Spring IOC 和 AOP
Spring框架中的 IOC 和 AOP
参考博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaoxing/p/5836835.html
一.什么是Spring?
Spring是一个轻量级开源框架,开发目的是为了解决企业应用开发的复杂性,Spring通过bean来管理java类,将java类封装进容器里,需要时便可以为你提供
对应类的对象。可以说,Spring是一个轻量级的控制反转IOC和面向切面AOP的容器框架。Spring框架简单、易于测试,最重要的是它可以做到松耦合,这不仅仅
对服务端应用受益,对所有java应用都有好处。
二.如何简单搭建一个Spring框架?
1.首先在maven中导入spring的整合包
1 <!--spring相关--> 2 <dependency> 3 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> 4 <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId> 5 <version>4.3.17.RELEASE</version> 6 </dependency>
2.在maven中可以看到以下jar包
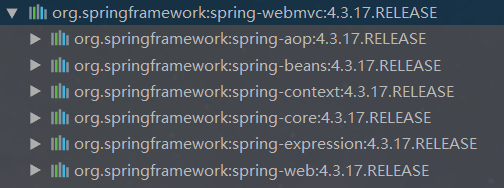
3.创建一个spring.xml文件,用作spring的配置
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" 5 xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" 6 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans 7 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> 8 9 <bean></bean> 10 11 </beans>
4.创建一个类,将其注入到Spring容器里
User类
1 public class User { 2 3 private String name; 4 private int age; 5 6 public User(String name, int age) { 7 this.name = name; 8 this.age = age; 9 } 10 11 public User(){ 12 13 } 14 15 public String getName() { 16 return name; 17 } 18 19 public void setName(String name) { 20 this.name = name; 21 } 22 23 public int getAge() { 24 return age; 25 } 26 27 public void setAge(int age) { 28 this.age = age; 29 } 30 31 @Override 32 public String toString() { 33 return "User{" + 34 "name='" + name + '\'' + 35 ", age=" + age + 36 '}'; 37 } 38 }
spring.xml
<bean id="entity" class="test.entity.User">
<property name="name" value="测试"/>
<property name="age" value="11"/>
</bean>
5创建一个Test类,测试是否能拿到Spring中返回的对象
1 <bean id="entity" class="test.entity.User"> 2 <property name="name" value="测试"/> 3 <property name="age" value="11"/> 4 </bean>
测试结果,成功拿到返回对象的成员变量的值

三.Spring框架中的主要模块
Spring框架中主要包含六大模块:Core、Dao、Orm、Jee、Web、Aop
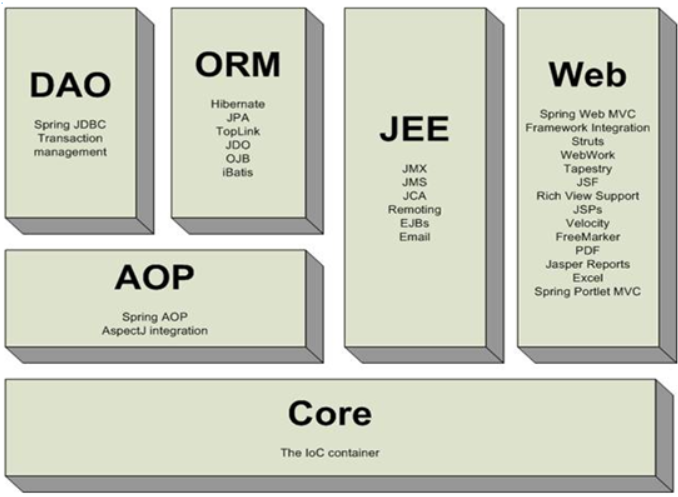
Spring DAO:Spring提供了对JDBC的操作支持:JdbcTemplate模板工具类 。
Spring ORM:Spring可以与ORM框架整合。例如Spring整合Hibernate框架,其中Spring还提供HibernateDaoSupport工具类,简化了Hibernate的操作 。
Spring WEB:Spring提供了对Struts、Springmvc的支持,支持WEB开发。与此同时Spring自身也提供了基于MVC的解决方案 。
Spring AOP:Spring提供面向切面的编程,可以给某一层提供事务管理,例如在Service层添加事物控制 。
Spring JEE:J2EE开发规范的支持,例如EJB 。
Spring Core:提供IOC容器对象的创建和处理依赖对象关系 。
四.什么是IOC?Spring中如何实现IOC?
IOC容器概念:IOC容器指具有依赖注入功能的容器,具有创建对象功能的容器。IOC容器负责实例化、定位、配置应用程序中的对象及建立这些对象间的依赖。在Java中
我们平时创建一个对象的做法就是去new它,但是IOC(控制反转)的思想就是不由程序员手动去做这个事,而是让程序自己去做这个事,在spring中实现IOC思想的就是Spring容器,
将创建对象的工作都交由Spring容器来做。
DI(依赖注入Dependency injection) :在容器创建对象后,处理对象的依赖关系。自动将配置好的内容填充到对象里。
依赖注入有以下几种方式:
1.set注入
创建一个Friend类
1 public class Friend { 2 3 private String name; 4 private int age; 5 private String address; 6 7 /* 8 get和set方法 9 */ 10 }
修改之前的User类
1 public class User { 2 3 private String name; 4 private int age; 5 private Friend friend; 6 7 /* 8 set和get方法 9 10 */ 11 12 /* 13 重写toString()方法 14 */ 15 }
在Spring.xml文件中配置
1 <bean id="friend" class="test.entity.Friend"> 2 <property name="name" value="张三"/> 3 <property name="age" value="13"/> 4 <property name="address" value="X街道X楼"/> 5 </bean> 6 7 <bean id="entity" class="test.entity.User"> 8 <property name="name" value="测试"/> 9 <property name="age" value="11"/> 10 <property name="friend" ref="friend"/> 11 </bean>
测试Spring是否能够成功创建User对象
1 ApplicationContext ac = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("classpath:spring.xml"); 2 User user = (User) ac.getBean("entity"); 3 System.out.println(user.toString());
输出结果:
![]()
2.构造器注入
分别给User类和Friend类设置有参构造方法
1 public User(String name, int age, Friend friend) { 2 this.name = name; 3 this.age = age; 4 this.friend = friend; 5 }
1 public Friend(String name, int age, String address) { 2 this.name = name; 3 this.age = age; 4 this.address = address; 5 }
Spring.xml配置
1 <!--构造器注入--> 2 <bean id="friend" class="test.entity.Friend"> 3 <constructor-arg name="age" value="11"/> 4 <constructor-arg name="name" value="李四"/> 5 <constructor-arg name="address" value="XX街道XX号楼"/> 6 </bean> 7 8 <bean id="entity" class="test.entity.User"> 9 <constructor-arg name="name" value="person"/> 10 <constructor-arg name="age" value="12"/> 11 <constructor-arg name="friend" ref="friend"/> 12 </bean>
构造器注入和类的构造方法相互对应,如果在xml文件中配置的参数个数和构造方法里的对应不上就会报错,实现原理就是通过参数来找到对应类
的构造方法并且创建出对象
测试输出结果:
![]()
3.基于注解
在User类和Friend类上加上@Component注解,表示把这两个类注入Spring容器,作为Spring的组件,去掉get和set方法
1 @Component 2 public class User { 3 4 private String name; 5 private int age; 6 7 @Autowired//自动注入 8 private Friend friend; 9 10 public User(String name, int age, Friend friend) { 11 this.name = name; 12 this.age = age; 13 this.friend = friend; 14 } 15 16 public User(){ 17 18 } 19 20 21 @Override 22 public String toString() { 23 return "User{" + 24 "name='" + name + '\'' + 25 ", age=" + age + 26 ", friend=" + friend + 27 '}'; 28 } 29 }
1 @Component 2 public class Friend { 3 4 private String name; 5 private int age; 6 private String address; 7 8 public Friend() { 9 } 10 11 public Friend(String name, int age, String address) { 12 this.name = name; 13 this.age = age; 14 this.address = address; 15 } 16 17 18 19 @Override 20 public String toString() { 21 return "Friend{" + 22 "name='" + name + '\'' + 23 ", age=" + age + 24 ", address='" + address + '\'' + 25 '}'; 26 } 27 }
spring.xml配置
1 <bean id="user" class="test.entity.User"/> 2 <bean id="friend" class="test.entity.Friend"/>
在User类中使用@Autowired自动注入friend对象
1 ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:spring.xml"); 2 User user = (User) ac.getBean("user"); 3 System.out.println(user.toString());
测试结果
![]()
成功获取user对象,friend对象也成功注入
4.在@configuration注解的配置类中注入
创建一个@configuration注解的类
1 @Configuration 2 public class Beans { 3 4 @Bean 5 public Friend friend(){ 6 return new Friend("张三", 12, "中央大街"); 7 } 8 9 @Bean 10 public User user(Friend friend){ 11 return new User(); 12 } 13 }
获取User类对象
1 ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:spring.xml"); 2 User user = (User) ac.getBean(User.class); 3 System.out.println(user.toString());
运行结果
![]()
成功获取user对象 ,并且Friend类成功注入到User类中
Spring注入相关的注解
@Component 把对象加入ioc容器,对象引用名称是类名,第一个字母小写
@Component(“name”) 把指定名称的对象,加入ioc容器
@Repository 主要用于标识加入容器的对象是一个持久层的组件(类)
@Service 主要用于标识加入容器的对象是一个业务逻辑层的组件
@Controller 主要用于标识加入容器的对象是一个控制层的组件
@Resource 注入属性(DI), 会从容器中找对象注入到@Resource修饰的对象上
@Autowired 注入属性(DI), 会从容器中找对象注入到@Autowired修饰的对象上
5.实现对接口的注入
创建一个接口,接口里的area方法计算各种图形的面积
public interface Shape { double area(); }
创建circle类和rectangle类实现shape接口的方法
circle类
public class Circle implements Shape { private final static double pai = 3.1415926; public double area() { System.out.println("计算圆形面积"); Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入圆的半径"); double radio = sc.nextDouble(); System.out.println("面积为:" + pai*pai*radio); return pai*pai*radio; } }
rectangle类
public class Rectangle implements Shape { public double area() { System.out.println("计算矩形面积"); Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("输入矩形的长度"); double length = sc.nextDouble(); System.out.println("输入矩形的宽度"); double width = sc.nextDouble(); System.out.println("面积为:" + length*width); return length*width; } }
spring.xml文件的配置
<bean id="circle" class="Pro456.bean.Circle"/> <bean id="rectangle" class="Pro456.bean.Rectangle"/>
创建shapeUtil类
public class ShapeUtil { public static void calculate(String shapeName){ ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml"); Shape shape = (Shape) ioc.getBean(shapeName); System.out.println(shape.area()); } }
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext方法获取spring读取spring的配置文件,通过传入的表示图形类型的字符串来决定实现接口的实现类,
通过getBean获取指定类的对象赋值给接口,最后调用接口中实现的方法计算图形的面积。
测试类
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { ShapeUtil.calculate("circle"); } }
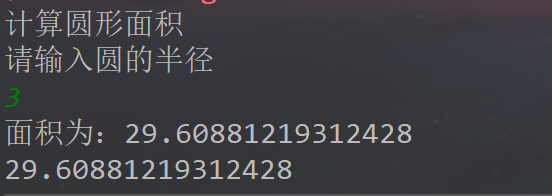
代码执行结果:
@Autowired和@resource的区别
一.
@Autowired是根据类型注入的
@Resource是先根据名字,再根据类型注入,@Resource后面可以指定bean的name注入,这样就只会通过名字来注入,如@Resource("test")只会查找id为test的bean注入
二.
@Autowired是Spring中的注解,而@Resource是jdk自带的,是属于j2ee的注解
五.什么是AOP?Spring中如何实现AOP?
AOP是面向切面编程,通俗来讲就是把每个业务中都需要写的同样的代码提取出来,写好后放入每个类的相应的切点,Spring容器会动态地在这些切点位置织入我们写好的代码。
这样做能够大大减少代码的冗余。
AOP涉及名称:
切面(Aspect):其实就是共有功能的实现。如日志切面、权限切面、事务切面等。在实际应用中通常是一个存放共有功能实现的普通Java类,之所以能被AOP容器识别成切面,是在配置中指定的。
通知(Advice):是切面的具体实现。以目标方法为参照点,根据放置的地方不同,可分为前置通知(Before)、后置通知(AfterReturning)、异常通知(AfterThrowing)、最终通知(After)与环绕通知(Around)5种。在实际应用中通常是切面类中的一个方法,具体属于哪类通知,同样是在配置中指定的。
连接点(Joinpoint):就是程序在运行过程中能够插入切面的地点。例如,方法调用、异常抛出或字段修改等,但Spring只支持方法级的连接点。
切入点(Pointcut):用于定义通知应该切入到哪些连接点上。不同的通知通常需要切入到不同的连接点上,这种精准的匹配是由切入点的正则表达式来定义的。
目标对象(Target):就是那些即将切入切面的对象,也就是那些被通知的对象。这些对象中已经只剩下干干净净的核心业务逻辑代码了,所有的共有功能代码等待AOP容器的切入。
代理对象(Proxy):将通知应用到目标对象之后被动态创建的对象。可以简单地理解为,代理对象的功能等于目标对象的核心业务逻辑功能加上共有功能。代理对象对于使用者而言是透明的,是程序运行过程中的产物。
织入(Weaving):将切面应用到目标对象从而创建一个新的代理对象的过程。这个过程可以发生在编译期、类装载期及运行期,当然不同的发生点有着不同的前提条件。譬如发生在编译期的话,就要求有一个支持这种AOP实现的特殊编译器;发生在类装载期,就要求有一个支持AOP实现的特殊类装载器;只有发生在运行期,则可直接通过Java语言的反射机制与动态代理机制来动态实现。
在Spring中实现AOP
首先创建一个切面类
1 @Aspect //设置为切面类 2 @Component //注入spring 3 public class LogAspect { 4 5 //以字符串形式表示执行目标条件,得使用final来修饰 6 //切点表达式 7 private final String Exec = "execution(* aop.test.service..*.*(..))"; 8 9 @Pointcut(Exec) 10 public void pointMethode(){}//设置切入点 11 12 //执行顺序:环绕通知(前),前置通知,环绕通知(后),后置通知,返回后通知 13 14 @Before("pointMethode()")// 方法执行前执行 15 public void before(){ 16 System.out.println("method before"); 17 } 18 19 @After("pointMethode()")// 方法执行后执行 20 public void after(){ 21 System.out.println("method after"); 22 } 23 24 @AfterReturning("pointMethode()")// 方法返回后执行 25 public void afterReturning(){ 26 System.out.println("method afterReturning"); 27 } 28 29 @AfterThrowing("pointMethode()")// 方法抛异常后执行 30 public void afterThrowing(){ 31 System.out.println("method afterThrowing"); 32 } 33 34 @Around("pointMethode()")// 环绕通知 35 public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint pr){ 36 System.out.println("method around bg"); 37 try { pr.proceed();// 执行目标方法 38 MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) pr.getSignature();//获取切点对象 39 Method method = signature.getMethod();//获取方法 40 } catch (Throwable e) { 41 e.printStackTrace(); 42 } 43 System.out.println("method around ed"); } 44 }
execution(* aop.test.service..*.*(..)) ,pointMethode中的三个"*"中,第一个*代表返回值,第二*代表service下子包,第三个*代表方法名,“(..)”代表方法参数。
现在的切入点为service类中的所有方法
创建一个service类,并且注入Spring容器
@Service(value = "aopService") public class AopTestService { @LogAspect("show") public void method1(){ System.out.println("执行method1"); } public void method2(){ System.out.println("执行method2"); } }
创建测试方法,执行service类中的切点方法
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration("classpath:spring.xml") public class Test { @Resource(name = "aopService") private AopTestService aopTestService; @org.junit.Test public void fun(){ aopTestService.method1(); aopTestService.method2(); } }
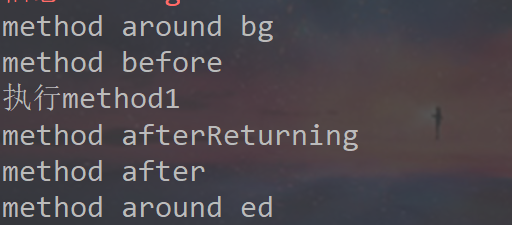
运行结果
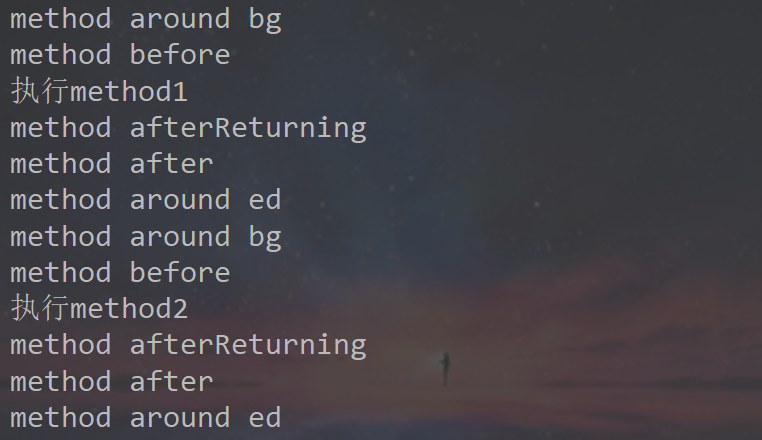
通过自定义注解实现AOP
自定义注解类
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(ElementType.METHOD) public @interface LogAspect { String value() default ""; }
在service类的切点方法上添加注解
@LogAspect("show")
public void method1(){
System.out.println("执行method1");
}
修改切面类
@Before("@annotation(aop.test.annoation.LogAspect)")// 方法执行前执行
public void before(){
System.out.println("method before");
}
@After("@annotation(aop.test.annoation.LogAspect)")// 方法执行后执行
public void after(){
System.out.println("method after");
}
@AfterReturning("@annotation(aop.test.annoation.LogAspect)")// 方法返回后执行
public void afterReturning(){
System.out.println("method afterReturning");
}
@AfterThrowing("@annotation(aop.test.annoation.LogAspect)")// 方法抛异常后执行
public void afterThrowing(){
System.out.println("method afterThrowing");
}
@Around("@annotation(aop.test.annoation.LogAspect)")// 环绕通知
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint pr){
System.out.println("method around bg");
try {
pr.proceed();// 执行目标方法
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) pr.getSignature();//获取切点对象
Method method = signature.getMethod();//获取方法
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("method around ed");
}
在测试方法中执行method1