c++ STL
1)顺序表
vector 表示顺序表,其内元素以相邻的顺序存放。从存储结构上来说,vector 与数组相同,不同之处在于其长度可变。
函数举例:
1 #include "stdafx.h" 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<vector> 4 using namespace std; 5 int main() 6 { 7 vector<int> vec = { 10,98,76 }; //定义一个顺序表 8 vec.push_back(100); //在顺序表末尾添加一个元素100 9 cout << "第三个元素的值:"; 10 cout << vec[2] << endl; 11 cout << "此时该顺序表的长度:"; 12 cout << vec.size() << endl; 13 cout << "此时顺序表内容:"; 14 for (int i = 0; i < vec.size(); i++) 15 cout << vec[i]<<" "; 16 cout << endl; 17 vec.pop_back(); //取出顺序表末尾元素 18 cout << "此时该顺序表的长度:"; 19 cout << vec.size() << endl; 20 cout << "此时顺序表内容:"; 21 for (int j = 0; j < vec.size(); j++) 22 cout << vec[j] << " "; 23 cout << endl; 24 return 0; 25 }
运行结果:

2)单链表:(该内容参考与https://blog.csdn.net/sin_geek/article/details/51089757)
forward_list 表示单链表,其内元素随机存放,以指针相连。
forward_list
操作构造、复制与析构
1 forward_list<Elem> c //默认构造函数;创建一个空forward_list 2 3 forward_list<Elem> c(c2) //复制构造函数;创建一个新的forward_list作为c2的副本(所有元素都被复制) 4 5 forward_list<Elem> c = c2 //复制构造函数;创建一个新的forward_list作为c2的副本(所有元素都被复制) 6 7 forward_list<Elem> c(rv) //移动构造函数;使用右值对象rv创建一个新forward_list 8 9 forward_list<Elem> c = rv //移动构造函数;使用右值对象rv创建一个新forward_list 10 11 forward_list<Elem> c(n) //使用默认构造函数创建含有n个元素的forward_list 12 13 forward_list<Elem> c(n,elem) //创建一个forward_list,并使用n个elem进行初始化 14 15 forward_list<Elem> c(beg,end) //创建一个forward_list,并使用beg到end范围内的值进行初始化 16 17 forward_list<Elem> c(initlist) //创建一个forward_list,并使用初始化列表进行初始化 18 19 forward_list<Elem> c = initlist //创建一个forward_list,并使用初始化列表进行初始化 20 21 c.~forward_list() //销毁所有元素并释放内存
非变动性操作
1 c.empty() //判断容器是否为空 2 3 c.max_size() //返回可容纳的元素最大数量 4 5 c1 == c2 //判断c1与c2是否相等 6 7 c1 != c2 //判断c1与c2是否不相等,等同于!(c1==c2) 8 9 c1 < c2 //判断c1是否小于c2 10 11 c1 > c2 //判断c1是否大于c2 12 13 c1 <= c2 //判断c1是否小于等于c2 14 15 c1 >= c2 //判断c1是否大于等于c2
赋值
1 c = c2 //将c2所有元素赋值给c 2 3 c = rv //将右值对象rv的所有元素移动赋值给c 4 5 c = initlist //使用初始化列表进行赋值 6 7 c.assign(initlist) //使用初始化列表进行赋值 8 9 c.assign(n,elem) //使用n个elem元素进行赋值 10 11 c.assign(beg,end) //使用beg到end范围内的元素进行赋值 12 13 c1.swap(c2) //交换c1和c2的数 14 15 swap(c1,c2) //交换c1和c2的数
元素存取
c.front() //返回第一个元素,不检查第一个元素是否存在
迭代器相关函数
1 c.begin() //返回一个双向迭代器,指向第一个元素 2 3 c.end() //返回一个双向迭代器,指向最后一个元素 4 5 c.cbegin() //返回一个双向常迭代器,指向第一个元素 6 7 c.cend() //返回一个双向常迭代器,指向最后一个元素 8 9 c.before_begin() //返回一个前向迭代器,指向第一个元素之前的位置 10 11 c.cbefore_begin() //返回一个前向常迭代器,指向第一个元素之前的位置
插入和移除元素
1 c.push_front(elem) //在头部添加一个elem副本 2 3 c.pop_front() //移除头部元素(但不回传) 4 5 c.insert_after(pos,elem) //在迭代器位置之后插入一个elem副本,并返回新元素的位置 6 7 c.insert_after(pos,n,elem) //在迭代器位置之后插入n个elem副本,并返回第一个新元素的位置;若无新插入值,返回原位置 8 9 c.insert_after(pos,beg,end) //在迭代器位置之后插入范围beg到end的所有元素的副本,并返回第一个新元素的位置;若无新插入值,返回原位置 10 11 c.insert_after(pos,initforward_list) //在迭代器位置之后插入初始化列表的所有元素的副本,并返回第一个新元素的位置;若无新插入值,返回原位置 12 13 c.emplace_after(pos,args...) //在迭代器位置之后插入一个使用args初始化的元素副本,并返回新元素的位置 14 15 c.emplace_front(args...) //在头部添加一个使用args初始化的元素副本,无返回值 16 17 c.erase_after(pos) //移除迭代器位置的元素,无返回值 18 19 c.erase_after(beg,end) //移除beg到end范围内的所有元素,无返回值 20 21 c.remove(val) //移除所有值为val的元素 22 23 c.remove_if(op) //移除所有满足op条件的元素 24 25 c.resize(num) //将元素数量设为num(如果size()增大,多出来的元素使用默认构造函数创建) 26 27 c.resize(num,elem) //将元素数量设为num(如果size()增大,多出来的元素都是elem的副本) 28 29 c.clear() //移除所以元素,清空容器
特殊修改操作
1 c.unique() //若存在相邻而数值相等的元素,移除重复元素 2 3 c.unique(op) //若存在相邻而数值相等的元素,且满足op条件时,移除重复元素 4 5 c.splice_after(pos,c2) //将c2内的所有元素转移到c1内pos所指的位置之后 6 7 c.splice_after(pos,c2,c2pos) //将c2内c2pos之后的元素转移到c1内pos所指的位置之后 8 9 c.splice_after(pos,c2,c2beg,c2end) //将c2内从c2beg到c2end区间内的所有元素转移到c1内pos所指的位置之后 10 11 c.sort() //以operator<为准则,对所有元素排序 12 13 c.sort(op) //以op为准则,对所有元素排序 14 15 c.merge(c2) //假设c1和c2都包含已序元素,将c2的全部元素转移到c1.并保证合并后的forward_list仍为已序 16 17 c.merge(c2,op) //假设c1和c2都包含op原则下已序元素,将c2的全部元素转移到c1.并保证合并后的forward_list在op原则下仍为已序 18 19 c.reverse() //将所有元素反序
代码示例:
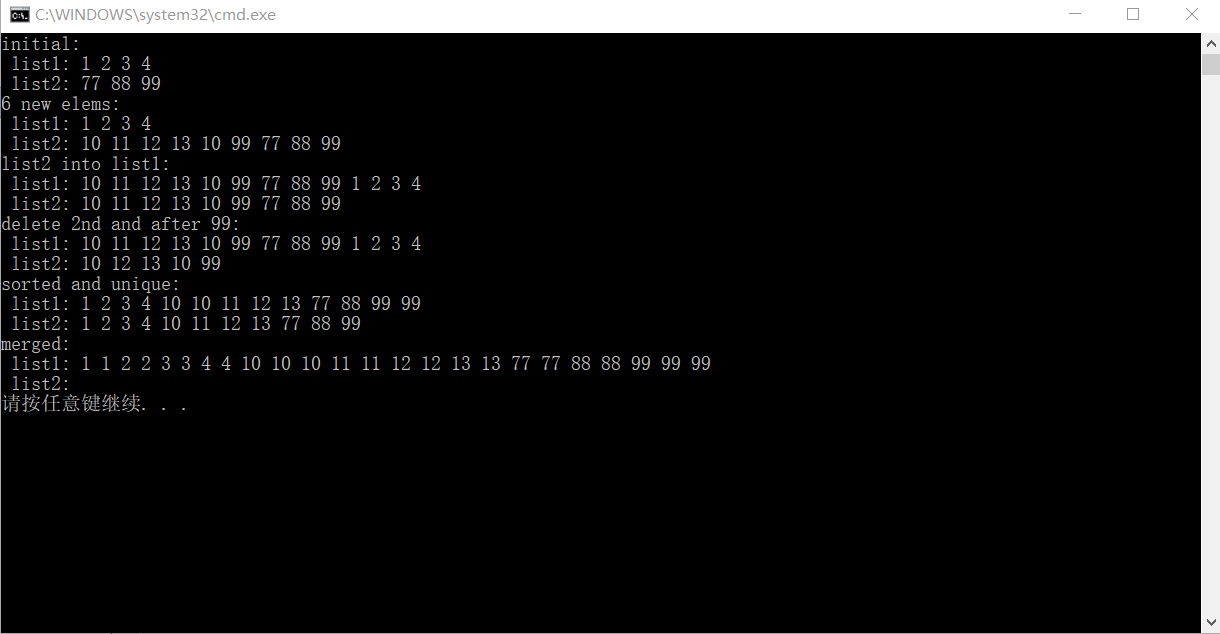
1 #include "stdafx.h" 2 #include <forward_list> 3 #include <iostream> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <iterator> 6 #include <string> 7 8 using namespace std; 9 10 void printLists (const string& s, const forward_list<int>& l1, 11 const forward_list<int>& l2) 12 { 13 cout << s << endl; 14 cout << " list1: "; 15 copy (l1.cbegin(), l1.cend(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout," ")); 16 cout << endl << " list2: "; 17 copy (l2.cbegin(), l2.cend(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout," ")); 18 cout << endl; 19 } 20 21 int main() 22 { 23 //创建两个前向列表 24 forward_list<int> list1 = { 1, 2, 3, 4 }; 25 forward_list<int> list2 = { 77, 88, 99 }; 26 printLists ("initial:", list1, list2); 27 28 //在list2头部插入6个新元素 29 list2.insert_after(list2.before_begin(),99); 30 list2.push_front(10); 31 list2.insert_after(list2.before_begin(), {10,11,12,13} ); 32 printLists ("6 new elems:", list1, list2); 33 34 //在list1头部插入list2全部元素 35 list1.insert_after(list1.before_begin(), 36 list2.begin(),list2.end()); 37 printLists ("list2 into list1:", list1, list2); 38 39 //删除list2的第二个元素,删除list2中值为99的元素后面的所有元素 40 list2.erase_after(list2.begin()); 41 list2.erase_after(find(list2.begin(),list2.end(), 42 99), 43 list2.end()); 44 printLists ("delete 2nd and after 99:", list1, list2); 45 46 //对list1排序,并把list1赋值给list2,对list2去重 47 list1.sort(); 48 list2 = list1; 49 list2.unique(); 50 printLists ("sorted and unique:", list1, list2); 51 52 //把已序的list2合并到list1中 53 list1.merge(list2); 54 printLists ("merged:", list1, list2); 55 56 return 0; 57 }
运行结果:
3)双向链表:
list 表示双链表,其内元素随机存放,以指针相连。
list可以在头部进行添加删除操作,但vector不行。
下面是几个list特有的函数。(从另一方面说明list在删除操作方面的速度之快)
1 remove() //从list删除元素 2 remove_if() //按指定条件删除元素 3 reverse() //把list的元素倒转 4 sort() //给list排序 5 unique() //删除list中重复的元素
示例代码如下:
1 #include "stdafx.h" 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include <iterator> 4 #include<algorithm> 5 #include<list> 6 using namespace std; 7 int main() 8 { 9 list<int>dlist; 10 list<int>dlist1 = { 1,2,3,4,5 }; 11 list<int>dlist2 = { 45,79,66,12,701 }; 12 list<int>dlist3 = { 1,22,22,3,5 }; 13 list<int>dlist4 = { 11,12,13,14,15 }; 14 dlist.push_front(10); //头插入 15 dlist.push_front(100); 16 dlist.push_front(37); 17 dlist.push_front(55); 18 dlist.push_back(89); //尾插入 19 dlist.push_back(64); 20 cout << "dlist:"; 21 copy(dlist.cbegin(), dlist.cend(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " ")); 22 cout << endl; 23 dlist1.reverse(); //把list的元素倒转 24 cout << "倒转后的dlist1:"; 25 copy(dlist1.cbegin(), dlist1.cend(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " ")); 26 cout << endl; 27 cout << "list2:"; 28 copy(dlist2.cbegin(), dlist2.cend(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " ")); 29 cout << endl; 30 dlist2.sort(); //给dlist2排序 31 cout << "排序后的list2:"; 32 copy(dlist2.cbegin(), dlist2.cend(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " ")); 33 cout << endl; 34 cout << "此时dlist3:"; 35 dlist3.unique(); // 删除dlist3中相邻并且重复的元素 36 copy(dlist3.cbegin(), dlist3.cend(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " ")); 37 cout << endl; 38 dlist4.remove(11); //从dist4中删除元素 39 copy(dlist4.cbegin(), dlist4.cend(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " ")); 40 cout << endl; 41 return 0; 42 }
运行结果:

4)双向队列:
![]()
示例代码如下:
1 #include "stdafx.h" 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<deque> 4 #include <iterator> 5 #include<algorithm> 6 using namespace std; 7 int main() 8 { 9 deque<int>dq; 10 dq.push_front(10); //进队头 11 dq.push_front(100); 12 dq.push_back(50); //进队尾 13 dq.push_back(55); 14 cout << "dq: "; 15 copy(dq.cbegin(), dq.cend(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " ")); 16 cout << endl; 17 dq.pop_back(); //队尾元素出队 18 dq.pop_front(); //队头元素出队 19 cout << "此时的dq: "; 20 copy(dq.cbegin(), dq.cend(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " ")); 21 cout << endl; 22 }
运行结果:

5)valarry数组:

示例代码如下:
1 #include "stdafx.h" 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<valarray> 4 #include <iterator> 5 #include<algorithm> 6 using namespace std; 7 int main() 8 { 9 valarray<int>va = { 1,2,3,4,5 }; 10 va[3] = 7; //修改va[3]的值 11 cout << "valarry: "; 12 for (int i = 0; i < va.size(); i++) 13 cout << va[i] << " "; 14 cout << endl; 15 cout << "数组中最大值: " <<va.max() << endl; 16 cout << "数组中最小值: " << va.min() << endl; 17 cout << "该数组所有元素和: " << va.sum() << endl; 18 return 0; 19 }
输出结果:

6)map容器:(参考于https://www.cnblogs.com/Braveliu/p/6427050.html)
map 类型存储的每个元素都是 pair 类型,称为“键-值”对,每个元素的位置
由其中的“键”来标识。
map 容器共包括 map、multimap、unordered_map 和 unordered_multimap。区别在于:
1.带有multi的可以有键重复的元素,
2.带有unordered的元素是无序的。
3.map 中的元素都是按照键排序的,且元素的键惟一。
(1)定义、插入数据方法实例
代码如下:
1 #include "stdafx.h" 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<map> 4 #include<string> 5 #include <iterator> 6 #include<algorithm> 7 using namespace std; 8 void print(map<int, string>& mapStu, int nValue) 9 { 10 cout << "mapStu" << nValue << "数据信息:" << endl; 11 cout << "size: " << mapStu.size() << endl; 12 map<int, string>::iterator iter = mapStu.begin(); 13 for (; iter != mapStu.end(); ++iter) 14 { 15 cout << "key: " << iter->first << " value: " << iter->second << endl; 16 } 17 cout << endl; 18 } 19 20 void main() 21 { 22 // 第一种定义map的方法 23 map<int, string> mapStu1; 24 // 第二种定义map的方法 25 typedef map<int, string> mapType; 26 mapType mapStu2, mapStu3, mapStu4; 27 28 // 第一种插入数据方法:用insert函数插入value_type数据 29 mapStu1.insert(map<int, string>::value_type(1, "Qin")); 30 mapStu1.insert(map<int, string>::value_type(2, "Sun")); 31 mapStu1.insert(map<int, string>::value_type(3, "Wang")); 32 mapStu1.insert(map<int, string>::value_type(2, "Zhao")); 33 print(mapStu1, 1); 34 // 第二种插入数据方法:用insert函数插入pair数据 35 mapStu2.insert(pair<int, string>(1, "Qin")); 36 mapStu2.insert(pair<int, string>(2, "Sun")); 37 mapStu2.insert(pair<int, string>(3, "Wang")); 38 mapStu2.insert(pair<int, string>(2, "Zhao")); 39 print(mapStu2, 2); 40 // 第三种插入数据方法:用insert函数插入make_pair数据 41 mapStu3.insert(make_pair<int, string>(1, "Qin")); 42 mapStu3.insert(make_pair<int, string>(2, "Sun")); 43 mapStu3.insert(make_pair<int, string>(3, "Wang")); 44 mapStu3.insert(make_pair<int, string>(2, "Zhao")); 45 print(mapStu3, 3); 46 // 第四种插入数据方法:数组插入法 47 mapStu4[1] = "Qin"; 48 mapStu4[2] = "Sun"; 49 mapStu4[3] = "Wang"; 50 mapStu4[2] = "Zhao"; 51 print(mapStu4, 4); 52 system("pause"); 53 }
输出结果:

第一、二、三种在效果上是完全一样的,用insert函数插入数据,在数据的插入过程中涉及到集合的唯一性这个概念:
即当map中有这个关键字时,insert操作再插入数据是不会成功的。
但是,用数组(第四种)方式就不同了,它可以覆盖以前该关键字对应的值,用程序说明如下:
mapStu1.insert(map<int, string>::value_type(2, "Sun"));
mapStu1.insert(map<int, string>::value_type(2, "Zhao"));
上面这两条语句执行后,mapStu1中2这个关键字对应的值是“Sun”,第二条语句并没有生效。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号