Java IO流(二)
一.字符编码
char
计算机存储的都是二进制数据,其实就是一个一个的数值
字符要存储,就必须让这个字符对应一个数
将一个字符转成数字,这个过程就叫编码,反过来将一个数字转成字符就叫解码
中国大陆 (GBK编码字符集)
中-->20013 编码
20013 -->中 解码
(Unicode编码字符集)
中-->10320 编码
10320-->中 解码
当编码和解码采用的字符集不同时就会产生乱码

二.桥接流
(1)何为桥椄流
2个大的用处
1 将字节流的流转换成字符流
//字节流转换为字符流,中文乱码处理
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(file);
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(in);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
2 可以指定编码和解码的字符集

(2)InputStreamReader
(3)OutputStreamWriter
三.缓冲流
(1)何为缓冲流
之前我们使用的流去读写数据,都是立刻打开磁盘的IO,然后往磁盘读写数据。
每次的磁盘的IO操作都是非常消耗性能,效率非常低。
如果在读写数据时,先不打开磁盘IO,而是把数据放到一个缓冲区(内存),当缓冲区满了时,才去打开磁盘IO,然后将缓冲区的数据一次读写,这样的话磁盘IO操作减少了,效率得到了大大的提升
典型的以空间换时间
(2)BufferedInputStream与BufferedOutputStream
(3)BuffredWriter 与 BuffredReader
public class TestFileWriter { public static void write() throws IOException { File file = new File("c:\\g.txt"); Writer out = new FileWriter(file); String str = "我是中国人"; long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++) { out.write(str); } long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println(end-start); out.close(); } public static void BufferedWrite() throws IOException { File file = new File("c:\\h.txt"); Writer out = new FileWriter(file); BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(out); String str = "我是中国人"; long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++) { bw.write(str); } long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println(end-start); bw.close(); out.close(); } public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { write(); BufferedWrite(); } }
四.数据流
(1)何为数据流
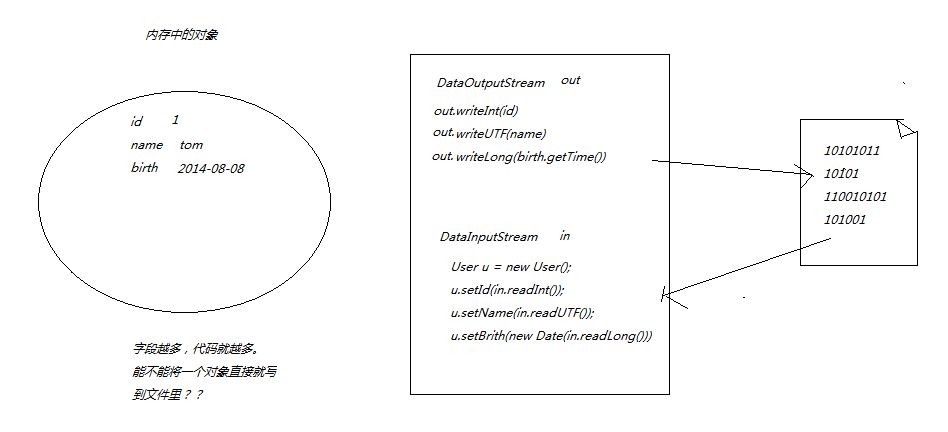
数据流指的是可以直接读写八种基本数据类型和字符串的流
二进制文件的读写
使用DataInputStream和DataOutputStream读写二进制文件
(2)DataOutputStream
(3)DataInputStream
五.打印流
(1)何为打印流
用来打印各种数据值,方便地打印各种数据值表示形式
是在其它流的基础上添加的一些功能
OutputStream
write(true); //没有的
=>write(String.valueOf(true).getBytes());//byte[] bs = "trut".getBytes();
Writer
write(true); //没有的
=》write(String.valueOf(true));
PrintStream//helloword用的打印流
print(true)
println(true);
上面2个方法最终会将任何类型的值转成字符串输出
printf()
(2)PrintStream
将任何java类型的数据都转成String输出去 System.out.println("Hello"); PrintStream out = System.out;//备份,输出到控制台,这是默认的 System.setOut(new PrintStream("test.txt"));//输出到文件 System.out.println("Hello"); System.setOut(out); System.out.println("Hello34434354");
(3)PrintWriter
六.随机访问文件RandomAccessFile
IO seek() public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { RandomAccessFile raf = null; try { raf = new RandomAccessFile("E:\\01.jpg","rwd"); byte[] b = new byte[1024 * 10]; int len = -1;//长度 while((len=raf.read(b))!=-1){ //加密 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { b[i] = (byte)(b[i]^8); } long pos = raf.getFilePointer();//得偏移量 raf.seek(pos-len);//设置 得偏移量回到上次读的位置 raf.write(b,0,len); } System.out.println("加密完成"); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
七.对象序例化
(1)何为对象序列化
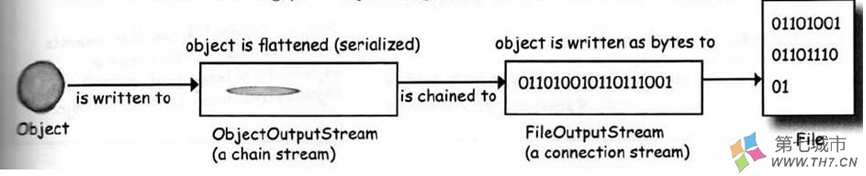
将一个对象用流的方式输出到文件或者网络等数据源,这个过程就叫序列化
传统方式
对象流序列化方式
场合
存储游戏数据
发送游戏数据
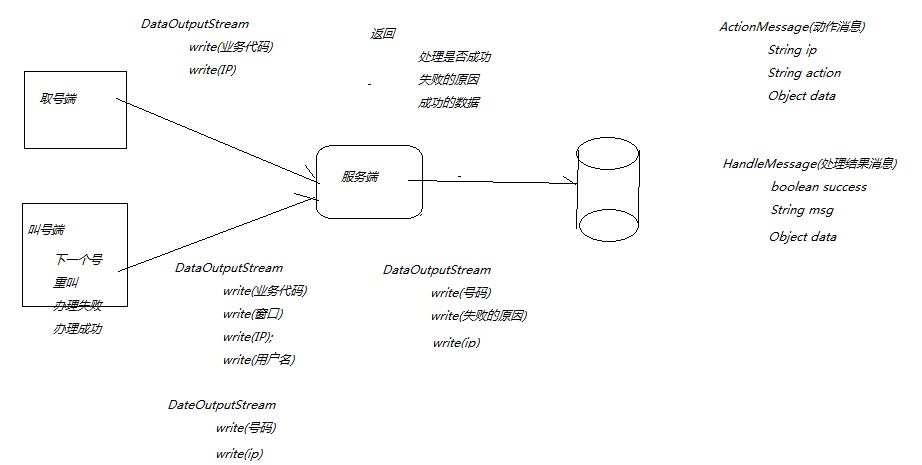
(2)ObjectOutputStream,ObjectInputStream
(3)transient
transient - 短暂的,瞬时的,透明的
transient 禁止对象中的某个属性进行序列化或反序列化
是一个关键字,加属性的定义上,表示该属性是一个瞬时的,不需要序列化的
八.Properties
属性类,用来读取属性文件(后缀是.properties),这种文件里存放的数据
key=value
key=value
需求: 项目完成,发给用户用,不给源代码,要求之间双击运行,如何修改配置信息,(数据库连接信息,窗口打开的信息等等)
可以用Properties作配置文件,它是Java内置解析工具,解析xxx.properties文件
Properties跟map很相似。有 key----->value
Properties是集合类
Properties prop = new Properties(); prop.setProperty("driver", "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");//driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver prop.setProperty("def", "456"); //写到指定数据源上 PrintStream out = new PrintStream("conf/jdbc.properties"); //将属性文件里的内容写到终端上 prop.list(out); Properties prop = new Properties(); InputStream in = new FileInputStream("conf/jdbc.properties"); //属性文件里的内容就在prop指向对象内部 prop.load(in); System.out.println(prop.getProperty("driverClass")); System.out.println(prop.getProperty("url")); public class Config { private Properties prop = new Properties(); public Config(String propertiesFile){ InputStream in = new FileInputStream(propertiesFile); prop.load(in); } public String get(String key){ return prop.getProperty(key); } }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号