz 16Bit Mono", 48000, AudioBitsPerSample.Sixteen, AudioChannel.Mono)); formatList.Add(new AudioFormatInfo("48kHz 16Bit Stereo", 48000, AudioBitsPerSample.Sixteen, AudioChannel.Stereo)); this.cbFormat.DataSource = formatList; this.cbFormat.DisplayMember = "FromatName"; this.formatInfo = this.cbFormat.SelectedItem as AudioFormatInfo; } /// <summary> /// 朗读进度监视 /// </summary> private void speechSynthesizer_SpeakProgress(object sender, SpeakProgressEventArgs e) { string selectedText = e.Text; int startIndex = text.IndexOf(selectedText); int length = selectedText.Length; int lastLength = this.txtContent.Text.Length - text.Length; this.txtContent.Focus(); this.txtContent.Select(startIndex + lastLength, length); text = text.Substring(startIndex + length); } /// <summary> /// 嘴型动画事件 /// </summary> private void speechSynthesizer_VisemeReached(object sender, VisemeReachedEventArgs e) { if (showEvents) { this.txtMsg.AppendText("Viseme\r\n"); } int viseme = e.Viseme; viseme = viseme > 11 ? viseme - 12 : viseme; int index = viseme % 2 == 0 ? 12 : 13; this.pic1.Image = imageList.Images[viseme]; this.pic2.Image = imageList.Images[index]; } /// <summary> /// 朗读完毕 /// </summary> private void speechSynthesizer_SpeakCompleted(object sender, SpeakCompletedEventArgs e) { this.pic1.Image = null; this.pic2.Image = null; speechSynthesizer.SetOutputToNull(); this.txtContent.SelectAll(); } /// <summary> /// 改变语音库 /// </summary> private void cbVoive_SelectedIndexChanged(object sender, EventArgs e) { speechSynthesizer.SelectVoice(this.cbVoive.Text); } /// <summary> /// 变更音频格式 /// </summary> private void cbFormat_SelectedIndexChanged(object sender, EventArgs e) { this.formatInfo = this.cbFormat.SelectedItem as AudioFormatInfo; } /// <summary> /// 改变语速 /// </summary> private void tbRate_Scroll(object sender, EventArgs e) { speechSynthesizer.Rate = this.tbRate.Value; } /// <summary> /// 改变音量 /// </summary> private void tbVolume_Scroll(object sender, EventArgs e) { speechSynthesizer.Volume = this.tbVolume.Value; } /// <summary> /// 点击打开文本文件(.txt) /// </summary> private void btnOpenFile_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { if (openFileDialog.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK) { this.txtContent.Text = File.ReadAllText(openFileDialog.FileName, Encoding.Default); } } /// <summary> /// 点击朗读 /// </summary> private void btnSpeak_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { this.txtMsg.AppendText("Speak\r\n"); text = this.txtContent.Text; speechSynthesizer.SetOutputToDefaultAudioDevice(); speechSynthesizer.SpeakAsync(text); } /// <summary> /// 点击暂停/恢复 /// </summary> private void btnPause_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { if (this.btnPause.Text == "Pause") { this.txtMsg.AppendText("Pause\r\n"); speechSynthesizer.Pause(); this.btnPause.Text = "Resume"; } else { this.txtMsg.AppendText("Resume\r\n"); speechSynthesizer.Resume(); this.btnPause.Text = "Pause"; } } /// <summary> /// 点击停止 /// </summary> private void btnStop_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { this.txtMsg.AppendText("Stop\r\n"); speechSynthesizer.SpeakAsyncCancelAll(); } /// <summary> /// 点击保存 /// </summary> private void btnSave_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { if (saveFileDialog.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK) { if (speechSynthesizer.State == SynthesizerState.Speaking) { speechSynthesizer.SpeakAsyncCancelAll(); } speechSynthesizer.SetOutputToWaveFile(saveFileDialog.FileName, formatInfo); speechSynthesizer.SpeakAsync(this.txtContent.Text); } } /// <summary> /// 使用Wav文件 /// </summary> private void btnSpeakWav_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { if (openWav.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK) { PromptBuilder pb = new PromptBuilder(); pb.AppendAudio(openWav.FileName); speechSynthesizer.SetOutputToDefaultAudioDevice(); speechSynthesizer.SpeakAsync(pb); } } /// <summary> /// 重置 /// </summary> private void btnReset_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { this.txtMsg.AppendText("Reset\r\n"); this.txtContent.Focus(); this.txtContent.Select(0, 0); } /// <summary> /// 是否显示所有事件信息 /// </summary> private void chkAllEvent_CheckedChanged(object sender, EventArgs e) { this.showEvents = this.chkAllEvent.Checked; } } }
这里要先说明一下,在我所做的语音合成案例中使用了两种方案。一种时实时合成,一种是录播方式。以上代码演示的是第一种方式。而后者使用的方式是先把合成的语音流输出到文件中(如.wav)或者直接使用语音流,然后使播放的方式再播放出来。为什么会用到两种方式呢?实时方案好处在于嘴型和朗读同步率高。而录播方式可以调整语音合成的质量,但是嘴型和朗读的同步可能稍微差些。这也是源于我寻遍所有文档资料也没找到在实时合成时怎么调整语音合成质量的。如果有知道的请务必告诉我。所以我就使用的备用录播方案来调整语音合成质量了。
语音合成引擎初始化时需要为其指明朗读的语音库,不显示指明则会使用缺省值。所以需要预先获取到系统所安装的语音库。
/// <summary> /// 绑定语音库列表 /// </summary> private void BindVoiceList() { this.cbVoive.DataSource = (from item in speechSynthesizer.GetInstalledVoices() select item.VoiceInfo.Name).ToList(); }
以上代码就是获取系统已安装的语音库列表并绑定到下拉框,以便选择。
/// <summary> /// 改变语音库 /// </summary> private void cbVoive_SelectedIndexChanged(object sender, EventArgs e) { speechSynthesizer.SelectVoice(this.cbVoive.Text); }
我们可以通过SelectVoice方法改变当前语音库。系统默认只安装了两个语音库,更多的语音库详见之前的文章介绍。备注:如果下载已失效请留言。
在F12源中可以看到有如下的方法签名:
public void SetOutputToAudioStream(Stream audioDestination, SpeechAudioFormatInfo formatInfo); public void SetOutputToDefaultAudioDevice(); public void SetOutputToNull(); public void SetOutputToWaveFile(string path); public void SetOutputToWaveFile(string path, SpeechAudioFormatInfo formatInfo); public void SetOutputToWaveStream(Stream audioDestination);
这些方法用于设置语音引擎的输出。不显示设置,默认会使用SetOutputToDefaultAudioDevice把合成结果输出到系统默认音频设备上。
语音引擎的输出方式总结有如下几种:
1.输出到设备
2.输出到文件
3.输出到内存
其中:SetOutputToAudioStream和SetOutputToWaveStream这两种方式到底有什么区别,在MSDN中我只找到SetOutputToWaveStream的案例。而SetOutputToAudioStream没有任何有用的案例。根据我试验所知,SetOutputToWaveStream生成的是WAV有格式的音频流,SetOutputToAudioStream生成的应该是PCM这种编码的二进制流,如果需要播放应该还需要转格式吧。如果我理解的不对还请指教。其中只有:SetOutputToAudioStream,SetOutputToWaveFile这两个方法可以使用SpeechAudioFormatInfo参数,也即我所说的影响语音合成品质的参数,这也是为什么需要用录播了。
SetOutputToNull方法:在需要输出到内存或文件时,合成完成后调用该方法可以释放所占用的流或文件。
注意:在调用Speak方法时需要先设定输出方式。
语音合成中Viseme和Phoneme姑且算是比较难弄懂的东西。Viseme我理解为嘴型。Phoneme是音位。
A viseme is the basic position of the mouth and face when pronouncing a phoneme. Visemes are visual representations of phonemes.
System.Speech supports 21 visemes for US English, each of which corresponds to one or more phonemes. VisemeReached events are raised when a new phoneme reached has a different corresponding viseme than the previous phoneme reached. Since some visemes represent more than one phoneme, a VisemeReached event is not generated if the next phoneme reached corresponds to the same viseme as the previous phoneme. For example, for the spoken words “this zone”, a PhonemeReached event is raised for the “s” in “this” and the “z” in “zone”. However, a VisemeReached event is not raised for the “z” in “zone” because it corresponds to the same viseme as the “s” in “this”.
The following is a list of the 21 SAPI phonemes and phoneme groups that correspond to a viseme in US English.
VisemePhoneme(s)
0 silence
1 ae, ax, ah
2 aa
3 ao
4 ey, eh, uh
5 er
6 y, iy, ih, ix
7 w, uw
8 ow
9 aw
10 oy
11 ay
12 h
13 r
14 l
15 s, z
16 sh, ch, jh, zh
17 th, dh
18 f, v
19 d, t, n
20 k, g, ng
21 p, b, m
这是MSDN上给的解释,我直接拿来用,感觉比我解释的会更好。也就是说,嘴型和音位/音素是有一个对应关系的。上面给的英文的对照表。而这种对照关系也是我们绘制嘴型动画所必须了解的。我使用的是最简单的方式,预先把各个音位的所对应的嘴型做成固定的图片,在合成语音时,到达哪一个音位就调用对应嘴型的图片即可。要做的精确的前提就是嘴型图片绘制的准确。最后合成的动画就比较符合一般发音的嘴型了。
当然我的绘制功底是不行的,这里嘴型的图片也是从其它程序里弄来的以方便我演示的。至于是不是完全对应的,我不能保证。因为这图片设计本身是不是正确的我也不得而知。
嘴型动画的实现据我测试如下:只有在实时合成状态下才有效,使用录播时是无效的。如何解决在录播时同步嘴型?我只做了一个预备的方案:在实时合成时将嘴型动画数据保存下来,到录播状态时再使用该数据手动合成动画。这里唯一无法解决的问题就是不能确保两者的对应关系。也就不能保证同步了。
其实只要解决实时合成时如何调整语音质量的问题,那么该备用方案就可以舍掉了。如果有知道的清务必告诉我。
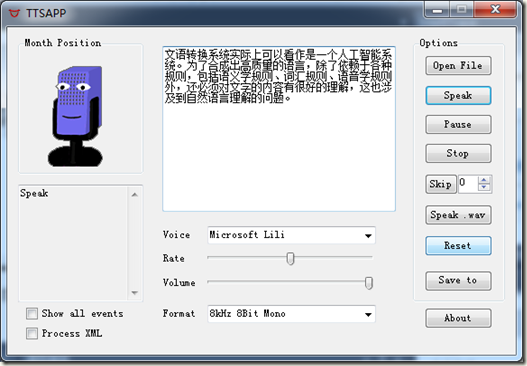
最终效果图如下:
另附上述实例源码:案例源码




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步