Java语法
equals与"=="的区别
equals比较的是成员变量的值是否相同,而"=="比较的是内存地址值是否相同,示例如下
每new一次就会产生新的内存空间
package test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
public class test2 {
@Test
public void test() throws Exception {
String a = new String("123");
String b = new String("123");
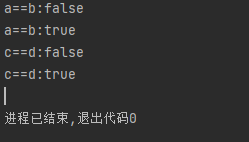
System.out.println("a==b:" + (a == b));
System.out.println("a==b:" + a.equals(b));
Integer c = new Integer(2);
Integer d = new Integer(2);
System.out.println("c==d:" + (c == d));
System.out.println("c==d:" + c.equals(d));
}
}
更改写法,不采用new的形式赋值则会指向同一引用地址
package test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
public class test2 {
@Test
public void test() throws Exception {
String a1 = "123";
String b1 = "123";
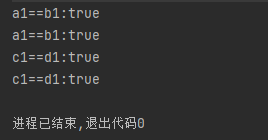
System.out.println("a1==b1:" + (a1 == b1));
System.out.println("a1==b1:" + a1.equals(b1));
Integer c1 = 2;
Integer d1 = 2;
System.out.println("c1==d1:" + (c1 == d1));
System.out.println("c1==d1:" + c1.equals(d1));
}
}
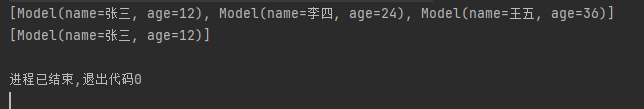
根据数组对象属性过滤不需要的信息
@Test
public void test2() throws Exception {
@Data
class Model {
public String name;
public Integer age;
}
List<Model> list = new ArrayList<>();
Model model1 = new Model();
model1.setAge(12);
model1.setName("张三");
Model model2 = new Model();
model2.setAge(24);
model2.setName("李四");
Model model3 = new Model();
model3.setAge(36);
model3.setName("王五");
Collections.addAll(list, model1, model2, model3);
System.out.println(list);
List<Model> result = list.stream().filter(e -> e.getAge().equals(12)).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(result);
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号