初识 Monad
简述
学前,Monads for functional programming
Case 1, introduces monads
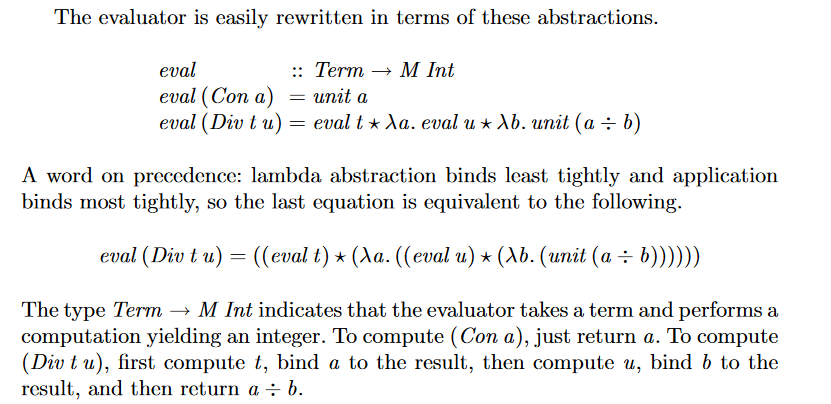
We begin with the basic evaluator for simple terms, then consider variations that mimic exceptions, state, and output.
Case 2, 经典问题之新解, efficient array update
How a functional language may provide in-place array update is an old problem. This section has presented a new solution, consisting of two abstract data types with eight operations between them.

Case 3, applies monads
This section shows how monads provide a simple framework for constructing recursive descent parsers.
Sequencing and alternation are fundamental not just to parsers but to much of computing. If monads capture sequencing, then it is reasonable to ask: what captures both sequencing and alternation? It may be that unit, bind, zero, and ⊕, together with the laws above, provide such a structure.
参考
-
Philip Wadler. Monads for functional programming. In J. Jeuring and E. Meijer, editors, Advanced Functional Programming, pp. 24–52, Springer Verlag, LNCS 925, 1995.
更多
- Continuation-based mutable abstract data types.




