数据结构之图(2-1)【十字链表】适用于有向图
邻接表固然优秀,但也有不足,例如对有向图的处理上,有时候需要再建立一个逆邻接表~
那我们思考了:有没有可能把邻接表和逆邻接表结合起来呢?
答案是肯定的,这就是我们现在要谈的十字链表(Orthogonal List)
为此我们重新定义顶点表结点结构:

接着重新定义边表结点结构

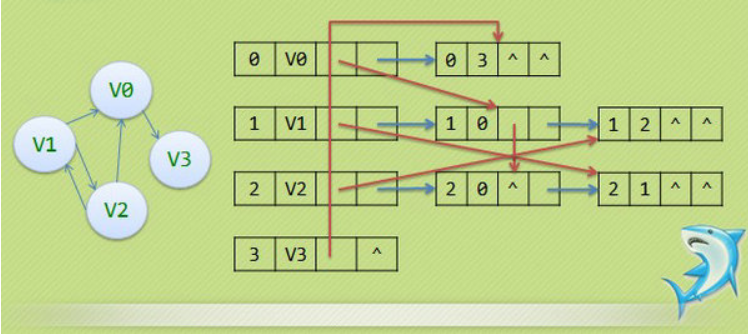
十字链表的好处就是因为把邻接表和逆邻接表整合在了一起,这样既容易找到以Vi为尾的弧,也容易找到以Vi为头的弧,因
而容易求得顶点的出度和入度。十字链表除了结构复杂一点外,其实创建图算法的时间复杂度是和邻接表相同的,因此,在
有向图的应用中,十字链表也是非常好的数据结构模型。
代码如下:
1 #include "stdafx.h" 2 #include<iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 #define MAX_VERTEX_NUM 20 5 typedef char InfoType; 6 7 typedef struct ArcBox 8 { 9 int tailvex, headvex; //该弧的尾和头顶点的位置 10 struct ArcBox *hlink, *tlink; //分别为弧头相同和弧尾相同的弧的链域 11 InfoType *info; //改弧相关信息的指针 12 }ArcBox; 13 typedef struct 14 { 15 char data; 16 ArcBox *firstin, *firstout; //分别指向该顶点第一条入弧和出弧 17 }VexNode; 18 typedef struct 19 { 20 VexNode xlist[MAX_VERTEX_NUM]; //表头向量 21 int vexnum, arcnum; //有向图的当前顶点数和弧数 22 }OLGraph; 23 24 int LocateVex(OLGraph G, char v) //// 返回顶点v在有向图G中的位置(序号),如不存在则返回-1 25 { 26 for (int u = 0; u<G.vexnum; u++) 27 if(G.xlist[u].data == v) 28 return u; 29 return -1; 30 } 31 32 void CreateDG(OLGraph &G) // 采用十字链表存储表示,构造有向图G 33 { 34 int i, j, k; 35 int IncInfo; 36 ArcBox *p; 37 char v1, v2; 38 cout << "请输入有向图的顶点数,弧数:"; 39 cin >> G.vexnum >> G.arcnum ; 40 cout << "输入顶点:"; 41 for (i = 0; i<G.vexnum; ++i) 42 { 43 cin >> G.xlist[i].data; 44 G.xlist[i].firstin = NULL; 45 G.xlist[i].firstout = NULL; 46 } 47 cout << "请输入" << G.arcnum << "条弧的弧尾和弧头(空格为间隔): " << endl; 48 for (k = 0; k<G.arcnum; ++k) 49 { 50 cin >> v1 >> v2; 51 i = LocateVex(G, v1); 52 j = LocateVex(G, v2); 53 p = new ArcBox; 54 p->tailvex = i; 55 p->headvex = j; 56 p->hlink = G.xlist[j].firstin; 57 p->tlink = G.xlist[i].firstout; 58 G.xlist[j].firstin = G.xlist[i].firstout = p; 59 } 60 } 61 62 void Display(OLGraph G) // 输出有向图G 63 { 64 int i; 65 ArcBox *p; 66 cout << "共" << G.vexnum << "个顶点," << G.arcnum << "条弧:" << endl; 67 for (i = 0; i<G.vexnum; i++) 68 { 69 cout << "顶点" << G.xlist[i].data << ": 入度: "; 70 p = G.xlist[i].firstin; 71 while (p) 72 { 73 cout << G.xlist[p->tailvex].data<<" "; 74 p = p->hlink; 75 } 76 cout << "出度: "; 77 p = G.xlist[i].firstout; 78 while (p) 79 { 80 cout << G.xlist[p->headvex].data<<" "; 81 p = p->tlink; 82 } 83 cout << endl; 84 } 85 } 86 87 int main() 88 { 89 OLGraph G; 90 CreateDG(G); 91 Display(G); 92 return 0; 93 }
输出结果:


