集合框架
集合框架
什么是集合
-
概念:对象的容器,定义了对多个对象进行操作的常用方法。可实现数组的功能。
-
和数组的区别:
-
数组长度固定,集合长度不固定
-
数组可以存储基本类型和引用类型,集合只能存储引用类型
-
-
位置:java.util.*
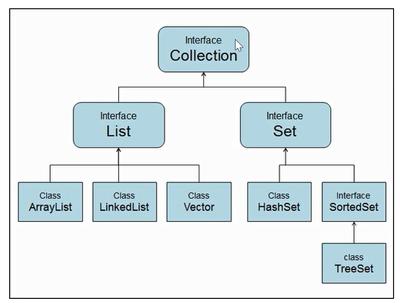
Collection体系结构
-
Collection接口:该体系结构的根接口,代表一组对象,称为“集合”。
-
List接口:有序、有下标、元素可重复
-
Set接口:无序、无下标、元素不能重复
Collection父接口
-
特点:代表一组任意类型的对象,无序、无下标、不能重复。
-
方法:
-
boolean add(Object obj) // 添加一个对象。
-
boolean addAll(Collection c) // 将一个集合中的所有对象添加到此集合中。
-
void clear() // 清空此集合中的所有对象。
-
boolean contains(Object o) // 检查此集合中是否包含o对象。
-
boolean equals(Object o) // 检查此集合是否与指定对象相等。
-
boolean isEmpty() // 判断此集合是否为空。
-
boolean remove(Object o) // 在此集合中移除o对象。
-
int size() // 返回此集合中的元素个数。
-
Object[] toArray() // 将此集合转换为数组。
-
1 package com.collection; 2 3 // Collection接口的使用 4 5 import com.sun.scenario.effect.impl.sw.sse.SSEBlend_SRC_OUTPeer; 6 7 import java.util.ArrayList; 8 import java.util.Collection; 9 import java.util.Iterator; 10 11 public class Demo01 { 12 public static void main(String[] args) { 13 // 创建集合 14 Collection collection = new ArrayList(); 15 16 // 添加元素 17 collection.add("西瓜"); 18 collection.add("苹果"); 19 collection.add("榴莲"); 20 collection.add("香蕉"); 21 System.out.println("元素个数:" + collection.size()); 22 System.out.println(collection); 23 24 // 删除元素 25 collection.remove("香蕉"); 26 System.out.println("删除香蕉后元素个数:" + collection.size()); 27 System.out.println(collection); 28 // collection.clear(); // 清空集合中的元素 29 30 // 遍历集合 31 // 1.增强for循环遍历集合 32 System.out.println("=========增强for遍历集合======="); 33 for (Object o : collection) { 34 System.out.println(o); 35 } 36 37 // 2.使用迭代器遍历集合 38 // 迭代器:专门用来遍历集合的一种方式 39 System.out.println("=========迭代器遍历集合======="); 40 Iterator it = collection.iterator(); 41 /** 42 * Iterator中的方法 43 * hasNext(); 判断有没有下一个元素 44 * next(); 获取下一个元素 45 * remove(); 删除当前元素 46 */ 47 while (it.hasNext()) { 48 String str = (String)it.next(); 49 System.out.println(str); 50 // 迭代器中不能使用Collection中的方法 51 // collection.remove(str); 迭代过程中不能出现并发操作 52 it.remove(); 53 } 54 System.out.println("元素个数:" + collection.size()); 55 56 // 判断 57 System.out.println("=========集合判断======="); 58 System.out.println(collection.contains("榴莲")); 59 System.out.println(collection.isEmpty()); 60 } 61 }
Collection集合用来存放学生信息:
1 package com.collection; 2 3 // Collection集合用来存放学生信息 4 5 import java.util.ArrayList; 6 import java.util.Collection; 7 import java.util.Iterator; 8 9 public class Demo02 { 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 // 创建Collection集合 12 Collection collection = new ArrayList(); 13 14 // 创建学生对象 15 Student s1 = new Student("张三", 18); 16 Student s2 = new Student("李四", 20); 17 Student s3 = new Student("王五", 19); 18 19 // 添加数据 20 collection.add(s1); 21 collection.add(s2); 22 collection.add(s3); 23 System.out.println("元素个数:" + collection.size()); 24 System.out.println(collection); 25 26 // 删除数据 27 collection.remove(s1); 28 System.out.println("删除之后元素个数:" + collection.size()); 29 System.out.println(collection); 30 collection.remove(new Student("王五", 19)); // s3不会从集合中删除 31 // collection.clear(); 清空数据 32 33 // 遍历元素 34 // 增强for循环遍历集合 35 System.out.println("=======增强for遍历集合======="); 36 for (Object o : collection) { 37 System.out.println(o); 38 } 39 40 // 迭代器遍历集合 41 System.out.println("=======迭代器遍历集合======="); 42 Iterator it = collection.iterator(); 43 while (it.hasNext()) { 44 System.out.println(it.next()); 45 } 46 47 // 判断 48 System.out.println("========================="); 49 System.out.println(collection.contains(s2)); // true 50 System.out.println(collection.contains(new Student("李四", 20))); // false 51 System.out.println(collection.isEmpty()); // false 52 } 53 } 54 55 // 定义学生类 56 class Student { 57 // 定义变量 58 private String name; 59 private int age; 60 61 // 定义构造方法 62 public Student() { 63 } 64 65 public Student(String name,int age) { 66 this.name = name; 67 this.age = age; 68 } 69 70 // get和set方法 71 public String getName() { 72 return name; 73 } 74 75 public void setName(String name) { 76 this.name = name; 77 } 78 79 public int getAge() { 80 return age; 81 } 82 83 public void setAge(int age) { 84 this.age = age; 85 } 86 87 // 重写toString()方法打印学生信息 88 @Override 89 public String toString() { 90 return "Student{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; 91 } 92 }
List子接口
-
特点:有序、有下标、元素可以重复。
-
方法:
-
void add(int index, Object o) // 在index位置插入对象o
-
boolean addAll(int index, Collection c) // 将一个集合中的元素添加到此集合中的index位置
-
Object get(int index) // 返回集合中指定位置的元素。
-
Lits subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) // 返回fromIndex和toIndex之间的集合元素。
-
List列表举例1
1 package com.collection; 2 3 // List子接口的使用 4 5 import java.util.ArrayList; 6 import java.util.Iterator; 7 import java.util.List; 8 import java.util.ListIterator; 9 10 public class Demo03 { 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 // 创建集合对象 13 List list = new ArrayList(); 14 list.add("苹果"); 15 list.add("小米"); 16 list.add("诺基亚"); 17 list.add(0,"华为"); 18 System.out.println("元素个数:" + list.size()); 19 System.out.println(list); 20 21 // 删除元素 22 list.remove("诺基亚"); 23 // list.remove(0); 24 // list.clear() // 清空集合 25 System.out.println("删除后元素个数:" + list.size()); 26 System.out.println(list); 27 28 // 遍历集合 29 // for循环遍历集合 30 System.out.println("========for循环遍历集合======="); 31 for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { 32 System.out.println(list.get(i)); 33 } 34 35 // 增强for循环遍历集合 36 System.out.println("========增强for遍历集合======="); 37 for (Object o : list) { 38 System.out.println(o); 39 } 40 41 // 迭代器遍历集合 42 System.out.println("========迭代器遍历集合======="); 43 Iterator it = list.iterator(); 44 while (it.hasNext()) { 45 System.out.println(it.next()); 46 } 47 48 // 列表迭代器遍历集合 49 System.out.println("========列表迭代器遍历集合======="); 50 ListIterator lit = list.listIterator(); 51 System.out.println("使用列表迭代器从前往后遍历:"); 52 while (lit.hasNext()) { 53 System.out.println(lit.nextIndex() + ":" + lit.next()); 54 } 55 56 System.out.println("使用列表迭代器从后往前遍历:"); 57 while (lit.hasPrevious()) { 58 System.out.println(lit.previousIndex() + ";" + lit.previous()); 59 } 60 61 // 判断 62 System.out.println(list.contains("苹果")); 63 System.out.println(list.isEmpty()); 64 65 // 获取元素或索引 66 System.out.println(list.get(0)); 67 System.out.println(list.indexOf("华为")); 68 69 } 70 }
List列表举例2
1 package com.collection; 2 3 // List接口的使用 4 5 import java.util.ArrayList; 6 import java.util.List; 7 8 public class Demo04 { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 // 创建集合 11 List list = new ArrayList(); 12 13 // 添加数据(自动装箱) 14 list.add(10); 15 list.add(20); 16 list.add(30); 17 list.add(40); 18 list.add(50); 19 System.out.println("元素个数:" + list.size()); 20 System.out.println(list); 21 22 // 删除操作 23 // list.remove(0); 24 list.remove(new Integer(20)); 25 System.out.println("删除后元素个数:" + list.size()); 26 System.out.println(list); 27 28 // subList()方法,返回子集合,左闭右开 29 List subList = list.subList(1,3); 30 System.out.println("元素个数:" + subList.size()); 31 System.out.println(subList); 32 } 33 }
List实现类
-
ArrayList【重点】:
-
数组结构实现,查询快、增删慢;
-
JDK1.2版本,运行效率快、线程不安全。
-
DEFAULT_CAPACITY 默认容量大小 = 10;如果没有向集合中添加任何元素时,容量为0
-
elementData 存放元素的数组
-
size 实际元素个数
-
boolean add() 添加元素
-
1 package com.collection; 2 3 // ArrayList类的使用 4 5 import java.util.ArrayList; 6 import java.util.Iterator; 7 import java.util.ListIterator; 8 9 public class Demo05 { 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 // 创建学生对象 12 Student s1 = new Student("张三",18); 13 Student s2 = new Student("李四",20); 14 Student s3 = new Student("王五",19); 15 // 创建集合 16 ArrayList list = new ArrayList(); 17 18 // 添加元素 19 list.add(s1); 20 list.add(s2); 21 list.add(s3); 22 System.out.println("元素个数:" + list.size()); 23 System.out.println(list); 24 25 // 删除元素 26 // list.remove(0); 27 list.remove(s3); 28 // list.clear(); // 清空元素 29 System.out.println("删除后元素个数:" + list.size()); 30 System.out.println(list); 31 32 // 遍历元素 33 // for循环遍历元素 34 System.out.println("============for循环遍历元素==========="); 35 for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { 36 System.out.println(list.get(i)); 37 } 38 39 // 增强for遍历元素 40 System.out.println("============增强for遍历元素==========="); 41 for (Object o : list) { 42 System.out.println(o); 43 } 44 45 // 迭代器遍历元素 46 System.out.println("============迭代器遍历元素==========="); 47 Iterator it = list.iterator(); 48 while (it.hasNext()) { 49 System.out.println(it.next()); 50 } 51 52 // 列表迭代器遍历元素 53 System.out.println("============列表迭代器从前往后遍历元素==========="); 54 ListIterator lit = list.listIterator(); 55 while (lit.hasNext()) { 56 System.out.println(lit.next()); 57 } 58 59 System.out.println("============列表迭代器从后往前遍历元素==========="); 60 while (lit.hasPrevious()) { 61 System.out.println(lit.previous()); 62 } 63 64 // 判断 65 System.out.println(list.contains(s1)); 66 System.out.println(list.isEmpty()); 67 68 // 查找 69 System.out.println(list.get(0)); 70 } 71 }
-
Vector:
-
数组结构实现,查询快、增删慢;
-
JDK1.0版本,运行效率慢、线程安全。
-
1 package com.collection; 2 3 // Vector集合类的使用 4 5 import java.util.Enumeration; 6 import java.util.Vector; 7 8 public class Demo06 { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 // 创建集合 11 Vector vector = new Vector(); 12 13 // 添加元素 14 vector.add("苹果"); 15 vector.add("西瓜"); 16 vector.add("芒果"); 17 System.out.println("元素个数:" + vector.size()); 18 System.out.println(vector); 19 20 /* 删除元素 21 vector.remove(0); 22 vector.remove("西瓜"); 23 vector.clear(); 24 */ 25 26 // 遍历 使用枚举器 27 Enumeration en = vector.elements(); 28 while (en.hasMoreElements()) { 29 System.out.println(en.nextElement()); 30 } 31 32 // 判断 33 System.out.println(vector.contains("苹果")); 34 System.out.println(vector.isEmpty()); 35 } 36 }
-
LinkedList:
-
链表结构实现,增删快,查询慢。
-
存储结构:双向链表
-
1 package com.collection; 2 3 // LinkedList集合类的使用 4 5 import java.util.Iterator; 6 import java.util.LinkedList; 7 import java.util.ListIterator; 8 9 public class Demo07 { 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 // 创建集合 12 LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList(); 13 14 // 创建学生对象 15 Student s1 = new Student("张三", 18); 16 Student s2 = new Student("李四", 20); 17 Student s3 = new Student("王五", 19); 18 19 // 向集合中添加元素 20 linkedList.add(s1); 21 linkedList.add(s2); 22 linkedList.add(s3); 23 System.out.println("元素个数:" + linkedList.size()); 24 System.out.println(linkedList); 25 26 /* 删除元素 27 linkedList.remove(); // 删除s1 28 linkedList.remove(0); 29 linkedList.remove(s2); 30 linkedList.clear(); 31 */ 32 33 // 遍历元素 34 System.out.println("=============for循环遍历元素==========="); 35 for (int i = 0; i < linkedList.size(); i++) { 36 System.out.println(linkedList.get(i)); 37 } 38 39 System.out.println("=============增强for循环遍历元素==========="); 40 for (Object o : linkedList) { 41 System.out.println(o); 42 } 43 44 System.out.println("=============迭代器遍历元素==========="); 45 Iterator it = linkedList.iterator(); 46 while (it.hasNext()) { 47 System.out.println(it.next()); 48 } 49 50 System.out.println("=============列表迭代器从前往后遍历元素==========="); 51 ListIterator lit = linkedList.listIterator(); 52 while (lit.hasNext()) { 53 System.out.println(lit.nextIndex() + ":" + lit.next()); 54 } 55 56 System.out.println("=============列表迭代器从后往前遍历元素==========="); 57 while (lit.hasPrevious()) { 58 System.out.println(lit.previousIndex() + ";" + lit.previous()); 59 } 60 } 61 }
泛型
-
Java泛型是JDK1.5中引入的一个新特性,其本质是参数化类型,把类型作为参数传递。
-
常见形式有泛型类、泛型接口、泛型方法。
-
语法:<T,...> T称为占位符,表示一种引用类型。
-
好处:提高代码的重用性;防止类型转换异常,提高代码的安全性。
泛型类
1 package com.collection; 2 3 /* 泛型类 4 * 语法:类名<T> 5 * T是类型占位符,表示一种引用类型,如果编写多个使用逗号隔开 6 * */ 7 8 public class Test { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 // 使用泛型类创建对象 11 // 注意:1.泛型只能使用引用类型;2.不同泛型对象不能相互赋值 12 MyGeneric<String> myGeneric1 = new MyGeneric<String>(); 13 myGeneric1.t = "Hello"; 14 myGeneric1.show("大家好,加油!"); 15 String str = myGeneric1.getT(); 16 System.out.println( str); 17 18 MyGeneric<Integer> myGeneric2 = new MyGeneric<Integer>(); 19 myGeneric2.setT(100); 20 myGeneric2.show(200); 21 Integer integer = myGeneric2.getT(); 22 System.out.println(integer); 23 } 24 } 25 26 // 创建泛型类 27 class MyGeneric<T> { 28 // 1.创建变量 29 T t; 30 31 // 2.泛型作为方法的参数 32 public void setT(T t) { 33 this.t = t; 34 } 35 public void show(T t) { 36 System.out.println(t); 37 } 38 39 // 3.泛型作为方法的返回值 40 public T getT() { 41 return t; 42 } 43 }
泛型接口
1 // 创建一个泛型接口 2 public interface MyInterface <T>{ 3 T serve(T t); 4 } 5 // 1.类实现泛型接口 6 public class MyInterfaceImp1 implements MyInterface<String>{ 7 @Override 8 public String serve(String s) { 9 System.out.println(s); 10 return s; 11 } 12 13 public static void main(String[] args) { 14 MyInterfaceImp1 imp1 = new MyInterfaceImp1(); 15 imp1.serve("汤姆"); 16 } 17 }
1 // 2.泛型类实现泛型接口 2 public class MyInterfaceImp2<T> implements MyInterface<T>{ 3 @Override 4 public T serve(T t) { 5 System.out.println(t); 6 return t; 7 } 8 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 MyInterfaceImp2<Integer> imp2 = new MyInterfaceImp2(); 11 imp2.serve(100); 12 } 13 }
泛型方法
1 // 泛型方法:在方法返回值类型前加上 <T> 2 public class MyGenericMethod { 3 public <T> T show(T t) { 4 System.out.println(t); 5 return t; 6 } 7 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 MyGenericMethod method = new MyGenericMethod(); 10 method.show("泛型方法"); 11 method.show(111); 12 method.show(1.2); 13 } 14 }
泛型集合
-
概念:参数化类型、类型安全的集合,强制集合元素的类型必须一致。
-
特点:
-
编译时即可检查,而非运行时抛出异常。
-
访问时,不必类型转换(拆箱)。
-
不同泛型之间引用不能相互赋值,泛型不存在多态。
-
1 // 泛型集合的使用 2 3 import com.oop.Student; 4 5 import java.util.ArrayList; 6 import java.util.Iterator; 7 8 public class Demo01 { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 ArrayList<String> list1 = new ArrayList<>(); 11 list1.add("苹果"); 12 list1.add("香蕉"); 13 // list1.add(10); 不能添加Integer对象 14 for (String s : list1) { 15 System.out.println(s); 16 } 17 18 ArrayList<Student> list2 = new ArrayList<>(); 19 // 创建学生对象 20 Student s1 = new Student("张三",18); 21 Student s2 = new Student("李四",20); 22 Student s3 = new Student("王五",19); 23 24 // 添加元素 25 list2.add(s1); 26 list2.add(s2); 27 list2.add(s3); 28 29 // 遍历元素 30 for (Student student : list2) { 31 Student s = student; 32 System.out.println(s); 33 } 34 35 // 迭代器遍历 36 Iterator<Student> it = list2.iterator(); 37 while (it.hasNext()) { 38 Student s = it.next(); 39 System.out.println(s); 40 } 41 } 42 }
Set子接口
-
特点:无序、无下标、元素不可重复。
-
方法:全部继承自Collection中的方法。
1 package com.collection; 2 3 import java.util.HashSet; 4 import java.util.Iterator; 5 import java.util.Set; 6 7 // Set子接口的使用 8 public class Demo08 { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 // 创建集合 11 Set<String> set = new HashSet<>(); 12 13 // 添加元素 14 set.add("小米"); 15 set.add("苹果"); 16 set.add("华为"); 17 // set.add("华为"); 重复元素不会被添加 18 System.out.println("元素个数:" + set.size()); 19 System.out.println(set); 20 21 /* 删除元素 22 set.remove("华为"); 23 set.clear(); // 清空 24 */ 25 26 // 遍历【重点】 27 System.out.println("===========增强for循环========="); 28 for (String s : set) { 29 System.out.println(s); 30 } 31 32 System.out.println("===========迭代器遍历========="); 33 Iterator<String> it = set.iterator(); 34 while (it.hasNext()) { 35 System.out.println(it.next()); 36 } 37 38 // 判断 39 System.out.println(set.contains("华为")); 40 System.out.println(set.isEmpty()); 41 } 42 }
Set实现类
-
HashSet【重点】:
-
基于HashCode计算元素存放位置。
-
当存入元素的哈希码相同时,会调用equals进行确认,如结果为true,则拒绝后者存入。
-
1 package com.collection.hashSet; 2 3 import java.util.HashSet; 4 import java.util.Iterator; 5 6 /** 7 * HashSet集合的使用 8 * 存储结构:哈希表(数组+链表+红黑树) 9 */ 10 public class Demo01 { 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 // 创建集合 13 HashSet<String> hashSet = new HashSet<>(); 14 15 // 添加元素 16 hashSet.add("苹果"); 17 hashSet.add("华为"); 18 hashSet.add("小米"); 19 // hashSet.add("苹果"); // 重复元素 20 System.out.println("元素个数:" + hashSet.size()); 21 System.out.println(hashSet); 22 23 /* 删除元素 24 hashSet.remove("苹果"); 25 hashSet.clear();*/ 26 27 // 遍历 28 System.out.println("==========增强for=========="); 29 for (String s : hashSet) { 30 System.out.println(s); 31 } 32 33 System.out.println("==========迭代器=========="); 34 Iterator<String> it = hashSet.iterator(); 35 while (it.hasNext()) { 36 System.out.println(it.next()); 37 } 38 39 // 判断 40 System.out.println(hashSet.contains("苹果")); 41 System.out.println(hashSet.isEmpty()); 42 43 } 44 }
-
HashSet存储方式
1 package com.collection.hashSet; 2 3 // Person类 4 public class Person { 5 private String name; 6 private int age; 7 8 // 构造方法 9 public Person(){ 10 11 } 12 13 public Person(String name,int age) { 14 this.name = name; 15 this.age = age; 16 } 17 18 // get和set方法 19 public String getName() { 20 return name; 21 } 22 23 public void setName(String name) { 24 this.name = name; 25 } 26 27 public int getAge() { 28 return age; 29 } 30 31 public void setAge(int age) { 32 this.age = age; 33 } 34 35 // 重写toString() 36 @Override 37 public String toString() { 38 return "Person{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; 39 } 40 41 // 重写hashCode()和equals() 42 @Override 43 public boolean equals(Object o) { 44 if (this == o) { 45 return true; 46 } 47 if (o == null) { 48 return false; 49 } 50 if (o instanceof Person) { 51 Person p = (Person)o; 52 if (this.name.equals(p.getName()) && this.age==p.getAge()) { 53 return true; 54 } 55 } 56 57 return false; 58 } 59 60 @Override 61 public int hashCode() { 62 int n1 = this.name.hashCode(); 63 int n2 = this.age; 64 return n1 + n2; 65 } 66 }
1 package com.collection.hashSet; 2 3 import java.util.HashSet; 4 import java.util.Iterator; 5 6 /** 7 * HashSet的使用 8 * 存储结构:哈希表(数组+链表+红黑树) 9 * 存储过程 10 * (1)根据hashcode计算保存的位置,如果此位置为空,则直接保存,如果不为空执行第二步。 11 * (2)再执行equals方法,如果equals方法为true,则认为是重复;否则,形成链表 12 */ 13 14 public class Demo02 { 15 public static void main(String[] args) { 16 // 创建集合 17 HashSet<Person> persons = new HashSet<>(); 18 19 // 创建Person对象 20 Person p1 = new Person("张三",19); 21 Person p2 = new Person("李四",20); 22 Person p3 = new Person("王五",18); 23 24 // 添加元素 25 persons.add(p1); 26 persons.add(p2); 27 persons.add(p3); 28 persons.add(new Person("王五",18)); // 重复元素 29 System.out.println("元素个数:" + persons.size()); 30 System.out.println(persons); 31 32 /* 删除元素 33 persons.remove(p1); 34 persons.remove(new Person("王五",18)); // 可以删除p3 35 persons.clear(); // 清空*/ 36 37 // 遍历 38 System.out.println("===========增强for========="); 39 for (Person person : persons) { 40 System.out.println(person); 41 } 42 43 System.out.println("===========迭代器========="); 44 Iterator<Person> it = persons.iterator(); 45 while (it.hasNext()) { 46 System.out.println(it.next()); 47 } 48 49 // 判断 50 System.out.println(persons.contains(p1)); 51 System.out.println(persons.contains(new Person("王五", 18))); // true 52 System.out.println(persons.isEmpty()); 53 } 54 }
-
TreeSet:
-
基于排列顺序实现元素不重复。
-
实现了SortedSet接口,对集合元素自动排序。
-
元素对象的类型必须实现Comparable接口,指定排序规则。
-
通过CompareTo方法确定是否为重复元素。
-
1 package com.collection.treeSet; 2 3 import java.util.Iterator; 4 import java.util.TreeSet; 5 6 /** 7 * TreeSet的使用 8 * 存储结构:红黑树 9 */ 10 11 public class Demo01 { 12 public static void main(String[] args) { 13 // 创建集合 14 TreeSet<String> treeSet = new TreeSet<>(); 15 16 // 添加元素 17 treeSet.add("xyz"); 18 treeSet.add("abc"); 19 treeSet.add("hello"); 20 System.out.println("元素个数:" + treeSet.size()); 21 System.out.println(treeSet); 22 23 /* 删除元素 24 treeSet.remove("xyz"); 25 treeSet.clear();*/ 26 27 // 遍历元素 28 System.out.println("===========增强for=========="); 29 for (String s : treeSet) { 30 System.out.println(s); 31 } 32 33 System.out.println("===========迭代器=========="); 34 Iterator<String> it = treeSet.iterator(); 35 while (it.hasNext()) { 36 System.out.println(it.next()); 37 } 38 39 // 判断 40 System.out.println(treeSet.contains("abc")); 41 System.out.println(treeSet.isEmpty()); 42 } 43 }
TreeSet集合存放Person对象
1 package com.collection.hashSet; 2 3 // Person类 4 public class Person implements Comparable<Person>{ 5 private String name; 6 private int age; 7 8 // 构造方法 9 public Person(){ 10 11 } 12 13 public Person(String name,int age) { 14 this.name = name; 15 this.age = age; 16 } 17 18 // get和set方法 19 public String getName() { 20 return name; 21 } 22 23 public void setName(String name) { 24 this.name = name; 25 } 26 27 public int getAge() { 28 return age; 29 } 30 31 public void setAge(int age) { 32 this.age = age; 33 } 34 35 // 重写toString() 36 @Override 37 public String toString() { 38 return "Person{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; 39 } 40 41 // 重写hashCode()和equals() 42 @Override 43 public boolean equals(Object o) { 44 if (this == o) { 45 return true; 46 } 47 if (o == null) { 48 return false; 49 } 50 if (o instanceof Person) { 51 Person p = (Person)o; 52 if (this.name.equals(p.getName()) && this.age==p.getAge()) { 53 return true; 54 } 55 } 56 57 return false; 58 } 59 60 @Override 61 public int hashCode() { 62 int n1 = this.name.hashCode(); 63 int n2 = this.age; 64 return n1 + n2; 65 } 66 67 // 先比较姓名,再比较年龄 68 @Override 69 public int compareTo(Person o) { 70 int n1 = this.getName().compareTo(o.getName()); 71 int n2 = this.getAge()-o.getAge(); 72 return n1!=0?n1:n2; 73 } 74 }
1 package com.collection.hashSet; 2 3 import java.util.Iterator; 4 import java.util.TreeSet; 5 6 /** 7 * 使用TreeSet保存数据 8 * 存储结构:红黑树 9 * 要求:元素必须实现Comparable接口,compareTo()方法返回值为0,认为是重复元素 10 */ 11 public class Demo03 { 12 public static void main(String[] args) { 13 // 创建集合 14 TreeSet<Person> persons = new TreeSet<>(); 15 16 // 创建Person对象 17 Person p1 = new Person("Tom",20); 18 Person p2 = new Person("Jack",18); 19 Person p3 = new Person("Mary",19); 20 Person p4 = new Person("Tom",18); 21 22 // 添加元素 23 persons.add(p1); 24 persons.add(p2); 25 persons.add(p3); 26 persons.add(p4); 27 persons.add(new Person("Mary",19)); // 重复元素 28 System.out.println("元素个数:" + persons.size()); 29 System.out.println(persons); 30 31 /* 删除 32 persons.remove(p1); 33 persons.remove(new Person("Mary",19)); // 也能进行删除 34 persons.clear(); // 清空 35 */ 36 37 // 遍历 38 System.out.println("============增强for============"); 39 for (Person person : persons) { 40 System.out.println(person); 41 } 42 43 System.out.println("============迭代器============"); 44 Iterator<Person> it = persons.iterator(); 45 while (it.hasNext()) { 46 System.out.println(it.next()); 47 } 48 49 // 判断 50 System.out.println(persons.contains(p1)); // true 51 System.out.println(persons.contains(new Person("Mary",19))); // true 52 System.out.println(persons.isEmpty()); // false 53 } 54 }
Comparator接口
-
实现定制比较(比较器)
1 package com.collection.treeSet; 2 3 // Comparator比较器在TreeSet中的使用 4 5 import com.oop.demo01.Person; 6 7 import java.util.Comparator; 8 import java.util.TreeSet; 9 10 public class Demo02 { 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 // 创建集合,并指定比较规则 13 TreeSet<Person> persons = new TreeSet<>(new Comparator<Person>() { 14 @Override 15 public int compare(Person o1, Person o2) { 16 int n1 = o1.age-o2.age; 17 int n2 = o1.name.compareTo(o2.name); 18 return n1!=0?n1:n2; 19 } 20 }); 21 22 // 添加元素 23 Person p1 = new Person("Tom", 19); 24 Person p2 = new Person("Jack", 18); 25 Person p3 = new Person("Marry", 20); 26 Person p4 = new Person("Tom", 20); 27 persons.add(p1); 28 persons.add(p2); 29 persons.add(p3); 30 persons.add(p4); 31 System.out.println("元素个数:" + persons.size()); 32 System.out.println(persons); 33 } 34 }
-
TreeSet案例
要求:使用TreeSet集合实现字符串按照字符串按照长度排序
helloworld zhang lisi wangwu beijing xian nanjing
1 package com.collection.treeSet; 2 3 import java.util.Comparator; 4 import java.util.TreeSet; 5 6 /* 7 要求:使用TreeSet集合实现字符串按照字符串按照长度排序 8 */ 9 public class Demo03 { 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 // 创建集合并指定比较规则 12 TreeSet<String> treeSet = new TreeSet<>(new Comparator<String>() { 13 @Override 14 public int compare(String o1, String o2) { 15 int n1 = o1.length()-o2.length(); 16 int n2 = o1.compareTo(o2); 17 return n1!=0?n1:n2; 18 } 19 }); 20 21 // 添加数据 22 treeSet.add("zhangsan"); 23 treeSet.add("beijing"); 24 treeSet.add("cat"); 25 treeSet.add("xian"); 26 treeSet.add("nanjing"); 27 System.out.println(treeSet); 28 } 29 }
Map集合
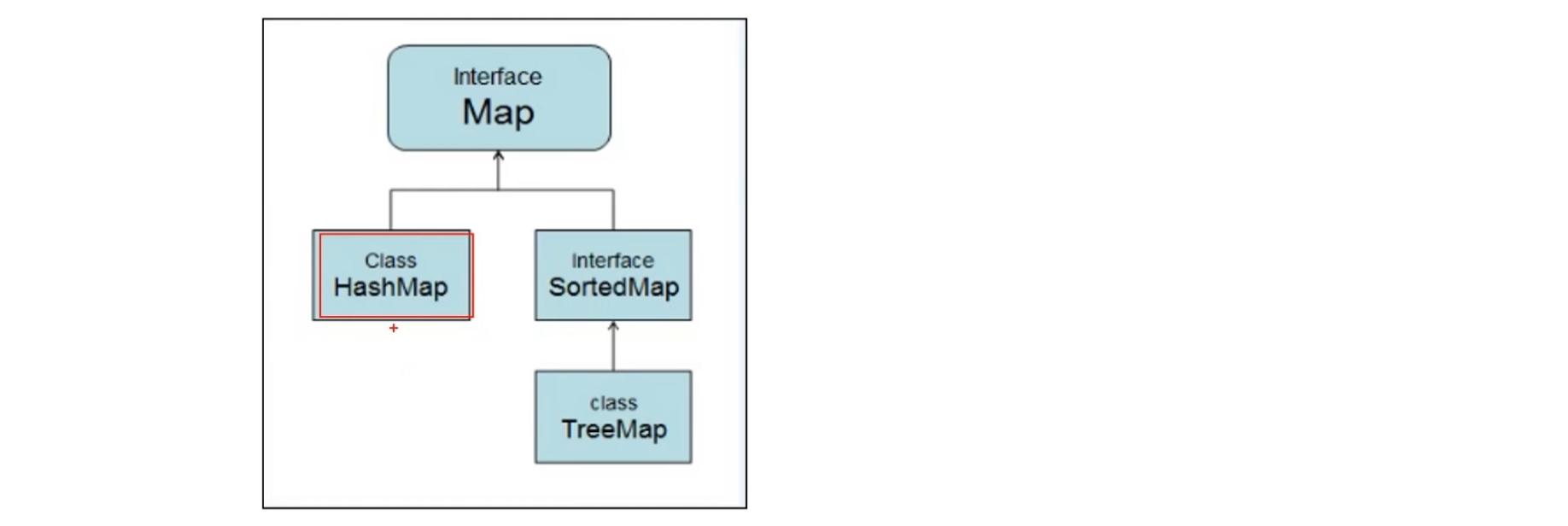
Map接口的特点:
-
用于存储任意键值对(Key - Value)
-
键:无序、无下标、不允许重复(唯一)
-
值:无序、无下标、允许重复
Map父接口
-
特点:存储一对数据(Key - Value),无序、无下标,键不可重复,值可重复。
-
方法:
-
V put(K key, V value) // 将对象存入到集合中,关联键值。key重复则覆盖原值。
-
Object get(Object key) // 根据键获取对应的值。
-
keySet<K> // 返回所有key。
-
Collection<V> values() // 返回包含所有值的Collection集合。
-
entrySet<Map.Entry<K,V>> // 键值匹配的Set集合
-
1 package com.collection.map; 2 3 // Map接口的使用 4 5 import java.util.HashMap; 6 import java.util.Map; 7 8 public class Demo1 { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 // 创建Map集合 11 Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>(); 12 13 // 添加元素 14 map.put("cn","zhongguo"); 15 map.put("uk","英国"); 16 map.put("usa","美国"); 17 map.put("cn","中国"); // 中国覆盖zhongguo 18 System.out.println("元素个数:" + map.size()); 19 System.out.println(map); 20 /* 21 删除元素 22 map.remove("usa"); 23 map.clear();*/ 24 25 // 遍历元素 26 System.out.println("========使用keySet()========"); 27 for (String s : map.keySet()) { 28 System.out.println(s + "==" + map.get(s)); 29 } 30 31 System.out.println("========使用values()========"); 32 for (String value : map.values()) { 33 System.out.println(value); 34 } 35 36 System.out.println("========使用entrySet()========"); 37 for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : map.entrySet()) { 38 System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "---" + entry.getValue()); 39 } 40 41 // 判断 42 System.out.println(map.containsKey("uk")); // true 43 System.out.println(map.containsValue("中国")); // true 44 System.out.println(map.isEmpty()); // false 45 } 46 }
Map集合的实现类
-
HashMap 【重点】:
-
JDK1.2版本,线程不安全,运行效率快;允许用null 作为key或是value。
-
-
HashMap源码分析:
-
HashMap刚创建时,table是null,为了节省空间,当添加第一个元素时,table容量调整为16
-
当元素个数大于阈值(16*0.75 = 12)时,会进行扩容,扩容后大小为原来的2倍.目的是减少调整元素的个数。
-
jdk1.8 当每个链表长度大于8,并且元素个数大于等于64时,会调整为红黑树,目的提高执行效率
-
jak1.8 当链表长度小于6时,调整成链表
-
jdk1.8以前,链表是头插入,jdk1.8之后是尾插入
-
1 package com.collection.map; 2 3 // 定义学生类 4 public class Student { 5 private String name; 6 private int id; 7 8 // 构造方法 9 public Student(){ 10 } 11 public Student(String name,int id) { 12 this.name = name; 13 this.id = id; 14 } 15 16 // get和set方法 17 public String getName() { 18 return name; 19 } 20 21 public void setName(String name) { 22 this.name = name; 23 } 24 25 public int getId() { 26 return id; 27 } 28 29 public void setId(int id) { 30 this.id = id; 31 } 32 33 // toString()方法 34 @Override 35 public String toString() { 36 return "Student{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", id=" + id + '}'; 37 } 38 39 // 重写hashCode()和equals() 40 @Override 41 public boolean equals(Object o) { 42 if (this == o) { 43 return true; 44 } 45 if (o == null) { 46 return false; 47 } 48 if (o instanceof Student) { 49 Student s = (Student)o; 50 if (this.getName().equals(s.name) && this.getId()==s.id) { 51 return true; 52 } 53 } 54 return false; 55 } 56 57 @Override 58 public int hashCode() { 59 int n1 = this.name.hashCode(); 60 int n2 = this.getId(); 61 return n1!=0?n1:n2; 62 } 63 }
1 package com.collection.map; 2 3 import java.util.HashMap; 4 import java.util.Map; 5 6 /** 7 * HashMap集合的使用 8 * 存储结构:数组+链表+红黑树 9 * 使用key的hashcode和equals作为重复依据 10 */ 11 public class Demo2 { 12 public static void main(String[] args) { 13 // 创建集合 14 HashMap<Student,String> students = new HashMap<>(); 15 16 // 创建学生对象 17 Student s1 = new Student("张三", 101); 18 Student s2 = new Student("李四", 102); 19 Student s3 = new Student("王五", 103); 20 21 // 添加元素 22 students.put(s1,"上海"); 23 students.put(s2,"杭州"); 24 students.put(s3,"北京"); 25 // students.put(s3,"北京"); 重复元素 26 // students.put(new Student("王五", 103),"上海"); // 重写hashCode()和equals()后变为重复元素 27 System.out.println("元素个数:" + students.size()); 28 System.out.println(students); 29 30 /* 删除元素 31 students.remove(s1); 32 students.clear();*/ 33 34 // 遍历 35 System.out.println("===========keySet========="); 36 for (Student key : students.keySet()) { 37 System.out.println(key + "==" + students.get(key)); 38 } 39 40 System.out.println("===========entrySet========="); 41 for (Map.Entry<Student, String> entry : students.entrySet()) { 42 System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "---" + entry.getValue()); 43 } 44 45 // 判断 46 System.out.println(students.containsKey(s1)); 47 System.out.println(students.containsValue("上海")); 48 System.out.println(students.isEmpty()); 49 } 50 }
-
Hashtable:
-
JDK1.0版本,线程安全,运行效率慢;不允许null作为key或是value。
-
-
Properties:
-
Hashtable的子类,要求key和value都是String。通常用于配置文件的读取。
-
-
TreeMap:
-
实现了SortedMap接口(是Map的子接口),可以对key自动排序。
-
存放的元素必须实现Comparable接口。
-
也可以使用比较器指定比较规则,不需要实现Comparable接口。
-
1 package com.collection.map; 2 3 // 定义学生类 4 public class Student implements Comparable<Student>{ 5 private String name; 6 private int id; 7 8 // 构造方法 9 public Student(){ 10 } 11 public Student(String name,int id) { 12 this.name = name; 13 this.id = id; 14 } 15 16 // get和set方法 17 public String getName() { 18 return name; 19 } 20 21 public void setName(String name) { 22 this.name = name; 23 } 24 25 public int getId() { 26 return id; 27 } 28 29 public void setId(int id) { 30 this.id = id; 31 } 32 33 // toString()方法 34 @Override 35 public String toString() { 36 return "Student{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", id=" + id + '}'; 37 } 38 39 // 重写hashCode()和equals() 40 @Override 41 public boolean equals(Object o) { 42 if (this == o) { 43 return true; 44 } 45 if (o == null) { 46 return false; 47 } 48 if (o instanceof Student) { 49 Student s = (Student)o; 50 if (this.getName().equals(s.name) && this.getId()==s.id) { 51 return true; 52 } 53 } 54 return false; 55 } 56 57 @Override 58 public int hashCode() { 59 int n1 = this.name.hashCode(); 60 int n2 = this.getId(); 61 return n1!=0?n1:n2; 62 } 63 64 @Override 65 public int compareTo(Student o) { 66 return this.id-o.id; 67 } 68 }
1 package com.collection.map; 2 3 import java.util.Map; 4 import java.util.TreeMap; 5 6 // TreeMap的使用 7 public class Demo3 { 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 // 创建集合 10 TreeMap<Student,String> students = new TreeMap<>(); 11 12 // 创建学生对象 13 Student s1 = new Student("张三", 101); 14 Student s2 = new Student("李四", 102); 15 Student s3 = new Student("王五", 103); 16 17 // 添加元素 18 students.put(s1,"上海"); 19 students.put(s2,"广州"); 20 students.put(s3,"北京"); 21 System.out.println("元素个数:" + students.size()); 22 System.out.println(students); 23 24 /* 删除元素 25 students.remove(s1); 26 students.clear();*/ 27 28 // 遍历元素 29 System.out.println("==========keySet========="); 30 for (Student key : students.keySet()) { 31 System.out.println(key + "==" + students.get(key)); 32 } 33 34 System.out.println("==========entrySet========="); 35 for (Map.Entry<Student, String> entry : students.entrySet()) { 36 System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "--" + entry.getValue()); 37 } 38 39 // 判断 40 System.out.println(students.containsKey(s1)); 41 System.out.println(students.isEmpty()); 42 43 } 44 }
Collections工具类
-
概念:集合工具类,定义了除了存储以外的集合常用方法。
-
方法:
-
public static void reverse(List<?> list) // 反转集合中元素的顺序
-
public static void shuffle(List<?> list) // 随机重置集合元素的顺序
-
public static void sort(List<T> list) // 升序排序(元素必须实现Comparable接口)
-
1 package com.collection.map; 2 3 import java.util.*; 4 5 // Collection工具类的使用 6 public class Demo5 { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); 9 list.add(7); 10 list.add(16); 11 list.add(10); 12 list.add(5); 13 list.add(20); 14 15 // sort排序 16 System.out.println("排序前:" + list); 17 Collections.sort(list); 18 System.out.println("排序后:" + list); 19 20 // binarySearch二分查找 21 int a = Collections.binarySearch(list,10); 22 System.out.println(a); 23 int b = Collections.binarySearch(list,9); // -(插入点)-1 24 System.out.println(b); // -3 25 26 // copy复制 27 List<Integer> dest = new ArrayList<>(); 28 for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { 29 dest.add(0); 30 } 31 Collections.copy(dest,list); 32 System.out.println("复制后:" + dest); 33 34 // reverse反转 35 Collections.reverse(list); 36 System.out.println("反转后:" + list); 37 38 // shuffle 打乱 39 Collections.shuffle(list); 40 System.out.println("打乱后:" + list); 41 42 System.out.println("================集合转换为数组================="); 43 // 补充:集合转换为数组 44 Integer[] array = list.toArray(new Integer[0]); 45 System.out.println("数组长度:" + array.length); 46 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array)); 47 48 System.out.println("================数组转换为集合================="); 49 // 数组转换为集合 50 String[] names = {"张三","李四","王五"}; 51 // 集合是一个受限集合,不能添加和删除 52 List<String> list1 = Arrays.asList(names); 53 System.out.println("集合大小:" + list1.size()); 54 System.out.println(list1); 55 56 // 基本类型数组转换为集合时,要修改为包装类型 57 int[] number = {100,200,300}; 58 List<int[]> ints = Arrays.asList(number); 59 System.out.println(ints); 60 61 Integer[] numbers = {100,200,300}; 62 List<Integer> integers = Arrays.asList(numbers); 63 System.out.println(integers); 64 65 } 66 }





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义