【TensorFlow】多GPU训练:示例代码解析
使用多GPU有助于提升训练速度和调参效率。
本文主要对tensorflow的示例代码进行注释解析:cifar10_multi_gpu_train.py
1080Ti下加速效果如下(batch=128)
单卡:
两个GPU比单个GPU加速了近一倍 :
1.简介
多GPU训练分为:
数据并行和模型并行
单机多卡和多机多卡
2.示例代码解读
官方示例代码给出了使用多个GPU计算的流程:
- CPU 做为参数服务器
- 多个GPU计算汇总更新
#--------------------------Multi-GPUs-code------------------------#
1.demo文件的说明部分
# Copyright 2015 The TensorFlow Authors. All Rights Reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
# ==============================================================================
"""A binary to train CIFAR-10 using multiple GPUs with synchronous updates.
在100k大概256epochs后可以达到约86%的精度
Accuracy:
cifar10_multi_gpu_train.py achieves ~86% accuracy after 100K steps (256
epochs of data) as judged by cifar10_eval.py.
Speed: With batch_size 128.
下面是一些训练参考时间:
System | Step Time (sec/batch) | Accuracy
--------------------------------------------------------------------
1 Tesla K20m | 0.35-0.60 | ~86% at 60K steps (5 hours)
1 Tesla K40m | 0.25-0.35 | ~86% at 100K steps (4 hours)
2 Tesla K20m | 0.13-0.20 | ~84% at 30K steps (2.5 hours)
3 Tesla K20m | 0.13-0.18 | ~84% at 30K steps
4 Tesla K20m | ~0.10 | ~84% at 30K steps
"""
from __future__ import absolute_import
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_function
#导入版本支持
from datetime import datetime #导入时间模块
import os.path #路径模块用于穿件文件夹
import re #正则表达式模块
import time
import numpy as np
from six.moves import xrange # pylint: disable=redefined-builtin
#这句类似python range,py2/py3兼容模块,也可将文中的xrange替换为range
import tensorflow as tf #导入tensorflow
import cifar10 #导入自定义的cifar10.py,包含了各种数据初始化、模型构建、损失和训练函数
2.定义一些flags
这里包含了对于数据目录、最大batch步数、gpu数目和日志文件定义等
FLAGS = tf.app.flags.FLAGS #定义参数flags,随后利用FLAGS读取参数
#https://blog.csdn.net/m0_37041325/article/details/77448971
#https://blog.csdn.net/weiqi_fan/article/details/72722510
#定义参数对应的默认值
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_string('train_dir', './your/path/to/data/cifar10_train',
"""Directory where to write event logs """
"""and checkpoint.""")
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_integer('max_steps', 1000000,
"""Number of batches to run.""")
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_integer('num_gpus', 1,
"""How many GPUs to use.""")
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_boolean('log_device_placement', False,
"""Whether to log device placement.""")
3.定义损失汇总函数和梯度平均函数
主要定义了各个GPU上的损失函数及其合并
def tower_loss(scope, images, labels):
"""Calculate the total loss on a single tower running the CIFAR model.
计算单个tower上的总损失
Args:
scope: 特定tower的命名空间, e.g. 'tower_0'
images: Images. 4D tensor of shape [batch_size, height, width, 3].
labels: Labels. 1D tensor of shape [batch_size].
Returns:
Tensor of shape [] containing the 某个批次数据的总损失
"""
# 计算图构建的输出
logits = cifar10.inference(images)
# 调用函数计算loss
_ = cifar10.loss(logits, labels)
# 综合tower的loss
losses = tf.get_collection('losses', scope)
# 计算当前tower的总loss
total_loss = tf.add_n(losses, name='total_loss')
# Attach a scalar summary to all individual losses and the total loss; do the
# same for the averaged version of the losses.
for l in losses + [total_loss]:
# Remove 'tower_[0-9]/' from the name in case this is a multi-GPU training
# session. 清理tensorboard
loss_name = re.sub('%s_[0-9]*/' % cifar10.TOWER_NAME, '', l.op.name)
tf.summary.scalar(loss_name, l) #tensorboard可视化
return total_loss
"""
#最后得到的total_loss
#每调用一次得到一个GPU的loss
Tensor("tower_0/total_loss_1:0", shape=(), dtype=float32, device=/device:GPU:0)
Tensor("tower_1/total_loss_1:0", shape=(), dtype=float32, device=/device:GPU:1)
"""
这部分梯度的综合比较复杂,把它拆分出来分析,主要过程可以总结为
-首先读入每个GPU(Tower)中的(梯度,变量),这些变量按照GPU 分为多个字列表存储,[[GPUi],.......,[GPUn]];
-每个子列表中包含了一整个模型,对应了一整套的[(梯度,变量),........,(梯度,变量)]<-gpui
-将不同GPU中的同一个变量及其梯度((grad0_gpu0, var0_gpu0),.....,(grad0_gpun, var0_gpun))抽取出来,
#定义梯度,这些梯度来自于各个GPU的综合
def average_gradients(tower_grads):
"""Calculate the average gradient for each shared variable across all towers.
#这个函数对塔式服务器中的GPU提供了同步点
Note that this function provides a synchronization point across all towers.
Args:
#输入参数为list格式,包含了由一系列元组(梯度,变量)组成的子列表
#外部的list计算独立梯度,内部计算综合梯度
tower_grads: List of lists of (gradient, variable) tuples. The outer list
is over individual gradients. The inner list is over the gradient
calculation for each tower.
Returns:
#在所有节点上平均后返回
List of pairs of (gradient, variable) where the gradient has been averaged
across all towers.
"""
"""实例
对于两个GPU来说,就是两个tower,针对这里例子,tower_gpu中包含了下面这些内容
tower_grads = [[tower0_grad],[tower1_grads]]>>>包含了第一块gpu的变量梯度和第二块GPU的变量梯度,他们被放在一个大的列表里outer-list;
而其中的每一个tower-n_grads 又是一个小的列表inner-list,包含了整个模型的梯度和变量。
[tower-n_grads] = [(grad0,variable0),.......,(gradn,variablen)
#我们将输入的变量打印出来观察
>>> tower_grads:
[
[
(<tf.Tensor 'tower_0/gradients/tower_0/conv1/Conv2D_grad/tuple/control_dependency_1:0' shape=(5, 5, 3, 64) dtype=float32>, <tf.Variable 'conv1/weights:0' shape=(5, 5, 3, 64) dtype=float32_ref>),
(<tf.Tensor 'tower_0/gradients/tower_0/conv1/BiasAdd_grad/tuple/control_dependency_1:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32>, <tf.Variable 'conv1/biases:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref>),
(<tf.Tensor 'tower_0/gradients/tower_0/conv2/Conv2D_grad/tuple/control_dependency_1:0' shape=(5, 5, 64, 64) dtype=float32>, <tf.Variable 'conv2/weights:0' shape=(5, 5, 64, 64) dtype=float32_ref>),
(<tf.Tensor 'tower_0/gradients/tower_0/conv2/BiasAdd_grad/tuple/control_dependency_1:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32>, <tf.Variable 'conv2/biases:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref>),
(<tf.Tensor 'tower_0/gradients/AddN_1:0' shape=(2304, 384) dtype=float32>, <tf.Variable 'local3/weights:0' shape=(2304, 384) dtype=float32_ref>),
(<tf.Tensor 'tower_0/gradients/tower_0/local3/add_grad/tuple/control_dependency_1:0' shape=(384,) dtype=float32>, <tf.Variable 'local3/biases:0' shape=(384,) dtype=float32_ref>),
(<tf.Tensor 'tower_0/gradients/AddN:0' shape=(384, 192) dtype=float32>, <tf.Variable 'local4/weights:0' shape=(384, 192) dtype=float32_ref>),
(<tf.Tensor 'tower_0/gradients/tower_0/local4/add_grad/tuple/control_dependency_1:0' shape=(192,) dtype=float32>, <tf.Variable 'local4/biases:0' shape=(192,) dtype=float32_ref>),
(<tf.Tensor 'tower_0/gradients/tower_0/softmax_linear/MatMul_grad/tuple/control_dependency_1:0' shape=(192, 10) dtype=float32>, <tf.Variable 'softmax_linear/weights:0' shape=(192, 10) dtype=float32_ref>),
(<tf.Tensor 'tower_0/gradients/tower_0/softmax_linear/softmax_linear_grad/tuple/control_dependency_1:0' shape=(10,) dtype=float32>, <tf.Variable 'softmax_linear/biases:0' shape=(10,) dtype=float32_ref>)],
[
(<tf.Tensor 'tower_1/gradients/tower_1/conv1/Conv2D_grad/tuple/control_dependency_1:0' shape=(5, 5, 3, 64) dtype=float32>, <tf.Variable 'conv1/weights:0' shape=(5, 5, 3, 64) dtype=float32_ref>),
(<tf.Tensor 'tower_1/gradients/tower_1/conv1/BiasAdd_grad/tuple/control_dependency_1:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32>, <tf.Variable 'conv1/biases:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref>),
(<tf.Tensor 'tower_1/gradients/tower_1/conv2/Conv2D_grad/tuple/control_dependency_1:0' shape=(5, 5, 64, 64) dtype=float32>, <tf.Variable 'conv2/weights:0' shape=(5, 5, 64, 64) dtype=float32_ref>),
(<tf.Tensor 'tower_1/gradients/tower_1/conv2/BiasAdd_grad/tuple/control_dependency_1:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32>, <tf.Variable 'conv2/biases:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref>),
(<tf.Tensor 'tower_1/gradients/AddN_1:0' shape=(2304, 384) dtype=float32>, <tf.Variable 'local3/weights:0' shape=(2304, 384) dtype=float32_ref>),
(<tf.Tensor 'tower_1/gradients/tower_1/local3/add_grad/tuple/control_dependency_1:0' shape=(384,) dtype=float32>, <tf.Variable 'local3/biases:0' shape=(384,) dtype=float32_ref>),
(<tf.Tensor 'tower_1/gradients/AddN:0' shape=(384, 192) dtype=float32>, <tf.Variable 'local4/weights:0' shape=(384, 192) dtype=float32_ref>),
(<tf.Tensor 'tower_1/gradients/tower_1/local4/add_grad/tuple/control_dependency_1:0' shape=(192,) dtype=float32>, <tf.Variable 'local4/biases:0' shape=(192,) dtype=float32_ref>),
(<tf.Tensor 'tower_1/gradients/tower_1/softmax_linear/MatMul_grad/tuple/control_dependency_1:0' shape=(192, 10) dtype=float32>, <tf.Variable 'softmax_linear/weights:0' shape=(192, 10) dtype=float32_ref>),
(<tf.Tensor 'tower_1/gradients/tower_1/softmax_linear/softmax_linear_grad/tuple/control_dependency_1:0' shape=(10,) dtype=float32>, <tf.Variable 'softmax_linear/biases:0' shape=(10,) dtype=float32_ref>)
]
]
"""
average_grads = []
#对输入元组进行解压
for grad_and_vars in zip(*tower_grads): #在各个变量var上循环
# grad_and_vars: ((grad0_gpu0, var0_gpu0), ... , (grad0_gpuN, var0_gpuN))
# 遍历var0及其梯度在不同GPU上的分布,此例子中
#((<tf.Tensor 'tower_0/gradients/tower_0/conv1/Conv2D_grad/tuple/control_dependency_1:0' shape=(5, 5, 3, 64) dtype=float32>, <tf.Variable 'conv1/weights:0' shape=(5, 5, 3, 64) dtype=float32_ref>),
#(<tf.Tensor 'tower_1/gradients/tower_1/conv1/Conv2D_grad/tuple/control_dependency_1:0' shape=(5, 5, 3, 64) dtype=float32>, <tf.Variable 'conv1/weights:0' shape=(5, 5, 3, 64) dtype=float32_ref>))
grads = []
for g, _ in grad_and_vars: #对所有GPU上的同一变量的梯度进行组合
# Add 0 dimension to the gradients to represent the tower.
expanded_g = tf.expand_dims(g, 0)
# Append on a 'tower' dimension which we will average over below.
#加上tower维度
grads.append(expanded_g)
#在tower维度上进行平均
grad = tf.concat(axis=0, values=grads) #在tower维度上,对不同的GPU求均值
grad = tf.reduce_mean(grad, 0) #得到所有变量及其梯度的均值
# 参数由于共享冗余,所以只需要返回变量在首个tower的指针
v = grad_and_vars[0][1] #指针varxx-gpuxx
grad_and_var = (grad, v) #合并为元组 得到某个变量综合后的平均梯度,及变量名指针。
average_grads.append(grad_and_var) #添加新的梯度和v指针,添加各个var
return average_grads
"""最后我们观察返回的参数
>>> print(average_grads)
[(<tf.Tensor 'Mean:0' shape=(5, 5, 3, 64) dtype=float32>, <tf.Variable 'conv1/weights:0' shape=(5, 5, 3, 64) dtype=float32_ref>),
(<tf.Tensor 'Mean_1:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32>, <tf.Variable 'conv1/biases:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref>),
(<tf.Tensor 'Mean_2:0' shape=(5, 5, 64, 64) dtype=float32>, <tf.Variable 'conv2/weights:0' shape=(5, 5, 64, 64) dtype=float32_ref>),
(<tf.Tensor 'Mean_3:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32>, <tf.Variable 'conv2/biases:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref>),
(<tf.Tensor 'Mean_4:0' shape=(2304, 384) dtype=float32>, <tf.Variable 'local3/weights:0' shape=(2304, 384) dtype=float32_ref>),
(<tf.Tensor 'Mean_5:0' shape=(384,) dtype=float32>, <tf.Variable 'local3/biases:0' shape=(384,) dtype=float32_ref>),
(<tf.Tensor 'Mean_6:0' shape=(384, 192) dtype=float32>, <tf.Variable 'local4/weights:0' shape=(384, 192) dtype=float32_ref>),
(<tf.Tensor 'Mean_7:0' shape=(192,) dtype=float32>, <tf.Variable 'local4/biases:0' shape=(192,) dtype=float32_ref>),
(<tf.Tensor 'Mean_8:0' shape=(192, 10) dtype=float32>, <tf.Variable 'softmax_linear/weights:0' shape=(192, 10) dtype=float32_ref>),
(<tf.Tensor 'Mean_9:0' shape=(10,) dtype=float32>, <tf.Variable 'softmax_linear/biases:0' shape=(10,) dtype=float32_ref>)
]
可以看到是多gpu平均后的梯度和对应的变量
"""
4.训练
训练部分主要包括了构建计算图、定义计算参数、优化器、
def train():
"""Train CIFAR-10 for a number of steps."""
with tf.Graph().as_default(), tf.device('/cpu:0'):
# Create a variable to count the number of train() calls. This equals the
# number of batches processed * FLAGS.num_gpus.
global_step = tf.get_variable(
'global_step', [],
initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0), trainable=False)
# Calculate the learning rate schedule.
num_batches_per_epoch = (cifar10.NUM_EXAMPLES_PER_EPOCH_FOR_TRAIN /
FLAGS.batch_size / FLAGS.num_gpus)
decay_steps = int(num_batches_per_epoch * cifar10.NUM_EPOCHS_PER_DECAY)
# Decay the learning rate exponentially based on the number of steps.
lr = tf.train.exponential_decay(cifar10.INITIAL_LEARNING_RATE,
global_step,
decay_steps,
cifar10.LEARNING_RATE_DECAY_FACTOR,
staircase=True)
# Create an optimizer that performs gradient descent.
opt = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(lr)
#-----------------------------上面定义参数、定义优化器-----------------------#
# 图像和标签的batch输入
images, labels = cifar10.distorted_inputs()
batch_queue = tf.contrib.slim.prefetch_queue.prefetch_queue(
[images, labels], capacity=2 * FLAGS.num_gpus)
# 计算每一个gpu上的梯度,放入tower_grads中.
tower_grads = []
with tf.variable_scope(tf.get_variable_scope()):
for i in xrange(FLAGS.num_gpus):
with tf.device('/gpu:%d' % i):
with tf.name_scope('%s_%d' % (cifar10.TOWER_NAME, i)) as scope:
# Dequeues one batch for the GPU
image_batch, label_batch = batch_queue.dequeue()
# Calculate the loss for one tower of the CIFAR model. This function
# constructs the entire CIFAR model but shares the variables across
# all towers.
loss = tower_loss(scope, image_batch, label_batch)
# Reuse variables for the next tower.
tf.get_variable_scope().reuse_variables()
# Retain the summaries from the final tower.
summaries = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.SUMMARIES, scope)
# Calculate the gradients for the batch of data on this CIFAR tower.
grads = opt.compute_gradients(loss)
# Keep track of the gradients across all towers.
tower_grads.append(grads)
# 计算平均梯度
# 注意同步指针.
grads = average_gradients(tower_grads)
# tensorboard显示学习率
summaries.append(tf.summary.scalar('learning_rate', lr))
# 各种梯度的tensorboard直方图显示
for grad, var in grads:
if grad is not None:
summaries.append(tf.summary.histogram(var.op.name + '/gradients', grad))
# 利用计算出的平均梯度来进行优化
apply_gradient_op = opt.apply_gradients(grads, global_step=global_step)
# 各种变量的直方图
for var in tf.trainable_variables():
summaries.append(tf.summary.histogram(var.op.name, var))
# 跟踪所有变量的移动平均
variable_averages = tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage(
cifar10.MOVING_AVERAGE_DECAY, global_step)
variables_averages_op = variable_averages.apply(tf.trainable_variables())
# 将所有操作组合进单一操作
train_op = tf.group(apply_gradient_op, variables_averages_op)
# 保存相关操作
saver = tf.train.Saver(tf.global_variables())
# 建立综合操作
summary_op = tf.summary.merge(summaries)
# 初始化
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# 开始计算
# Start running operations on the Graph. allow_soft_placement must be set to
# True to build towers on GPU, as some of the ops do not have GPU
# implementations.
sess = tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(
allow_soft_placement=True,
log_device_placement=FLAGS.log_device_placement))
sess.run(init)
# Start the queue runners.
tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess)
#将训练过程记录下来,tensorboard可视化
summary_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(FLAGS.train_dir, sess.graph)
#最大步数迭代训练,显示时间和loss
for step in xrange(FLAGS.max_steps):
start_time = time.time()
_, loss_value = sess.run([train_op, loss])
duration = time.time() - start_time
assert not np.isnan(loss_value), 'Model diverged with loss = NaN'
#---------------------------下面是不同check steps的时候显示的信息-----------------#
if step % 10 == 0:
num_examples_per_step = FLAGS.batch_size * FLAGS.num_gpus
examples_per_sec = num_examples_per_step / duration
sec_per_batch = duration / FLAGS.num_gpus
format_str = ('%s: step %d, loss = %.2f (%.1f examples/sec; %.3f '
'sec/batch)')
print (format_str % (datetime.now(), step, loss_value,
examples_per_sec, sec_per_batch))
if step % 100 == 0:
summary_str = sess.run(summary_op)
summary_writer.add_summary(summary_str, step)
# Save the model checkpoint periodically.
if step % 1000 == 0 or (step + 1) == FLAGS.max_steps:
checkpoint_path = os.path.join(FLAGS.train_dir, 'model.ckpt')
saver.save(sess, checkpoint_path, global_step=step)
#注,此处代码较长,运行时需要注意tab键/空格键是否正确---indent
启动主函数训练
def main(argv=None): # pylint: disable=unused-argument
cifar10.maybe_download_and_extract() #没数据需要下载,这个函数在cifar10.py里
if tf.gfile.Exists(FLAGS.train_dir):
tf.gfile.DeleteRecursively(FLAGS.train_dir)
tf.gfile.MakeDirs(FLAGS.train_dir)
train()
if __name__ == '__main__':
tf.app.run()
#可以愉快的运行了
ref:
demo:https://github.com/tensorflow/models/blob/master/tutorials/image/cifar10/cifar10_multi_gpu_train.py
https://blog.csdn.net/lqfarmer/article/details/70339330
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_40546602/article/details/81414321
https://blog.csdn.net/guotong1988/article/details/74355637


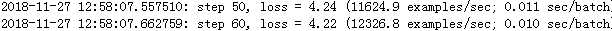
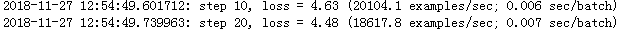



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号