使用队列来模拟栈
使用队列实现栈的下列操作:
- push(x) -- 元素 x 入栈
- pop() -- 移除栈顶元素
- top() -- 获取栈顶元素
- empty() -- 返回栈是否为空
注意:
- 你只能使用队列的基本操作-- 也就是 push to back, peek/pop from front, size, 和 is empty 这些操作是合法的。
- 你所使用的语言也许不支持队列。 你可以使用 list 或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个队列 , 只要是标准的队列操作即可。
- 你可以假设所有操作都是有效的(例如, 对一个空的栈不会调用 pop 或者 top 操作)。
首先我们来看张图:
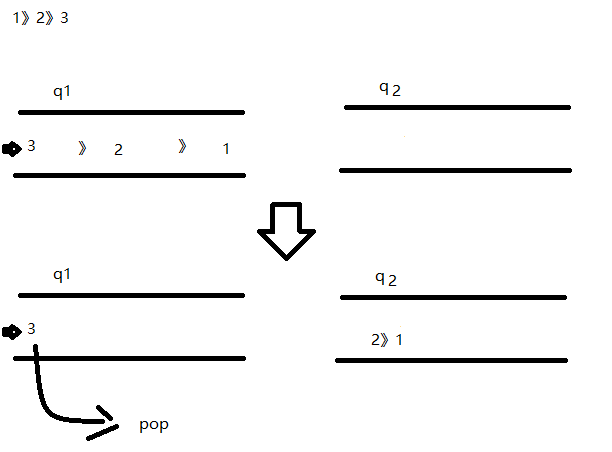
我们先来模拟队列的方法:
//构造队列 type Queue struct { queue []int } func NewQueue() *Queue { return &Queue{[]int{}} } //将n放进队列中 func (queue *Queue) Push(n int) { queue.queue = append(queue.queue, n) } //弹出最先进入队列的值 func (queue *Queue) Pop() int { res := queue.queue[0] queue.queue = queue.queue[1:] return res } //查看队列的第一个元素 func (queue *Queue) Peek() int { res := queue.queue[0] return res } func (queue *Queue) Len() int { return len(queue.queue) }
那我们就来考虑如何来利用队列来模拟栈了:
- push:对于push,我们只需要把所有元素都放进q1中就行
- pop:对于pop,当q1的长度为1的时候,直接pop,当不等于1的时候,我们就要把前n-1个元素放进q2中,然后pop q1的值,再把q1和q2调换
- top:对于top,其实与pop差不多,只是不减少元素而已
- empty:只需要比较q1和q2的元素和是不是等于0即可
package main import ( "fmt" ) type MyStack struct { q1, q2 *Queue } /** Initialize your data structure here. */ func Constructor() MyStack { stack := MyStack{&Queue{}, &Queue{}} return stack } /** Push element x onto stack. */ func (this *MyStack) Push(x int) { this.q1.Push(x) } /** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */ func (this *MyStack) Pop() int { if this.q1.Len() == 1 { return this.q1.Pop() } for this.q1.Len() > 1 { this.q2.Push(this.q1.Pop()) } res := this.q1.Pop() this.q1, this.q2 = this.q2, this.q1 return res } /** Get the top element. */ func (this *MyStack) Top() int { if this.q1.Len() == 1 { res := this.q1.Pop() this.q1.Push(res) return res } for this.q1.Len() > 1 { this.q2.Push(this.q1.Pop()) } res := this.q1.Pop() this.q2.Push(res) this.q1, this.q2 = this.q2, this.q1 return res } /** Returns whether the stack is empty. */ func (this *MyStack) Empty() bool { return this.q1.Len()+this.q2.Len() == 0 } //构造队列 type Queue struct { queue []int } func NewQueue() *Queue { return &Queue{[]int{}} } //将n放进队列中 func (queue *Queue) Push(n int) { queue.queue = append(queue.queue, n) } //弹出最先进入队列的值 func (queue *Queue) Pop() int { res := queue.queue[0] queue.queue = queue.queue[1:] return res } //查看队列的第一个元素 func (queue *Queue) Peek() int { res := queue.queue[0] return res } func (queue *Queue) Len() int { return len(queue.queue) } func main() { stack := Constructor() stack.Push(1) stack.Push(2) fmt.Println(stack.Top()) fmt.Println(stack.Pop()) fmt.Println(stack.Top()) fmt.Println(stack.Pop()) fmt.Println(stack.Empty()) }
还在找我的道



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号