【经典题型】需要理解并记忆的题目(定期复习)
数据结构
链表
33. 链表中倒数第k个节点
从0开始跳n-k步,即可找到倒数第k个点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* findKthToTail(ListNode* pListHead, int k) {
int n = 0;
for(auto p = pListHead; p; p = p->next) n ++ ;
if(k > n) return NULL;
auto p = pListHead;
for(int i = 0; i < n - k; i ++ ) p = p->next;
return p;
}
};
36. 合并两个排序的链表
相当于对链表进行归并排序
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* merge(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
auto dummy = new ListNode(-1), tail = dummy;
while(l1 && l2)
{
if(l1->val < l2->val)
{
tail = tail->next = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
}
else
{
tail = tail->next = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}
}
if(l1) tail->next = l1;
if(l2) tail->next = l2;
return dummy->next;
}
};
作者:Once.
链接:https://www.acwing.com/activity/content/code/content/3140709/
来源:AcWing
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
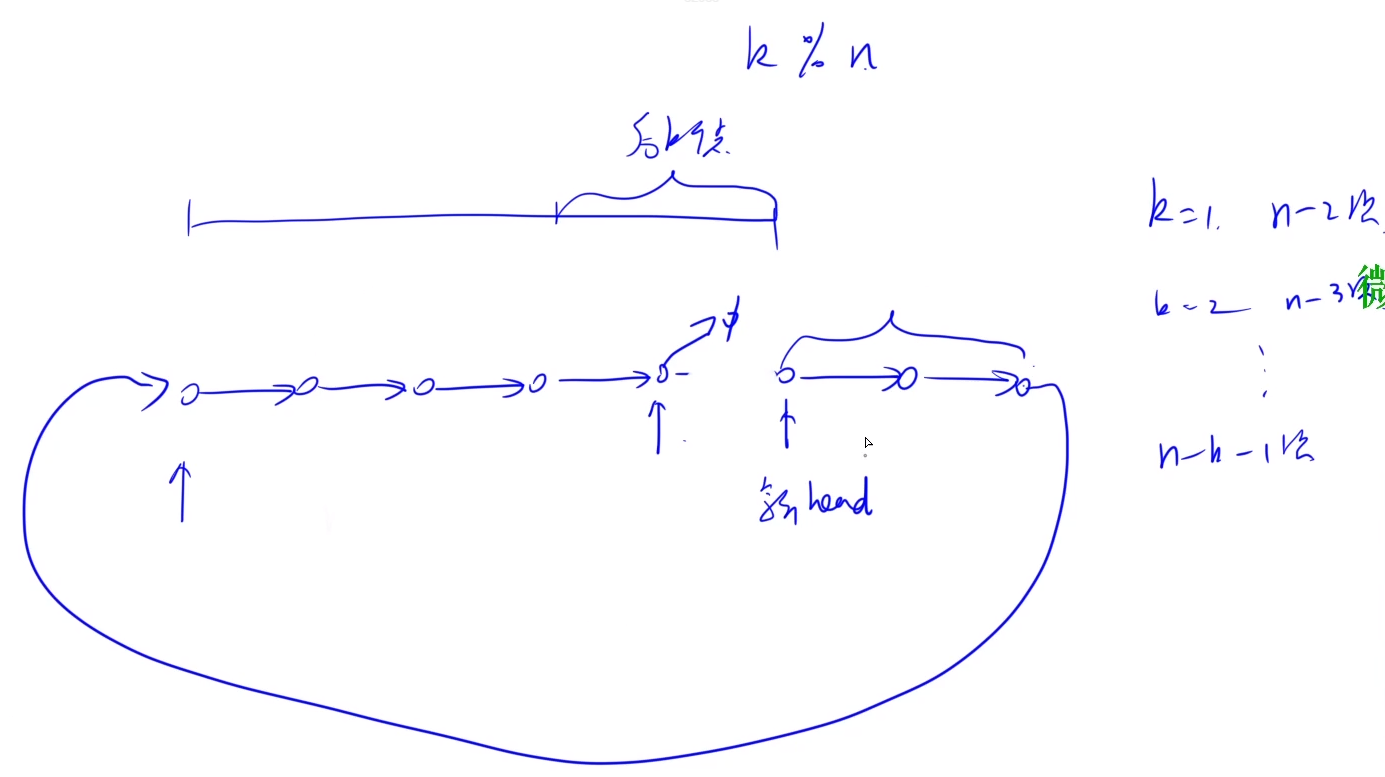
ListNode* rotateRight(ListNode* head, int k) {
if(!head) return head;
int n = 0;
for(auto p = head; p; p = p->next) n ++ ;
k %= n;
if(!k) return head;
auto p = head;
for(int i = 0; i < n - k - 1; i ++ ) p = p->next;
auto tail = head;
while(tail->next) tail = tail->next;
tail->next = head;
head = p->next;
p->next = NULL;
return head;
}
};
作者:Once.
链接:https://www.acwing.com/activity/content/code/content/3238417/
来源:AcWing
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *findFirstCommonNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
auto p = headA, q = headB;
while(p != q)
{
p = p ? p = p->next : headB;
q = q ? q = q->next : headA;
}
return p;
}
};
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {
auto dummy = new ListNode(-1); //建立虚拟头结点
dummy->next = head;
auto p = dummy;
while(p->next) //当p后面有结点的时候
{
auto q = p->next;
while(q && q->val == p->next->val) q = q->next;
if(q == p->next->next) // 说明p,q之间只有一个点(因为只走了一步)
{
p = p->next; // p往后走一位
}
else //p, q之间有大于1个结点,将p,q之间的部分删掉
{
p->next = q;
}
}
return dummy->next;
}
};
作者:Once.
链接:https://www.acwing.com/activity/content/code/content/3141452/
来源:AcWing
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
35. 反转链表
迭代做法
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if(!head || !head->next) return head; // 如果是空节点或只有一个结点,直接返回
auto a = head, b = a->next;
while(b)
{
auto c = b->next;
b->next = a;
a = b, b = c;
}
head->next = NULL;
return a; //此时a为原来的尾结点,即反转链表后的新结点
}
};
作者:Once.
链接:https://www.acwing.com/activity/content/code/content/3122502/
来源:AcWing
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
递归做法
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if(!head || !head->next) return head;
auto tail = reverseList(head->next);
head->next->next = head;
head->next = NULL;
return tail;
}
};
作者:Once.
链接:https://www.acwing.com/activity/content/code/content/3122502/
来源:AcWing
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseBetween(ListNode* head, int left, int right) {
auto dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy->next = head;
auto a = dummy;
for(int i = 0; i < left - 1; i ++ ) a = a->next;
auto b = a->next, c = b->next;
for(int i = 0; i < right - left; i ++ )
{
auto d = c->next;
c->next = b;
b = c, c = d;
}
a->next->next = c;
a->next = b;
return dummy->next;
}
};
作者:Once.
链接:https://www.acwing.com/activity/content/code/content/3122692/
来源:AcWing
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
3757. 重排链表
反转链表与合并链表综合
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
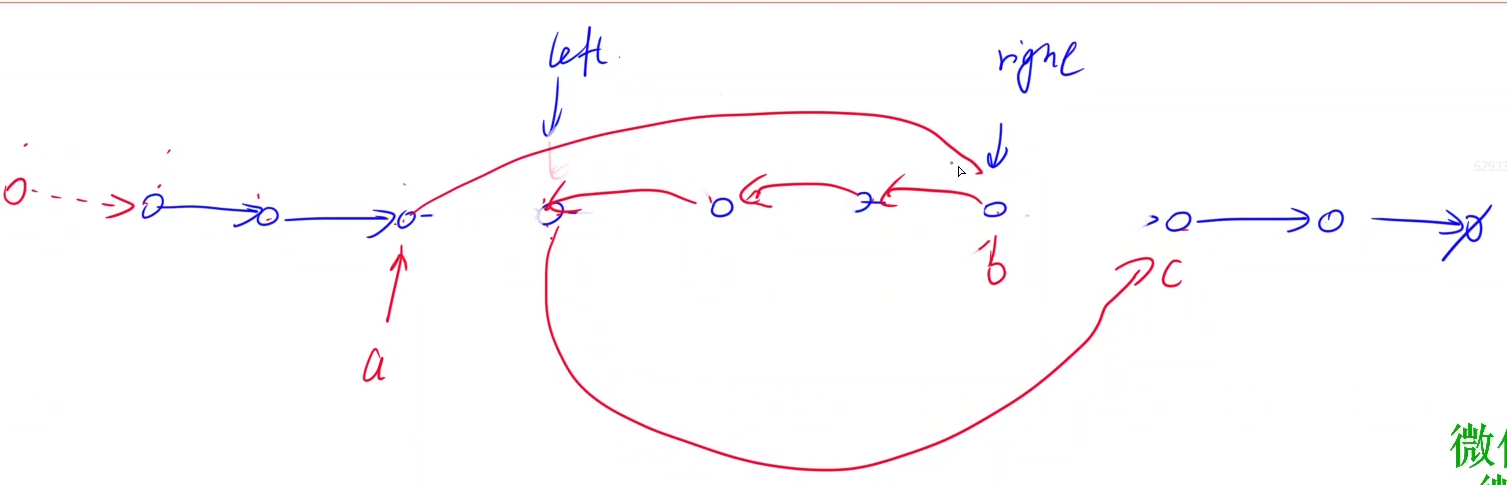
void rearrangedList(ListNode* head) {
if(!head->next) return; //只有一个元素,直接返回
int n = 0;
for(auto p = head; p; p = p->next) n ++ ; //链表结点总数
int left = (n + 1) / 2; //找到中间结点下标
auto a = head;
for(int i = 0; i < left - 1; i ++ ) a = a->next; //找到中间结点
auto b = a->next, c = b->next; //定义中间结点的下一个结点b,以及b的下一个结点c
a->next = b->next = NULL; //将链表从中劈开,分成两个链表,a,b分别为两个链表的尾结点,置为空
while(c) //利用b,c两个结点将第二段链表中的所有结点反转,当c不空就一直做
{
auto p = c->next; //用中间变量p存c的下一个位置
c->next = b; //c的指针指向b
b = c, c = p; //c的值赋给b,c移动到下一个位置
}
for(auto p = head, q = b; q;) //合并两个链表,p, q分别为两个链表的头结点,第二个链表q比较短
{
auto t = q->next;
/*
想象一下,链表p在上面,链表q在下面
1, 2, 3, ..., (n + 1) /2,
a(n),a(n-1),a(n-2),..., (n+1)/2 + 1
*/
q->next = p->next; // a(n)->2
p->next = q; // 1->an
p = p->next->next; // 2->a(n-1)
q = t; // q移动到下一个位置,即a(n-1)
}
}
};
作者:Once.
链接:https://www.acwing.com/activity/content/code/content/2481649/
来源:AcWing
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
栈
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <stack>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
stack<char> op; //操作符栈
stack<int> num; //数字栈
void eval()
{
auto b = num.top(); num.pop();
auto a = num.top(); num.pop();
auto c = op.top(); op.pop();
int x;
if(c == '+') x = a + b;
else if(c == '-') x = a - b;
else if(c == '*') x = a * b;
else x = a / b;
num.push(x);
}
int main()
{
string s;
cin >> s;
unordered_map<char, int> pr{{'+', 1}, {'-', 1}, {'*', 2}, {'/', 2}}; //定义运算符优先级
for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); i ++ )
{
if(isdigit(s[i])) //是数,压入数字栈
{
int j = i, x = 0;
while(isdigit(s[j]) && j < s.size())
x = x * 10 + s[j ++ ] - '0';
num.push(x);
i = j - 1;
}
else if(s[i] == '(') //是左括号,压入操作符栈
{
op.push(s[i]);
}
else if(s[i] == ')') //是右括号,计算前面的数直到遇到左括号为止
{
while(op.top() != '(') eval();
op.pop(); //弹出左括号
}
else //是操作符
{
// 栈顶操作符优先级大于等于当前操作符优先级,则要先计算
while(op.size() && op.top() != '(' && pr[op.top()] >= pr[s[i]])
eval();
op.push(s[i]);
}
}
while(op.size()) eval();
cout << num.top() << endl;
return 0;
}
中缀表达式转后缀表达式的方法:
去掉数栈,遇到数直接输出,其他不变。因为上面这个表达式求值的原理就是先把中缀表达式转为后缀表达式然后借助一个栈来计算。
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
stack<char> op;
void eval()
{
auto c = op.top(); op.pop();
cout << c << ' ';
}
int main()
{
string s;
cin >> s;
unordered_map<char, int> pr{{'+', 1}, {'-', 1}, {'*', 2}, {'/', 2}};
for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); i ++ )
{
if(isdigit(s[i]))
{
int j = i, x = 0;
while(j < s.size() && isdigit(s[j]))
x = x * 10 + s[j ++ ] - '0';
//num.push(x);
cout << x << ' ';
i = j - 1;
}
else if(s[i] == '(') op.push(s[i]);
else if(s[i] == ')')
{
while(op.top() != '(') eval();
op.pop();
}
else
{
while(op.size() && op.top() != '(' && pr[op.top()] >= pr[s[i]])
eval();
op.push(s[i]);
}
}
while(op.size()) eval();
return 0;
}
表达式计算终极版(含乘方,括号数量不等,负数)
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
stack<char> op;
stack<int> num;
int qmi(int a, int k) //快速幂
{
int res = 1;
while(k)
{
if(k & 1) res = res * a;
a = a * a;
k >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
void eval()
{
int b = num.top(); num.pop();
int a = num.top(); num.pop();
char c = op.top(); op.pop();
int x;
if(c == '+') x = a + b;
else if(c == '-') x = a - b;
else if(c == '*') x = a * b;
else if(c == '/') x = a / b;
else if(c == '^') x = qmi(a, b);
num.push(x);
}
int main()
{
string s;
cin >> s;
unordered_map<char, int> pr{{'+', 1}, {'-', 1}, {'*', 2}, {'/', 2}, {'^', 3}};
//l, r分别为输入串中左右括号数量
int l = 0, r = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); i ++ )
if(s[i] == '(') l ++ ;
else if(s[i] == ')') r ++ ;
char c;
if(l > r) c = ')'; // 右括号少,补右括号
else if(l < r) c = '('; // 左括号少,补左括号
string add;
for(int i = 0; i < abs(l - r); i ++ ) add += c;
// 使表达式中左右括号数量相等,以便直接套模板
if(l > r) s = s + add;
else if(l < r) s = add + s;
// 处理-为负号的情况,在前面补0即可
for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); i ++ )
{
if(s[i] == '-' && i == 0) s = '0' + s;
else if(s[i] == '-' && i > 0 && !isdigit(s[i - 1]) && s[i - 1] != ')')
{
s.insert(i - 1, "0");
i ++ ;
}
}
// 基础课模板
for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); i ++ )
{
if(isdigit(s[i]))
{
int j = i, x = 0;
while(j < s.size() && isdigit(s[j]))
x = x * 10 + s[j ++ ] - '0';
num.push(x);
i = j - 1;
}
else if(s[i] == '(') op.push(s[i]);
else if(s[i] == ')')
{
while(op.top() != '(') eval();
op.pop();
}
else
{
while(op.size() && op.top() != '(' && pr[op.top()] >= pr[s[i]])
eval();
op.push(s[i]);
}
}
while(op.size()) eval();
cout << num.top() << endl;
return 0;
}
作者:NFYD
链接:https://www.acwing.com/solution/content/130147/
来源:AcWing
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
class Solution {
public:
stack<int> num;
void eval(string c)
{
auto b = num.top(); num.pop();
auto a = num.top(); num.pop();
if(c == "+") num.push(a + b);
else if(c == "-") num.push(a - b);
else if(c == "*") num.push(a * b);
else num.push(a / b);
}
int evalRPN(vector<string>& tokens) {
unordered_set<string> S{"+", "-", "*", "/"};
for(auto& c : tokens)
{
if(S.count(c)) eval(c);
else num.push(stoi(c));
}
return num.top();
}
};
作者:Once.
链接:https://www.acwing.com/activity/content/code/content/3122936/
来源:AcWing
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
树
层序遍历二叉树
二叉树的层序遍历模板题
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> printFromTopToBottom(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
if(!root) return res;
//层序遍历
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while(q.size())
{
auto t = q.front();
q.pop();
res.push_back(t->val);
if(t->left) q.push(t->left); // 如果当前结点的左儿子存在,左儿子入队
if(t->right) q.push(t->right); // 如果当前结点的右儿子存在,右儿子入队
}
return res;
}
};
1497. 树的遍历
已知中序、后序(或前序)序列,构建二叉树并遍历
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 40;
int n;
unordered_map<int, int> l, r, pos;
int inorder[N], postorder[N];
int build(int il, int ir, int pl, int pr)
{
int root = postorder[pr]; // 后序遍历的最后一个结点为根结点
int k = pos[root]; // 在哈希表中找到根结点在中序遍历中的下标k
if(il < k) l[root] = build(il, k - 1, pl, pl + k - 1 - il); // 如果左子树存在,递归构建左子树
if(ir > k) r[root] = build(k + 1, ir, pl + k - 1 - il + 1, pr - 1); //如果右子树存在,递归构建右子树
return root; // 返回根结点
}
void bfs(int root)
{
queue<int> q;
q.push(root);
while(q.size())
{
int t = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << t << ' ';
if(l.count(t)) q.push(l[t]); //如果左子树存在,左子树入队
if(r.count(t)) q.push(r[t]); //如果右子树存在,右子树入队
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) cin >> postorder[i];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
{
cin >> inorder[i];
pos[inorder[i]] = i; // 存一下中序遍历结点的下标
}
int root = build(0, n - 1, 0, n - 1);
bfs(root);
return 0;
}
1631. 后序遍历
已知前序、中序序列,求后序序列。(本题也是建树,只不过不用真的建出来,在建树过程中只存后序序列即可)
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
const int N = 5e4 + 10;
int n;
int preorder[N], inorder[N];
unordered_map<int, int> pos;
int post[N], cnt; // post数组存后序遍历序列
void build(int il, int ir, int pl, int pr)
{
int root = preorder[pl]; //根结点为前序遍历的第一个节点
int k = pos[root]; //在哈希表中找到根结点在中序遍历中的下标
if(il < k) build(il, k - 1, pl + 1, pl + 1 + k - 1 - il);
if(ir > k) build(k + 1, ir, (pl + 1 + k - 1 - il) + 1, pr); // 前序的右边为pr,因为根结点在最前面(对比后序)
post[cnt ++ ] = root;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) cin >> preorder[i];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
{
cin >> inorder[i];
pos[inorder[i]] = i;
}
build(0, n - 1, 0, n - 1);
cout << post[0] << endl;
return 0;
}
19. 二叉树的下一个节点
即求二叉树中某个结点的后继结点
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode *father;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL), father(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* inorderSuccessor(TreeNode* p) {
if(p->right) // 右子树存在
{
p = p->right;
while(p->left) p = p->left;
return p;
}
while(p->father && p == p->father->right) p = p->father;
return p->father;
}
};
作者:Once.
链接:https://www.acwing.com/activity/content/code/content/3153457/
来源:AcWing
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
搜索与图论
拓扑排序
848. 有向图的拓扑序列
结构体写法
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n, m;
int d[N], q[N];
struct Node
{
int id;
Node* next;
Node(int _id): id(_id), next(NULL) {}
}*head[N];
void add(int a, int b)
{
auto p = new Node(b);
p->next = head[a];
head[a] = p;
}
bool topsort()
{
int hh = 0, tt = -1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
if(!d[i])
q[++ tt] = i;
while(hh <= tt)
{
int t = q[hh ++ ];
for(auto p = head[t]; p; p = p->next)
{
if(-- d[p->id] == 0)
q[++ tt] = p->id;
}
}
return tt == n - 1;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
while(m -- )
{
int a, b;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
add(a, b);
d[b] ++ ;
}
if(!topsort()) puts("-1");
else
{
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
printf("%d ", q[i]);
}
return 0;
}
静态链表写法
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n, m;
int h[N], e[N], ne[N], idx;
int d[N], q[N];
void add(int a, int b)
{
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx ++ ;
}
bool topsort()
{
int hh = 0, tt = -1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
if(!d[i])
q[++ tt ] = i;
while(hh <= tt)
{
int t = q[hh ++ ];
for(int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if(-- d[j] == 0)
q[++ tt] = j;
}
}
return tt == n - 1;
}
int main()
{
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
while(m -- )
{
int a, b;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
add(a, b);
d[b] ++ ;
}
if(!topsort()) puts("-1");
else
{
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
printf("%d ", q[i]);
}
return 0;
}
字符串
KMP
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10, M = 1e6 + 10;
int n, m;
char p[N], s[M];
int ne[N];
int main()
{
scanf("%d%s", &n, p + 1); //下标从1开始
scanf("%d%s", &m, s + 1); //下标从1开始
//求短串next数组 ,n为短串长度
for(int i = 2, j = 0; i <= n; i ++ )
{
while(j && p[i] != p[j + 1]) j = ne[j];
if(p[i] == p[j + 1]) j ++ ;
ne[i] = j;
}
//对长串进行匹配,m为长串长度
for(int i = 1, j = 0; i <= m; i ++ )
{
while(j && s[i] != p[j + 1]) j = ne[j];
if(s[i] == p[j + 1]) j ++ ;
if(j == n) printf("%d ", i - n);
}
return 0;
}