【pyrender】基于PyRender的深度图渲染
一、安装pyrender
- pyrender简介:
Pyrender is a pure Python (2.7, 3.4, 3.5, 3.6) library for physically-based rendering and visualization. It is designed to meet the glTF 2.0 specification from Khronos - 安装
pyrender: https://pyrender.readthedocs.io/en/latest/install/index.html - 跑通Offscreen Rendering程序,验证环境是否配置成功:https://pyrender.readthedocs.io/en/latest/examples/quickstart.html#minimal-example-for-offscreen-rendering
- [可选] 跑通3D Viewer程序:https://pyrender.readthedocs.io/en/latest/examples/quickstart.html#minimal-example-for-3d-viewer
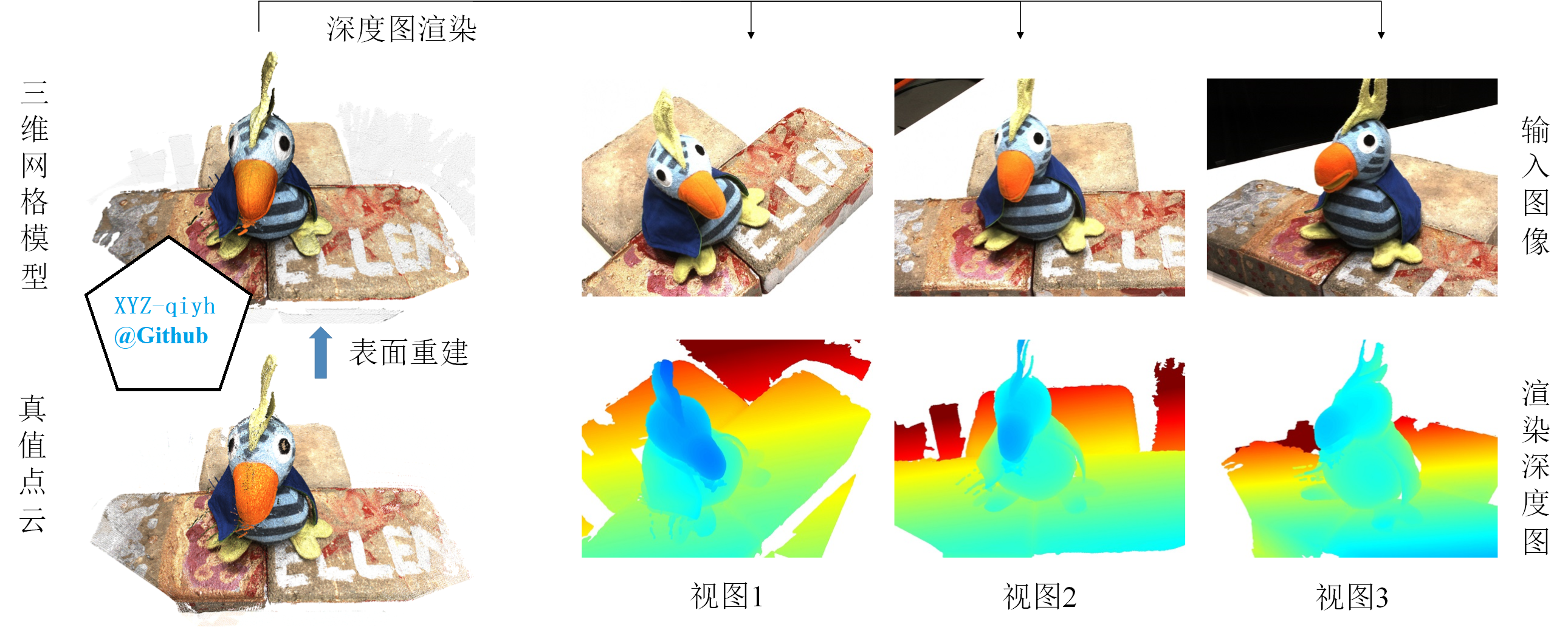
深度图渲染示意图 for DTU dataset
二、加载Mesh模型与相机参数
- 加载Mesh模型
- colmap fused.ply --> PoissonRecon
- 相机参数的转换
- colmap (world-to-camera) vs pyrender (camera-to-world)
- y-z axis reverse
# Creates the scene and adds the mesh.
scene = pyrender.Scene()
scene.add(mesh)
# Creates a renderer of suitable height and width
cam_data = cameras[images[i].camera_id]
renderer = pyrender.OffscreenRenderer(cam_data.width,
cam_data.height)
# Extracts focal length and principal point information.
# Important: This code snippet assumes that the camera
# is a PINHOLE camera.
fx = np.float32(cam_data.params[0])
fy = np.float32(cam_data.params[1])
cx = np.float32(cam_data.params[2])
cy = np.float32(cam_data.params[3])
# Extracts the pose of the image.
# Note that pyrender poses transform from camera
# to world coordinates while colmap poses transform
# from world to camera.
R = np.asmatrix(qvec2rotmat(images[i].qvec)).transpose()
T = np.identity(4)
T[0:3,0:3] = R
T[0:3,3] = -R.dot(images[i].tvec)
# Takes into account that colmap uses the computer vision
# camera coordinate system (x = right, y = down, z = front)
# while pyrender uses the computer graphics conventions
# (x = right, y = up, -z = front).
T[:, 1:3] *= -1
# Sets up the camera with the intrinsics and extrinsics.
pyrender_camera = pyrender.IntrinsicsCamera(fx, fy, cx, cy,
zfar=800.0) # 425~935
cam_node = scene.add(pyrender_camera, pose=T)
参考资料:
https://github.com/colmap/colmap/issues/704#issuecomment-954161261
分类:
多视图三维重建




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人