C++ 迷宫寻路问题
迷宫寻路应该是栈结构的一个非常经典的应用了, 最近看数据结构算法应用时看到了这个问题, 想起来在校求学时参加算法竞赛有遇到过相关问题, 感觉十分亲切, 在此求解并分享过程, 如有疏漏, 欢迎指正
问题描述: 非常简洁明了的问题, 即对于一个由1,0构成的矩阵, 找到一条用0连接起来的从(1,1)到(10,10)的路径
思路: 用栈结构存储路径, 每经过一个点, 将点坐标存入栈, 并在矩阵中将此坐标点值置1, 循环直至找到点(10,10), 若中途没找到可以继续前进的点且栈为空, 则说明当前迷宫无解
代码如下:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <stack> 3 4 //坐标 5 typedef struct _struct_pos 6 { 7 _struct_pos() 8 { 9 x = 0; 10 y = 0; 11 } 12 13 int x; 14 int y; 15 }Pos; 16 17 //地图 18 int g_maze_arr[12][12] = {{1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1}, 19 {1,0,1,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,1}, 20 {1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,1}, 21 {1,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,1}, 22 {1,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,0,1,1}, 23 {1,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,1}, 24 {1,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,1}, 25 {1,0,0,0,1,0,0,1,1,1,1,1}, 26 {1,0,1,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,1}, 27 {1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,1}, 28 {1,1,1,1,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,1}, 29 {1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1}}; 30 31 //路径栈 32 std::stack<Pos> g_stack_path; 33 34 /*************************************************************** 35 * 36 */ 37 void print_pos(const Pos &pos) 38 { 39 std::cout << "[" << pos.x 40 << "," << pos.y 41 << "]" << std::endl; 42 } 43 44 //检查出口 45 bool find_next(const Pos &curr_pos, Pos &next_pos) 46 { 47 //当前坐标 48 int x = curr_pos.x; 49 int y = curr_pos.y; 50 51 //生成四个方向的坐标 52 Pos top, down, left, right; 53 top.x = x; 54 top.y = y - 1; 55 down.x = x; 56 down.y = y + 1; 57 left.x = x - 1; 58 left.y = y; 59 right.x = x + 1; 60 right.y = y; 61 62 //判断四个方向有无通路 63 if (g_maze_arr[top.x][top.y] == 0) 64 { 65 next_pos.x = top.x; 66 next_pos.y = top.y; 67 std::cout << "find way : "; 68 print_pos(next_pos); 69 return true; 70 } 71 else if (g_maze_arr[down.x][down.y] == 0) 72 { 73 next_pos.x = down.x; 74 next_pos.y = down.y; 75 std::cout << "find way : "; 76 print_pos(next_pos); 77 return true; 78 } 79 else if (g_maze_arr[left.x][left.y] == 0) 80 { 81 next_pos.x = left.x; 82 next_pos.y = left.y; 83 std::cout << "find way : "; 84 print_pos(next_pos); 85 return true; 86 } 87 else if (g_maze_arr[right.x][right.y] == 0) 88 { 89 next_pos.x = right.x; 90 next_pos.y = right.y; 91 std::cout << "find way : "; 92 print_pos(next_pos); 93 return true; 94 } 95 else 96 { 97 std::cout << "no way find in :"; 98 print_pos(curr_pos); 99 return false; 100 } 101 } 102 103 //寻找路径 104 bool find_path() 105 { 106 Pos st_curr_pos, st_next_pos; 107 108 //起点 109 st_curr_pos.x = 1; 110 st_curr_pos.y = 1; 111 g_maze_arr[1][1] = 1; 112 113 //不为终点坐标,继续查找路径 114 while ((st_curr_pos.x != 10) || (st_curr_pos.y != 10)) 115 { 116 //找到下一路径 117 if (find_next(st_curr_pos, st_next_pos)) 118 { 119 //记录下一个位置并置标记为1 120 g_stack_path.push(st_next_pos); 121 st_curr_pos = st_next_pos; 122 g_maze_arr[st_next_pos.x][st_next_pos.y] = 1; 123 } 124 //无路可走 125 else 126 { 127 //路径栈为空,且无路可退,此迷宫无解 128 if (g_stack_path.empty()) 129 { 130 return false; 131 } 132 //根据栈内信息,回退一步 133 else 134 { 135 st_curr_pos = g_stack_path.top(); 136 g_stack_path.pop(); 137 } 138 } 139 } 140 141 return true; 142 } 143 144 //输出路径 145 void print_path() 146 { 147 while (!g_stack_path.empty()) 148 { 149 Pos st_curr_pos = g_stack_path.top(); 150 151 std::cout << "[" << st_curr_pos.x 152 << "," << st_curr_pos.y 153 << "]" << std::endl; 154 155 g_stack_path.pop(); 156 } 157 }
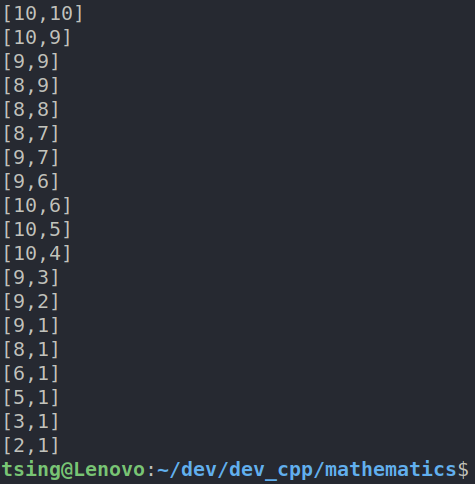
测试如下:

结果